吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (7): 1719-1732.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210138
• 农业工程·仿生工程 • 上一篇
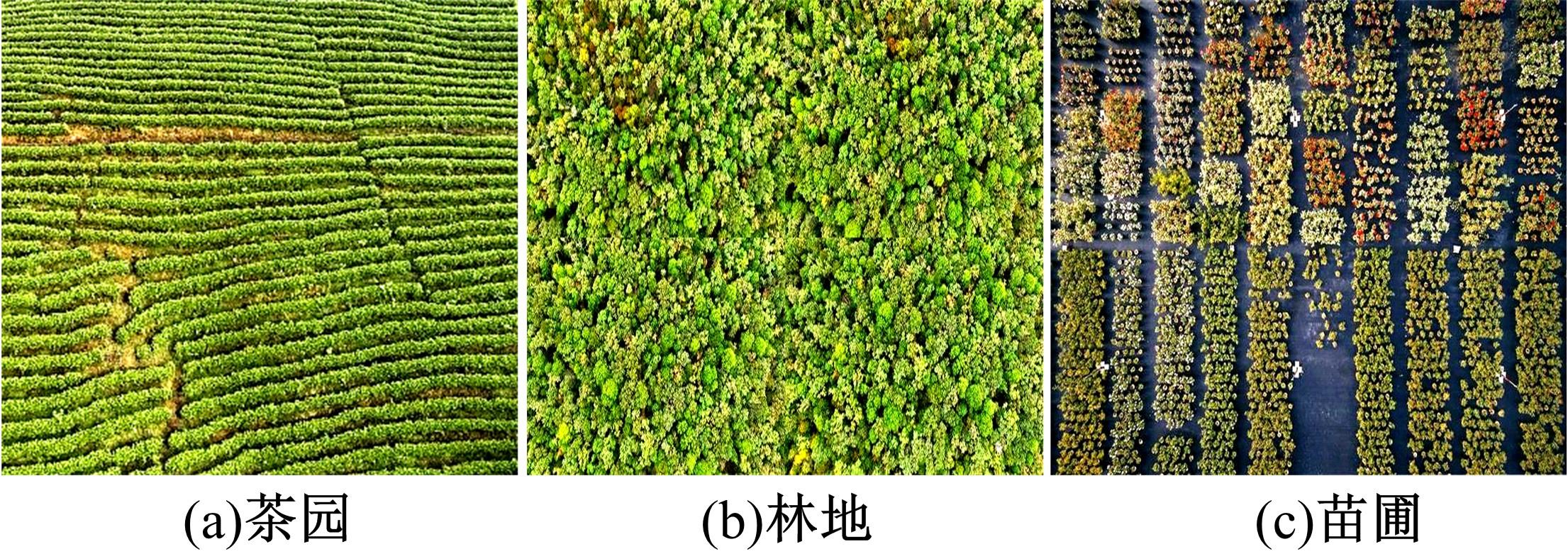
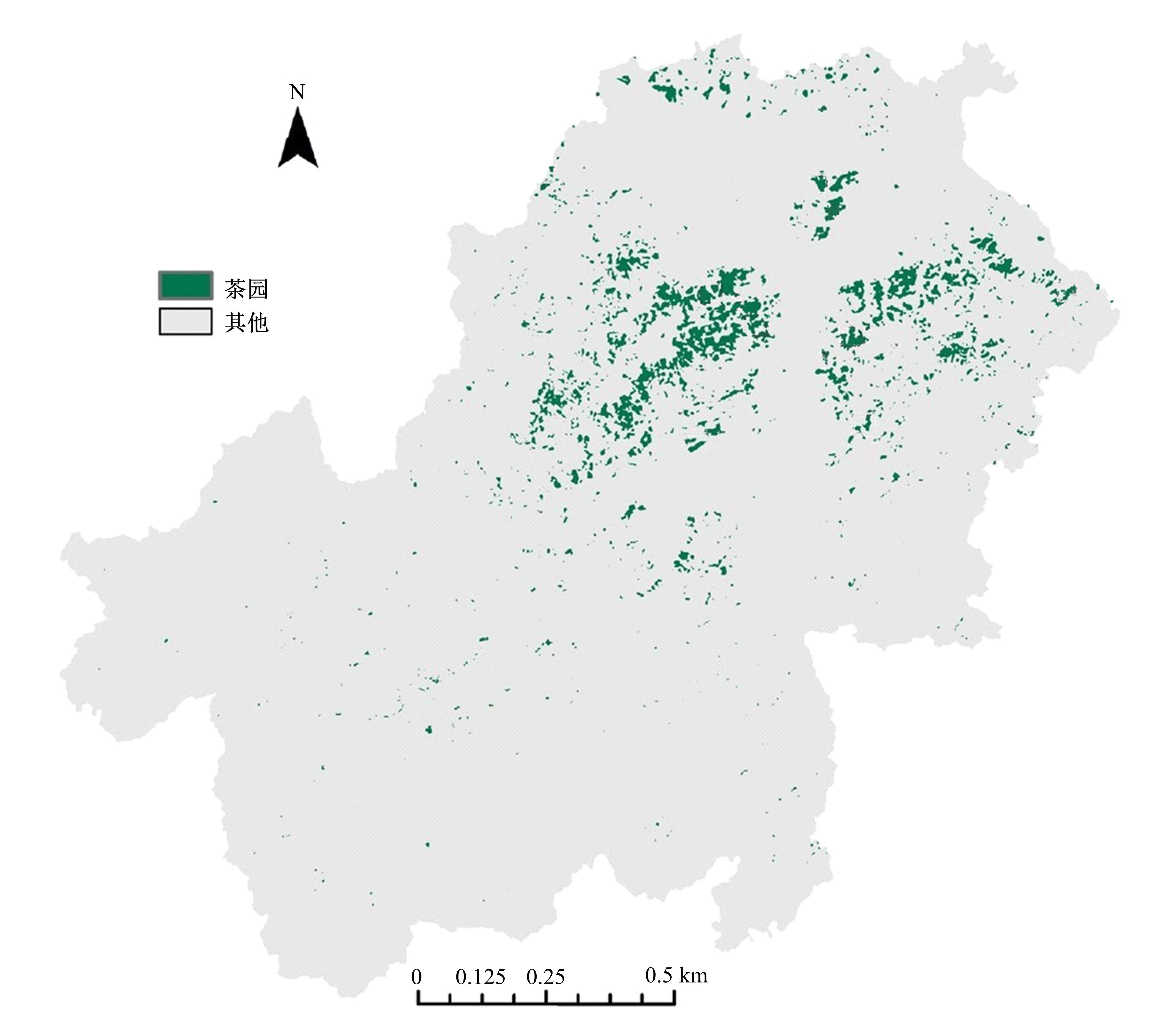
基于随机森林特征选择的茶园遥感提取
- 1.西南大学 资源环境学院,重庆 400715
2.重庆市地理信息和遥感应用中心,重庆 401147
3.重庆交通大学 土木工程学院,重庆 400074
Tea plantation remote sensing extraction based on random forest feature selection
Bin WANG1,2( ),Bing-hui HE1(
),Bing-hui HE1( ),Na LIN3,Wei WANG3,Tian-yang LI1
),Na LIN3,Wei WANG3,Tian-yang LI1
- 1.College of Resources and Environment,Southwest University,Chongqing 400715,China
2.Chongqing Geomatics and Remote Sensing Center,Chongqing 401147,China
3.School of Civil Engineering,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
摘要:
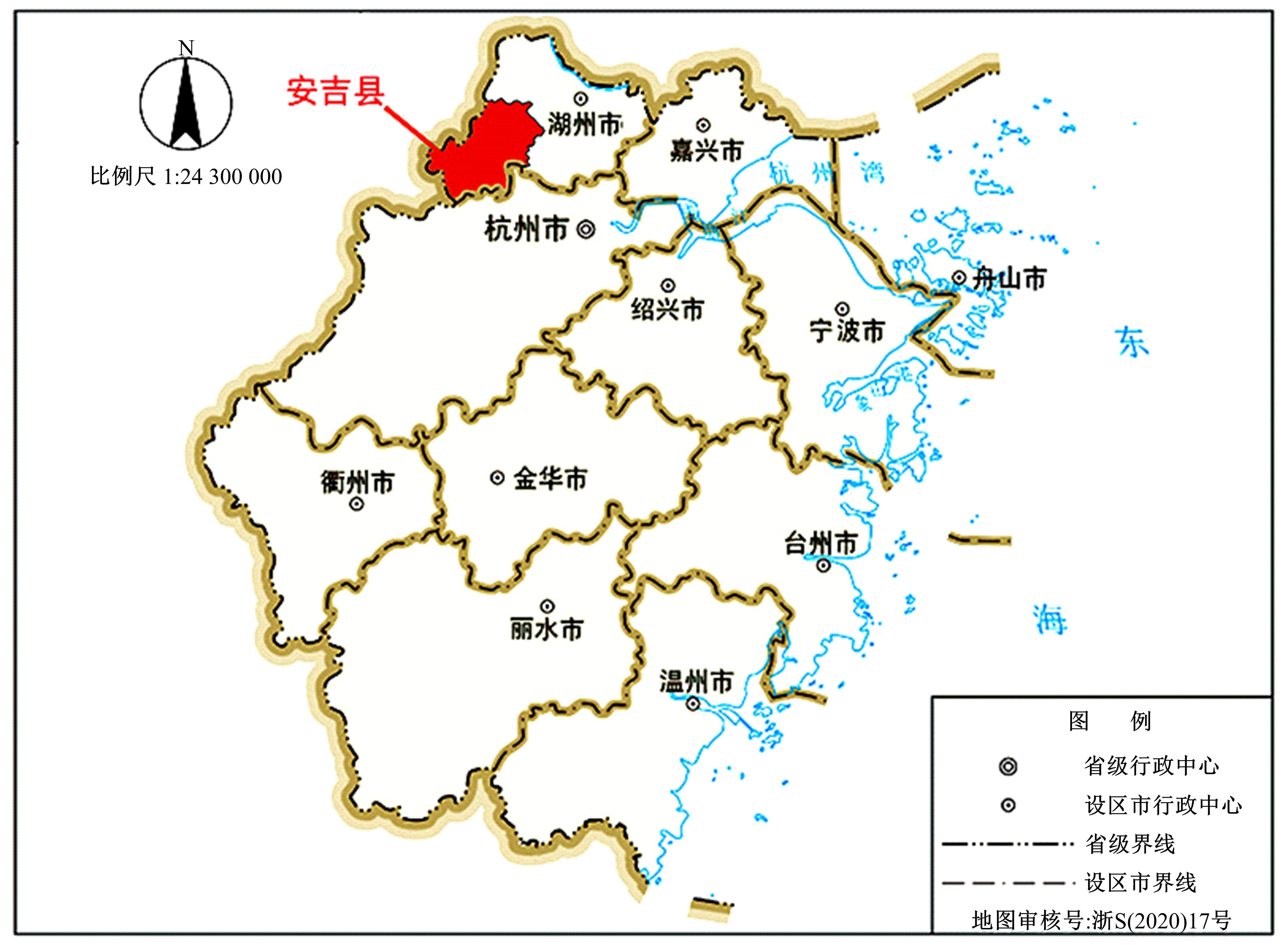
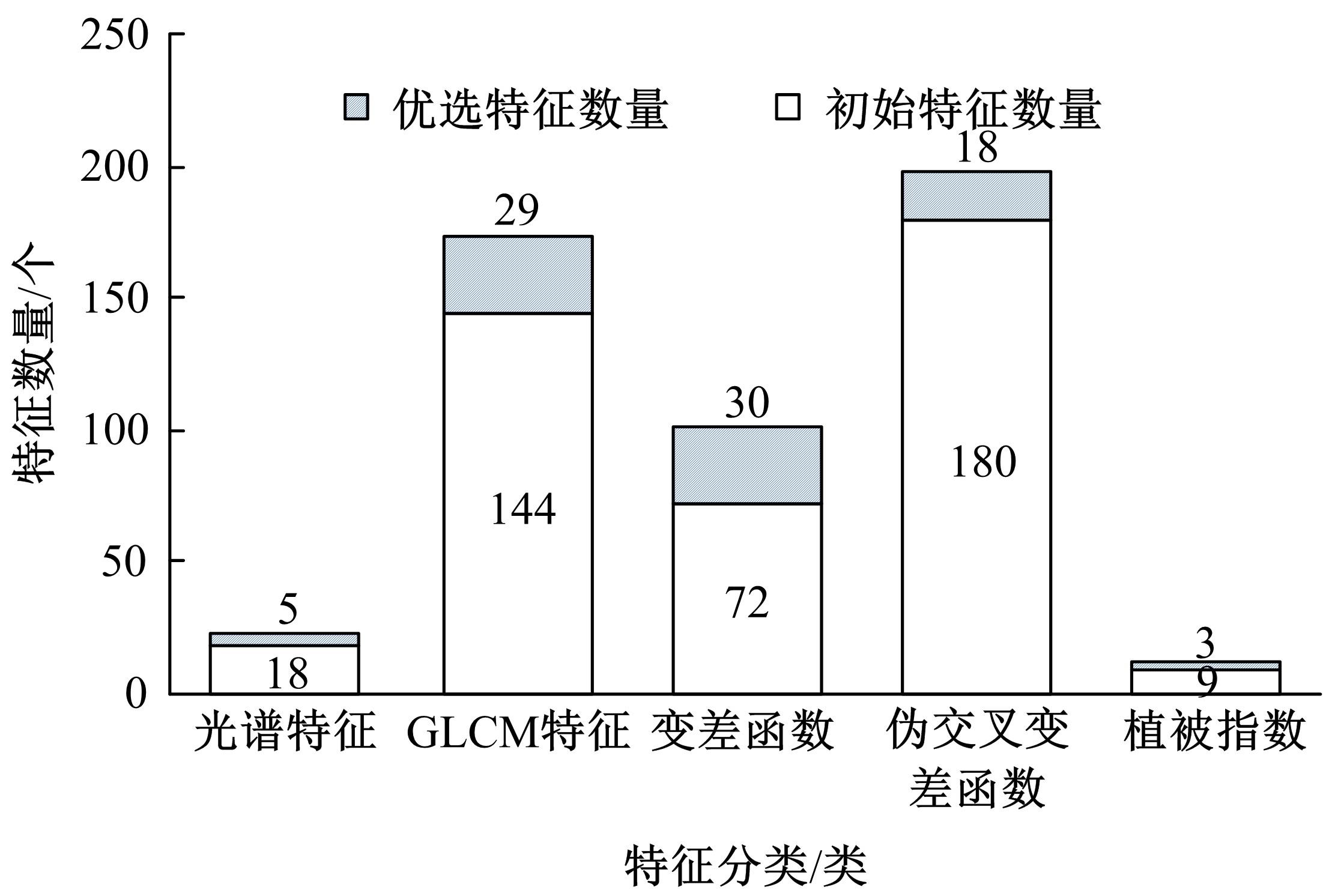
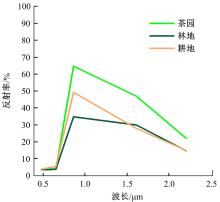
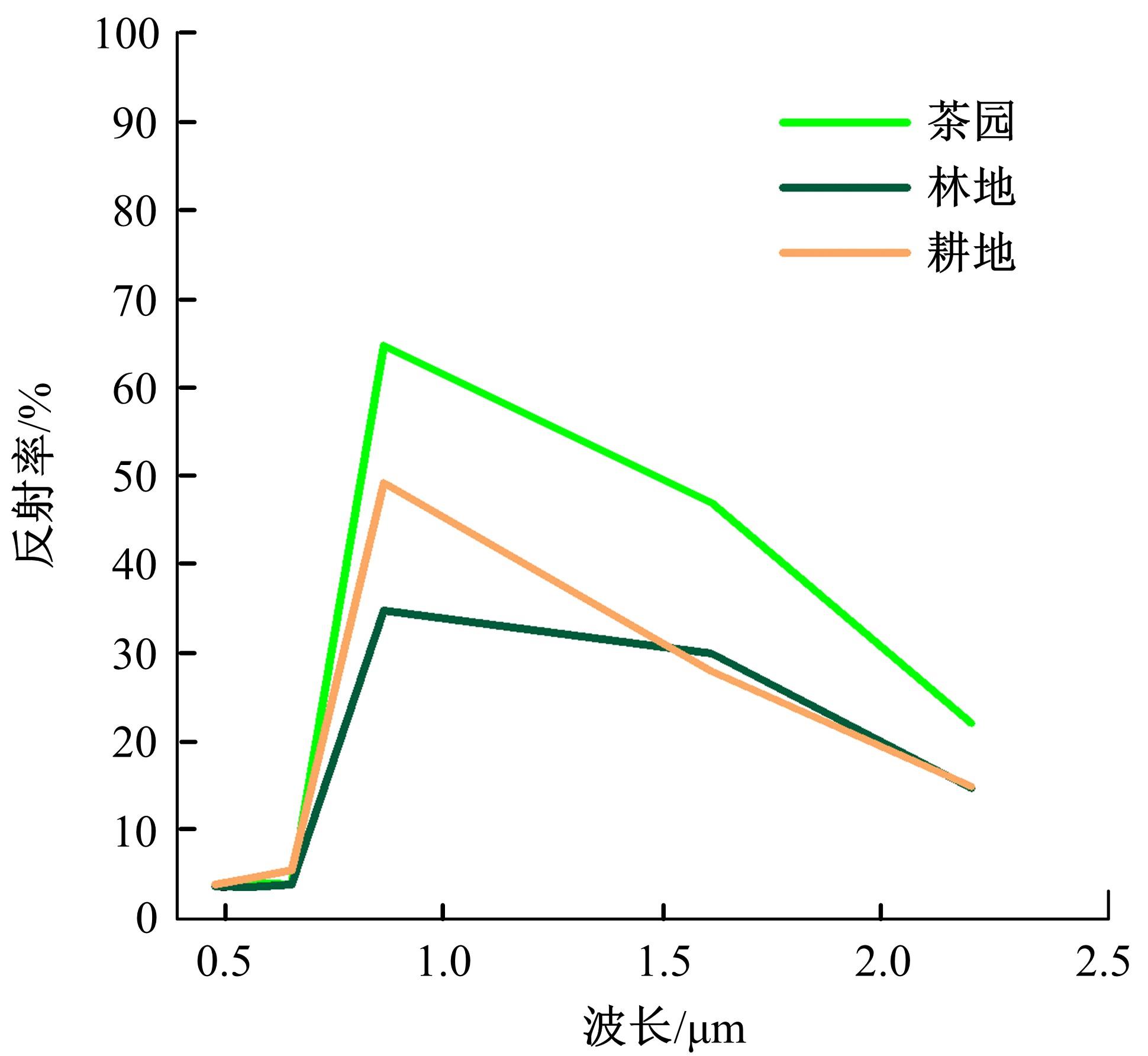
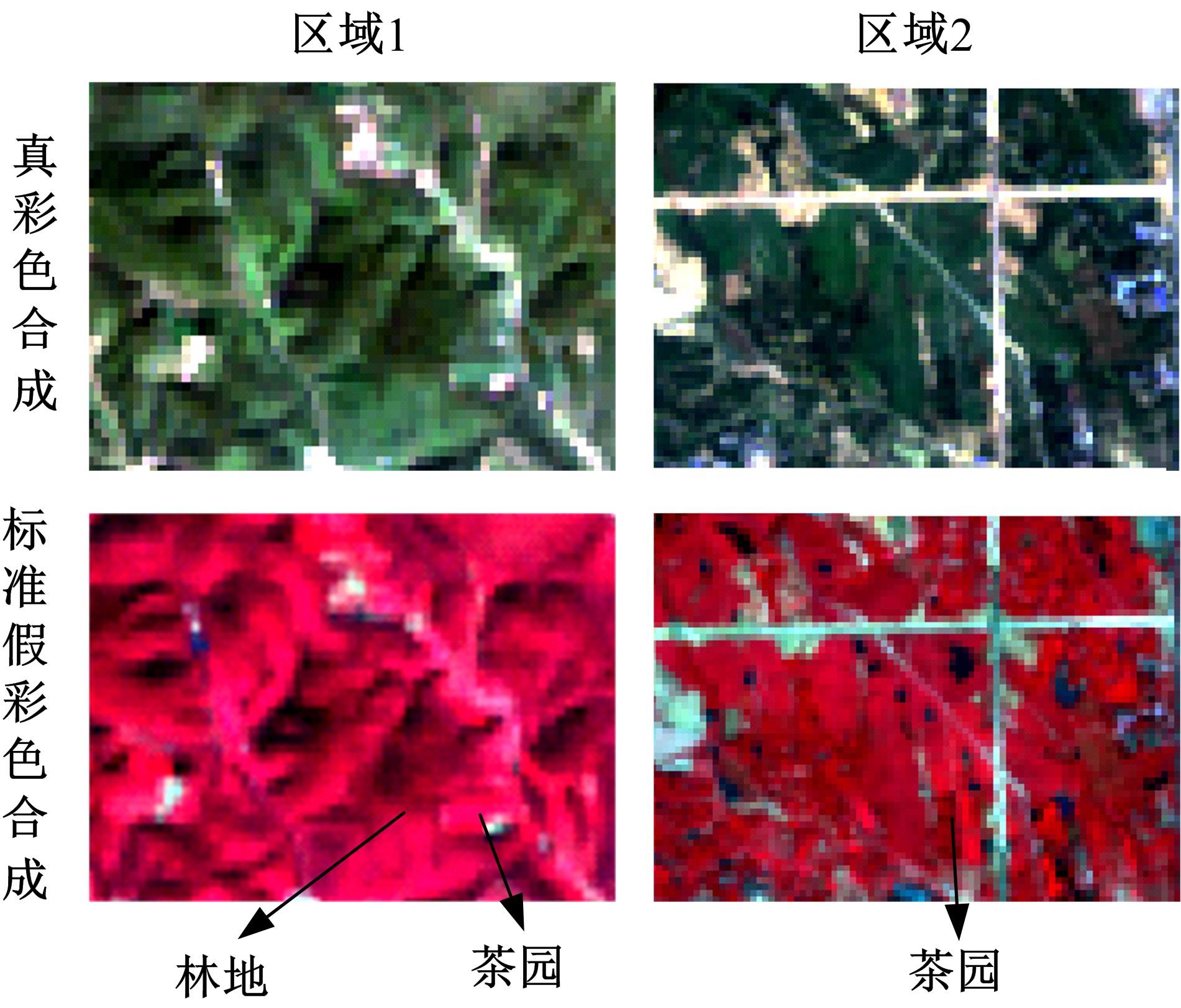
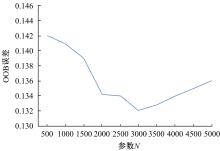
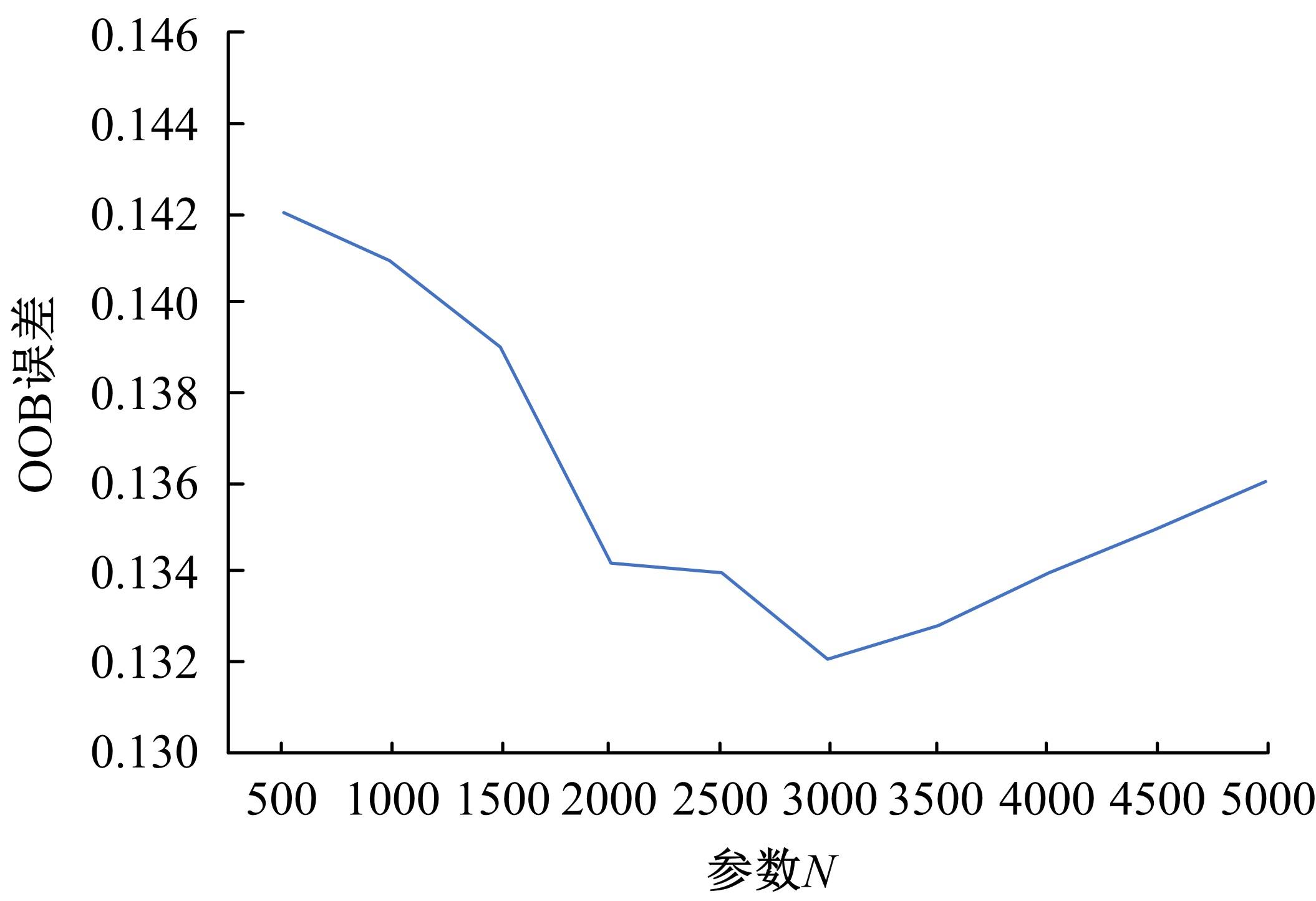
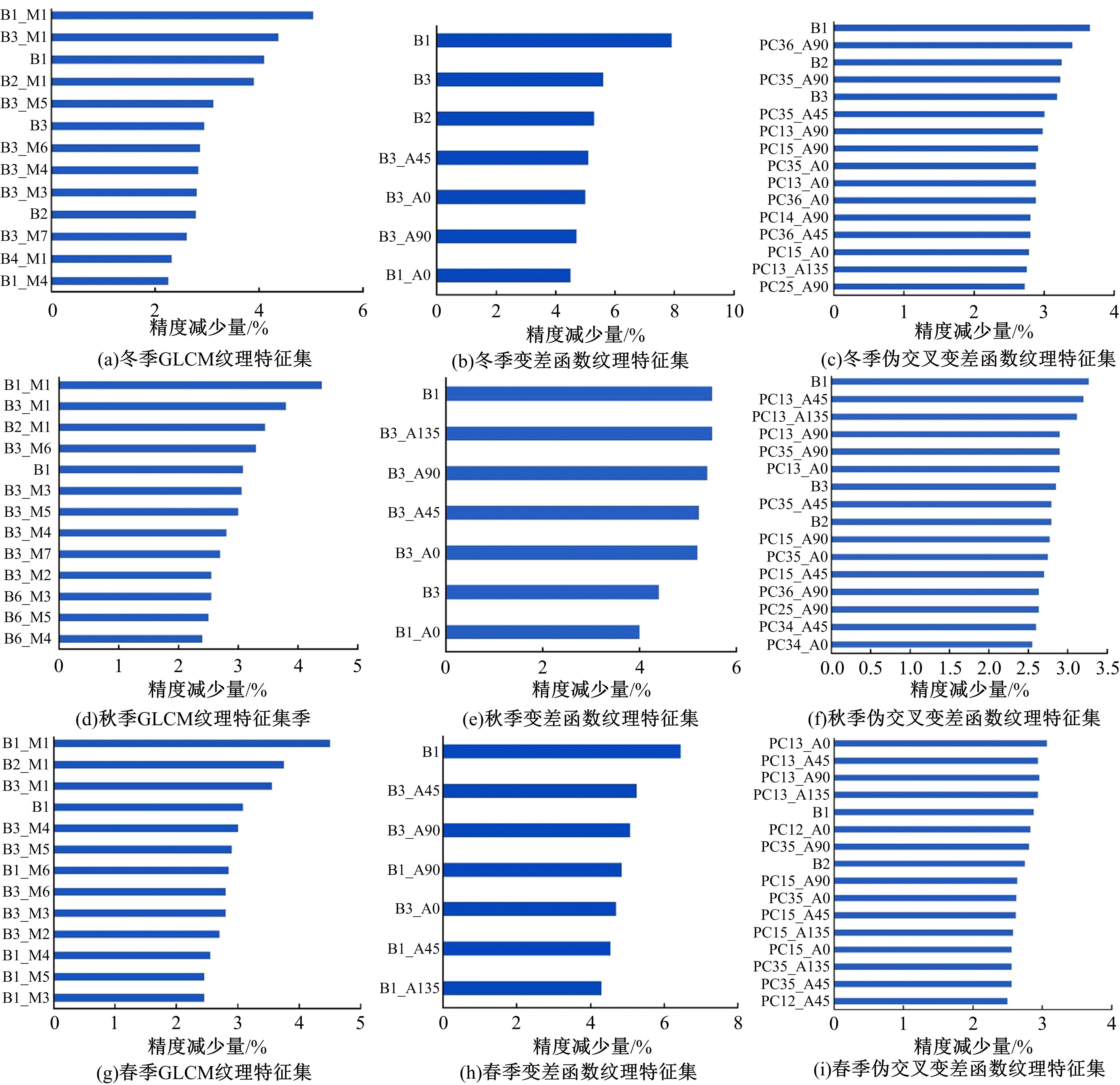
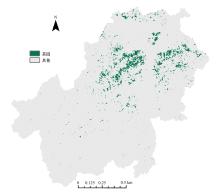
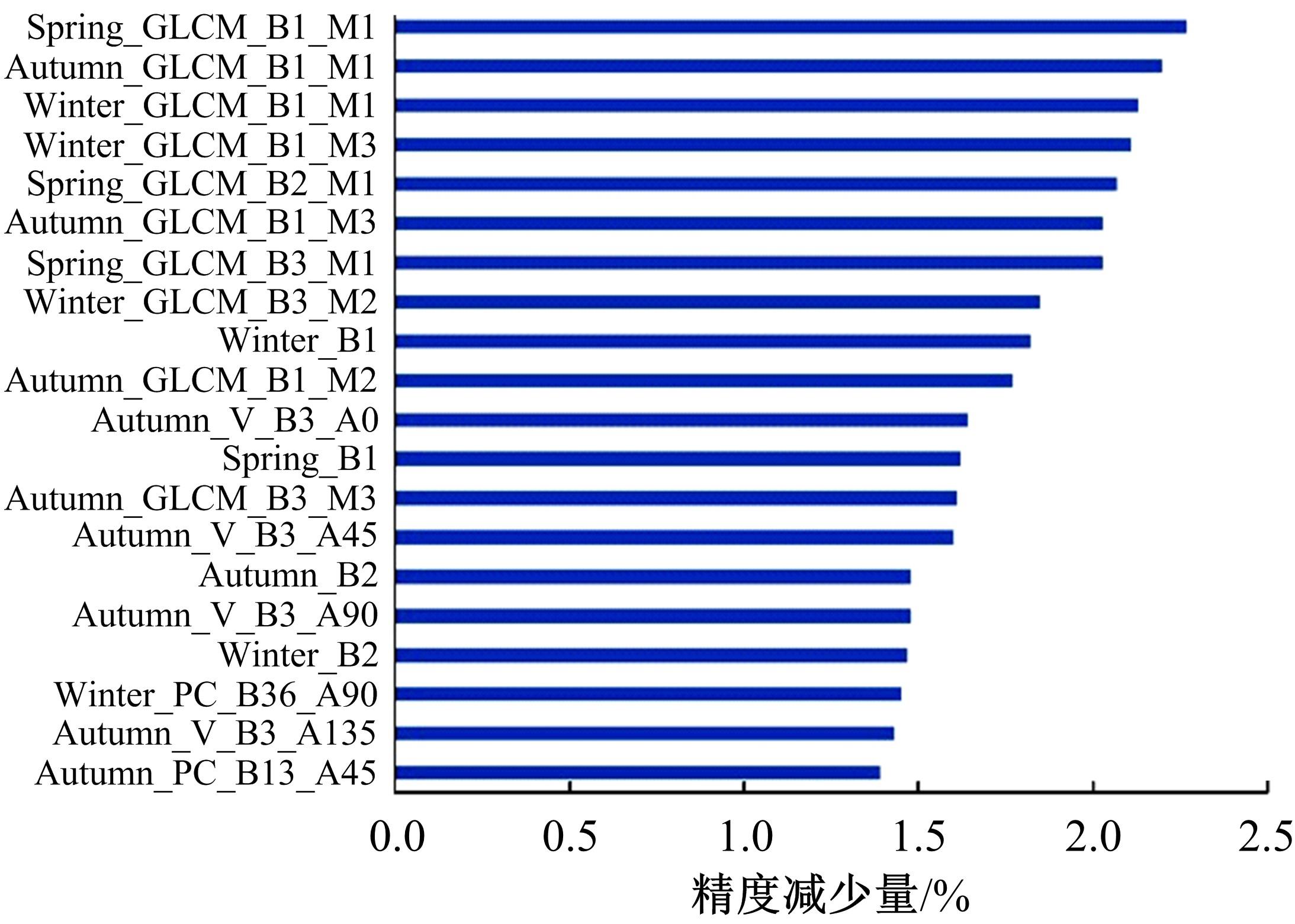
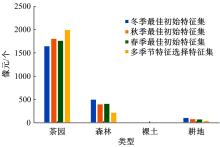
