吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1413-1421.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210027
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
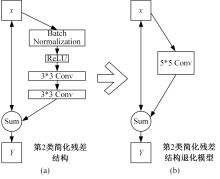
简化型残差结构和快速深度残差网络
杨怀江1,2( ),王二帅1,3,隋永新1,2,闫丰1,2,周跃1,2
),王二帅1,3,隋永新1,2,闫丰1,2,周跃1,2
- 1.中国科学院 长春光学精密机械与物理研究所,长春 130033
2.长春国科精密光学技术有限公司,长春 130033
3.中国科学院大学 大珩学院,北京 100049
Simplified residual structure and fast deep residual networks
Huai-jiang YANG1,2( ),Er-shuai WANG1,3,Yong-xin SUI1,2,Feng YAN1,2,Yue ZHOU1,2
),Er-shuai WANG1,3,Yong-xin SUI1,2,Feng YAN1,2,Yue ZHOU1,2
- 1.Changchun Institute of Optics,Fine Mechanics and Physics,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Changchun 130033,China
2.Changchun National Extreme Precision Optics Co. ,Ltd. ,Changchun 130033,China
3.Daheng College,University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
摘要:
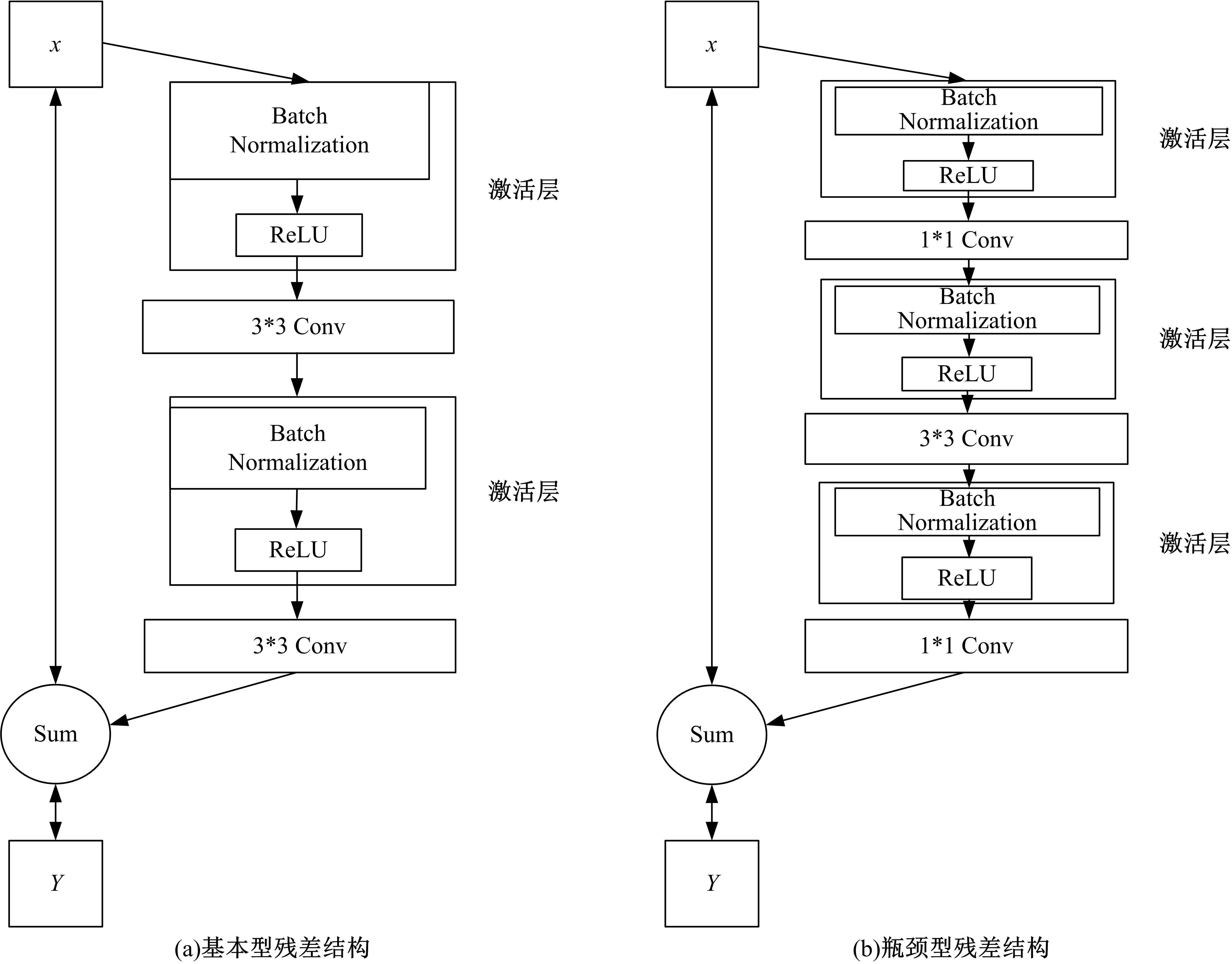
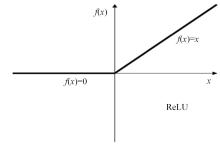
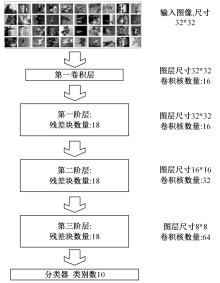
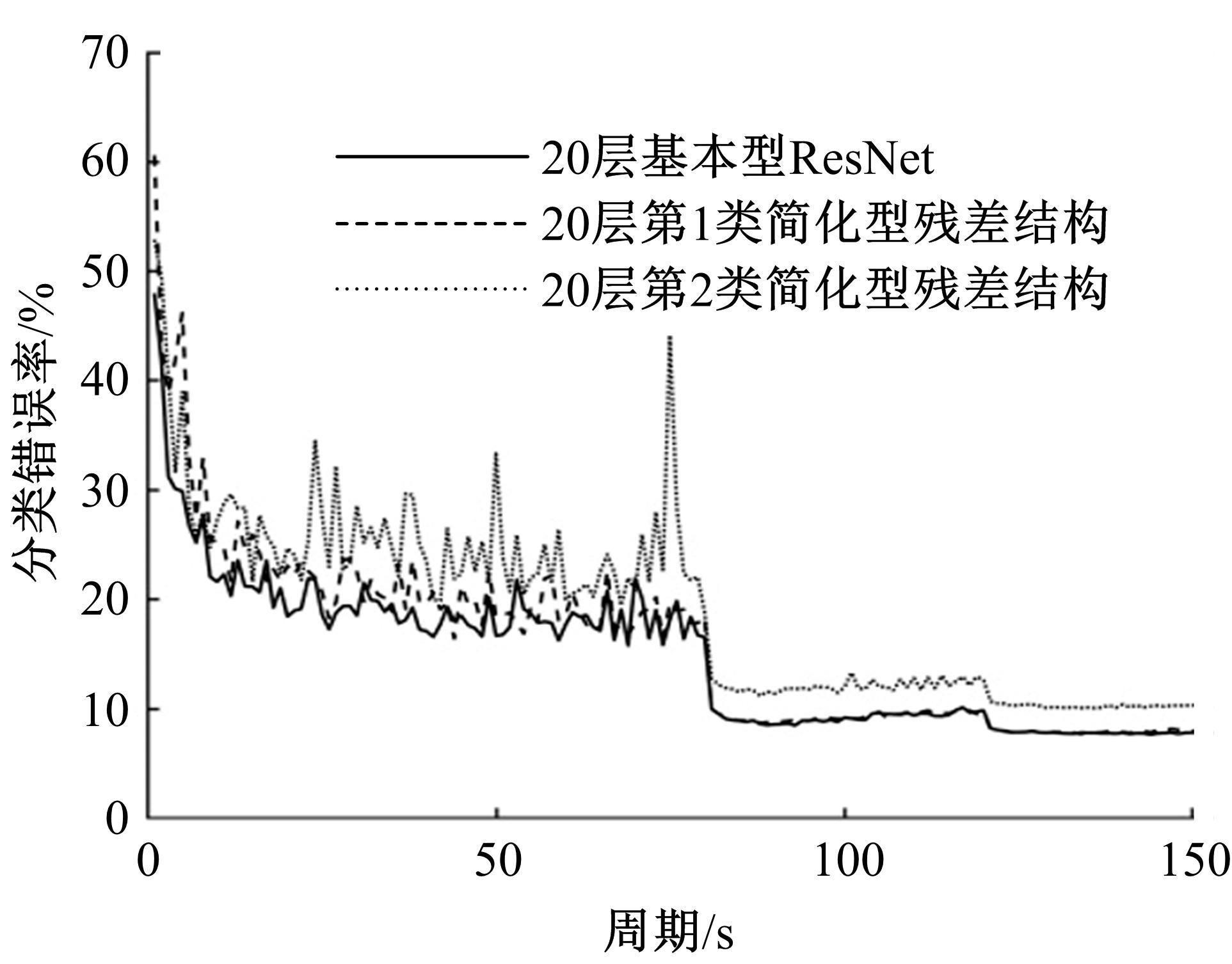
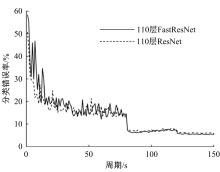
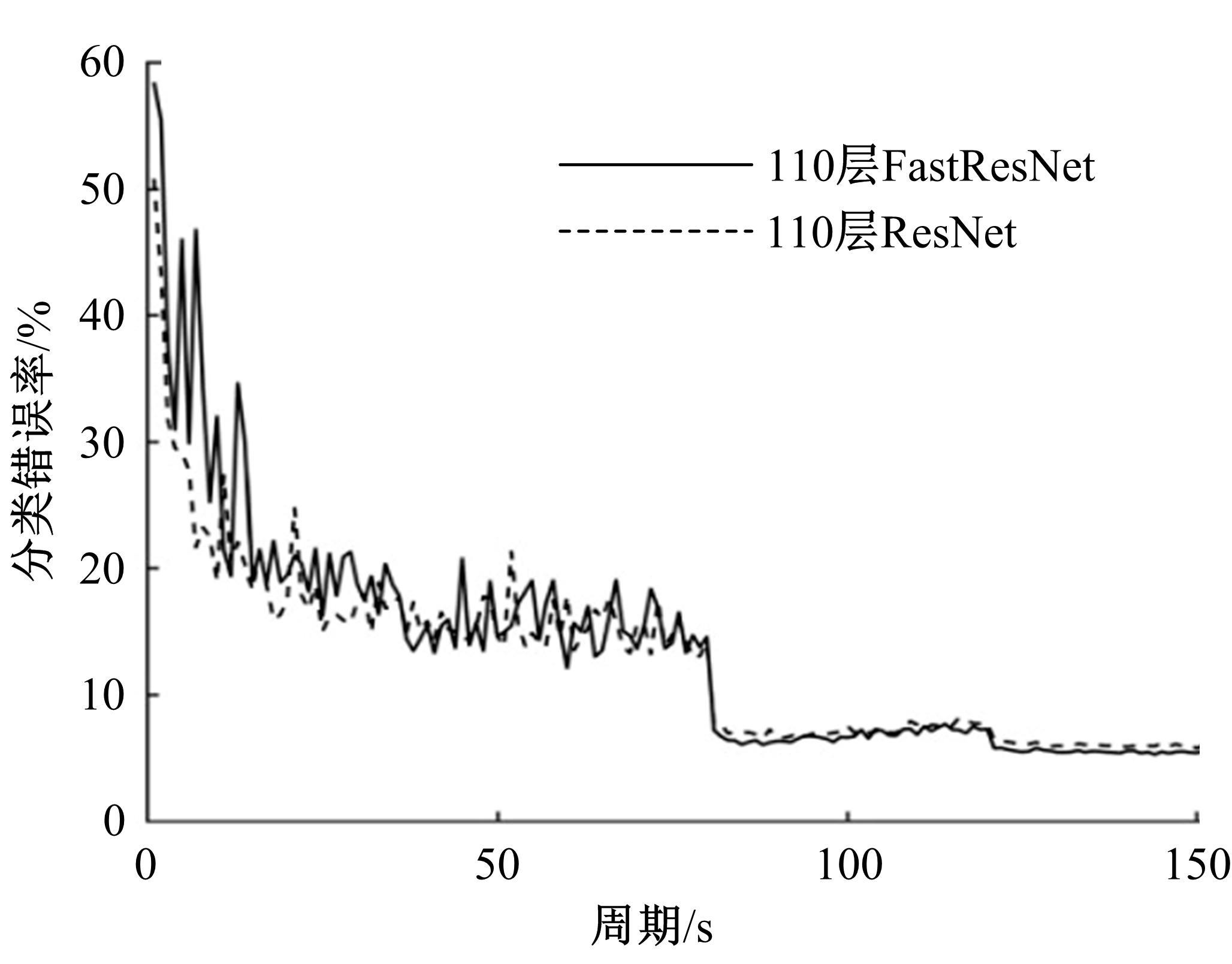
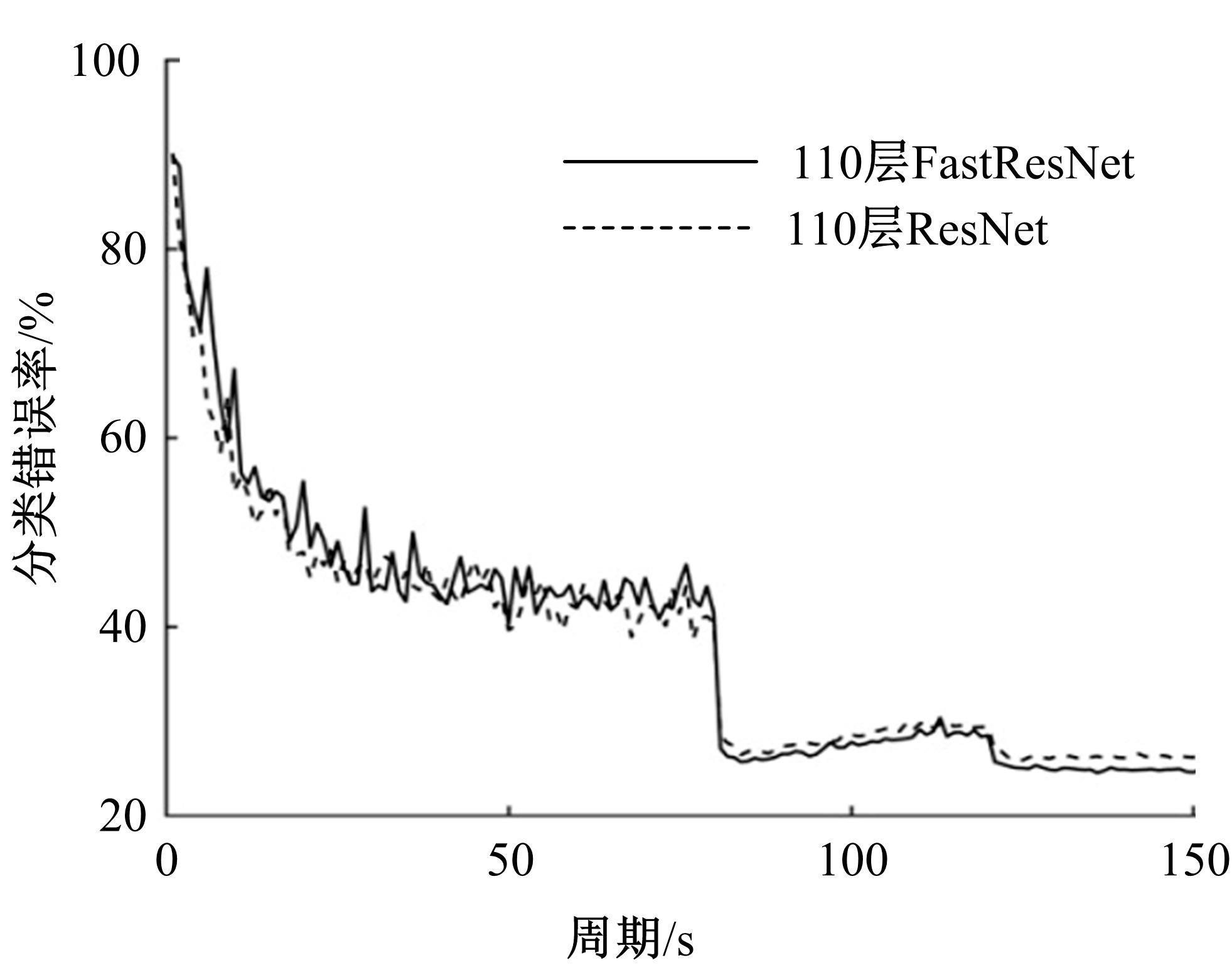
