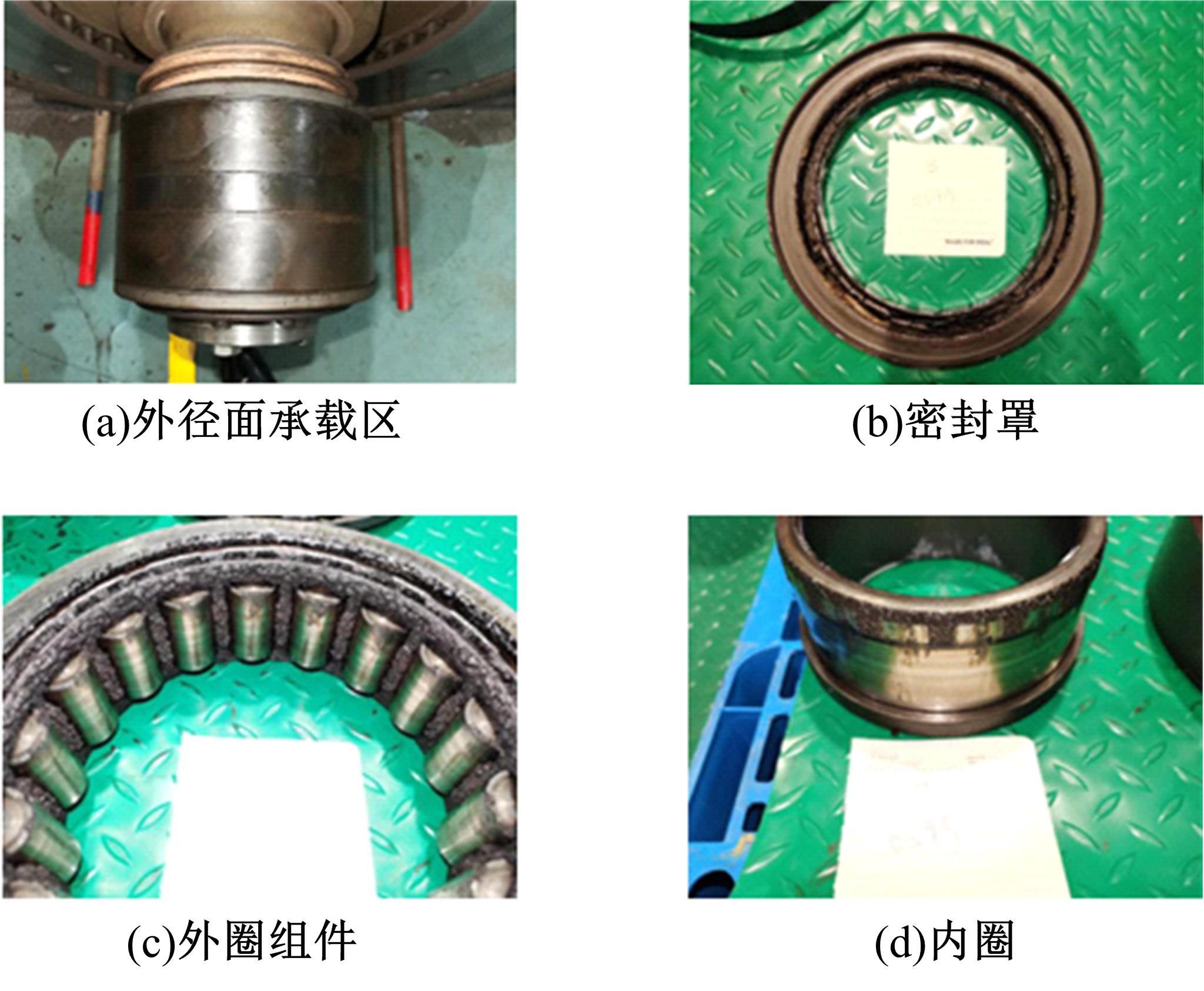
吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 53-62.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200751
基于机器学习的高速列车轴承温度状态识别
- 中车长春轨道客车股份有限公司 国家轨道客车工程研究中心,长春 130002
State recognition in bearing temperature of high-speed train based on machine learning algorithms
Liang DUAN( ),Chun-yuan SONG,Chao LIU,Wei WEI,Cheng-ji LYU
),Chun-yuan SONG,Chao LIU,Wei WEI,Cheng-ji LYU
- National Railway Vehicle Engineering R&D Center,CRRC Changchun Railway Vehicles Co. ,Ltd. ,Changchun 130002,China
摘要:
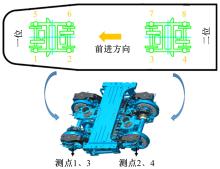
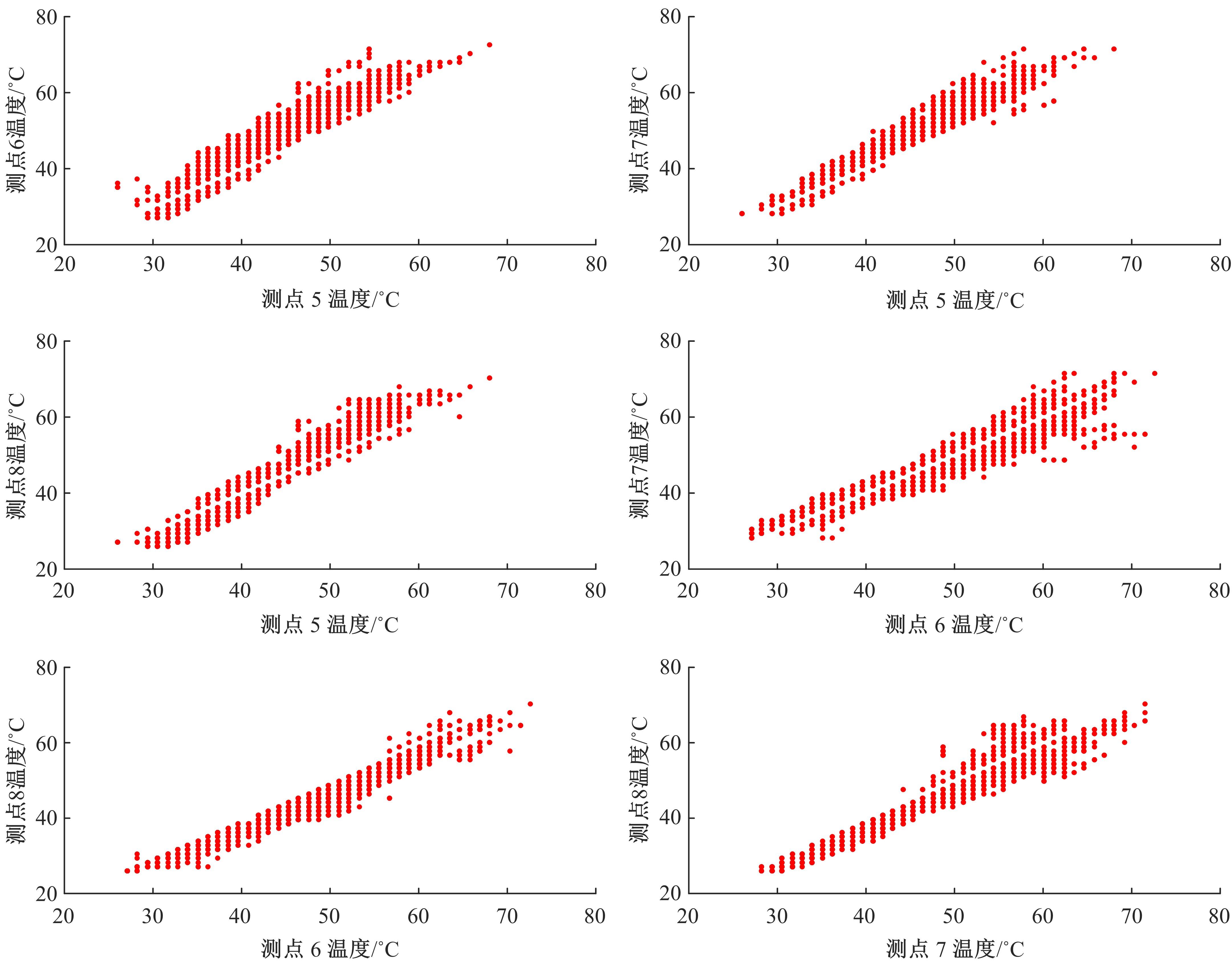
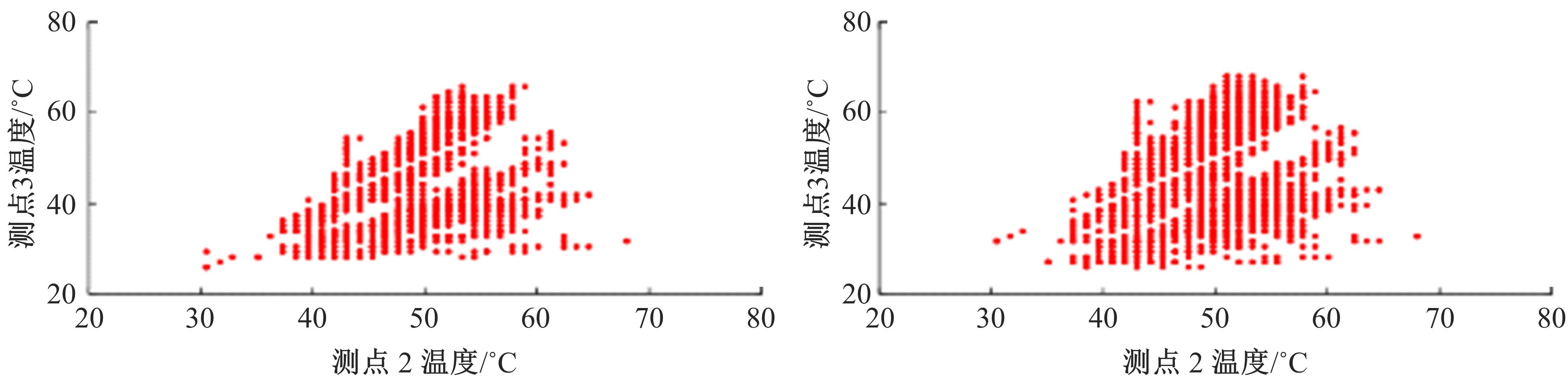
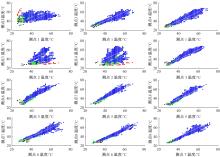
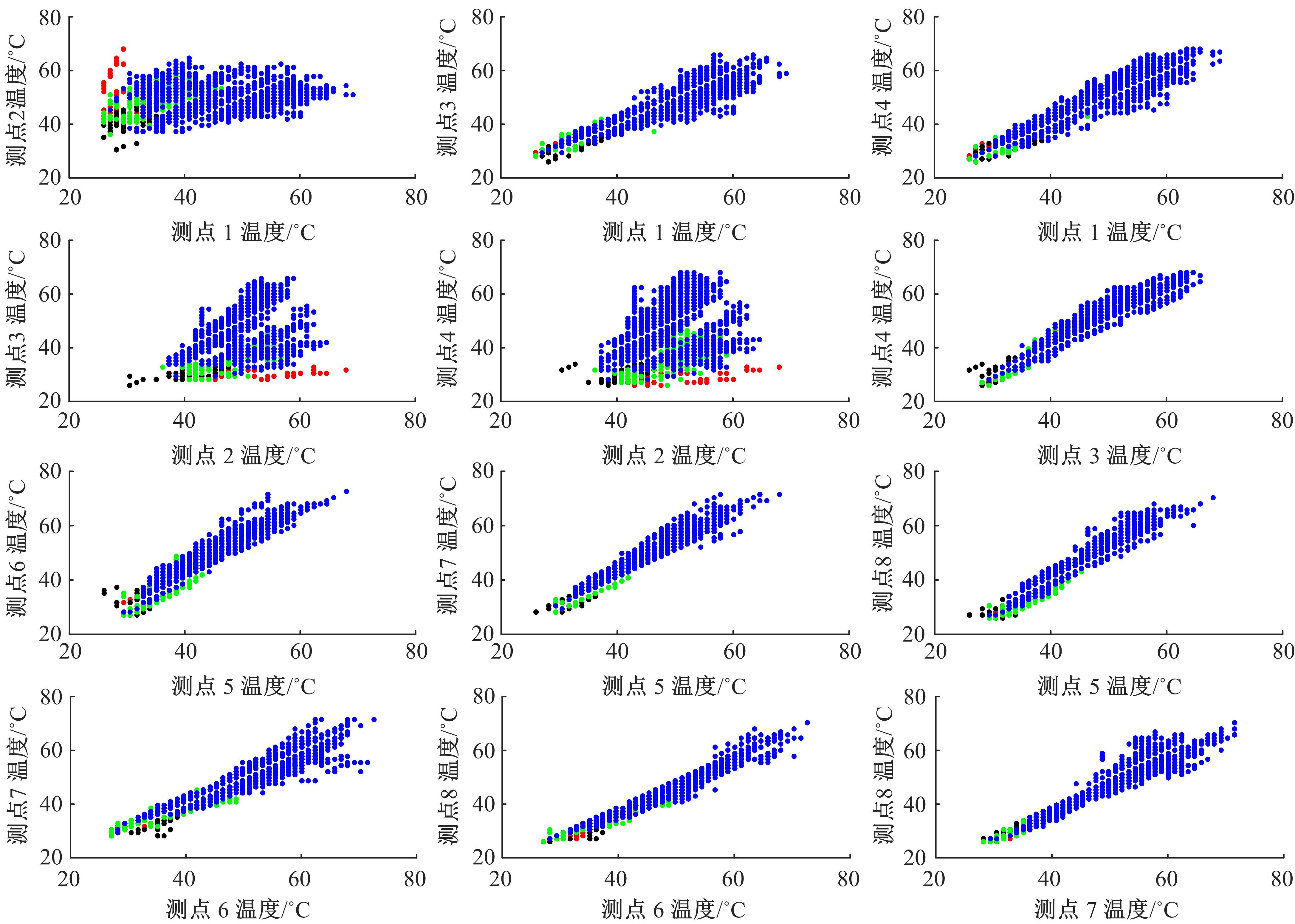
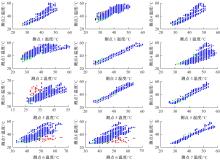
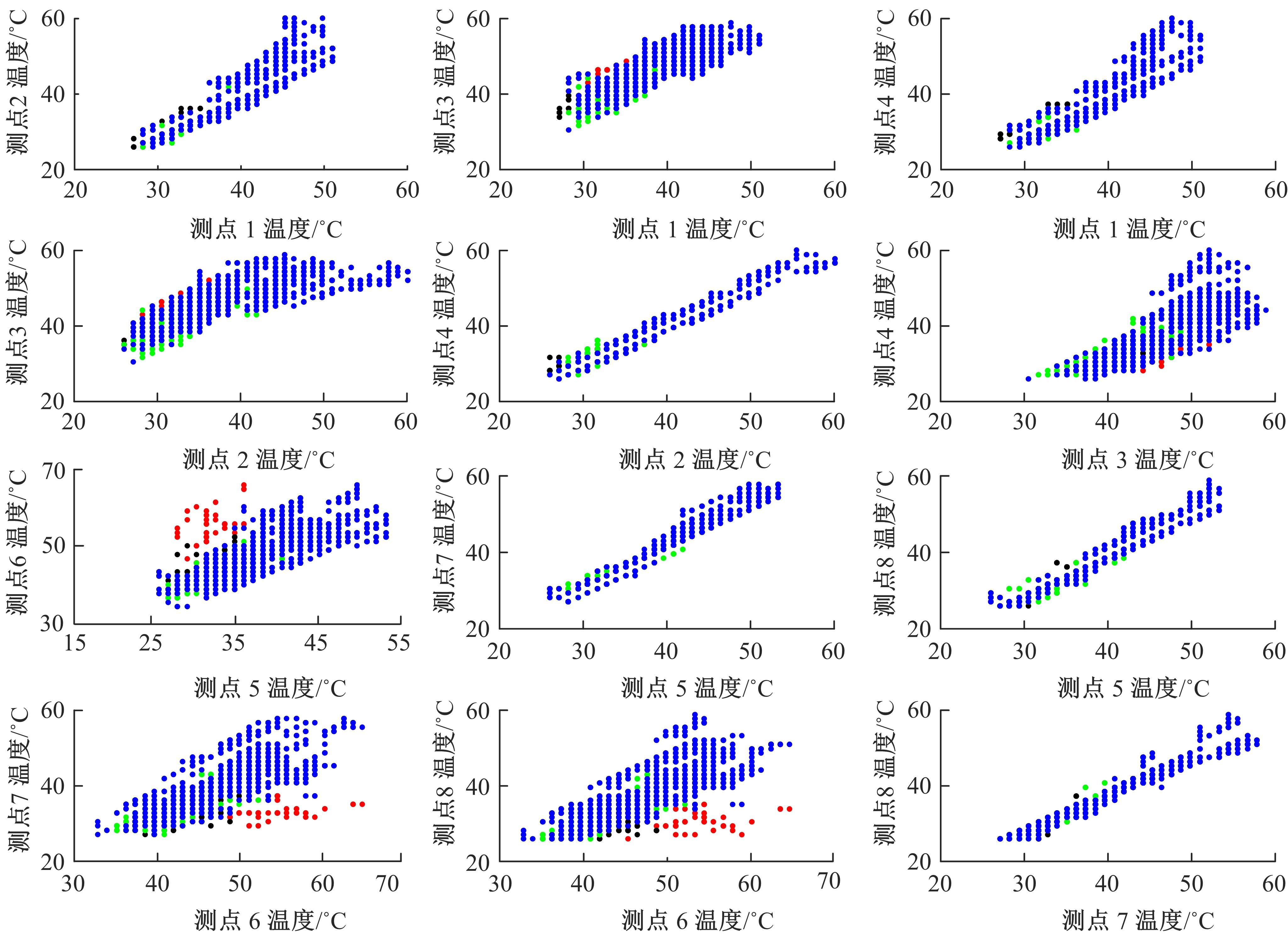
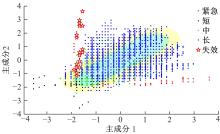
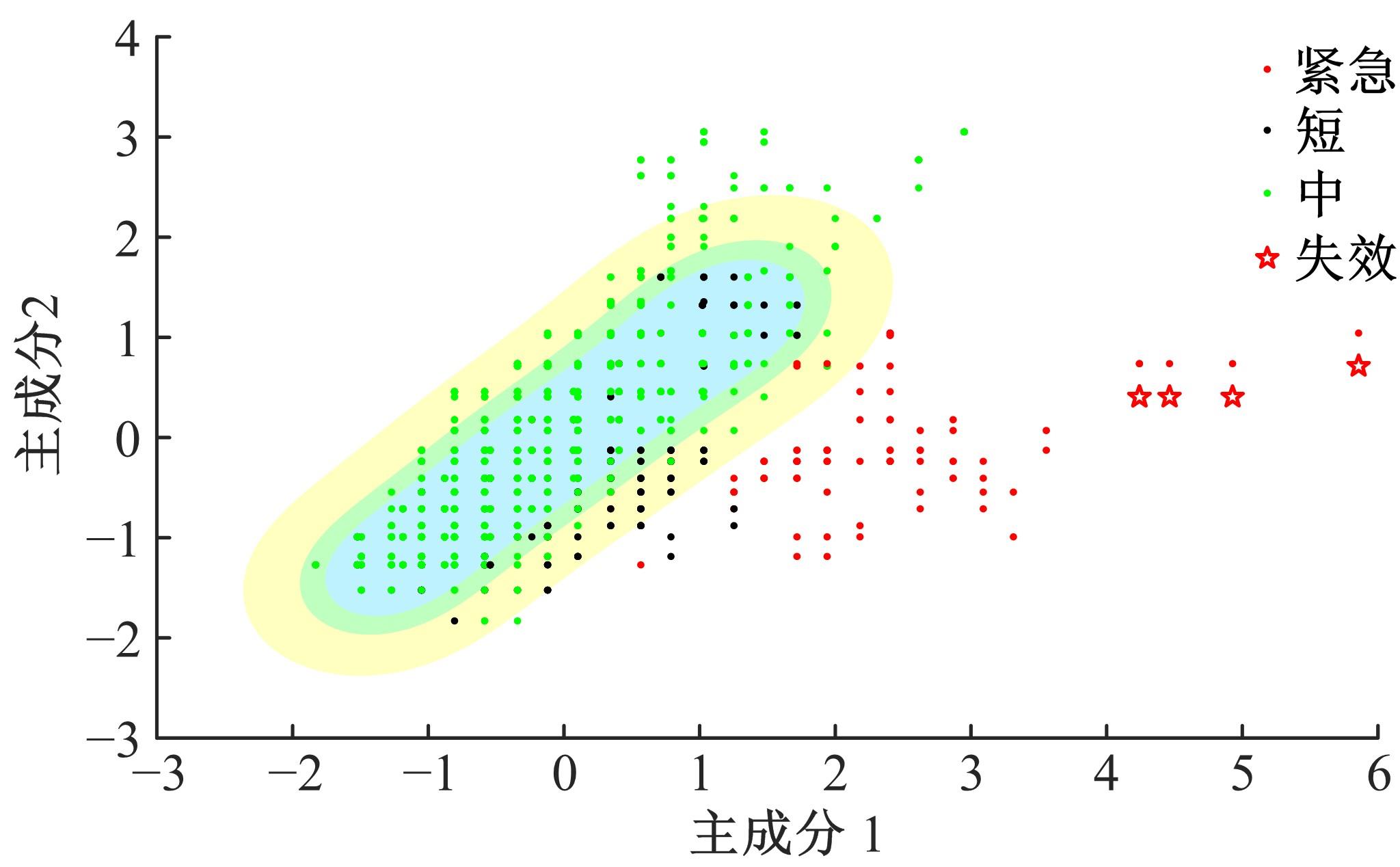
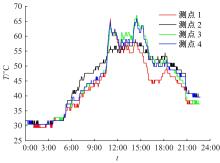
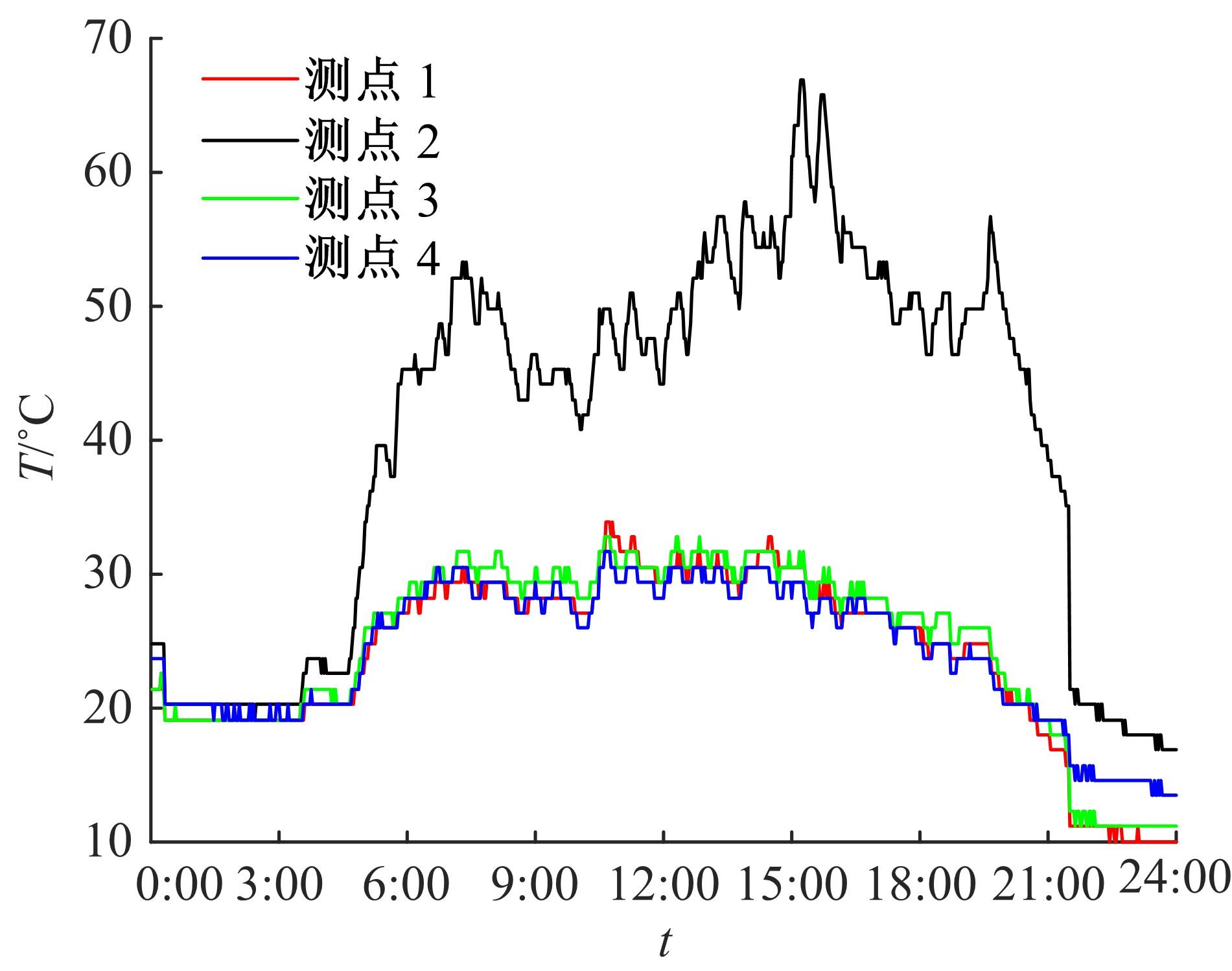
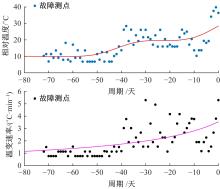
