吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 318-328.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200856
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
基于自适应变分模态分解和集成极限学习机的滚动轴承多故障诊断
- 1.兰州理工大学 电气工程与信息工程学院,兰州 730050
2.兰州理工大学 甘肃工业过程先进控制重点实验室,兰州 730050
3.兰州理工大学 电气与控制工程国家实验教学中心,兰州 730050
4.甘肃省制造信息工程研究中心,兰州 730050
5.中国市政工程西北设计研究院有限公司,兰州 730000
Multi⁃fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on adaptive variational modal decomposition and integrated extreme learning machine
Jin-hua WANG1,2,3( ),Jia-wei HU1,Jie CAO1,4,Tao HUANG5
),Jia-wei HU1,Jie CAO1,4,Tao HUANG5
- 1.College of Electrical & Information Engineering,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
2.Key Laboratory of Gansu Advanced Control for Industrial Processes,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
3.National Experimental Teaching Center of Electrical and Control Engineering,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
4.Engineering Research Center of Manufacturing Information of Gansu Province,Lanzhou 730050,China
5.China Municipal Engineering Northwest Design and Research Institute Co. ,Ltd. ,Lanzhou 730000,China
摘要:
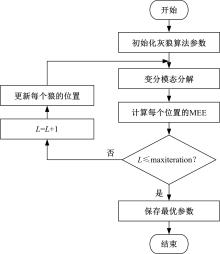
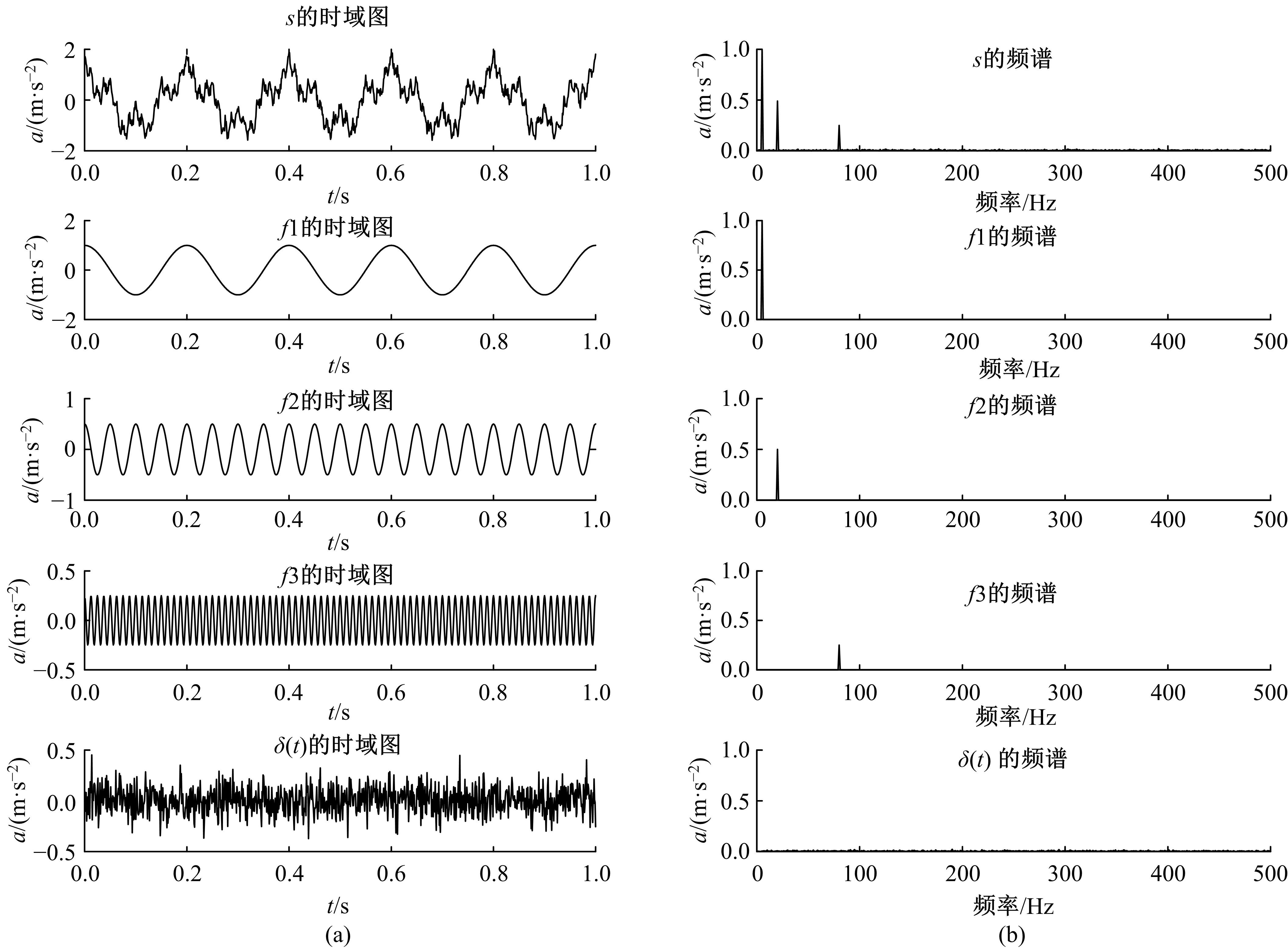
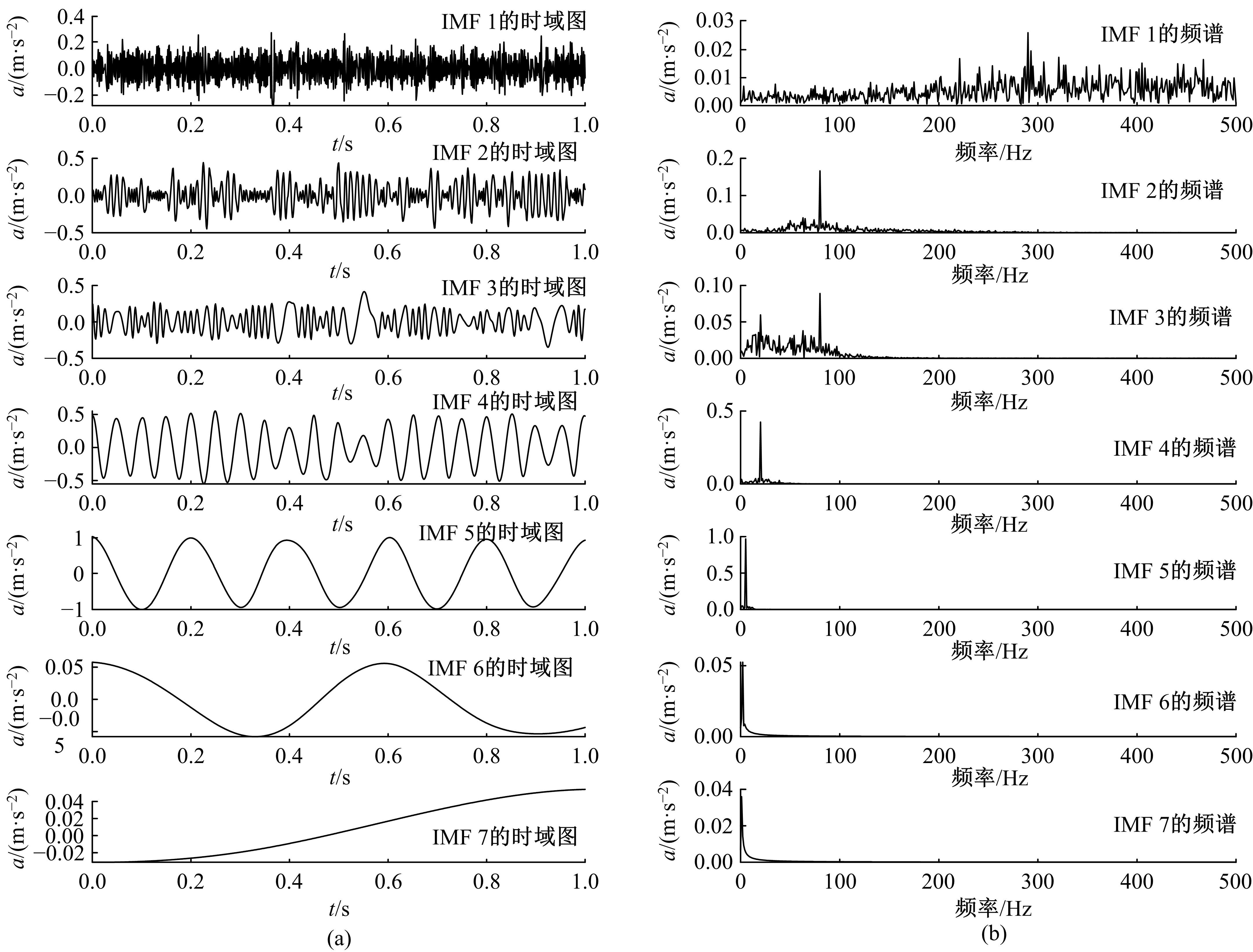
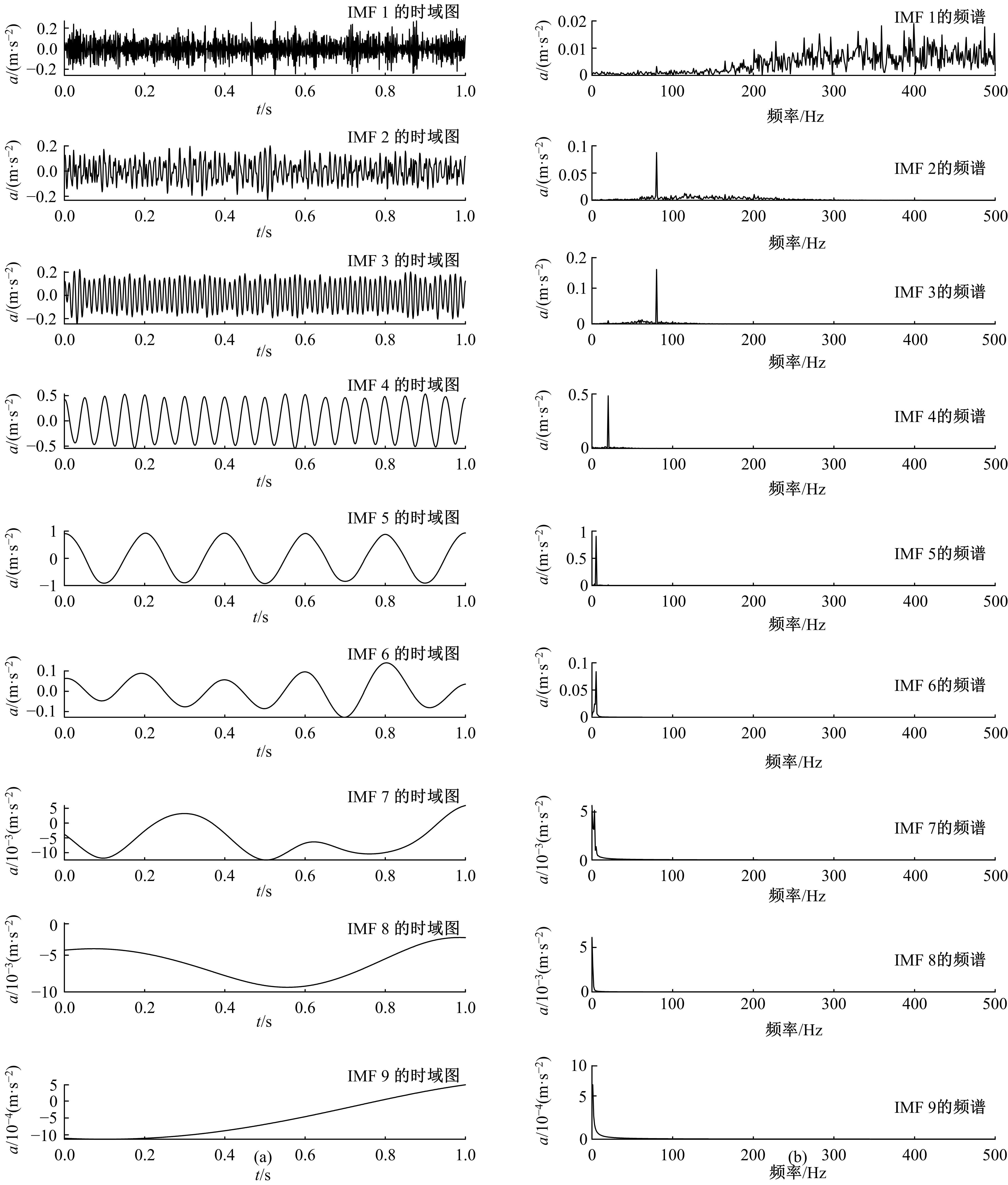
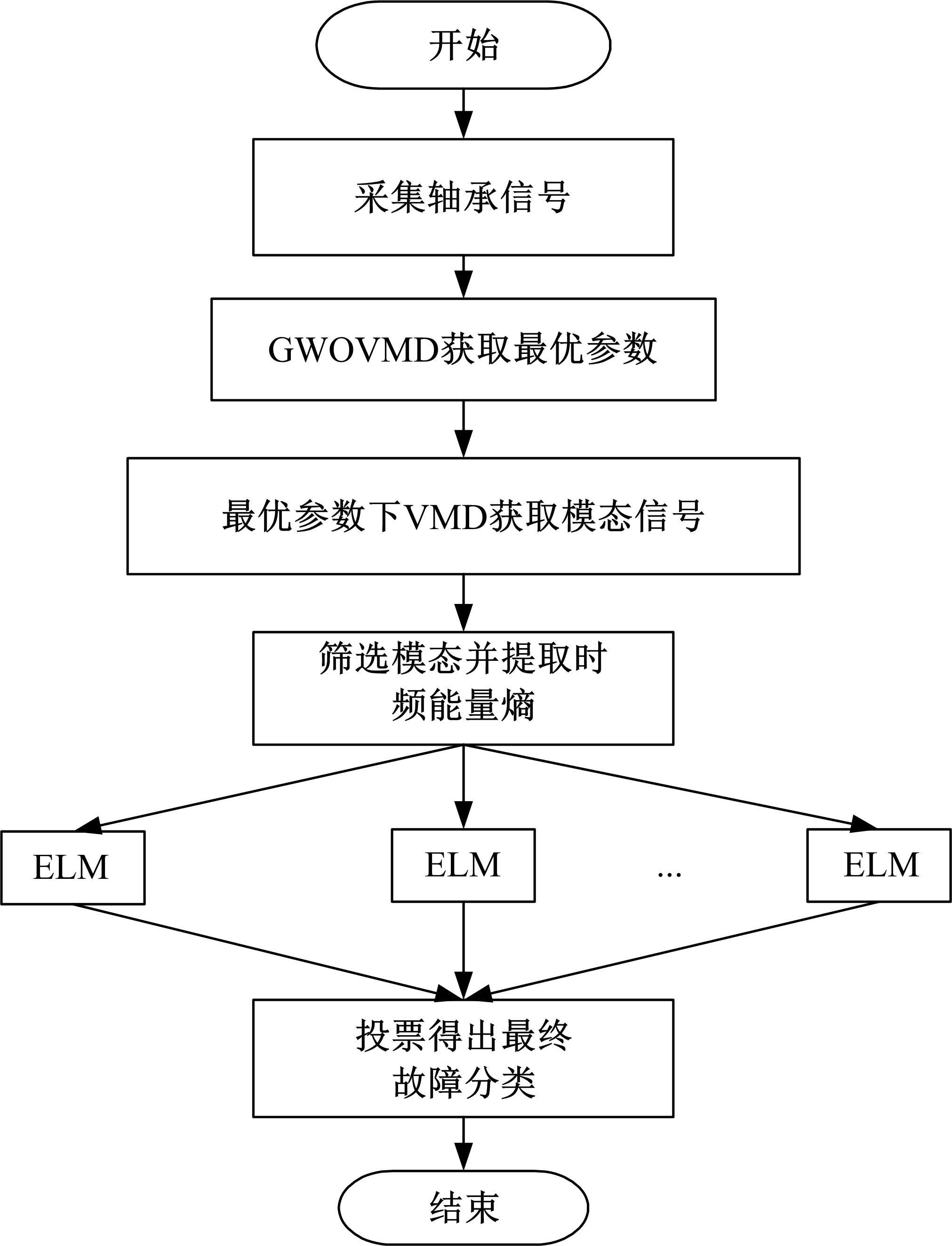
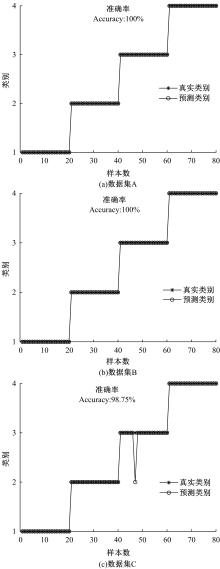