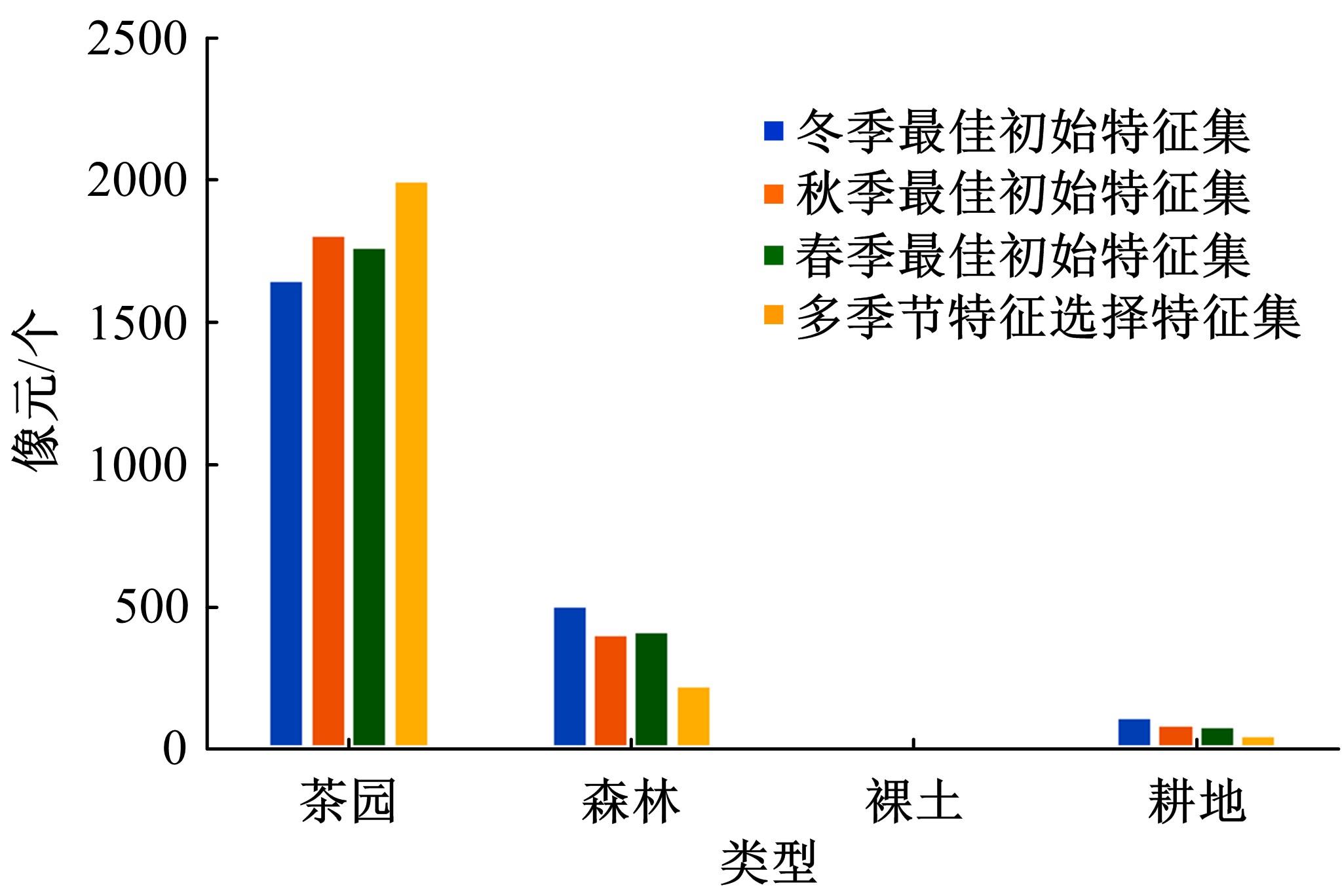
由于茶园空间分布零散、形状不规则、与周围植被光谱特征接近等原因,从卫星影像中提取茶园非常具有挑战性。针对这一问题,本文研究提出了基于随机森林特征选择方法和Landsat-8 OLI影像进行茶园提取的技术路线,以浙江省安吉县为例,采用春、秋、冬季Landsat-8 OLI影像作为主要数据源,利用随机森林对茶园影像特征进行重要性评估、排序和特征选择,设计了单季节初始特征集、单季节优选特征集、多季节优选特征集,并进行了9组茶园提取实验。结果表明,融合了特征选择和多季节信息优势于一体的多季节优选特征集具有最好的性能表现,其精度如下:生产者精度为87.5%、总体精度为92.4%、Kappa系数为0.897。本文提出的技术路线充分发挥了其在提高遥感分类精度和降低维度等方面的作用,实现了对空间分布离散、形状欠规则的茶园的有效提取。
中图分类号:
- F307.1
| 1 | Liu Y L, Feng Y H, Zhao Z, et al. Socioeconomic drivers of forest loss and fragmentation: a comparison between different land use planning schemes and policy implications[J]. Land Use Policy, 2016, 54: 58-68. |
| 2 | Su S L, Zhou X C, Wan C, et al. Land use changes to cash crop plantations: crop types, multilevel determinants and policy implications[J]. Land Use Policy, 2016, 50: 379-389. |
| 3 | 徐乔,张霄,余绍淮,等. 综合多特征的极化SAR图像随机森林分类算法[J]. 遥感学报, 2019, 23(4): 685-694. |
| Xu Qiao, Zhang Xiao, Yu Shao-huai, et al. Multi-feature-based classification method using random forest and superpixels for polarimetric SAR images[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2019, 23(4): 685-694. | |
| 4 | 王娜,李强子,杜鑫,等. 单变量特征选择的苏北地区主要农作物遥感识别[J]. 遥感学报, 2017, 21(4): 519-530. |