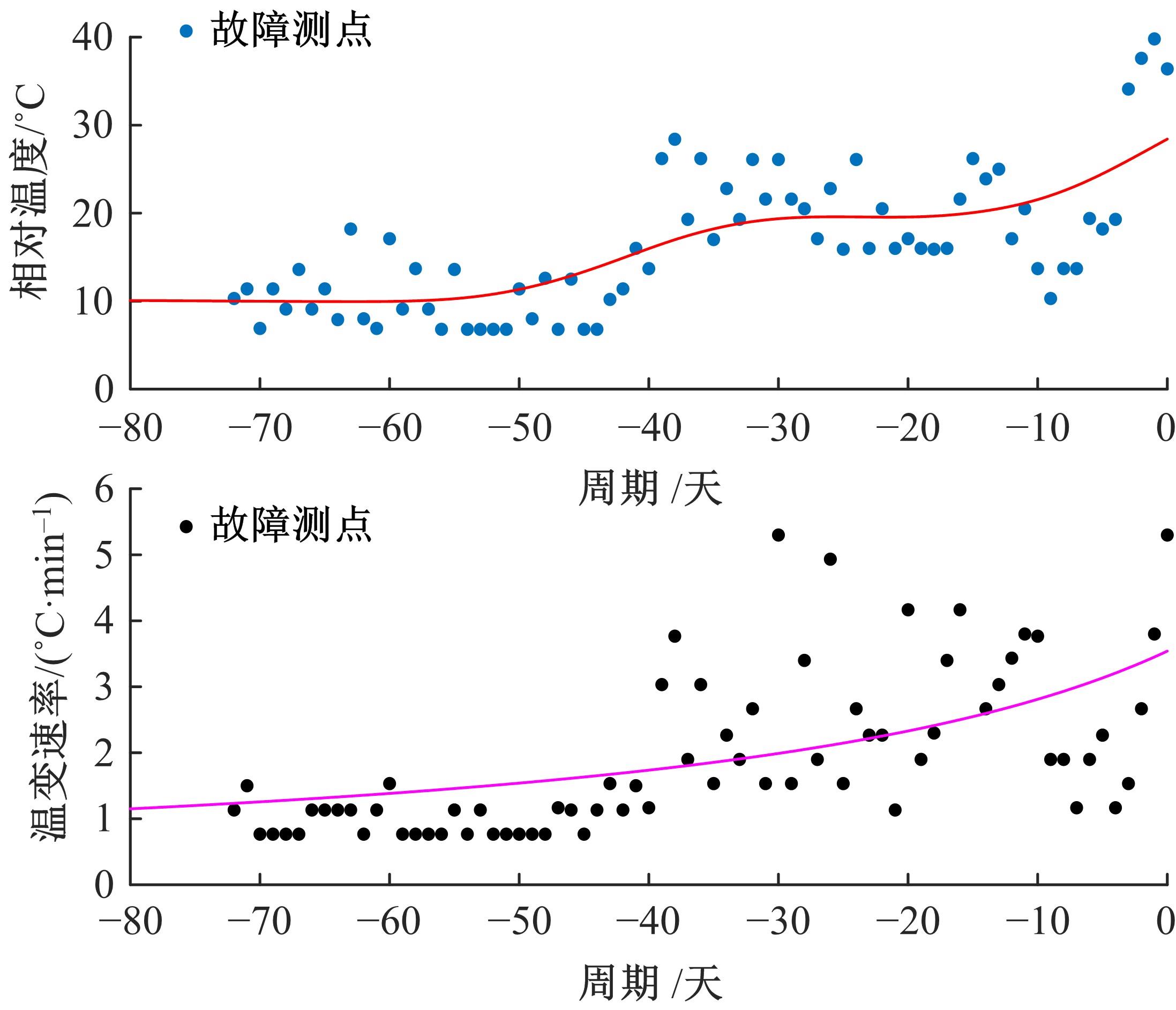
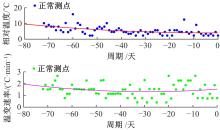
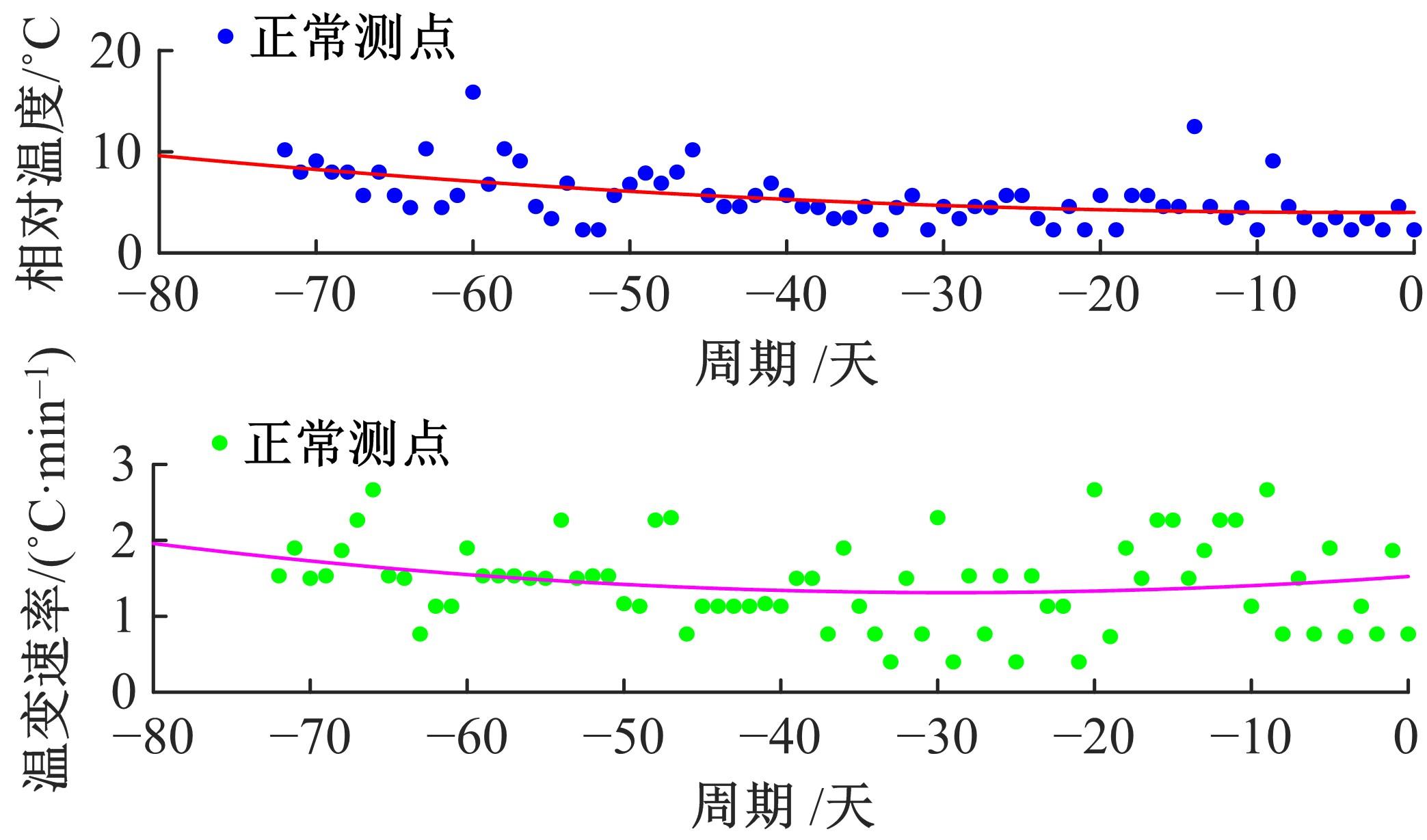
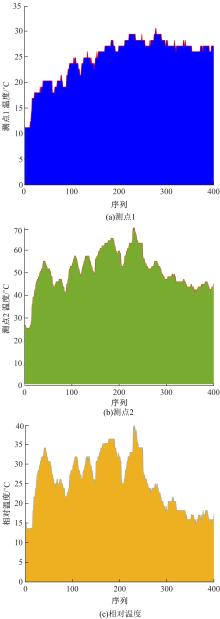
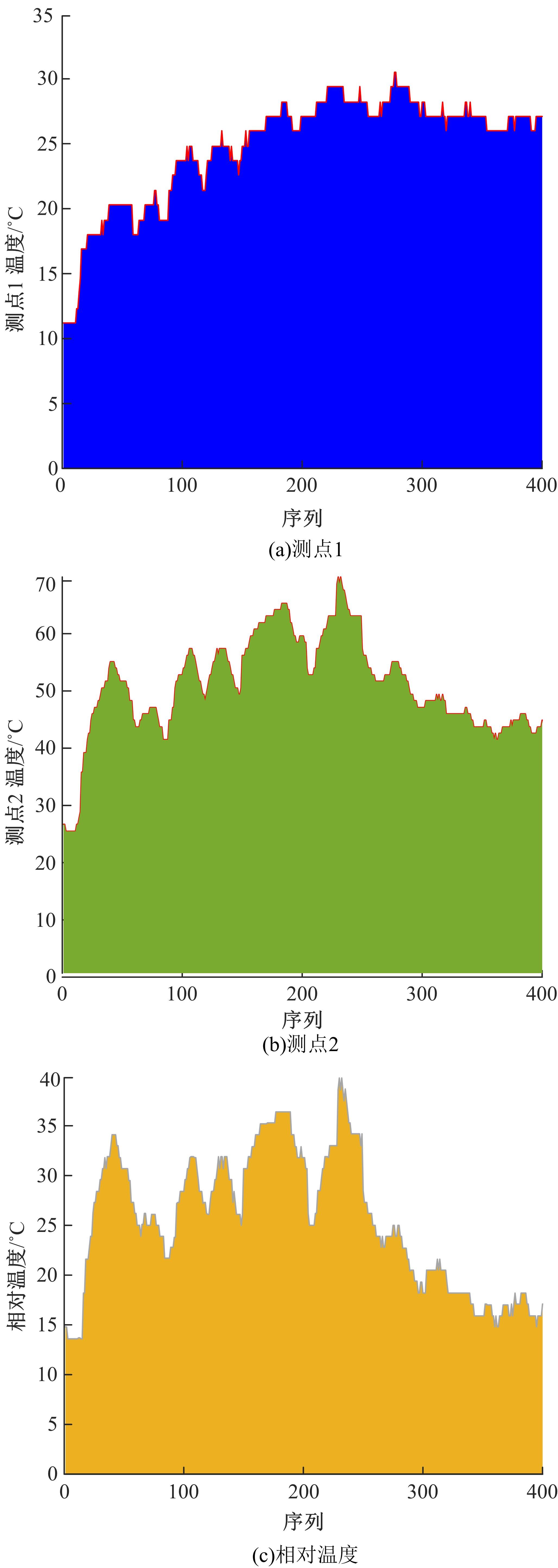
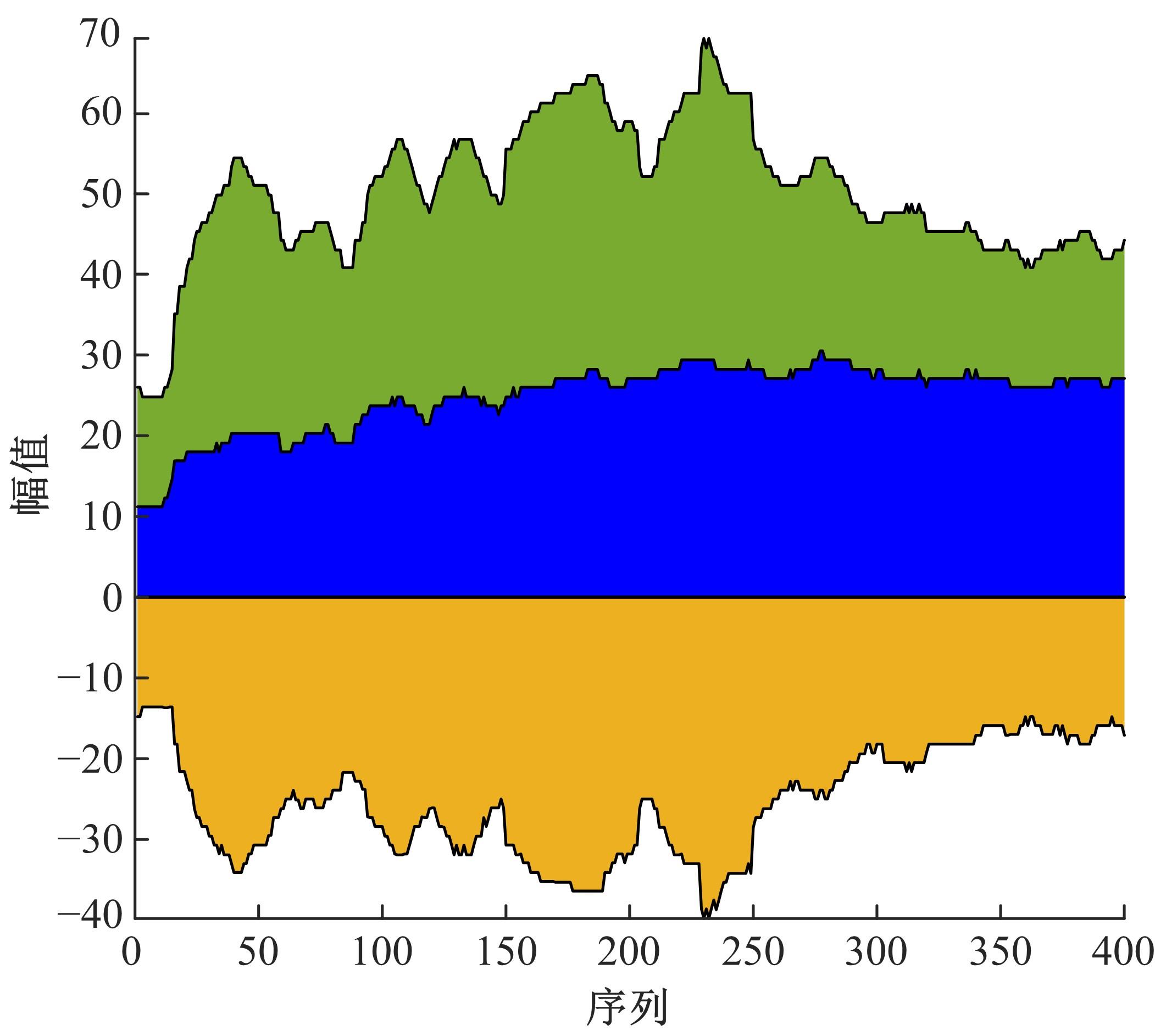
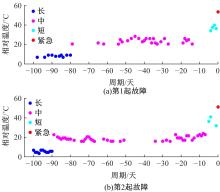
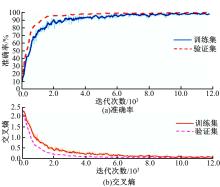
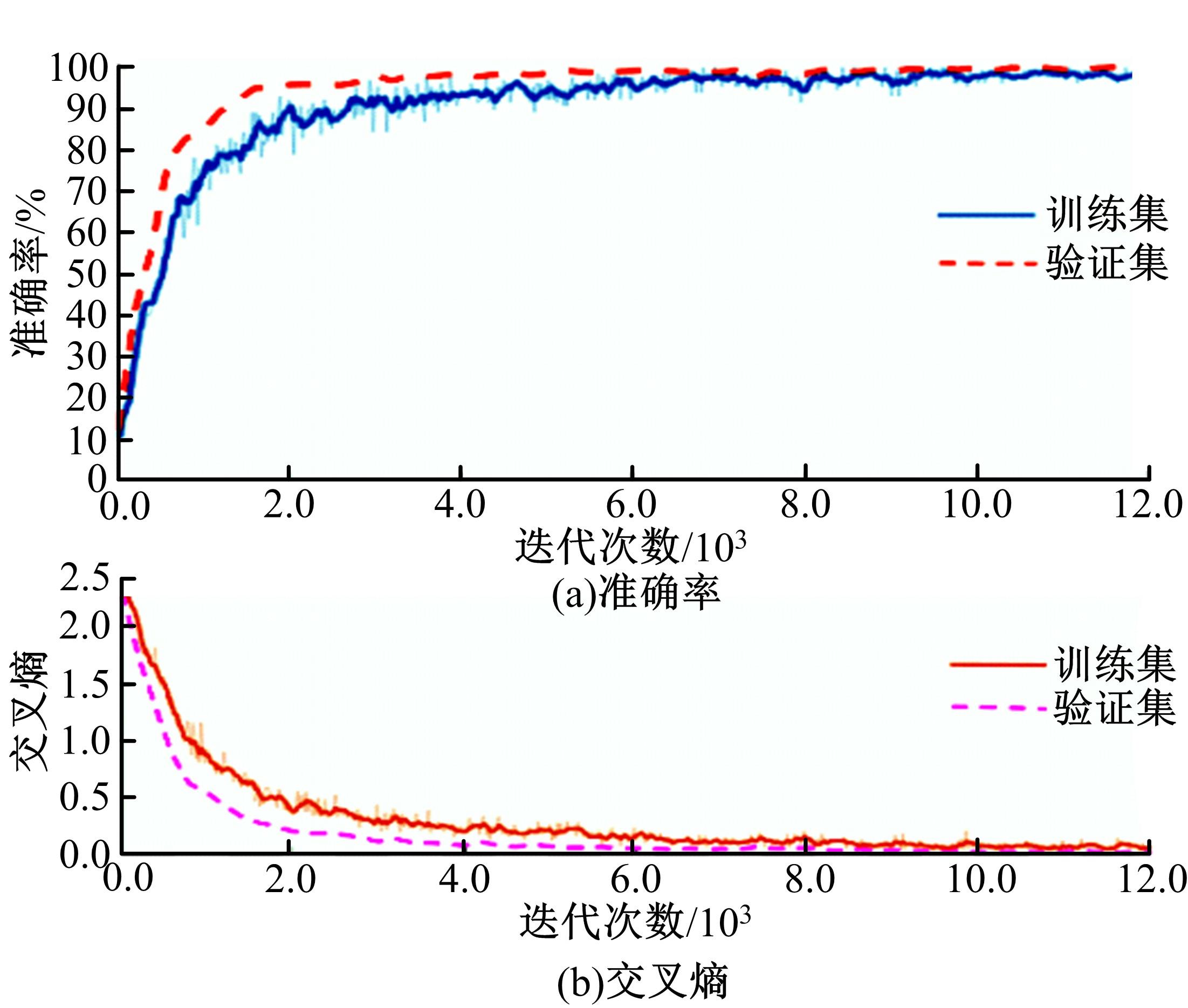
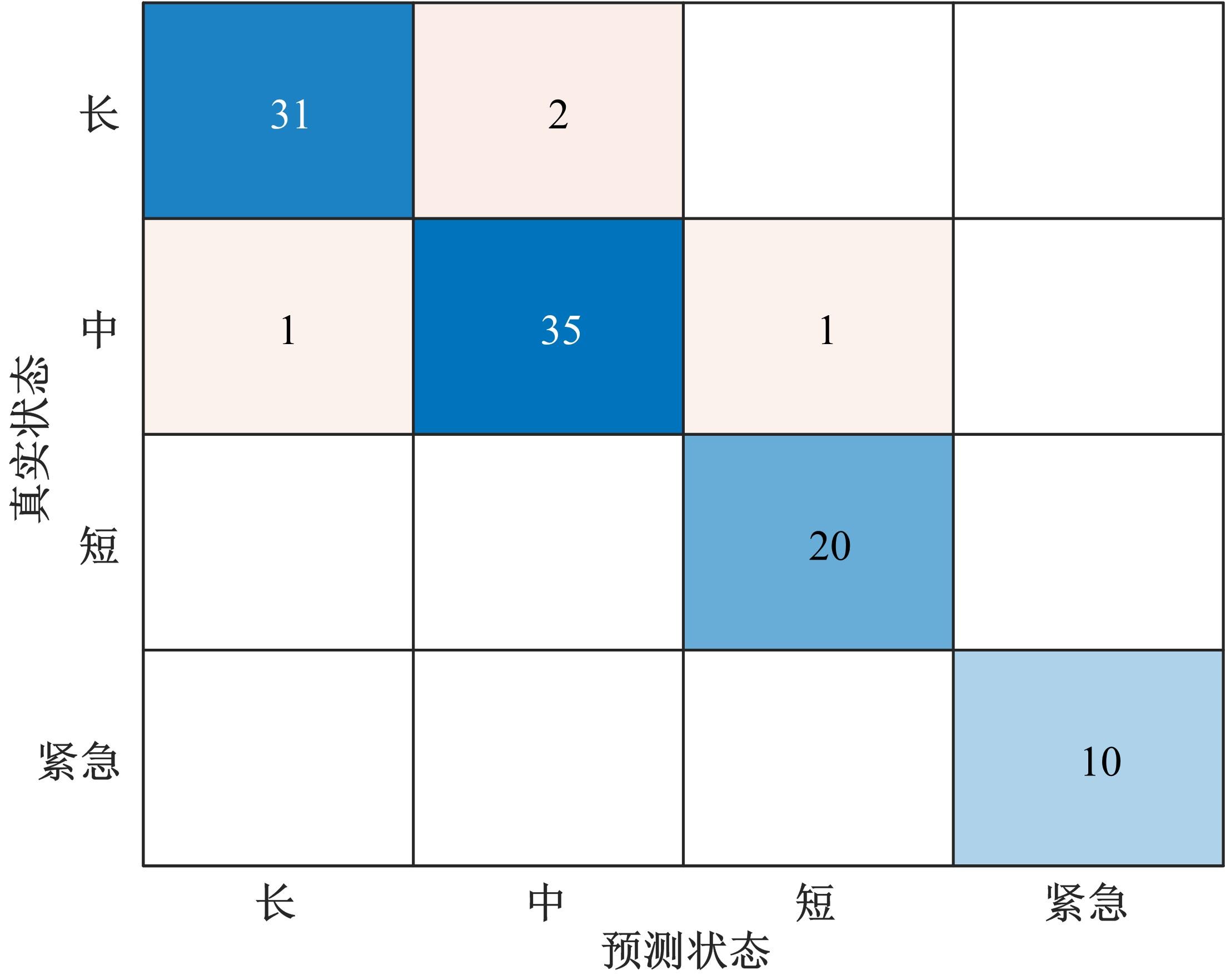
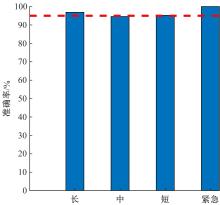
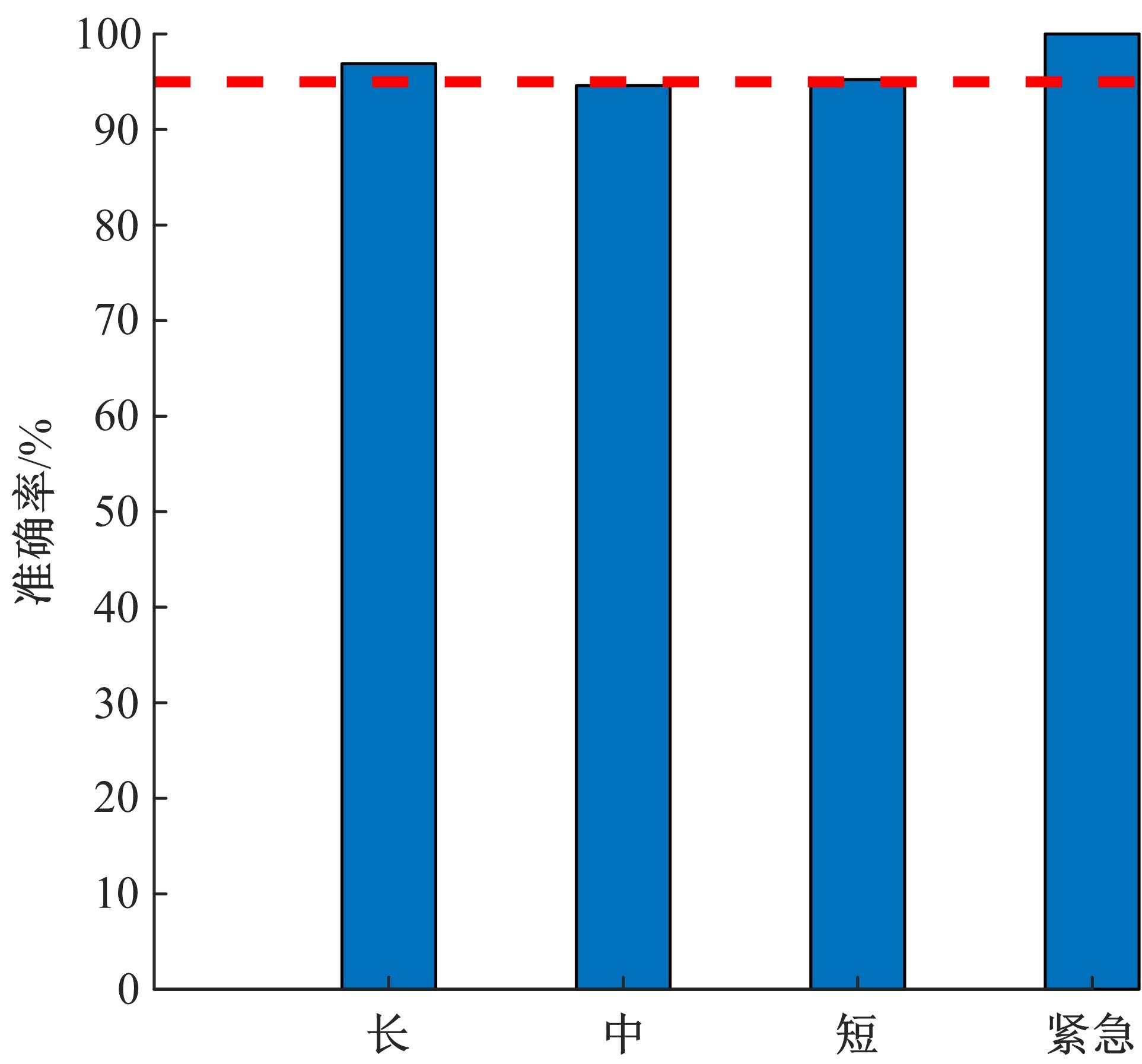
通过研究大量的高速列车轴承温度实测历史数据,提出了利用轴承温度关联测点之间的变化相似作为实现轴承温度状态连续性识别的依据。首先,应用无监督学习One-class SVM算法进行异常识别,结果表明该算法虽然可以较好地识别异常即“紧急”状态,但无法实现轴承温度状态的连续性识别。然后,进一步地根据相对温度变化将轴承从正常到故障失效整个过程定义为4个阶段,即长、中、短、紧急,并提出了以包含相对温度及温变速率等信息的图像样本来描述轴承温度状态变化的数据表达方式。最后,应用深度学习CNN算法进行轴承温度状态的连续性识别,结果表明CNN模型能够可靠地识别轴承温度的不同状态,从而为实现高速列车轴承预测性维护提供了一定支撑。
中图分类号:
- U271
| 1 | Olver A V. The mechanism of rolling contact fatigue: an update[J]. Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2005, 219(5):313-330. |