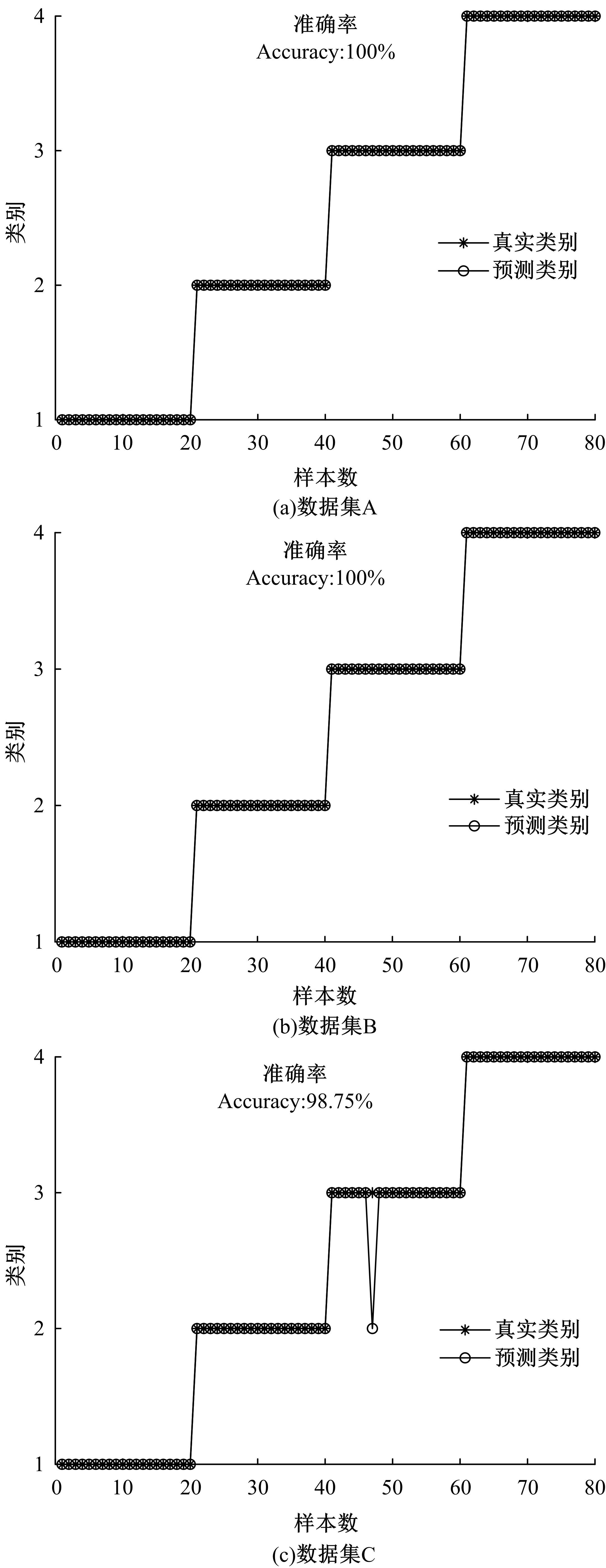
针对滚动轴承多故障诊断中特征提取困难和分类准确性低的问题,从有效特征提取和故障分类准确性两方面出发,将变分模态分解(VMD)和极限学习机(ELM)方法结合,提出了一种自适应滚动轴承多故障诊断方法。针对VMD参数需人为事先设定导致信号分解效果差的情况,提出了灰狼算法(GWO)优化VMD实现自适应地获取最佳分解参数k和α。进一步,为了克服单个ELM模型分类精度不高和分类结果不稳定的问题,提出集成极限学习机(IELM)实现多故障的分类和识别,提高故障分类的准确性和稳定性。首先,采用GWO优化VMD,自适应地获取最佳分解参数;其次,选择并提取模态信号的时频特征向量;最后,将特征向量输入到IELM中进行训练和分类。实验表明:本文方法可以自适应地分解信号并产生最佳分解效果,实现滚动轴承故障的准确早期预警和识别。
中图分类号:
- TP277
| 1 | Amirat Y, Benbouzid M E H, Al-Ahmar E, et al. A brief status on condition monitoring and fault diagnosis in wind energy conversion systems[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2009, 13(9): 2629-2636. |
| 2 | Tian Z, Jin T, Wu B, et al. Condition based maintenance optimization for wind power generation systems under continuous monitoring[J]. Renewable Energy, 2011, 36(5): 1502-1509. |
| 3 | Umamaheswari R, Maheswari R U. Trends in non-stationary signal processing techniques applied to vibration analysis of wind turbine drive train—a contemporary survey[J]. Mechanical Systems & Signal Processing, 2017, 85: 296-311 |
| 4 | Fan J, Zhu Z C, Wei L. An improved VMD with empirical mode decomposition and its application in incipient fault detection of rolling bearing[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 44483-44493. |
| 5 | Pang B, Tang G, Tian T, et al. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on an improved HTT transform[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(4): 1203-1211. |
