吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (8): 1834-1841.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210115
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于三段式特征选择策略的脑电情感识别算法SEE
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.吉林大学 符号计算与知识工程教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
SEE: sense EEG⁃based emotion algorithm via three⁃step feature selection strategy
Feng-feng ZHOU1,2( ),Hai-yang ZHU1,2
),Hai-yang ZHU1,2
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
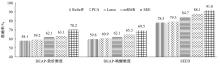
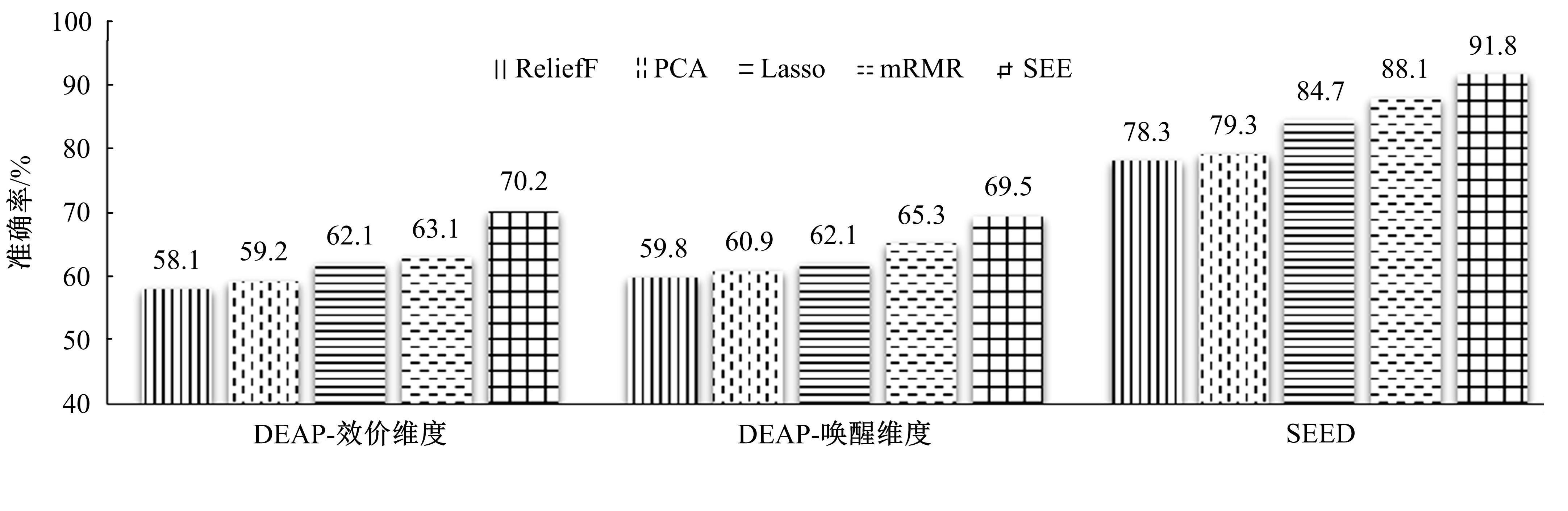
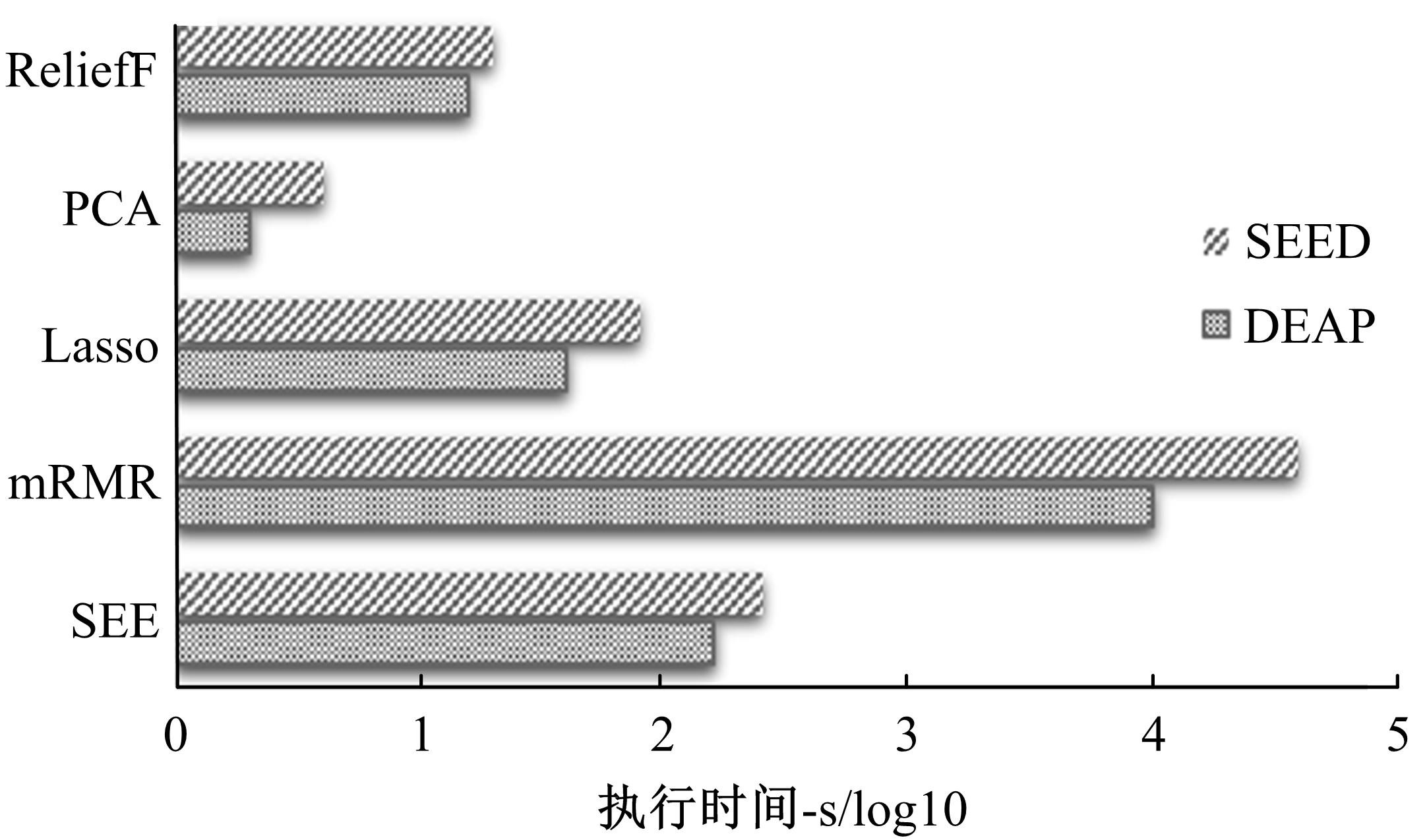
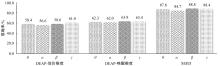
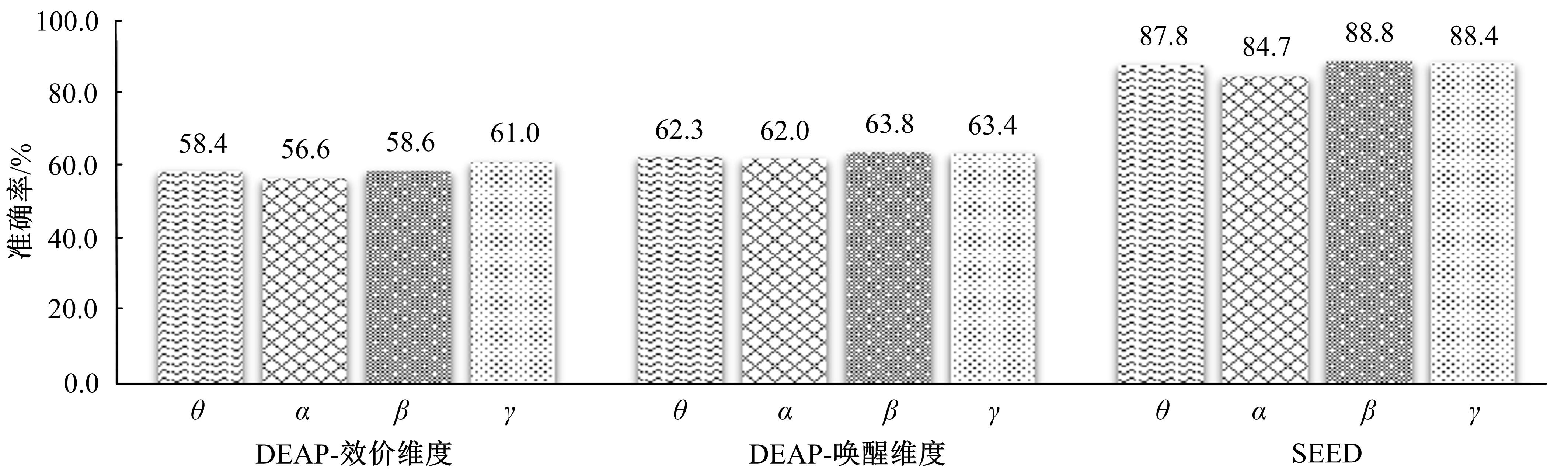
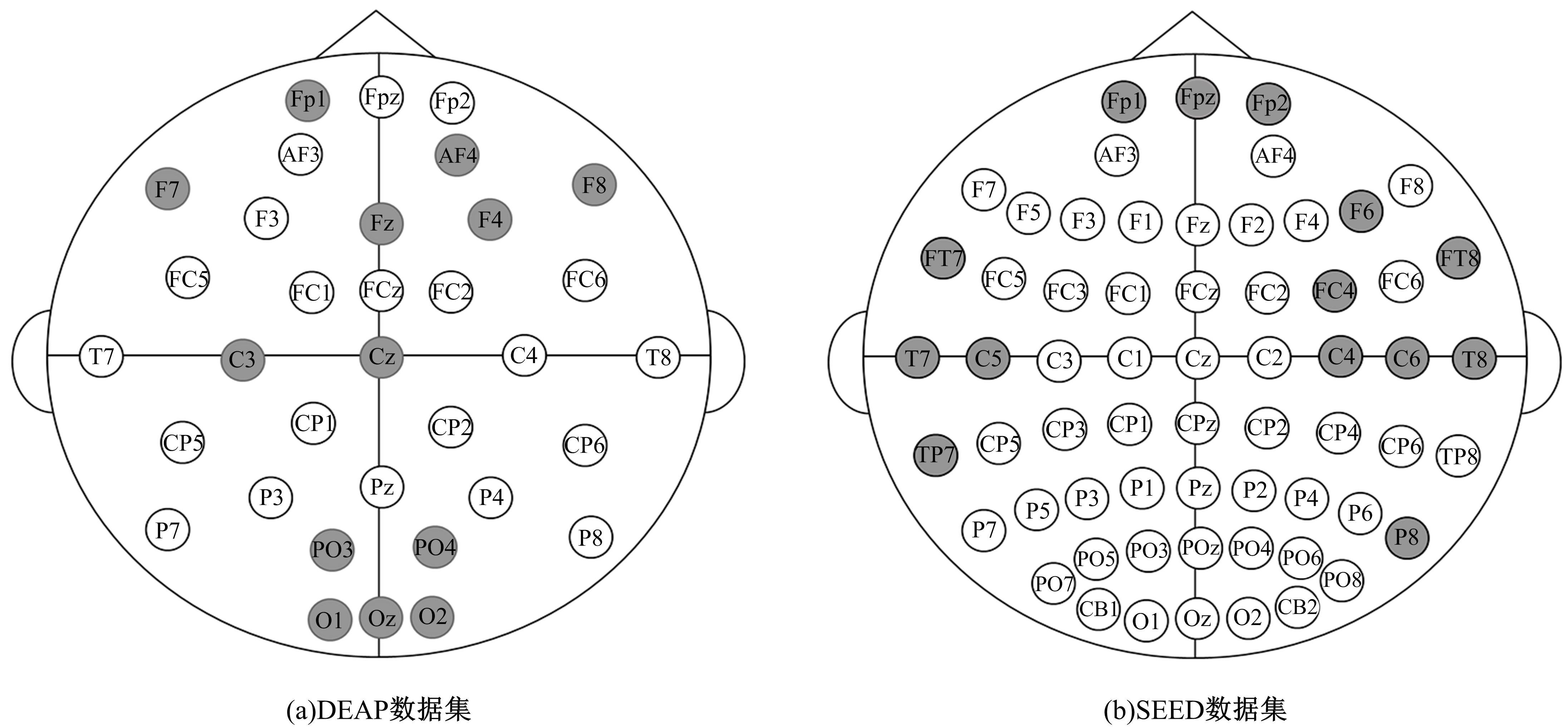
情感可以通过脑电信号中的隐藏模式来识别,基于众多的脑电通道提取的脑电特征数量庞大,使情感识别任务非常复杂。针对上述问题,提出了基于三段式特征选择策略的脑电情感识别算法(SEE)。本文从时域、频域、空间域系统地提取脑电特征,基于提取的脑电特征集合,首先通过t检验去除类间无显著差异的特征,再使用递归特征消除策略进行目标相关的特征选择,最后通过顺序后向特征选择策略确定最终的特征子集用于情感识别。实验结果表明:相较于其他方法,本文构建的模型有更好的情感识别能力。与现有的特征选择算法相比,SEE具有较低的时间复杂度并且能筛选出较优的特征子集。此外,分析了与情感相关的脑电通道和频带,实验结果体现了一定的生理学意义,为开发情绪靶向的脑电设备提供可能。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Fraschini M, Meli M, Demuru M, et al. EEG fingerprints under naturalistic viewing using a portable device[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(22): 20226565. |
| 2 | 方明, 陈文强. 结合残差网络及目标掩膜的人脸微表情识别[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(1): 303-313. |
