吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 675-683.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210608
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
融合迁移学习的土壤湿度预测时空模型
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.长春师范大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130032
Spatio⁃temporal model of soil moisture prediction integrated with transfer learning
Xue-zhi WANG1( ),Qing-liang LI2,Wen-hui LI1(
),Qing-liang LI2,Wen-hui LI1( )
)
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.School of Computer Science and Technology,Changchun Normal University,Changchun 130032,China
摘要:
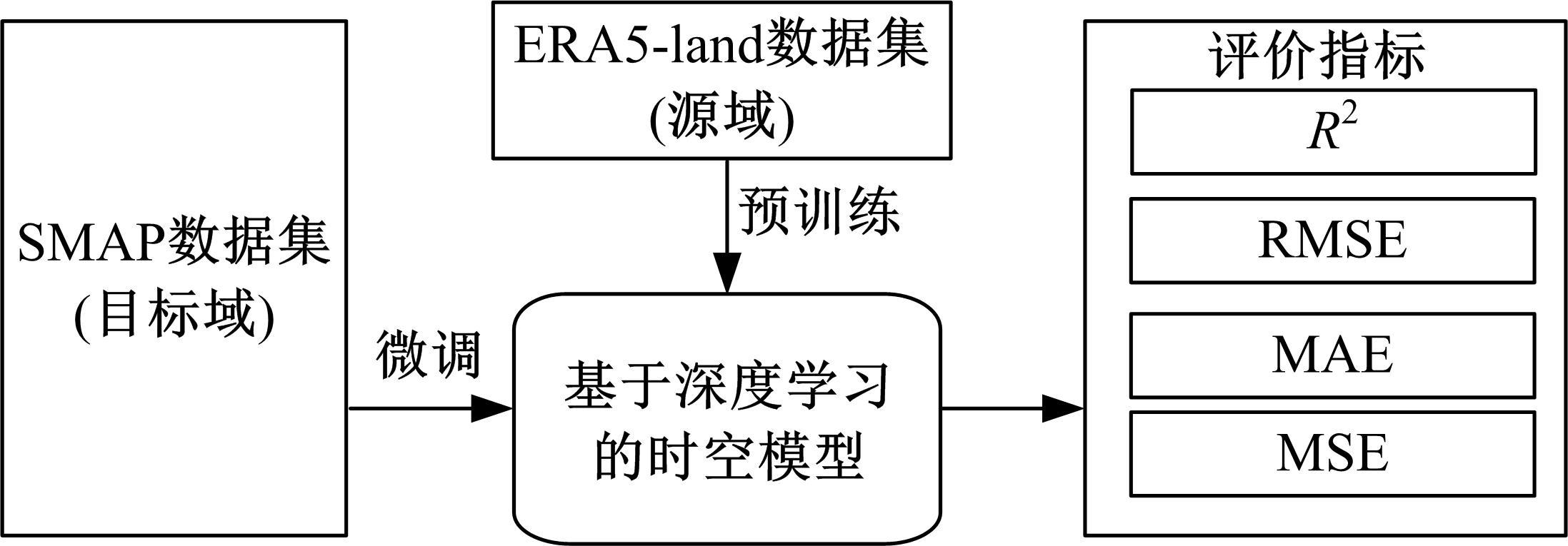
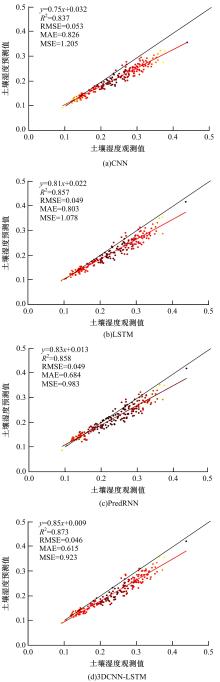
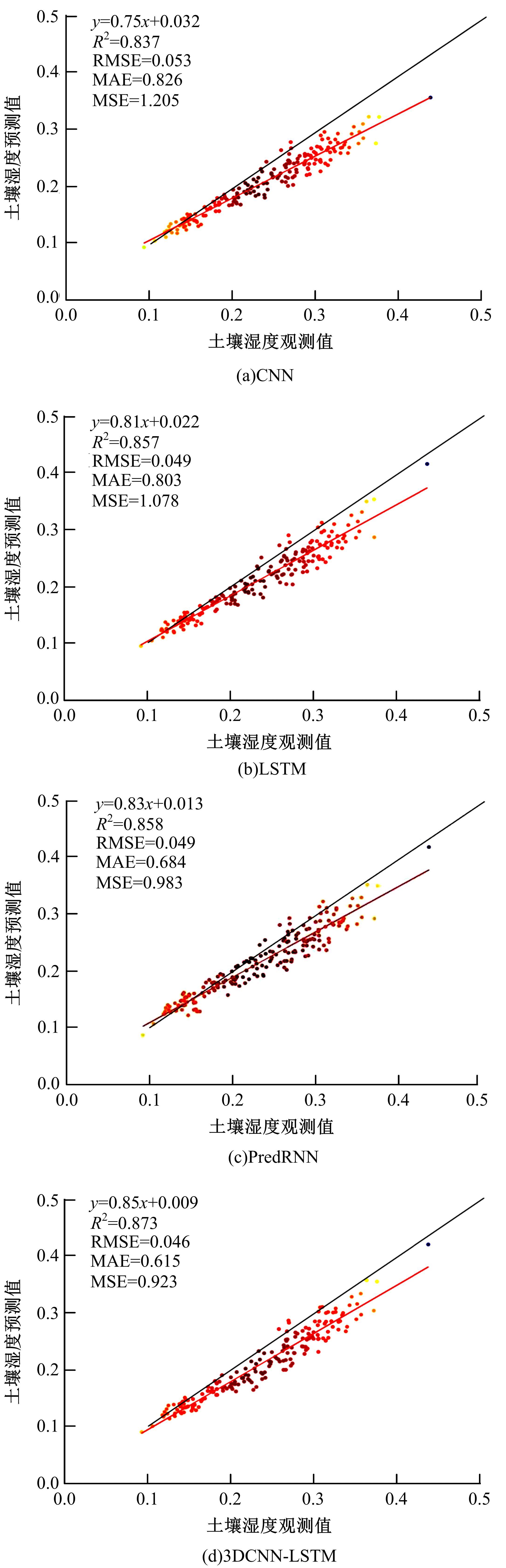
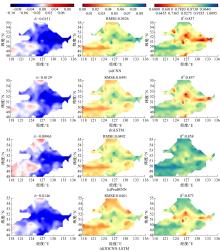
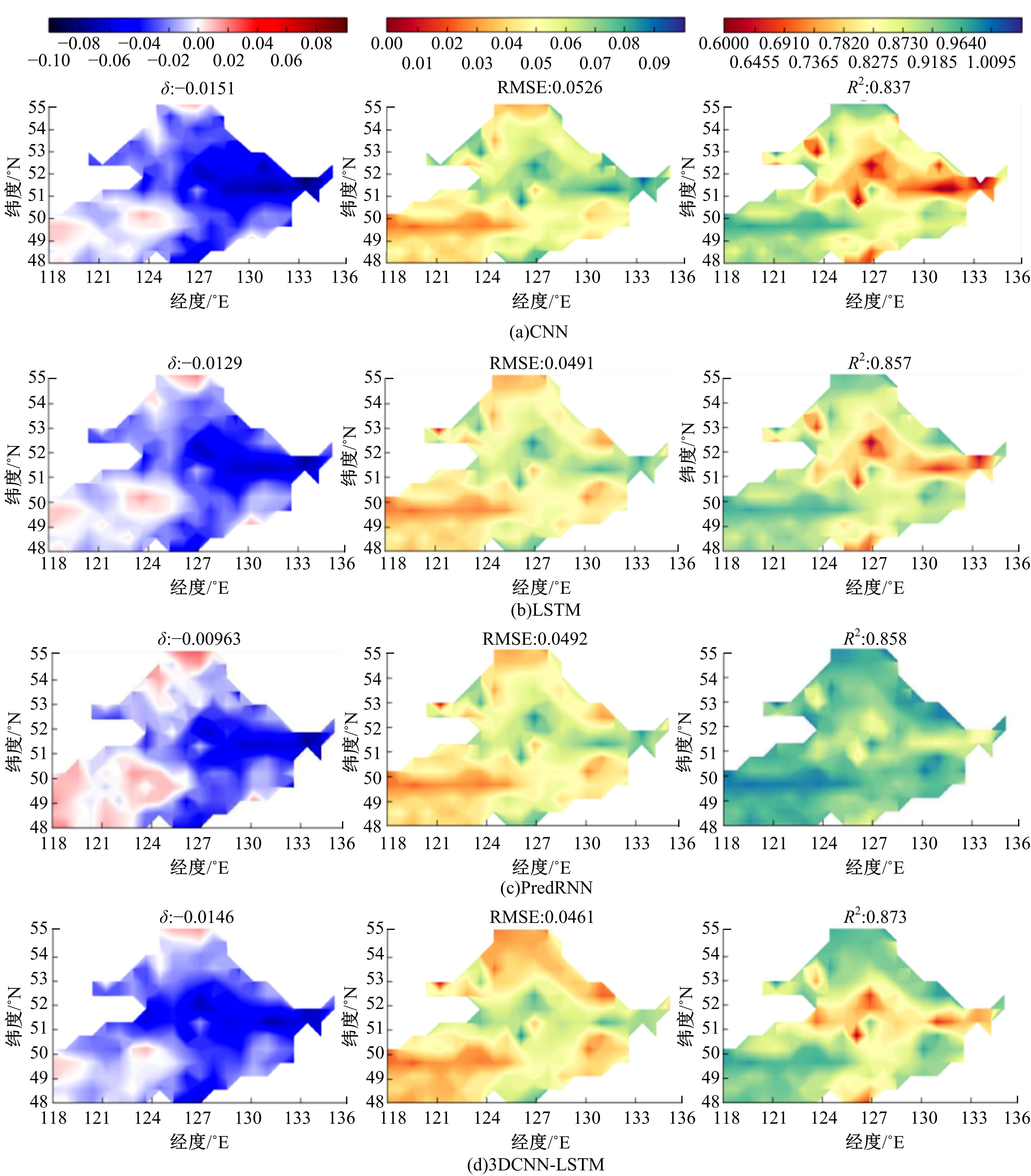
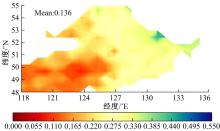
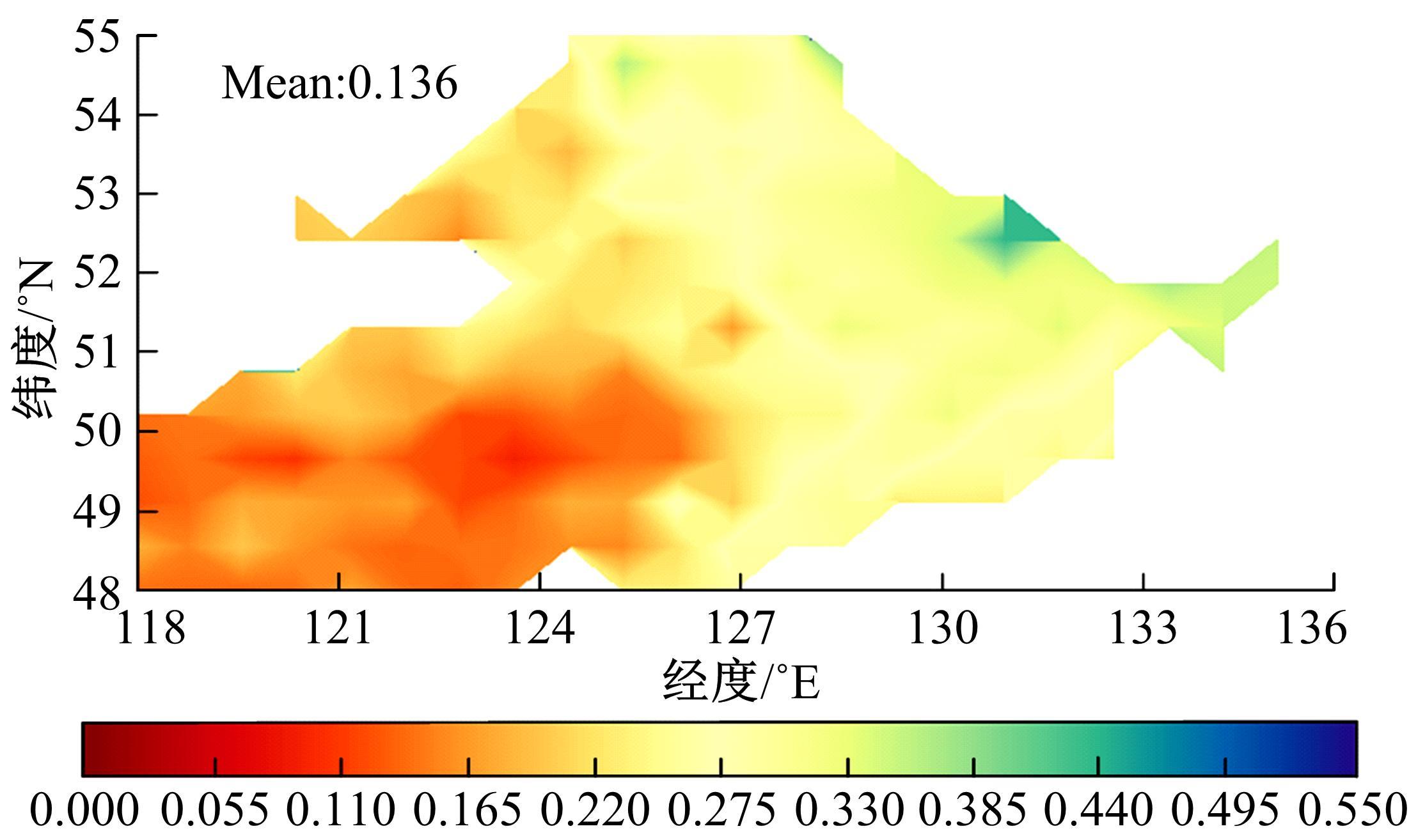
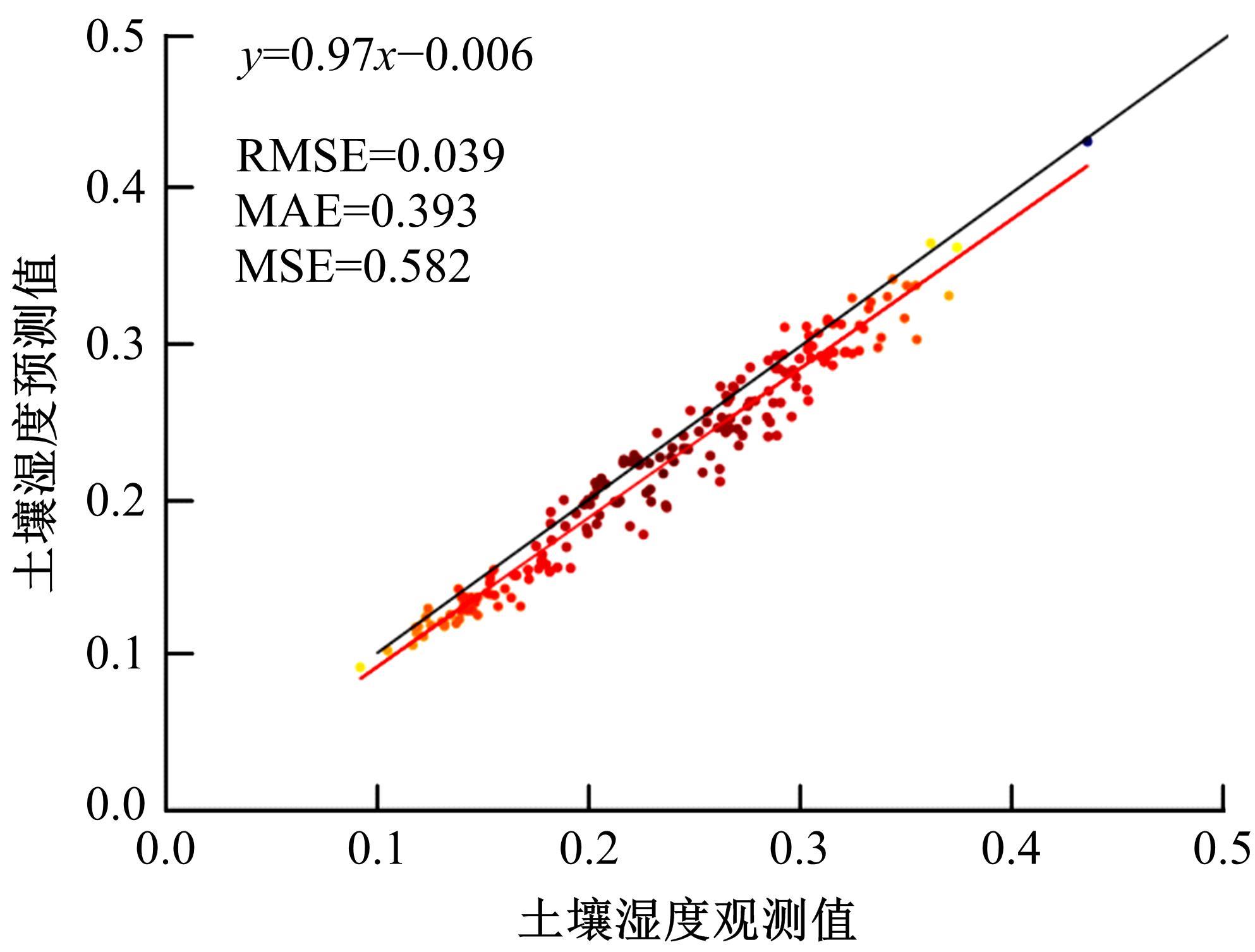
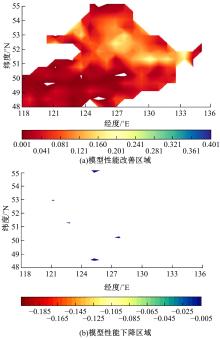
针对土壤湿度观测数据量过少导致模型出现过拟合而影响预测精度的问题,本文提出了融合迁移学习的土壤湿度预测时空模型。首先,将ERA5-land数据集作为源域。然后,通过三维卷积层提取土壤湿度滞后时刻的空间特征,并融入长短期记忆网络提取其时间特征,对网络模型进行预训练。最后,以微调方式在SMAP数据集中调整网络参数,进而预测未来土壤湿度。实验结果表明,本文提出的时空深度学习模型相对于卷积神经网络、长短期记忆网络和PredRNN时空预测模型预测精度更高,同时通过迁移学习方法可以进一步提升模型的预测精度。