吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1386-1393.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210019
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
导电沥青及混合料裂缝局部温度场及愈合效果
郭庆林1( ),刘强1,吴春利2(
),刘强1,吴春利2( ),李黎丽1,李懿明1,刘富春1
),李黎丽1,李懿明1,刘富春1
- 1.河北工程大学 土木工程学院,河北 邯郸 056038
2.吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
Local temperature field and healing level of crack in conductive asphalt and mixture
Qing-lin GUO1( ),Qiang LIU1,Chun-li WU2(
),Qiang LIU1,Chun-li WU2( ),Li-li LI1,Yi-ming LI1,Fu-chun LIU1
),Li-li LI1,Yi-ming LI1,Fu-chun LIU1
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Hebei University of Engineering,Handan 056038,China
2.College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
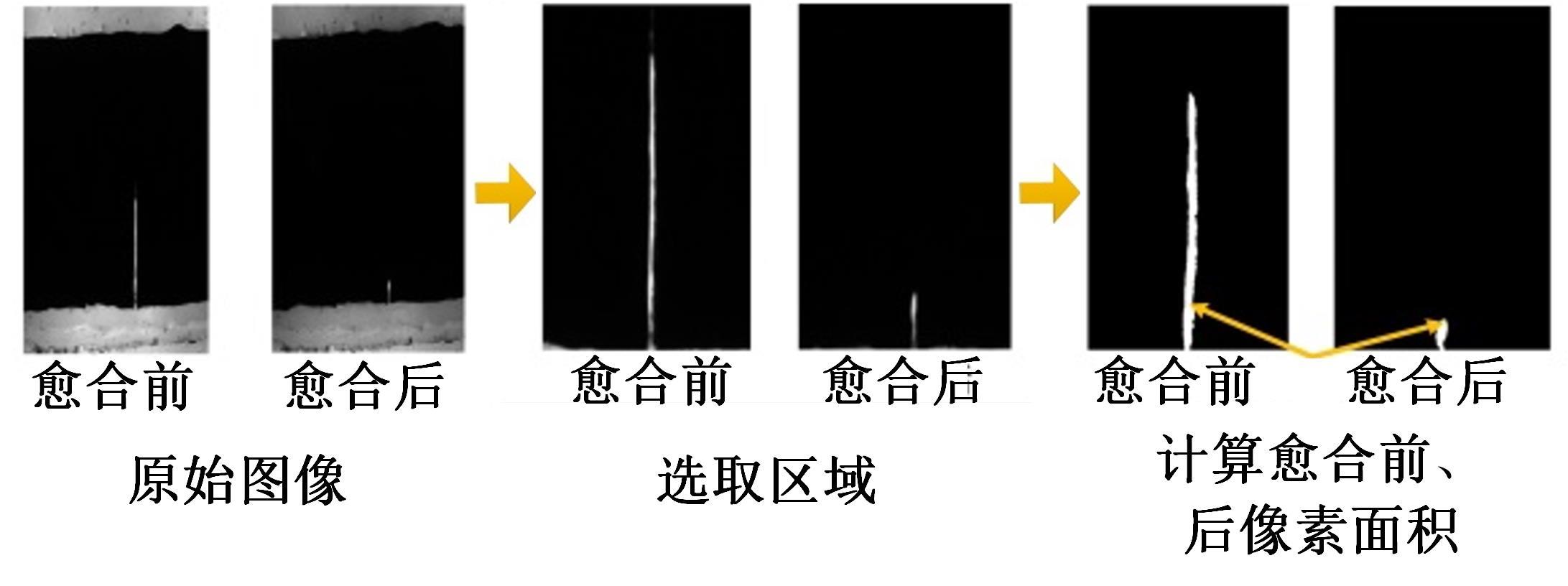
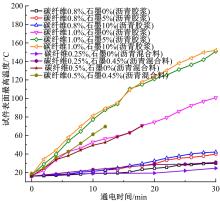
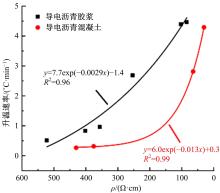
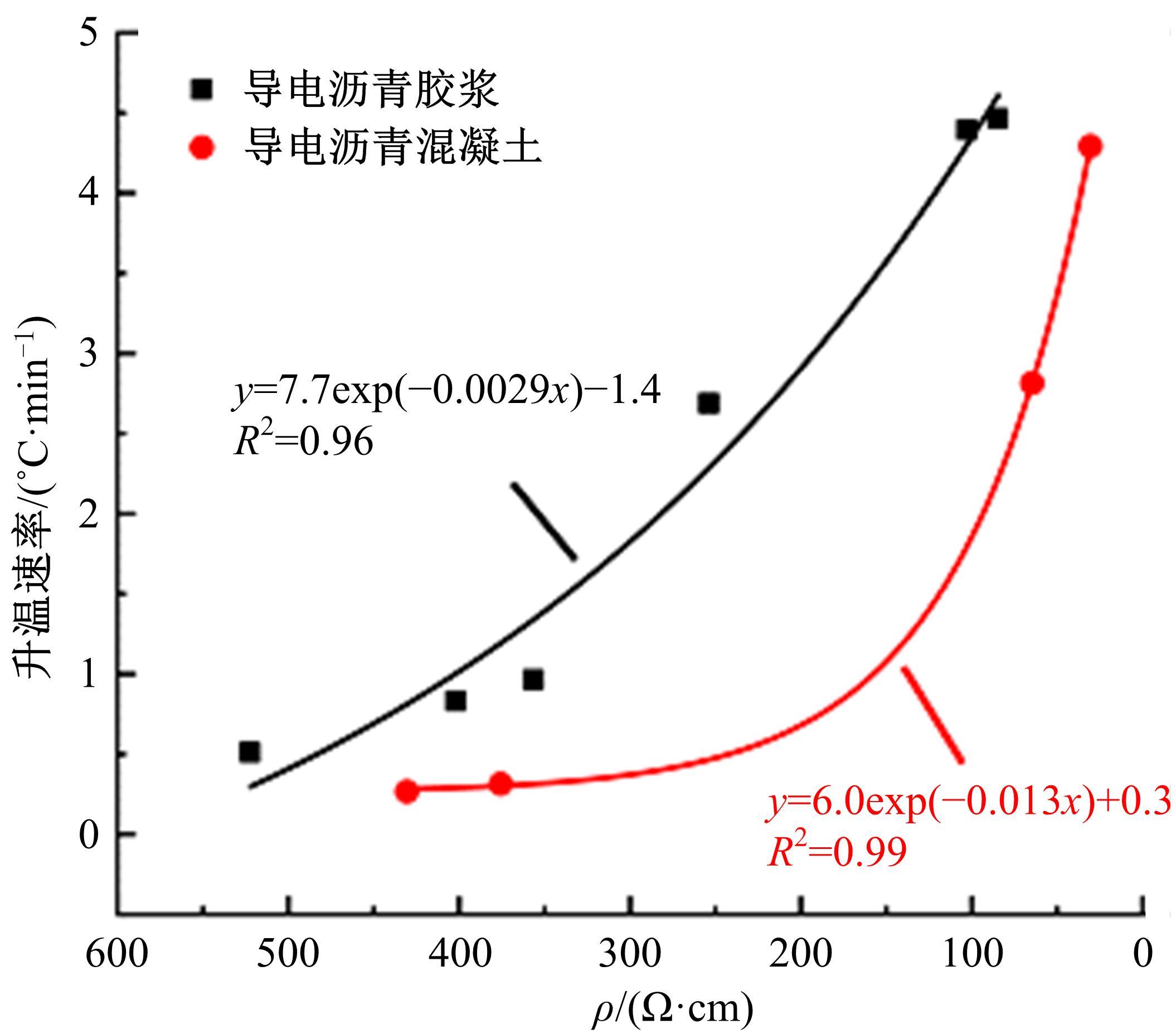
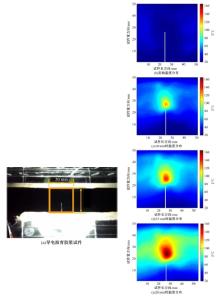
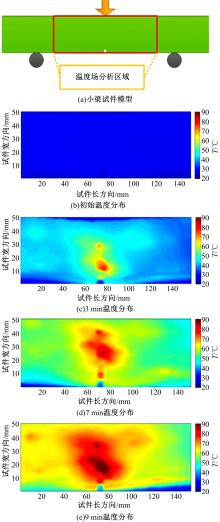
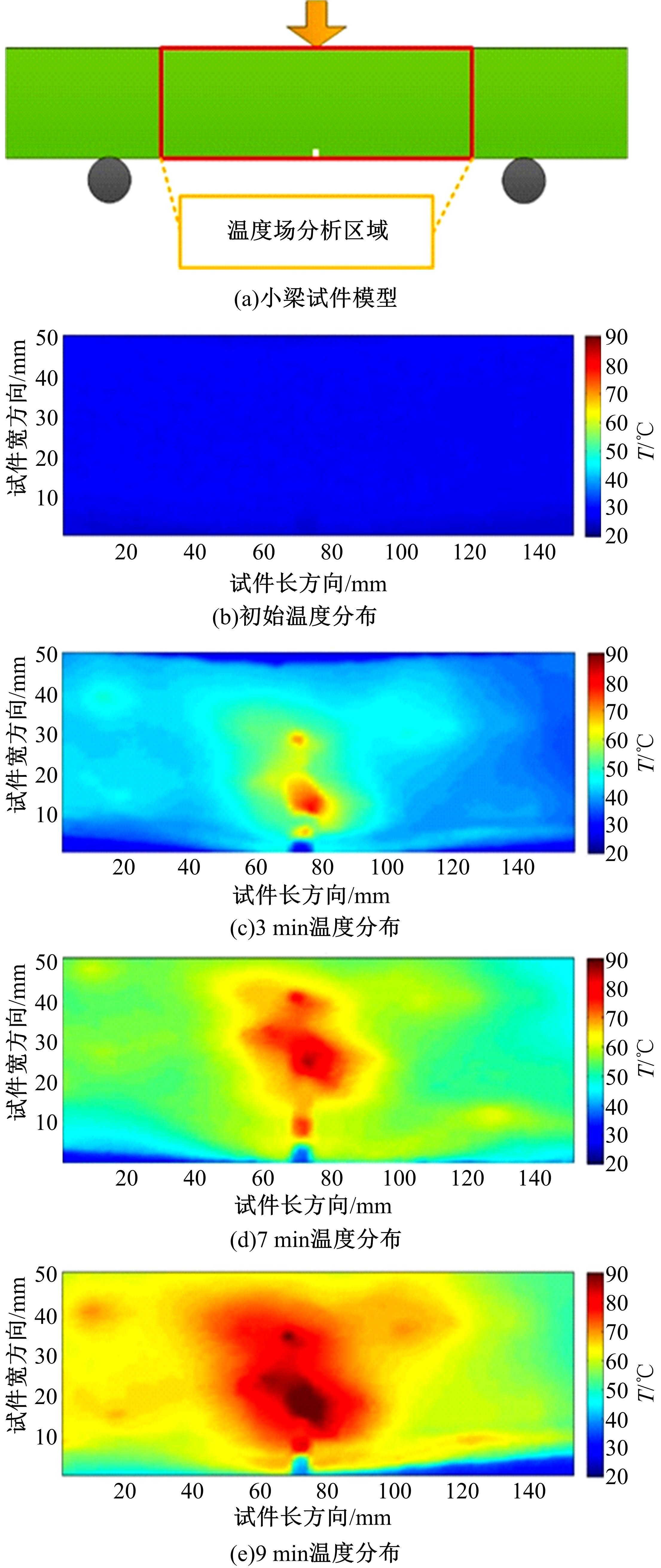
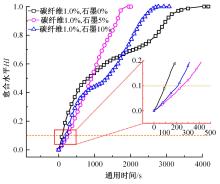
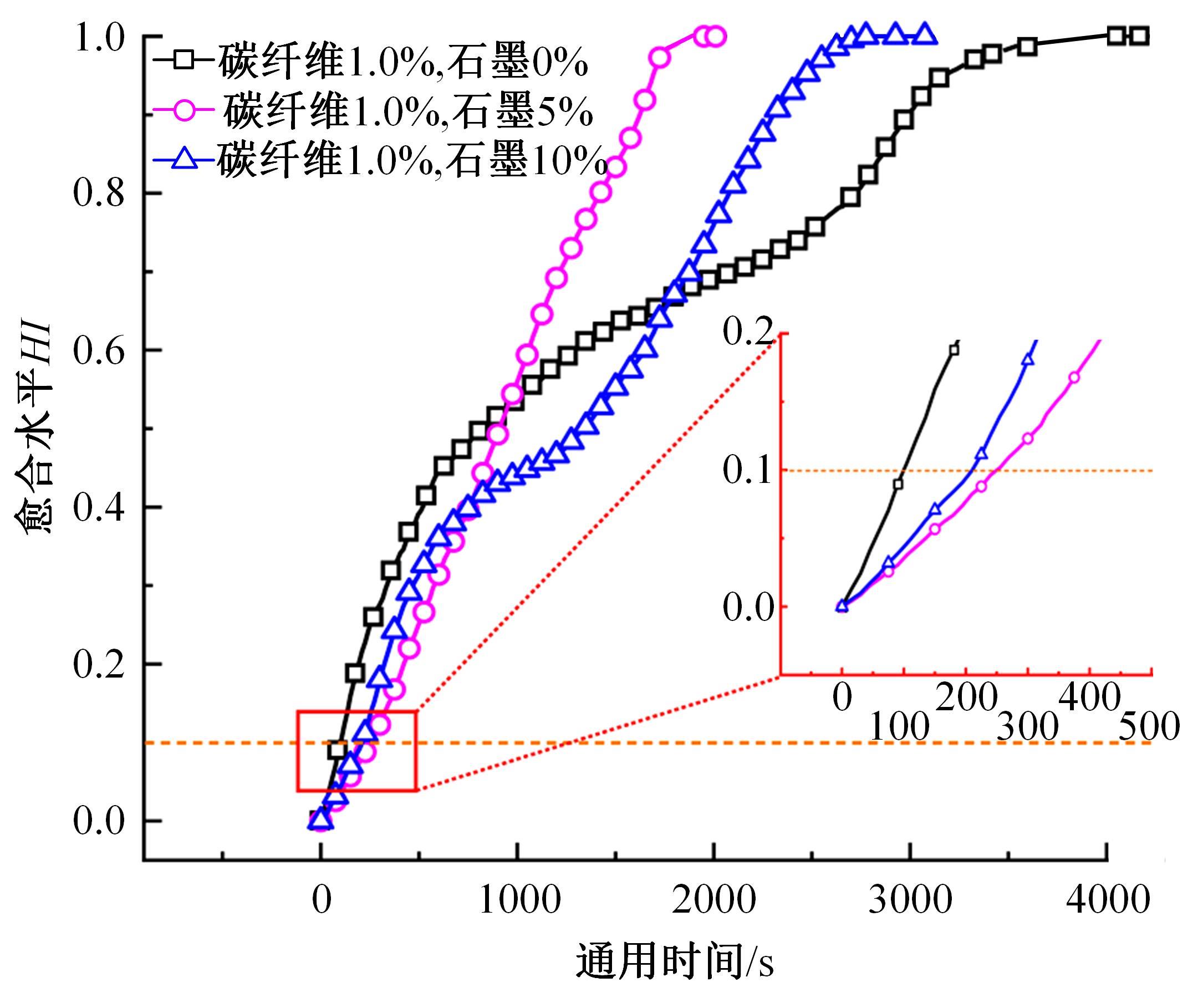
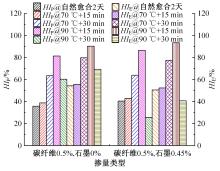
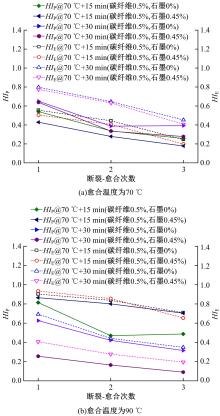
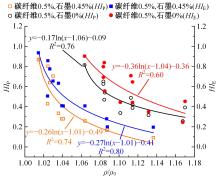
为探究导电沥青胶浆及混合料裂缝附近区域的导电升温效应,制备了不同配比的导电沥青胶浆及混合料,进行了导电愈合试验,利用红外摄像仪测定了导电沥青胶浆和沥青混合料裂缝周围的温度场。采用图像处理技术定量分析了导电沥青胶浆裂缝愈合水平,同时探讨了沥青混合料的反复愈合性能。