| 6 | Huang N E, Shen Z, Long S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings Mathematical Physical & Engineering Ences, 1998, 454(1971): 903-995. |
| 7 | Liu B, Riemenschneider S, Xu Y. Gearbox fault diagnosis using empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert spectrum[J]. Mechanical Systems & Signal Processing, 2006, 20(3): 718-734. |
| 8 | Smith J S. The local mean decomposition and its application to EEG perception data[J]. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2005, 2(5): 443-454. |
| 9 | Liu W Y, Gao Q W, Ye G, et al. A novel wind turbine bearing fault diagnosis method based on integral extension LMD[J]. Measurement, 2015, 74: 70-77. |
| 10 | Gao W, Wai R J, Qiao S P, et al. Mechanical faults diagnosis of high-voltage circuit breaker via hybrid features and integrated extreme learning machine[J], IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 60091-60103. |
| 11 | 黄鑫, 张小栋, 刘洪成, 等. 涡轮叶片早期裂纹的三维叶尖间隙EEMD能量熵融合诊断方法[J]. 航空动力学报, 2020, 35(5): 918-927. |
| Huang Xin, Zhang Xiao-dong, Liu Hong-cheng, et al. Approach to early crack diagnosis of turbine blade based on EEMD energy entropy fusion of three-dimensional tip clearance[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2020, 5: 918-927. | |
| 12 | Wu Z H, Huang N E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(1): 1-41. |
| 13 | 徐艳春, 高永康, 李振兴, 等. 改进LMD算法在微电网电能质量扰动信号检测中的应用[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43(1): 332-339. |