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Yu Feng, Cui Ning-bo, Hao Wei-ping, et al. Estimation of soil temperature from meteorological data using different machine learning models[J]. Geoderma, 2019, 338: 67-77. |
| 2 | Sanikhania H, Deo R C, Yaseen Z M, et al. Non-tuned data intelligent model for soil temperature estimation: a new approach[J]. Geoderma, 2018, 330: 52-64. |
| 3 | Yang J M, Busen H, Scherb H, et al. Modeling of radon exhalation from soil influenced by environmental parameters[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 656: 1304-1311. |
| 4 | Bhadani P, Vashisht V. Soil moisture, temperature and humidity measurement using arduino[C]∥2019 9th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering, Amity Univ, Noida, India, 2019: 567-571. |
| 5 | Hu Guo-jie, Zhao Lin, Wu Xiao-dong, et al. An analytical model for estimating soil temperature profiles on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau of China[J]. Journal of Arid Land, 2016, 8(2): 232-240. |
| 6 | Liang L L, Riveros-Iregui D A, Emanuel R E, et al. A simple framework to estimate distributed soil temperature from discrete air temperature measurements in data-scarce regions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 2014, 119(2): 407-417. |
| 7 | Entekhabi D, Njoku E G, O"Neill P E, et al. The soil moisture active passive (SMAP) mission[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2010, 98(5): 704-716. |
| 8 | Fang Kuai, Shen Chao-peng, Kifer D, et al. Prolongation of SMAP to spatio-temporally seamless coverage of continental U.S. using a deep learning neural network[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2017, 44(21): 11030-11039. |
| 9 | Fang Kuai, Shen Chao-peng. Near-real-time forecast of satellite-based soil moisture using long short-term memory with an adaptive data integration kernel[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2020, 21(3): 399-413. |
| 10 | Reichstein M, Camps-Valls G, Stevens B, et al. Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science[J]. Nature, 2019, 566(7743): 195-204. |
| 11 | Cobaner M, Citakoglu H, Kisi O, et al. Estimation of mean monthly air temperatures in Turkey[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2014, 109: 71-79. |
| 12 | Kisi O, Sanikhani H. Modelling long-term monthly temperatures by several data-driven methods using geographical inputs[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2015, 35(13): 3834-3846. |
