吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (11): 2662-2668.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20211013
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
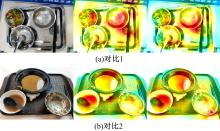
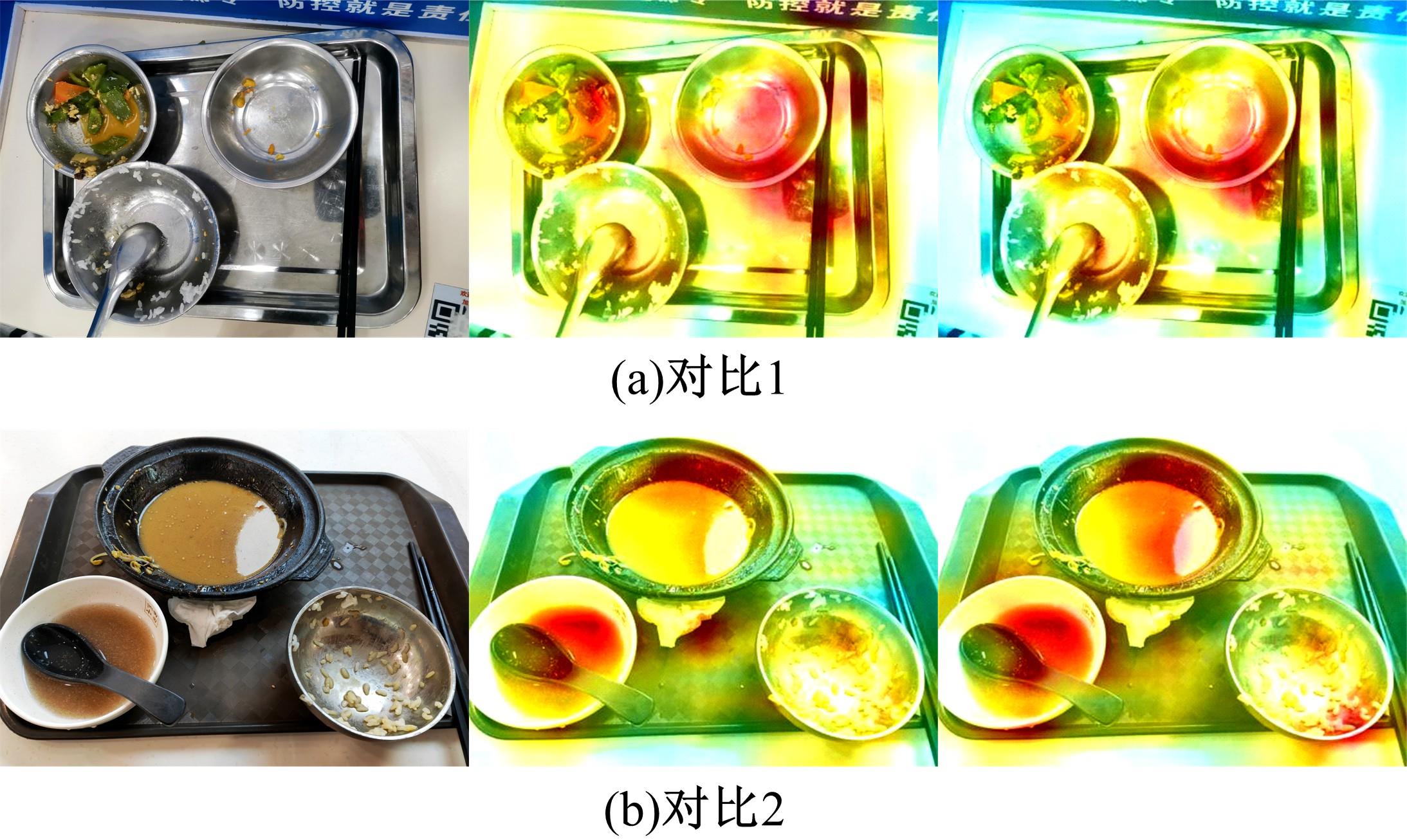
基于改进YOLOv4的多目标光盘检测算法
- 吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
Muti⁃Object dishes detection algorithm based on improved YOLOv4
- College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
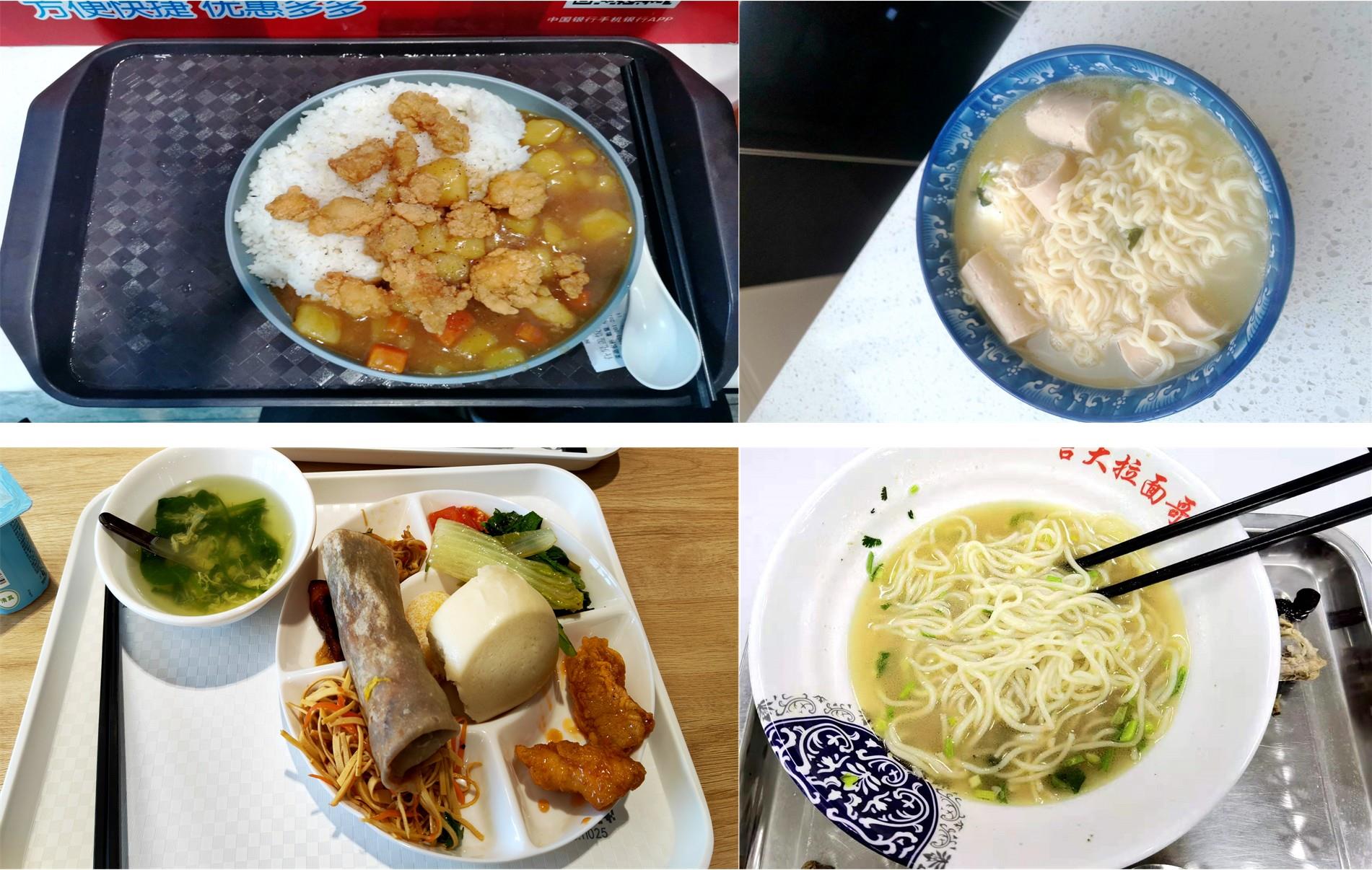
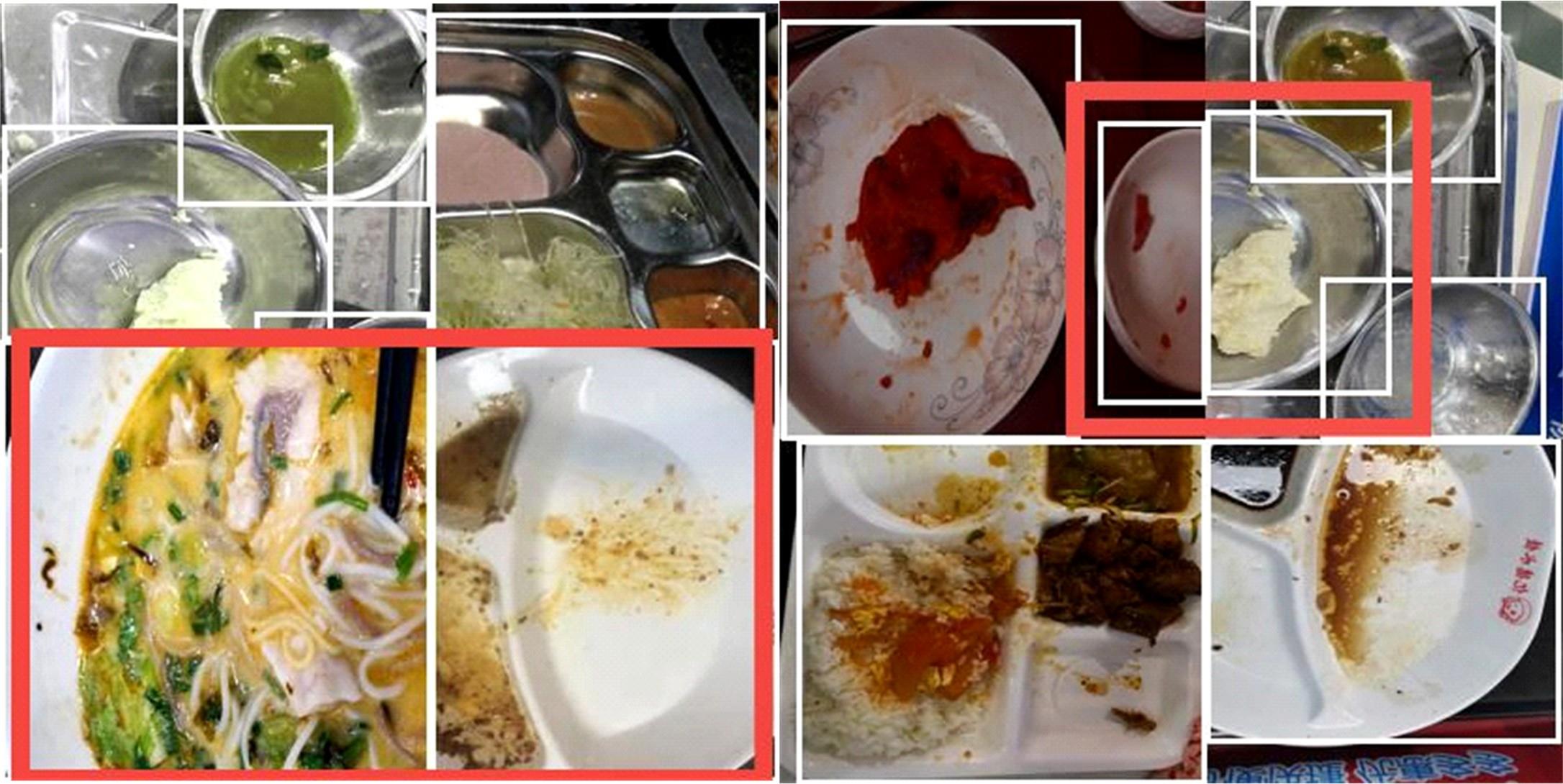
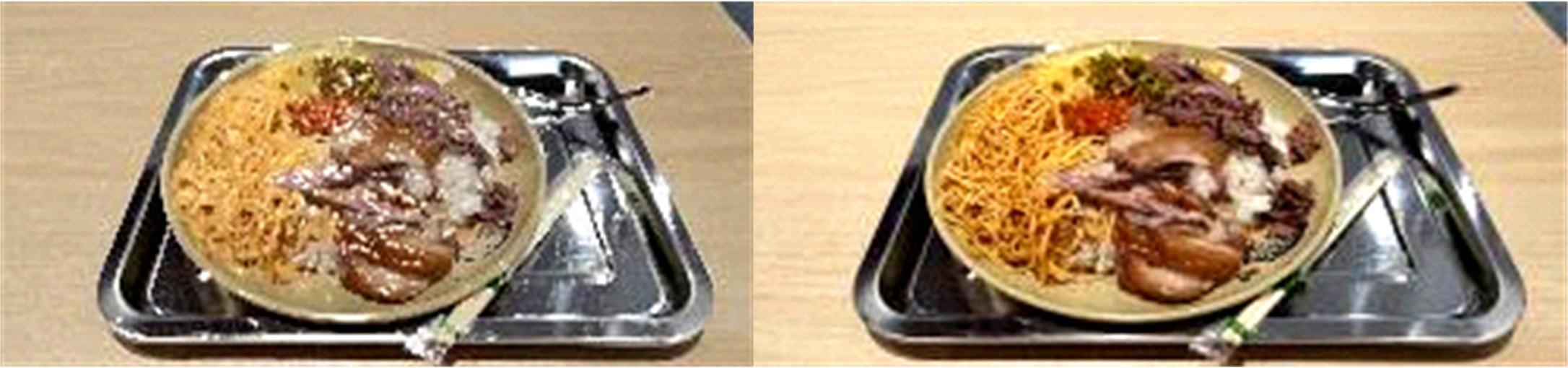
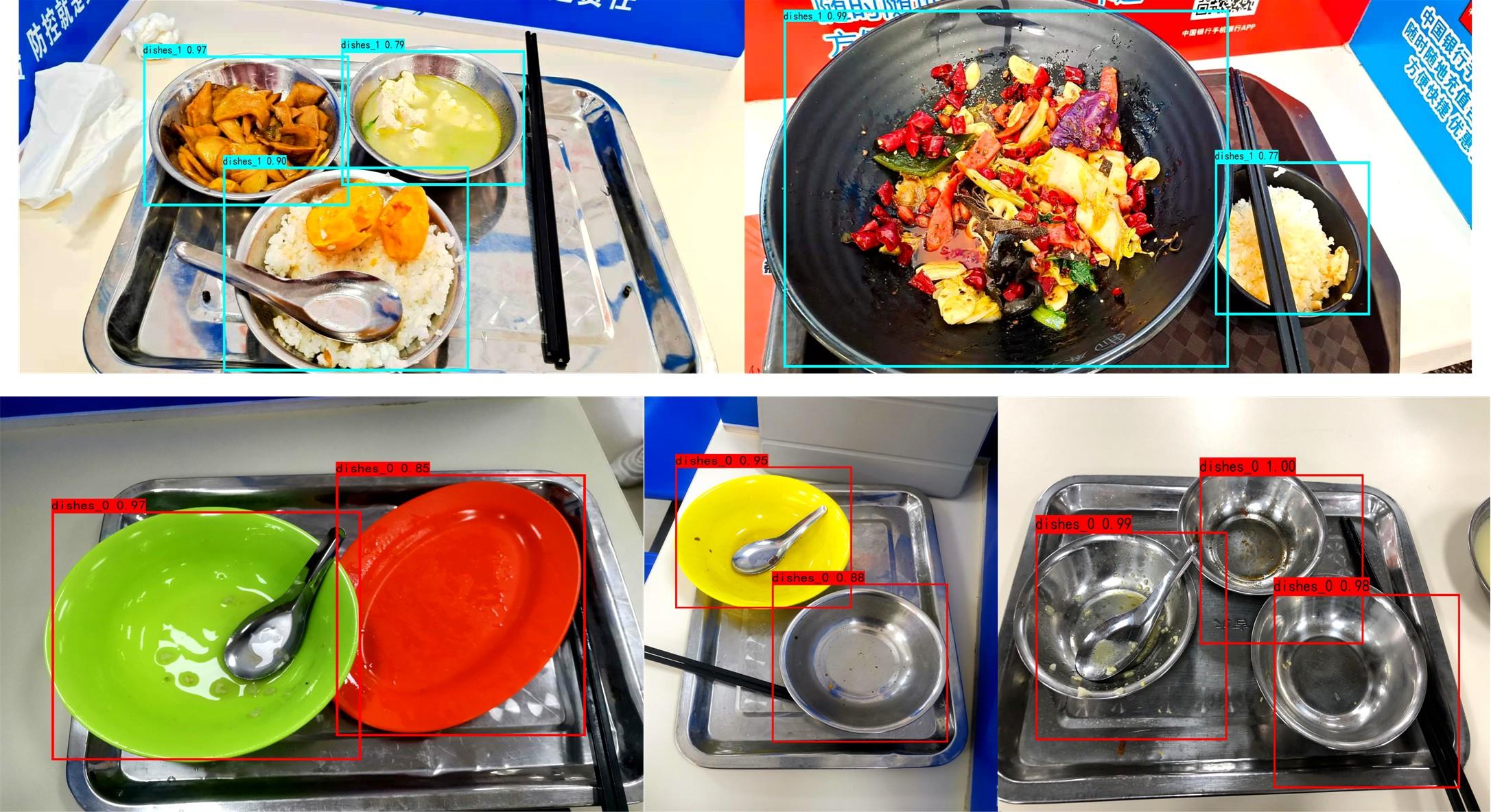
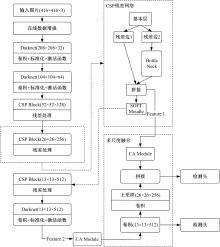
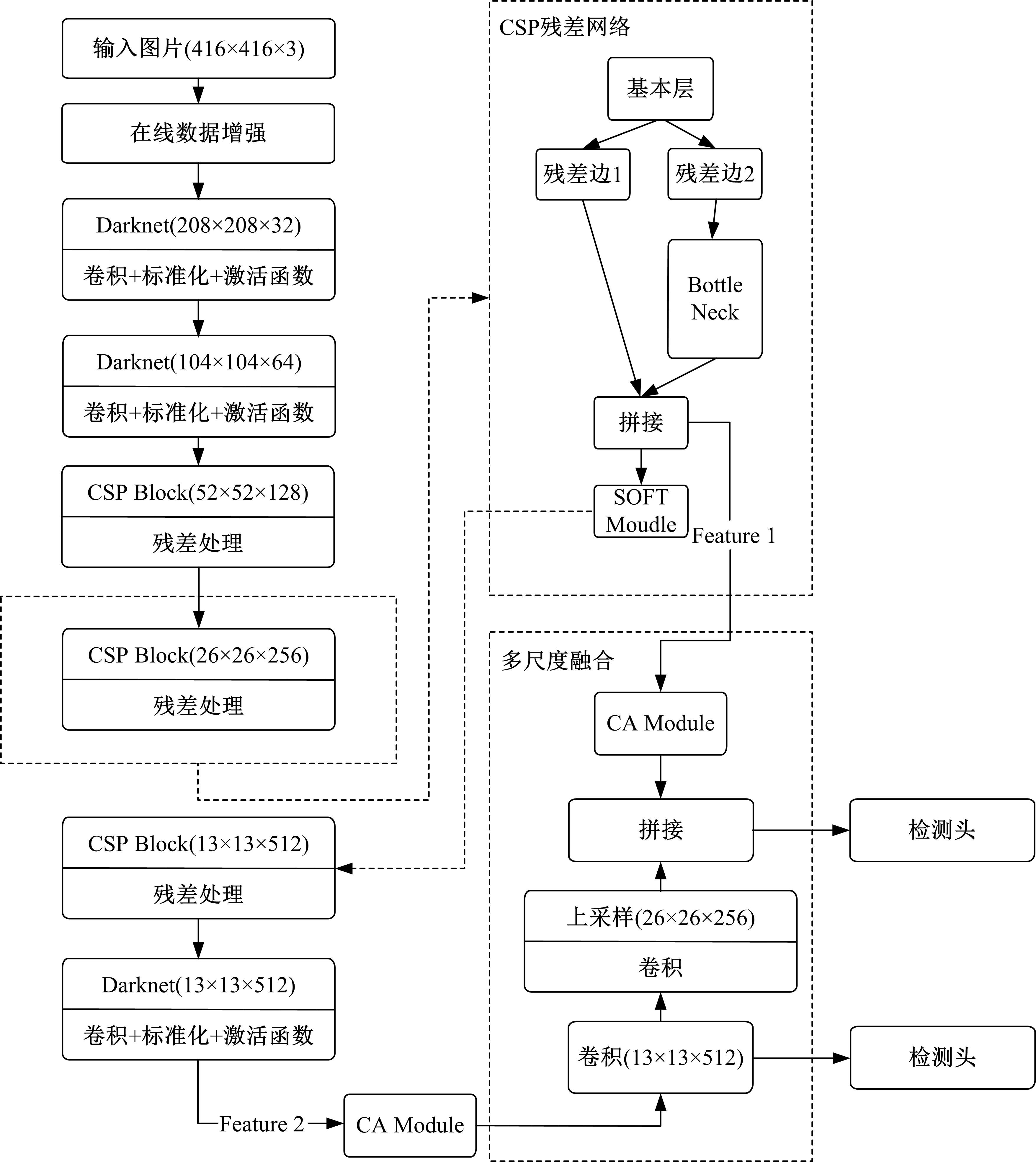
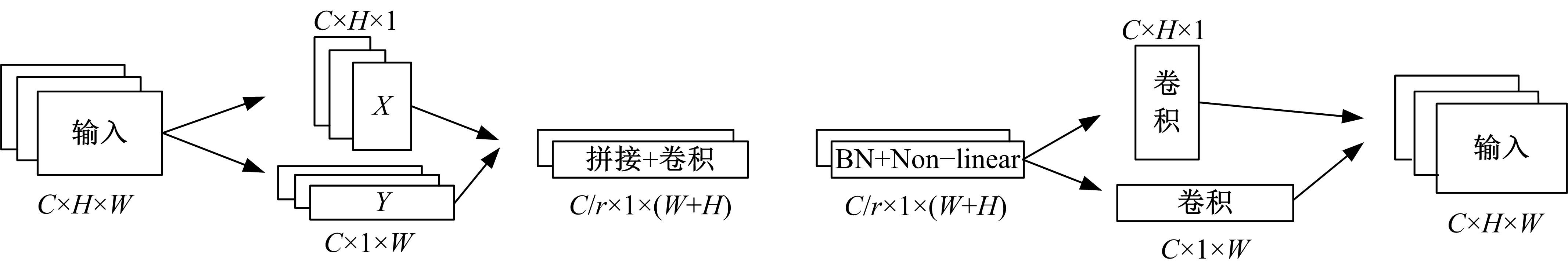
