吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1838-1844.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210400
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于注意力卷积神经网络的图像篡改定位算法
- 1.吉林大学 大数据和网络管理中心,长春 130012
2.深圳中兴网信科技有限公司,深圳 518000
3.吉林大学 公共计算机教学与研究中心,长春 130012
Image manipulation localization algorithm based on channel attention convolutional neural networks
Hui ZHONG1( ),Heng KANG2,Ying-da LYU3,Zhen-jian LI1,Hong LI1,Ruo-chuan OUYANG1
),Heng KANG2,Ying-da LYU3,Zhen-jian LI1,Hong LI1,Ruo-chuan OUYANG1
- 1.Management Center of Big Data and Network,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.ZICT Technology Co. ,Ltd. ,Shenzhen 518000,China
3.Center for Computer Fundamental Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
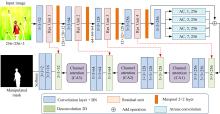
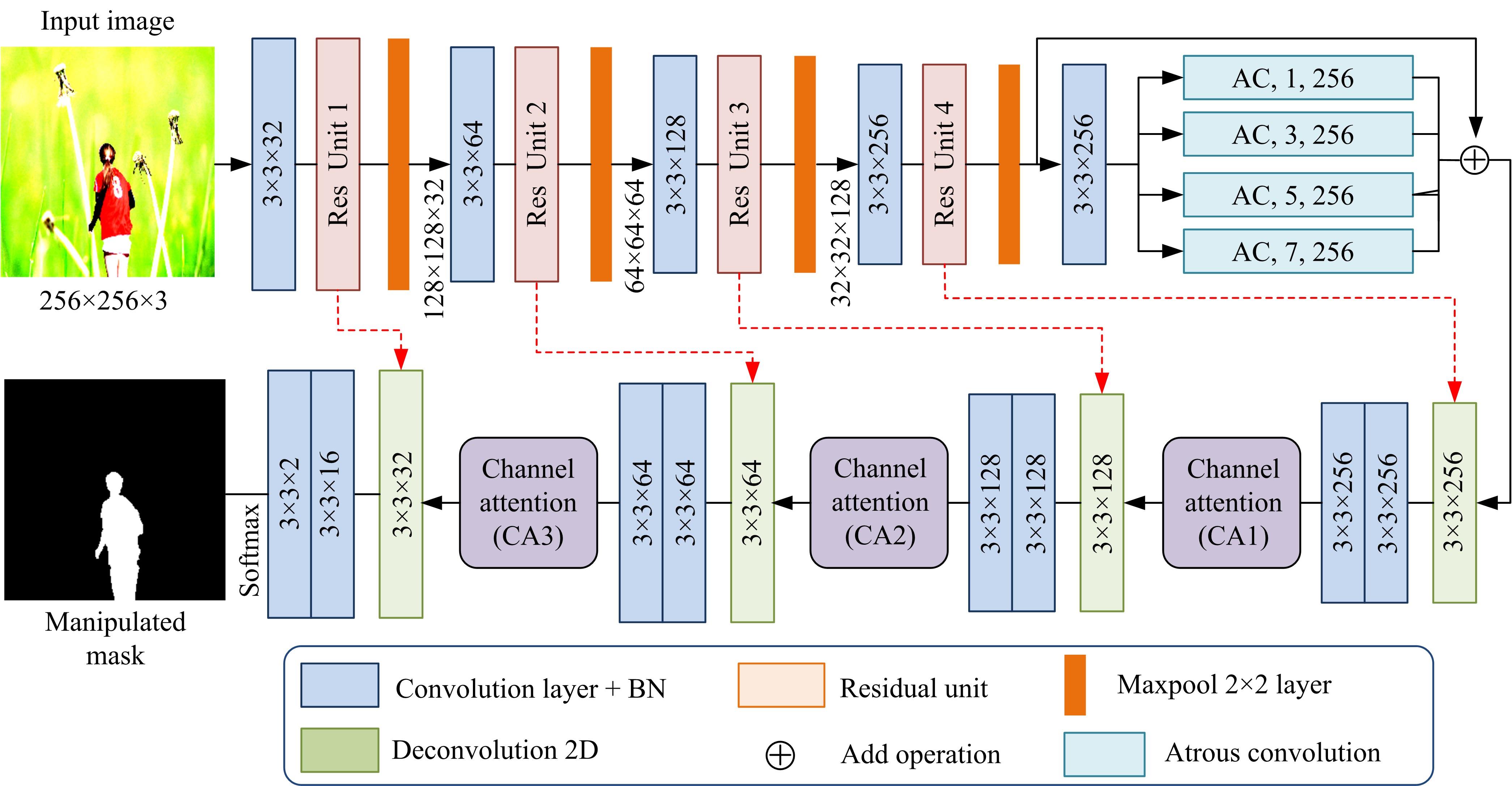
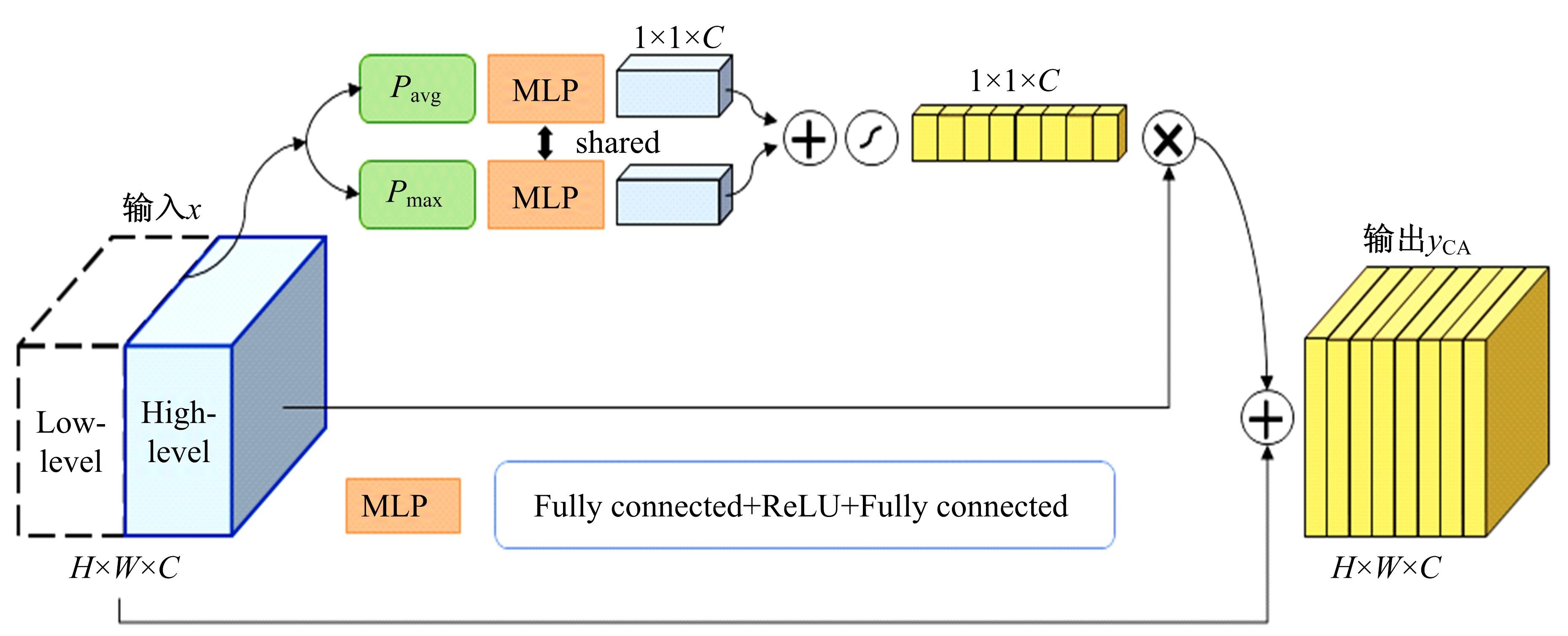
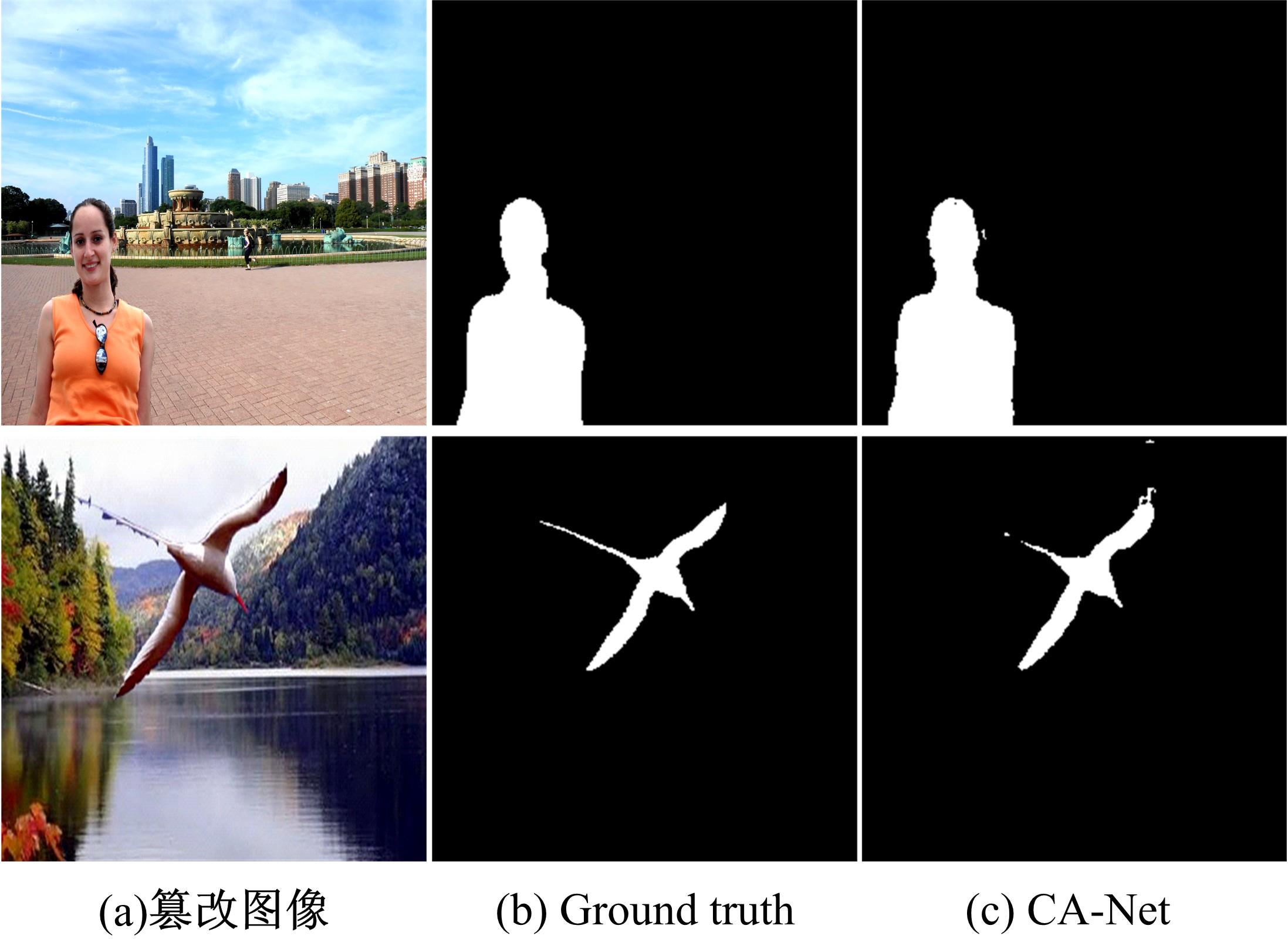
为防止对图像内容进行操作(如拼接),提出一种基于注意力卷积神经网络的图像篡改定位算法,称为CA-Net。尽管卷积神经网络强大的特征学习和映射能力可依次获取丰富的空间特征,但是本文提出使用不同采样步长的并行孔洞卷积层以提取多尺度特征。同时,为了更好地利用特征通道信息,在解码网中额外引入通道注意力模块。实验采用Synthesized图像库进行训练,在两组图像库上NC2016和CASIA进行微调和测试。实验结果表明:提出的并行孔洞卷积层和通道注意力模块能明显提高篡改定位结果,与一些最新主流算法相比,CA-Net在两个标准图像库上表现最优。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | 赵宏伟, 刘晓涵, 张媛, 等. 基于关键点注意力和通道注意力的服装分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(5): 1765-1770. |
| Zhao Hong-wei, Liu Xiao-han, Zhang Yuan, et al. Clothing classification algorithm based on landmark attention and channel attention[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020,50(5): 1765-1770. | |
| 2 | Zhuang P, Li H, Tan S, et al. Image tampering localization using a dense fully convolutional network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2021, 16: 2986-2999. |
| 3 | Ng T T, Chang S F, Sun Q. Blind detection of photomontage using higher order statistics[C]∥International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Canada, 2004: 8189867. |