| Fang Ming, Chen Wen-qiang. Face micro-expression recognition based on ResNet with object mask[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 303-313. | |
| 3 | Li X, Song D, Zhang P, et al. Exploring EEG features in cross-subject emotion recognition[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2018, 12(1): 162-176. |
| 4 | 代琨, 于宏毅, 仇文博, 等. 基于SVM的网络数据无监督特征选择算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2015, 45(2): 576-582. |
| Dai Kun, Yu Hong-yi, Qiu Wen-bo, et al. Unsupervised feature selection algorithm based on support vector machine for network data[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(2): 576-582. | |
| 5 | Gupta V, Chopda M D, Pachori R B. Cross-subject emotion recognition using flexible analytic wavelet transform from EEG signals[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(6): 2266-2274. |
| 6 | Duan R N, Zhu J Y, Lu B L. Differential entropy feature for EEG-based emotion classification[C]∥6th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, San Diego, USA, 2013: 81-84. |
| 7 | Zheng W L, Lu B L. Investigating critical frequency bands and channels for EEG-based emotion recognition with deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Autonomous Mental Development, 2015, 7(3): 162-175. |
| 8 | Zhang J H, Chen M, Zhao S K, et al. Relieff-based EEG sensor selection methods for emotion recognition[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(10): 1558-1572. |