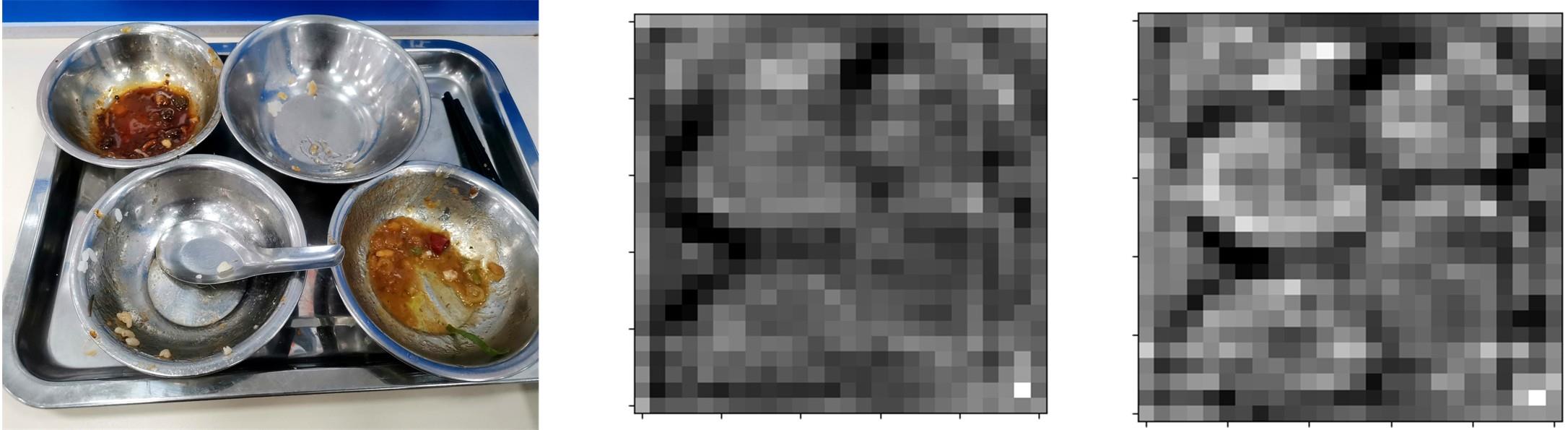
针对已有两阶段目标检测算法推理速度较慢,轻量化模型在小数据集上效果较差的问题,提出了一种基于单阶段目标检测YOLOv4改进的多目标识别算法。本文以光盘检测为例,利用多目标检测完成对光盘图片的识别与分类。利用餐盘边缘特征相似的特点,对逐个餐盘进行识别,判定是否为光盘。为保留显著特征而加入注意力机制以及池化方式,并采用轻量化网络加快推理速度。通过多尺度融合的方式提高模型准确率,达到快速识别并区分多目标餐盘的光盘情况。在一个具有1000张图片的餐盘数据集上进行实验。结果表明:本文算法与改进前相比准确率提高了4.25%,与Faster RCNN等经典的目标检测器相比,FPS是后者的8~9倍。本文算法改善了轻量化模型的精度下降问题,可更加便捷并快速地部署到移动或嵌入式设备中完成任务。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Matsuda Y, Hoashi H, Yanai K. Recognition of multiplefood images by detecting candidate regions[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Melbourne, Australia, 2012: 25-30. |
| 2 | 车翔玖, 王利, 郭晓新. 基于多尺度特征融合的边界检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2018, 48(5): 1621-1628. |