| 2 | Sadeghi F, Jalalahmadi B, Slack T S, et al. A review of rolling contact fatigue[J]. Journal of Tribology, 2009,131 (4):1-15. |
| 3 | Harvey T J, Wood R J, Powrie H E. Electrostatic wear monitoring of rolling element bearings[J]. Wear, 2007, 263(7-12):1492-1501. |
| 4 | Tarawneh C M, Sotelo L. Temperature profilesof railroad tapered roller bearings with defective inner and outer rings[C]∥Proceedings of the ASME Joint Rail Conference, Columbia, USA,2015:12-15. |
| 5 | Kim W, Seo J, Hong D. Infrared thermographic inspection of ball bearing; condition monitoring for defects under dynamic loading stages[C]∥The 18th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, Durban, South Africa, 2012:16-20. |
| 6 | Kim D, Yun H, Yang S, et al. Fault diagnosis of ball bearings within rotational machines using the infrared thermography method[J]. Journal of the Korean Society for Nondestructive Testing, 2010, 30(6):558-563. |
| 7 | Sciascera C, Giangrande P, Papini L, et al. Analytical thermal model for fast stator winding temperature prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(8): 6116-6126. |
| 8 | Madonna V, Walker A, Giangrande P, et al. Improved thermal management and analysis for stator end-windings of electrical machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(7): 5057-5069. |
| 9 | Pouly F, Changenet C, Ville F, et al. Investigations on the power losses and thermal behavior of rolling element bearings[J]. Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2010, 224(9): 925-933. |
| 10 | Neurouth A, Changenet C, Ville F, et al. Thermal modeling of a grease lubricated thrust ball bearing[J]. Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2014, 228(11): 1266-1275. |
| 11 | 丁洪福, 王风涛, 景敏卿,等. 高速球轴承热稳定性研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2017, 36(14):168-173. |
| Ding Hong-fu, Wang Feng-tao, Jing Min-qing, et al. The thermal stability of high-speed ball bearings[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(14):168-173. | |
| 12 | 胡腾, 殷国富, 邓聪颍. 角接触球轴承热力学耦合模型与分析方法[J]. 四川大学学报:工程科学版, 2014, 46(4):189-198. |