为解决当前深度残差网络模型训练缓慢的问题,设计了一种新型的残差结构。与典型的残差结构相比,该结构仅含有一个Batch Normalization和ReLU模块,通过减少网络训练过程的计算量降低了耗时,提升了模型训练速度。在常用的CIFAR10/100图像分类数据库上进行了对比实验分析,以该方法构建的深度为110层的网络CIFAR10分类错误率为5.29%,CIFAR100分类错误率为24.80%,典型的110层深度残差网络分类错误率分别为5.75%和26.02%;在训练耗时方面,该方法平均周期耗时为133.47 s,典型的残差网络平均周期耗时为208.26 s,提升了35.91%;结果表明,该网络结构在保证分类性能的基础上极大地提升了训练速度,具有较好的实用价值。
中图分类号:
- TP183
| 1 | He Kai-ming, Zhang Xiang-yu, Ren Shao-qing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, LasVegas, NV, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 2 | He Kai-ming, Zhang Xiang-yu, Ren Shao-qing, et al. Identity mappings in deep residual networks[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Cham, 2016: 630-645. |
| 3 | Targ S, Almeid A D, Lyman K. Resnet in resnet: Generalizing residual architectures[EB/OL]. [2016-03-25]. |
| 4 | Zagoruyko S, Komodakis N. Wide residual networks[EB/OL]. [2017-06-14]. |
| 5 | Veit A, Wilber M, Belongie S. Residual networks behave like ensembles of relatively shallow networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Newyork: Curran Associates Inc, 2016:550-558. |
| 6 | Wu Z F, Shen C H, van den Hengel A. Wider or deeper: revisiting the resnet model for visual recognition[EB/OL]. [2016-11-30]. |
| 7 | 王若瑜. 基于Resnet-50的智能驾驶红绿灯分类研究[J]. 电子测试,2019, 25():143-145. |
| Wang Ruo-yu. Research on classification of intelligent driving traffic light based on Resnet-50[J]. Electronic Test, 2019, 25(Sup.1):143-145. | |