| Che Xiang-jiu, Wang Li, Guo Xiao-xin. Improved boundary detection based on multiscale cues fusion[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1621-1628. | |
| 3 | Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: unified, realtime object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779-788. |
| 4 | Ege T, Yanai K. Estimating food calories for multipledish food photos[C]∥4th IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition, Nanjing, China, 2017: 646-651. |
| 5 | 车翔玖, 刘华罗, 邵庆彬. 基于Fast RCNN改进的布匹瑕疵识别算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(6): 2038-2044. |
| Che Xiang-jiu, Liu Hua-luo, Shao Qing-bin. Fabric defect recognition algorithm based on improved Fast RCNN[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 2038-2044. | |
| 6 | Shimoda W, Yanai K. Foodness proposal for multiple food detection by training of single food images[C]∥Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Multimedia Assisted Dietary Management, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 13-21. |
| 7 | Bochkovskiy A, Wang C Y, Liao H Y M. Yolov4: optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[J/OL]. [2020-04-23]. |
| 8 | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 9 | Huang G, Liu S, van der Maaten L, et al. Condensenet: an efficient densenet using learned group convolutions[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 2752-2761. |
| 10 | Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Region-based convolutional networks for accurate object detection and segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 38(1): 142-158. |
| 11 | Girshick R. Fast r-cnn[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440-1448. |
| 12 | Ren S, He K, Girshick R, et al. Faster r-cnn: towards realtime object detection with region proposal networks[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2015, 28: 91-99. |
| 13 | Redmon J, Farhadi A. Yolov3: an incremental improvement[J/OL]. [2018-04-08]. |
| 14 | Everingham M, van Gool L, Williams C K I, et al. The pascal visual object classes (voc) challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 88(2): 303-338. |
| 15 | Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M, et al. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4510-4520. |