| 13 | Kisi O, Kim S, Shiri J. Estimation of dew point temperature using neuro-fuzzy and neural network techniques[J]. Theoretical & Applied Climatology, 2013, 114(3/4): 365-373. |
| 14 | Kisi O, Sanikhani H. Prediction of long-term monthly precipitation using several soft computing methods without climatic data[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2015, 35(14): 4139-4150. |
| 15 | Mohammadi K, Shamshirband S, Kamsin A, et al. Identifying the most significant input parameters for predicting global solar radiation using an ANFIS selection procedure[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 63: 423-434. |
| 16 | Sobayo R, Wu H H, Ray R L, et al. Integration of convolutional neural network and thermal images into soil moisture estimation[C]∥1st International Conference on Data Intelligence and Security, South Padre Island, USA, 2018: 207-210. |
| 17 | Pan B X, Hsu K H, Aghakouchak A, et al. Improving precipitation estimation using convolutional neural network[J]. Water Resources Research, 2019, 55(3): 2301-2321. |
| 18 | Li Qing-liang, Zhao Yang, Yu Fan-hua. A novel multichannel long short-term memory method with time series for soil temperature modeling[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 182026-182043. |
| 19 | Hu Qing-hua, Zhang Ru-jia, Zhou Yu-can. Transfer learning for short-term wind speed prediction with deep neural networks[J]. Renewable Energy, 2016, 85: 83-95. |
| 20 | Chen Yu-wen, Huang Xiao-meng, Yi Li, et al. Improving machine learning-based weather forecast post-processing with clustering and transfer learning[J/OL]. [2021-06-19]. |
| 21 | Rasp S, Dueben P D, Scher S, et al. WeatherBench: a benchmark dataset for data-driven weather forecasting[J/OL]. [2021-06-21]. |
| 22 | Cao B, Gruber S, Zheng D H, et al. The ERA5-land soil temperature bias in permafrost regions[J]. Cryosphere, 2020, 14(8): 2581-2595. |
| 23 | Wang Yun-bo, Long Ming-sheng, Wang Jian-min, et al. PredRNN: recurrent neural networks for predictive learning using spatiotemporal LSTMs[C]∥31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Bench, CA, 2017:879-888. |
| [1] | 毛琳,任凤至,杨大伟,张汝波. 双向特征金字塔全景分割网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 657-665. |
| [2] | 李先通,全威,王华,孙鹏程,安鹏进,满永兴. 基于时空特征深度学习模型的路径行程时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [3] | 王雪,李占山,吕颖达. 基于多尺度感知和语义适配的医学图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 640-647. |
| [4] | 欧阳继红,郭泽琪,刘思光. 糖尿病视网膜病变分期双分支混合注意力决策网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 648-656. |