| Wang Na, Li Qiang-zi, Du Xin, et al. Identification of main crops based on the univariate feature selection in Subei[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2017, 21(4): 519-530. | |
| 5 | 耿仁方,付波霖,蔡江涛,等. 基于无人机影像和面向对象随机森林算法的岩溶湿地植被识别方法研究[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2019, 21(8): 1295-1306. |
| Geng Ren-fang, Fu Bo-lin, Cai Jiang-tao, et al. Object-based karst wetland vegetation classification method using unmanned aerial vehicle images and random forest algorithm[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2019, 21(8): 1295-1306. | |
| 6 | 董强,刘晶红,周前非. 用于遥感图像拼接的改进SURF算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(5): 1644-1652. |
| Dong Qiang, Liu Jin-hong, Zhou Qian-fei. Improved SURF algorithm used in image mosaic[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(5): 1644-1652. | |
| 7 | 刘凯,龚辉,曹晶晶,等. 基于多类型无人机数据的红树林遥感分类对比[J]. 热带地理, 2019, 39(4): 492-501. |
| Liu Kai, Gong Hui, Cao Jing-jing, et al. Comparison of mangrove remote sensing classification based on multi-type UAV data[J]. Tropical Geography, 2019, 39(4): 492-501. | |
| 8 | 陈媛媛,郑加柱,魏浩翰,等. 基于不同特征的随机森林极化SAR图像分类[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2019, 28(8): 183-189. |