| Hu Teng, Yin Guo-fu, Deng Cong-ying. Integrated thermo-mechanical model and analysis of angular contact ball bearing[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2014, 46(4):189-198. | |
| 13 | 何兴平, 耿远松, 郭志伟,等. 基于差分自回归移动平均模型的电气设备温度预测[J]. 自动化与仪器仪表, 2016(12):96-98. |
| He Xing-ping, Geng Yuan-song, Guo Zhi-wei, et al. The substation equipment temperature prediction based on time sequence ARIMA model[J]. Automation & Instrumentation, 2016(12):96-98. | |
| 14 | 邹永久, 张跃文, 孙培廷,等. 基于 RKGM-AR 模型的船舶主机排气温度预测[J]. 船舶工程, 2015,37(7):46-49, 58. |
| Zou Yong-jiu, Zhang Yue-wen, Sun Pei-ting, et al. Prediction of exhaust gas temperature of ship main engine based on RKGM-AR model[J]. Ship Engineering, 2015,37(7):46-49, 58. | |
| 15 | 孙建平, 朱雯. 基于小波 BP-时间序列的齿轮箱温度预警[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2012, 26(3):197-201. |
| Sun Jian-ping, Zhu Wen. Gearbox temperature prewarning based on wavelets BP-time series method[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrument, 2012, 26(3):197-201. | |