| 9 | 周怡娜, 董宏丽, 张勇, 等. 基于VMD去噪和散布熵的管道信号特征提取方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(4): 959-969. |
| Zhou Yi-na, Dong Hong-li, Zhang Yong, et al. Feature extraction method of pipeline signals based on VMD de-noising and dispersion entropy[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 959-969. | |
| 10 | Yang S, Li B, Zhang Y, et al. Selection of features for patient-independent detection of seizure events using scalp EEG signals[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2020, 119: 103671. |
| 11 | 张冠华, 余旻婧, 陈果, 等. 面向情绪识别的脑电特征研究综述[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2019, 49(9):1097-1118. |
| Zhang Guan-hua, Yu Min-jing, Chen Guo, et al. A review of EEG features for emotion recognition[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2019, 49(9): 1097-1118. | |
| 12 | Koelstra S, Muhl C, Soleymani M, et al. DEAP: a database for emotion analysis; using physiological signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2012, 3(1): 18-31. |
| 13 | Arnau-Gonzalez P, Arevalillo-Herraez M, Ramzan N. Fusing highly dimensional energy and connectivity features to identify affective states from EEG signals[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 244: 81-89. |
| 14 | Yang B, Han X, Tang J. Three class emotions recognition based on deep learning using staked autoencoder[C]∥10th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics, Shanghai, China, 2017: 1-5. |