| Chen Yuan-yuan, Zheng Jia-zhu, Wei Hao-han, et al. Tidal flat classification based on random forest model using different features of polarimetric SAR[J]. Computer Systems & Applications, 2019, 28(8): 183-189. | |
| 9 | 许章华,黄旭影,林璐,等. 基于Fisher判别分析与随机森林的马尾松毛虫害检测[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(9): 2888-2896. |
| Xu Zhang-hua, Huang Xu-ying, Lin Lu, et al. Dendrolimus punctatus walker damage detection based on fisher discriminant analysis and random forest[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2018, 38(9): 2888-2896. | |
| 10 | 陈妍,宋豫秦,王伟. 基于随机森林回归的草场植被盖度反演模型研究——以新疆阿勒泰地区布尔津县为例[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(7): 2384-2394. |
| Chen Yan, Song Yu-qin, Wang Wei. Grassland vegetation cover inversion model based on random forest regression: a case study in Burqin county, Altay, Xinjiang uygur autonomous region[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(7): 2384-2394. | |
| 11 | 詹国旗,杨国东,王凤艳,等. 基于特征空间优化的随机森林算法在GF-2影像湿地分类中的研究[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2018, 20(10): 1520-1528. |
| Zhang Guo-qi, Yang Guo-dong, Wang Feng-yan, et al. The random forest classification of wetland from GF-2 imagery based on the optimized feature space[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2018, 20(10): 1520-1528. | |