| 16 | 王新全, 孙培廷, 邹永久,等. 基于 GA-BP 模型的船舶柴油机排气温度趋势预测[J]. 大连海事大学学报, 2015, 41(3):73-76. |
| Wang Xin-quan, Sun Pei-ting, Zou Yong-jiu, et al. Prediction of marine main engine exhaust temperature changing trend based on GA-BP model[J]. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 2015, 41(3):73-76. | |
| 17 | 梅启智. 系统可靠性工程基础[M].北京:科学出版社, 1992. |
| 18 | 刘丽娟,陈果,郝腾飞. 基于流形学习与一类支持向量机的滚动轴承早期故障识别方法[J]. 中国机械工程, 2013, 24(5):628-633. |
| Liu Li-juan, Chen Guo, Hao Teng-fei. Incipient fault recognition of rolling bearings based on manifold learning and one-class SVM[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 24(5):628-633. | |
| 19 | Arlot S,Celisse A. A survey of cross-validation procedures for model selection[J]. Statistics Surveys,2010,4:40-79. |
| 20 | 龚丁禧,曹长荣.基于卷积神经网络的植物叶片分类[J].计算机与现代化, 2014(4):12-15, 19. |
| Gong Ding-xi, Cao Chang-rong. Plant leaf classification based on cnn[J]. Computer and Modernization, 2014 (4):12-15, 19. | |
| 21 | 董峻妃,郑伯川,杨泽静.基于卷积神经网络的车牌字符识别[J].计算机应用,2017,37(7):2014-2018. |