| 8 | 宋倩, 黄昶, 余慧瑶. 基于TensorFlow的交通标志形状识别[J]. 信息通信, 2017, 32(12): 286-288. |
| Song Qian, Huang Chang, Yu Hui-yao. Traffic sign shape recognition based on tensorflow[J]. Information & Communications, 2017, 32(12): 286-288. | |
| 9 | 王文成, 蒋慧, 乔倩, 等. 基于ResNet50网络的十种鱼类图像分类识别研究[J]. 农村经济与科技, 2019, 30(19): 60-62. |
| Wang Wen-cheng, Jiang Hui, Qiao Qian, et al. Research on classification and recognition of ten fish images based on Resnet-50[J]. Rural Economy and Science-Technology, 2019, 30(19): 60-62. | |
| 10 | 常川. 基于ResNet深度网络的人类蛋白质图谱图像分类方法研究[J]. 医学信息学, 2019, 40(7): 45-49. |
| Chang Chuan. Study of image classification method of human protein atlas based on resnet deep network[J]. Journal of Medical Intelligence, 2019, 40(7): 45-49. | |
| 11 | 王恒,李霞,刘晓芳, 等. 基于ResNet50网络的乳腺癌病理图像分类研究[J]. 中国计量大学学报, 2019, 30(1): 72-77. |
| Wang Heng, Li Xia, Liu Xiao-fang, et al. Classification of breast cancer histopathological images based on ResNet50 network[J]. Journal of China Jiliang University, 2019, 30(1): 72-77. | |
| 12 | 张枫, 田联房, 杜启亮. 基于残差网络与中心损失的人脸识别[J].计算机工程与设计, 2019, 40(6): 1689-1695. |
| Zhang Feng, Tian Lian-fang, Du Qi-liang. Face recognition based on Resnet and center loss[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2019, 40(6): 1689-1695. | |
| 13 | 刘媛. 基于深度学习的说话人识别研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学信息与通信工程学院,2015. |