| 12 | Chen T, Trinder J, Niu R Q. Object-oriented landslide mapping using ZY-3 satellite imagery, random forest and mathematical morphology, for the Three-Gorges Reservoir, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9: 333. |
| 13 | Zhu J, Pan Z W, Wang H, et al. An improved multi-temporal and multi-feature tea plantation identification method using Sentinel-2 imagery[J]. Sensors(Basel, Switzerland), 2019, 19(9): 2087. |
| 14 | 马玥,姜琦刚,孟治国,等. 基于随机森林算法的农耕区土地利用分类研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(1): 297-303. |
| Ma Yue, Jiang Qi-gang, Meng Zhi-guo, et al. Classification of land use in farming area based on random forest algorithm[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(1): 297-303. | |
| 15 | Zhou F Q, Zhang A N. Optimal subset selection of time-Series MODIS images and sample data transfer with random forests for supervised classification modelling[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16: 1783. |
| 16 | Whiteside T, Bartolo R. Mapping aquatic vegetation in a tropical wetland using high spatial resolution multispectral satellite imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2015, 7: 11664-11694. |
| 17 | 杨艳魁,陈芸芝,吴波,等. 基于高分二号影像结合纹理信息的茶园提取[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(2): 210-214. |
| Yang Yan-kui, Chen Yun-zhi, Wu Bo, et al. Extraction of tea plantation image based on GF-2 image and texture information[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(2): 210-214. | |
| 18 | Gao T, Zhu J J, Zheng X, et al. Mapping spatial distribution of larch plantations from multi-seasonal Landsat-8 OLI imagery and multi-scale textures using random forests[J]. Remote Sensing, 2015, 7: 1702-1720. |
| 19 | Wang B, Li J, Jin X F, et al. Mapping tea plantations from multi-seasonal Landsat-8 OLI imageries using a random forest classifier[J]. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 2019, 47: 1315-1329. |
| 20 | 范敏,韩琪,王芬,等. 基于多层次特征表示的场景图像分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(6): 1909-1917. |
| Fan Min, Han Qi, Wang Fen, et al. Scene image categorization algorithm based on multi-level features representation[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(6): 1909-1917. | |
| 21 | 郑国忠.地方政府在安吉白茶产业集群发展中的作用研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学经济管理学院, 2018. |