| [5] | 李向军,涂洁莹,赵志宾. 基于多尺度融合卷积神经网络的熔解曲线有效性分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 633-639. |
| [6] | 康苏明,张叶娥. 基于Hadoop的跨社交网络局部时序链路预测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 626-632. |
| [7] | 张龙,徐天鹏,王朝兵,易剑昱,甄灿壮. 基于卷积门控循环网络的齿轮箱故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 368-376. |
| [8] | 高文志,王彦军,王欣伟,张攀,李勇,董阳. 基于卷积神经网络的柴油机失火故障实时诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 417-424. |
| [9] | 曲优,李文辉. 基于锚框变换的单阶段旋转目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 162-173. |
| [10] | 段亮,宋春元,刘超,魏苇,吕成吉. 基于机器学习的高速列车轴承温度状态识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 53-62. |
| [11] | 赵宏伟,霍东升,王洁,李晓宁. 基于显著性检测的害虫图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2174-2181. |
| [12] | 刘洲洲,张倩昀,马新华,彭寒. 基于优化离散差分进化算法的压缩感知信号重构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2246-2252. |
| [13] | 徐艳蕾,何润,翟钰婷,赵宾,李陈孝. 基于轻量卷积网络的田间自然环境杂草识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2304-2312. |
| [14] | 王生生,陈境宇,卢奕南. 基于联邦学习和区块链的新冠肺炎胸部CT图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2164-2173. |
| [15] | 孙东明,胡亮,邢永恒,王峰. 基于文本融合的物联网触发动作编程模式服务推荐方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2182-2189. |
|
||