| Dong Jun-fei, Zheng Bo-chuan, Yang Ze-jing. Character recognition of license plate based on convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2017, 37(7):2014-2018. | |
| 22 | Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]∥The Twenty-sixth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing System, Lake Tahoe,USA,2012:1097-1105. |
| [1] | 胡兴军,张靖龙,罗雨霏,辛俐,李胜,胡金蕊,兰巍. 冷却管结构及进气方向对空冷中冷器性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1933-1942. |
| [2] | 陈剑斌,周宋泽,费峰永,陈永龙,凌国平. 过盈量及滚花方式对装配式凸轮轴压装失效的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1959-1966. |
| [3] | 钟辉,康恒,吕颖达,李振建,李红,欧阳若川. 基于注意力卷积神经网络的图像篡改定位算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1838-1844. |
| [4] | 罗勇,韦永恒,黄欢,肖人杰,任淋,崔环宇. 驾驶员意图识别的P2.5插混构型双离合器起步控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1575-1582. |
| [5] | 曾小华,宋美洁,宋大凤,王越. 基于车联网信息的公交客车行驶工况数据处理方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1692-1699. |
| [6] | 马超,高云凯,刘哲,段月星,田林雳. 骨架式车身多材料及梁截面形状和尺寸优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1583-1592. |