| Liu Yuan. Research on deep leaning based speaker recognition[D]. Shanghai: School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2015. | |
| 14 | 朱超平, 杨艺. 基于YOLO2和ResNet算法的监控视频中的人脸检测与识别[J]. 重庆理工大学学报: 自然科学, 2018, 32(8): 170-175. |
| Zhu Chao-ping, Yang Yi. Face Detection and recognition in monitoring video based on YOLO2 and ResNet algorithm[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology(Natural Science), 2018, 32(8): 170-175. | |
| 15 | 熊才华,巩言丽,廉华, 等. 基于ResNet-50改进的Faster R-CNN手势识别算法[J]. 计算机时代, 2019, 36(9): 1-4. |
| Xiong Cai-hua, Gong Yan-li, Lian Hua, et al. An improved Faster R-CNN hand gesture recognition algorithm based on ResNet-50[J]. Computer Era, 2019, 36(9):1-4. | |
| 16 | 刘子毅. 基于图谱特征分析的农业虫害检测方法研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学生物系统工程与食品科学学院, 2017. |
| Liu Zi-yi. Detection of agricultural pest insects based on imaging and spectral feature analysis[D]. Hangzhou: College of Biosystems Engineering and Food Science, Zhejiang University, 2017. | |
| 17 | 张银松,赵银娣,袁慕策. 基于改进Faster-RCNN模型的粘虫板图像昆虫识别与计数[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2019, 24(5): 115-122. |
| Zhang Yin-song, Zhao Yin-di, Yuan Mu-ce. Insect identification and counting based on an improved Faster-RCNN model of the sticky board image[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2019, 24(5): 115-122. | |