| Xu Yan-chun, Gao Yong-kang, Li Zhen-xing, et al. Application of improved LMD algorithm in signal detection of power quality disturbance in microgrid[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43(1): 332-339. | |
| 14 | Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D. Variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(3): 531-544. |
| 15 | 刘秀丽, 徐小力, 吴国新, 等. 基于变分模态分解的故障弱信息提取方法[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 48(7): 117-121. |
| Liu Xiu-li, Xu Xiao-li, Wu Guo-xin, et al. Extraction method of weak fault information based on variational mode decomposition[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(7): 117-121. | |
| 16 | 姚晰童, 代煜, 张建勋, 等. 陡脉冲干扰下的心电信号滤波及QRS提取[J]. 工程科学学报, 2020, 42(5): 654-662. |
| Yao Xi-tong, Dai Yu, Zhang Jian-xun, et al. ECG filtering and QRS extraction under steep pulse interference[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2020, 42(5): 654-622. | |
| 17 | 李华, 伍星, 刘韬, 等. 基于信息熵优化变分模态分解的滚动轴承故障特征提取[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(23): 219-225. |
| Li Hua, Wu Xing, Liu Tao, et al. Bearing fault feature extraction based on VMD optimized with information entropy[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(23): 219-225. | |
| 18 | 谷然, 陈捷, 洪荣晶, 等. 基于改进自适应变分模态分解的滚动轴承微弱故障诊断[J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(8): 1-7, 22. |