| [7] | 兰凤崇,李继文,陈吉清. 面向动态场景复合深度学习与并行计算的DG-SLAM算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1437-1446. |
| [8] | 杨建,夏琦,周海超,王国林. 修正胎体弦轮廓载重子午线轮胎的降噪机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1198-1203. |
| [9] | 龙江启,向锦涛,俞平,王骏骋. 适用于非线性主动悬架滑模控制的线性干扰观测器[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1230-1240. |
| [10] | 王德兴,吴若有,袁红春,宫鹏,王越. 基于多尺度注意力融合和卷积神经网络的水下图像恢复[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1396-1404. |
| [11] | 陈鑫,于贵申,张彪,潘凯旋,杨立飞. 搅拌摩擦点焊接头拉伸-剪切行为的等效建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1190-1197. |
| [12] | 李光松,李文清,李青. 基于随机性特征的加密和压缩流量分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1375-1386. |
| [13] | 何仁,赵晓聪,杨奕彬,王建强. 基于驾驶人风险响应机制的人机共驾模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 799-809. |
| [14] | 朱小龙,谢忠. 基于机器学习的地理空间数据抽取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1011-1016. |
| [15] | 张家旭,王欣志,赵健,施正堂. 汽车高速换道避让路径规划及离散滑模跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1081-1090. |
|
||