| Zheng Guo-zhong. Study on the role of local government in the development of Anji white tea industry cluster[D]. Hangzhou: College of Economics and Management,Zhejiang Agriculture & Forestry University, 2018. | |
| 22 | 李光华,李俊清,张亮,等. 一种融合蚁群算法和随机森林的特征选择方法[J]. 计算机科学, 2019, 46(11): 212-215. |
| Li Guang-hua, Li Jun-qing, Zhang Liang, et al. Feature selection method based on ant colony optimization and random forest[J]. Computer Science, 2019, 46(11): 212-215. | |
| 23 | 李平湘,刘致曲,杨杰,等. 利用随机森林回归进行极化SAR土壤水分反演[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2019, 44(3): 405-412. |
| Li Ping-xiang, Liu Zhi-qu, Yang Jie, et al. Soil moisture retrieval of winter wheat fields based on random forest regression using quad-polarimetric SAR images[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(3): 405-412. |
| [1] | 王生生,姜林延,杨永波. 基于最优传输特征选择的医学图像分割迁移学习[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1626-1638. |
| [2] | 刘铭,杨雨航,邹松霖,肖志成,张永刚. 增强边缘检测图像算法在多书识别中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 891-896. |
| [3] | 周怡娜,董宏丽,张勇,路敬祎. 基于VMD去噪和散布熵的管道信号特征提取方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 959-969. |
| [4] | 耿端阳,孙延成,牟孝栋,张国栋,姜慧新,朱俊科. 基于差速辊的青贮玉米籽粒破碎仿真试验及优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 693-702. |