| 15 | Wu X, Zheng W L, Lu B L. Identifying functional brain connectivity patterns for EEG-based emotion recognition[C]∥9th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 235-238. |
| 16 | Zhang W, Wang F, Jiang Y, et al. Cross-subject EEG-Based emotion recognition with deep domain confusion[C]∥International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications, Shenyang, China, 2019: 558-570. |
| 17 | Sarlo M, Buodo G, Poli S, et al. Changes in EEG alpha power to different disgust elicitors: the specificity of mutilations[J]. Neuroscience Letters, 2005, 382(3): 291-296. |
| 18 | Li M, Lu B L. Emotion classification based on gamma-band EEG[C]∥Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, USA, 2009: 1223-1226. |
| 19 | Saarimki H, Gotsopoulos A, Jskelinen I P, et al. Discrete neural signatures of basic emotions[J]. Cerebral Cortex, 2015, 26(6): 2563-2573. |
| 20 | Lin Y P, Yang Y H, Jung T P. Fusion of electroencephalographic dynamics and musical contents for estimating emotional responses in music listening[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2014, 8: 94-107. |
| [1] | 周丰丰,张亦弛. 基于稀疏自编码器的无监督特征工程算法BioSAE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1645-1656. |
| [2] | 王斌,何丙辉,林娜,王伟,李天阳. 基于随机森林特征选择的茶园遥感提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1719-1732. |