| Gu Ran, Chen Jie, Hong Rong-jing, et al. Early fault diagnosis of rolling bearings based on adaptive variational mode decomposition and the Teager energy operator[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(8): 1-7, 22. | |
| 19 | 刘建昌, 权贺, 于霞, 等. 基于参数优化VMD和样本熵的滚动轴承故障诊断[J/OL]. [2020-08-27]. |
| 20 | 焦博隆, 钟志贤, 刘翊馨, 等. 基于蝙蝠算法优化的变分模态分解的转子裂纹检测方法[J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(6): 98-103, 124. |
| Jiao Bo-long, Zhong Zhi-xian, Liu Yi-xin, et al. Rotor crack detection method based on variational mode decomposition based on optimization parameters of bat algorithm[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(6): 98-103, 124. | |
| 21 | Mirjalili S, Mirjalili S M, Lewis A. Grey wolf optimizer[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2014, 69: 46-61. |
| 22 | Gu R, Chen J, Hong R J, et al. Incipient fault diagnosis of rolling bearings based on adaptive variational mode decomposition and Teager energy operator[J]. Measurement, 2020, 14: 106941. |
| 23 | Huang G B, Zhou H, Ding X, et al. Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man & Cybernetics Part B, 2012, 42(2): 513-529. |
| 24 | Zhao Z, Chen Z, Chen Y, et al. A class incremental extreme learning machine for activity recognition[J]. Cognitive Computation, 2014, 6(3): 423-431. |