| 16 | Howard A G, Zhu M, Chen B,et al.Mobilenets:efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[J].arXiv Preprint arXiv:,2017. |
| 17 | Stergiou A, Poppe R, Kalliatakis G. Refining activation downsampling with Softpool[J].[2021-03-18]. |
| 18 | Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, 5: 5998-6008. |
| 19 | Hu J, Shen L, Albanie S, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(8): 2011-2023. |
| 20 | Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3-19. |
| 21 | Hou Q, Zhou D, Feng J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 13713-13722. |
| 22 | Zhou B, Khosla A, Lapedriza A, et al. Learning deep features for discriminative localization[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2921-2929. |
| [1] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [2] | 曲福恒,丁天雨,陆洋,杨勇,胡雅婷. 基于邻域相似性的图像码字快速搜索算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1865-1871. |
| [3] | 申铉京,张雪峰,王玉,金玉波. 像素级卷积神经网络多聚焦图像融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1857-1864. |
| [4] | 秦贵和,黄俊锋,孙铭会. 基于双手键盘的虚拟现实文本输入[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1881-1888. |
| [5] | 杨怀江,王二帅,隋永新,闫丰,周跃. 简化型残差结构和快速深度残差网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1413-1421. |
| [6] | 高明华,杨璨. 基于改进卷积神经网络的交通目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1353-1361. |
| [7] | 刘铭,杨雨航,邹松霖,肖志成,张永刚. 增强边缘检测图像算法在多书识别中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 891-896. |
| [8] | 方世敏. 基于频繁模式树的多来源数据选择性集成算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 885-890. |
| [9] | 王学智,李清亮,李文辉. 融合迁移学习的土壤湿度预测时空模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 675-683. |
| [10] | 李向军,涂洁莹,赵志宾. 基于多尺度融合卷积神经网络的熔解曲线有效性分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 633-639. |
| [11] | 李先通,全威,王华,孙鹏程,安鹏进,满永兴. 基于时空特征深度学习模型的路径行程时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [12] | 高文志,王彦军,王欣伟,张攀,李勇,董阳. 基于卷积神经网络的柴油机失火故障实时诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 417-424. |
| [13] | 张龙,徐天鹏,王朝兵,易剑昱,甄灿壮. 基于卷积门控循环网络的齿轮箱故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 368-376. |
| [14] | 王生生,李晨旭,王翔宇,姚志林,刘一申,吴佳倩,杨晴然. 基于改进残差胶囊网络和麻雀搜索的脑瘤图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2653-2661. |
| [15] | 曹洁,何智栋,余萍,王进花. 数据不平衡分布下轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2523-2531. |
|
||