| 4 | Verdoliva L. Media forensics and deepfakes: an overview[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2020, 14(5): 910-932. |
| 5 | Gaborini L, Bestagini P, Milani S, et al. Multi-clue image tampering localization[C]∥IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security, Atlanta, 2014: 125-130. |
| 6 | Ferrara P, Bianchi T, Rosa A D, et al. Image forgery localization via fine-grained analysis of CFA artifacts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2012, 7(5): 1566-1577. |
| 7 | Amerini I, Uricchio T, Ballan L, et al. Localization of JPEG double compression through multi-domain convolutional neural networks[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, 2017: 1865-1871. |
| 8 | Salloum R, Ren Y, Kuo C-C J. Image splicing localization using a multi-task fully convolutional network[J]. Journal of Visual Communication Image Representation, 2018, 51: 201-209. |
| 9 | Bappy J H, Simons C, Nataraj L, et al. Hybrid LSTM and Encoder-Decoder architecture for detection of image forgeries[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(7): 3286-3300. |
| 10 | 陈绵书, 于录录, 苏越, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的多标签图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(3): 1077-1084. |
| Chen Mian-shu, Yu Lu-lu, Su Yue, et al. Multi-label images classification based on convolutional neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(3): 1077-1084. | |
| 11 | Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]∥Proceedings of Europeon Conference on Computer Vision, Cham, Springer: 2018: 3-19. |
| 12 | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]∥International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Cham, Springer: 2015: 234-241. |
| 13 | Wu Y, Abd-Almageed W, Natarajan P. Deep matching and validation network: an end-to-end solution to constrained image splicing localization and detection[C]∥Proceedings of the 25th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, CA, 2017: 1480-1502. |