| 25 | Laddada S, Si-Chaib M O, Benkedjouh T, et al. Tool wear condition monitoring based on wavelet transform and improved extreme learning machine[J]. ARCHIVE Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part C, Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2020, 234(5): 095440621988854. |
| 26 | Qiao S P, Gao W, Wai R J, et al. A method of mechanical fault feature extraction for high-voltage circuit breaker via CEEMDAN and weighted time-frequency entropy[C]∥4th International Conference on Intelligent Green Building and Smart Grid, Yichang, 2019: 25-29. |
| 27 | Chen X J, Yang Y M, Cui Z X, et al. Vibration fault diagnosis of wind turbines based on variational mode decomposition and energy entropy[J]. Energy, 2019, 174: 1100-1109. |
| 28 | Zhang X L, Yan Q, Yang J, et al. An assembly tightness detection method for bolt-jointed rotor with wavelet energy entropy[J]. Measurement, 2019, 136:212-244. |
| 29 | Li J C. A novel recognition algorithm based on holder coefficient theory and interval gray relation classifier[J]. Ksii Transactions on Internet & Information Systems, 2015, 9(11): 4573-4584. |
| 30 | Li H, Fan B, Jia R, et al. Research on multi-domain fault diagnosis of gearbox of wind turbine based on adaptive variational mode decomposition and extreme learning machine algorithms[J]. Energies, 2020, 13(6): 1-20. |
| [1] | 董绍江,朱朋,裴雪武,李洋,胡小林. 基于子领域自适应的变工况下滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 288-295. |
| [2] | 陈晓雷,孙永峰,李策,林冬梅. 基于卷积神经网络和双向长短期记忆的稳定抗噪声滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 296-309. |