| 18 | Huang Gao, Sun Yu, Liu Zhuang, et al. Deep networks with stochastic depth[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Cham, 2016: 646-661. |
| 19 | Glorot X, Bengio Y. Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Canada, 2010:249-256. |
| 20 | Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. |
| 21 | Lin Min, Chen Qiang, Yan Shui-cheng. Network in network[EB/OL]. [2014-03-04]. |
| 22 | Springenberg J, Dosovitskiy A, Brox T, et al. Striving for simplicity: the all convolutional net[EB/OL]. [2015-04-13]. |
| 23 | Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y Q, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, 2015: 1-9. |
| 24 | Ioffe S, Szegedy C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[EB/OL]. [2015-03-02]. |
| 25 | Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. [2015-04-10]. |
| 26 | Santurkar S, Tsipras D, Ilyas A, et al. How does batch normalization help optimization?[EB/OL]. [2021-01-02]. |
| [1] | 高明华,杨璨. 基于改进卷积神经网络的交通目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1353-1361. |
| [2] | 贾海洋,夏睿,吕安祺,管噌璇,陈娟,王雷. 基于模板融合的超声医学影像全景拼接方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 916-924. |
| [3] | 李先通,全威,王华,孙鹏程,安鹏进,满永兴. 基于时空特征深度学习模型的路径行程时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [4] | 李向军,涂洁莹,赵志宾. 基于多尺度融合卷积神经网络的熔解曲线有效性分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 633-639. |