| 14 | Chen L, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, et al. Deeplab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis Machine Intelligence, 2017, 40(4): 834-848. |
| 15 | Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R. Segnet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for scene segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481-2495. |
| 16 | Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[C]∥3rd International Conference for Learning Representations, San Diego, 2015: arXiv:. |
| 17 | Guan H, Kozak M, Robertson E, et al. MFC datasets: large-scale benchmark datasets for media forensic challenge evaluation[C]∥IEEE Winter Applications of Computer Vision Workshops, Waikoloa, 2019: 63-72. |
| 18 | Dong J, Wang W, Tan T. Casia image tampering detection evaluation database[C]∥IEEE China Summit and International Conference on Signal and Information Processing, Beijing, 2013: 422-426. |
| 19 | Chen L, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, et al. DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834-848. |
| 20 | Luo W, Huang J, Qiu G. JPEG error analysis and its applications to digital image forensics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics & Security, 2010, 5(3): 480-491. |
| 21 | Mahdian B, Saic S. Using noise inconsistencies for blind image forensics[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2009, 27(10): 1497-1503. |
| 22 | Zhou P, Han X, Morariu V, et al. Learning rich features for image manipulation detection[C]∥Proceedings of IEEE Conference Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, 2018: 1053-1061. |
| 23 | Bappy M, Roy-Chowdhury A K, Bunk J, et al. Exploiting spatial structure for localizing manipulated image regions[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, 2017: 17467965. |