| [5] | 温昌凯,谢斌,宋正河,韩建刚,杨倩雯. 拖拉机耐久性加速结构试验设计方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 703-715. |
| [6] | 陈晓雷,孙永峰,李策,林冬梅. 基于卷积神经网络和双向长短期记忆的稳定抗噪声滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 296-309. |
| [7] | 李国发,王彦博,何佳龙,王继利. 机电装备健康状态评估研究进展及发展趋势[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 267-279. |
| [8] | 许鸿奎,姜彤彤,李鑫,姜斌祥,王永雷. 结合降噪自编码与极限学习机的LTE上行干扰分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 195-203. |
| [9] | 刘桂霞,裴志尧,宋佳智. 基于深度学习的蛋白质⁃ATP结合位点预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 187-194. |
| [10] | 耿端阳,牟孝栋,张国栋,王宗源,朱俊科,徐海刚. 小麦联合收获机清选机理分析与优化试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 219-230. |
| [11] | 王国伟,朱庆辉,于海业,黄东岩. 基于数字化农机装备的青贮饲料可追溯系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 242-252. |
| [12] | 梁方,王德成,尤泳,王光辉,王宇兵,张晓明,冯金奎. 草地切根施肥补播复式改良机设计与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 231-241. |
| [13] | 刘远红,郭攀攀,张彦生,李鑫. 基于黎曼流形的稀疏图保持投影的特征提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2268-2279. |
| [14] | 王新彦,江泉,吕峰,易政洋. 基于参数化模型的零转弯半径割草机侧翻稳定性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1908-1918. |
| [15] | 李雄飞,吴佳婧,张小利,王泽宇,冯云丛. 基于相对总变差结构提取的遥感图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1775-1784. |
|
||