| [3] | 王军,徐彦惠,李莉. 低能耗支持完整性验证的数据融合隐私保护方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1657-1665. |
| [4] | 王生生,姜林延,杨永波. 基于最优传输特征选择的医学图像分割迁移学习[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1626-1638. |
| [5] | 康耀龙,冯丽露,张景安,陈富. 基于谱聚类的高维类别属性数据流离群点挖掘算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1422-1427. |
| [6] | 王文军,余银峰. 考虑数据稀疏的知识图谱缺失连接自动补全算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1428-1433. |
| [7] | 陈雪云,贝学宇,姚渠,金鑫. 基于G⁃UNet的多场景行人精确分割与检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 925-933. |
| [8] | 方世敏. 基于频繁模式树的多来源数据选择性集成算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 885-890. |
| [9] | 李大湘,陈梦思,刘颖. 基于STA⁃LSTM的自发微表情识别算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 897-909. |
| [10] | 魏晓辉,苗艳微,王兴旺. Rhombus sketch:自适应和准确的流数据sketch[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 874-884. |
| [11] | 刘铭,杨雨航,邹松霖,肖志成,张永刚. 增强边缘检测图像算法在多书识别中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 891-896. |
| [12] | 毛琳,任凤至,杨大伟,张汝波. 双向特征金字塔全景分割网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 657-665. |
| [13] | 王雪,李占山,吕颖达. 基于多尺度感知和语义适配的医学图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 640-647. |
| [14] | 欧阳继红,郭泽琪,刘思光. 糖尿病视网膜病变分期双分支混合注意力决策网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 648-656. |
| [15] | 王学智,李清亮,李文辉. 融合迁移学习的土壤湿度预测时空模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 675-683. |
|
||