| [3] | 欧阳丹彤,张必歌,田乃予,张立明. 结合格局检测与局部搜索的故障数据缩减方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2144-2153. |
| [4] | 院老虎,连冬杉,张亮,刘义. 基于密集连接卷积网络和支持向量机的飞行器机械部件故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1635-1641. |
| [5] | 李伟,陈剑,陶善勇. 自适应耦合周期势系统随机共振信号增强方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1091-1096. |
| [6] | 欧阳丹彤,刘扬,刘杰. 故障响应指导下基于测试集的故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1017-1025. |
| [7] | 潘凤文,弓栋梁,高莹,徐明伟,麻斌. 基于锂离子电池线性化模型的电流传感器故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 435-441. |
| [8] | 张根保,李浩,冉琰,李裘进. 一种用于轴承故障诊断的迁移学习模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1617-1626. |
| [9] | 王德军, 魏薇郦, 鲍亚新. 考虑侧风干扰的电子稳定控制系统执行器故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1548-1555. |
| [10] | 毛宇泽, 王黎钦. 鼠笼支撑一体化结构对薄壁球轴承承载性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1508-1514. |
| [11] | 宋大凤, 李广含, 张琳, 潘冰, 曾小华, 彭宇君, 王庆年. 模糊逻辑在混合动力汽车电机故障检测中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 354-359. |
| [12] | 欧阳丹彤,迟晋进,王晓宇,赵相福,孟祥宇. 一种高阶离散事件系统的诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 562-568. |
| [13] | 陶涛,徐洪泽. 高速列车浸入与不变自适应容错控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 554-561. |
| [14] | 宋宝玉,解志杰,张锋,王瑞泽,郝明晖,苏代忠. 基于角度域同步平均和阶次分析的低速斜齿轮故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 454-459. |
| [15] | 吴坚, 赵阳, 何睿. 基于支持向量机回归算法的电子机械制动传感器系统故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(05): 1178-1183. |
|
||