| [5] | 王学智,李清亮,李文辉. 融合迁移学习的土壤湿度预测时空模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 675-683. |
| [6] | 张龙,徐天鹏,王朝兵,易剑昱,甄灿壮. 基于卷积门控循环网络的齿轮箱故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 368-376. |
| [7] | 李茂月,刘硕,田帅,肖桂风. 薄壁件铣削加工颤振的图像特征提取与识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 425-432. |
| [8] | 高文志,王彦军,王欣伟,张攀,李勇,董阳. 基于卷积神经网络的柴油机失火故障实时诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 417-424. |
| [9] | 段亮,宋春元,刘超,魏苇,吕成吉. 基于机器学习的高速列车轴承温度状态识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 53-62. |
| [10] | 钟辉,康恒,吕颖达,李振建,李红,欧阳若川. 基于注意力卷积神经网络的图像篡改定位算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1838-1844. |
| [11] | 王德兴,吴若有,袁红春,宫鹏,王越. 基于多尺度注意力融合和卷积神经网络的水下图像恢复[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1396-1404. |
| [12] | 王康,姚猛,李立犇,李建桥,邓湘金,邹猛,薛龙. 基于月面表取采样触月压痕的月壤力学状态分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1146-1152. |
| [13] | 许骞艺,秦贵和,孙铭会,孟诚训. 基于改进的ResNeSt驾驶员头部状态分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 704-711. |
| [14] | 李健,刘孔宇,任宪盛,熊琦,窦雪峰. 基于自适应阈值的Canny算法在MRI边缘检测中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 712-719. |
| [15] | 刘富,刘璐,侯涛,刘云. 基于优化MSR的夜间道路图像增强方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 323-330. |
|
||