| 24 | Wu Y, Abdalmageed W, Natarajan P. Mantra-Net: manipulation tracing network for detection and localization of image forgeries with anomalous features[C]∥Proceedings of IEEE Conference Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, 2019: 9543-9552. |
| [1] | 王德兴,吴若有,袁红春,宫鹏,王越. 基于多尺度注意力融合和卷积神经网络的水下图像恢复[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1396-1404. |
| [2] | 朱小龙,谢忠. 基于海量文本数据的知识图谱自动构建算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1358-1363. |
| [3] | 徐涛,马克,刘才华. 基于深度学习的行人多目标跟踪方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 27-38. |
| [4] | 王柯俨,王迪,赵熹,陈静怡,李云松. 基于卷积神经网络的联合估计图像去雾算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1771-1777. |
| [5] | 刘国华,周文斌. 基于卷积神经网络的脉搏波时频域特征混叠分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1818-1825. |
| [6] | 李志军,杨楚皙,刘丹,孙大洋. 基于深度卷积神经网络的信息流增强图像压缩方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1788-1795. |
| [7] | 谌华,郭伟,闫敬文,卓文浩,吴良斌. 基于深度学习的SAR图像道路识别新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1778-1787. |
| [8] | 车翔玖,董有政. 基于多尺度信息融合的图像识别改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. |
| [9] | 马子骥,卢浩,董艳茹. 双通道单图像超分辨率卷积神经网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2089-2097. |
| [10] | 车翔玖,刘华罗,邵庆彬. 基于Fast RCNN改进的布匹瑕疵识别算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2038-2044. |
| [11] | 周柚,杨森,李大琳,吴春国,王岩,王康平. 基于现场可编程门电路的人脸检测识别加速平台[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2051-2057. |
| [12] | 赵宏伟,王鹏,范丽丽,胡黄水,刘萍萍. 相似性保持实例检索方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2045-2050. |
| [13] | 郭继昌,吴洁,郭春乐,朱明辉. 基于残差连接卷积神经网络的图像超分辨率重构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1726-1734. |
| [14] | 徐岩,孙美双. 基于卷积神经网络的水下图像增强方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1895-1903. |
| [15] | 耿庆田, 于繁华, 王宇婷, 高琦坤. 基于特征融合的车型检测新算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 929-935. |
|
||