结果表明:导电沥青胶浆及混合料温度均随通电时间线性升高,升温速率与材料电阻率呈指数函数关系;导电沥青胶浆及混合料裂缝附近区域温度明显高于其他区域,局部升温明显,局部高温有利于实现裂缝定向愈合;沥青混合料反复愈合水平随断裂次数的增多逐渐降低,愈合温度和通电时间对反复愈合水平具有显著影响;利用愈合前、后电阻率比值可估计导电沥青混合料的愈合效果。
中图分类号:
- U416.217
| 1 | Garcia A, Schlangen E, van de Ven M. Two ways of closing cracks on asphalt concrete pavements: microcapsules and induction heating[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2009, 417-418: 573-576. |
| 2 | Garcia A, Schlangen E, van de Ven M, et al. Induction heating of mastic containing conductive fibers and fillers[J]. Materials and Structures, 2011, 44(2): 499-508. |
| 3 | Garcia A, Bueno M, Norambuena-Contreras J, et al. Induction healing of dense asphalt concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 49: 1-7. |
| 4 | Sun Yi-han, Wu Shao-peng, Liu Quan-tao, et al. Self-healing performance of asphalt mixtures through heating fibers or aggregate[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 150: 673-680. |
| 5 | Liu Q T, Garcia A, Schlangen E, et al. Induction healing of asphalt mastic and porous asphalt concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2011, 25(9): 3746-3752. |
| 6 | Wang Z G, Dai Q L, Porter D, et al. Investigation of microwave healing performance of electrically conductive carbon fiber modified asphalt mixture beams[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2016, 126: 1012-1019. |
| 7 | 张永健, 袁玉卿, 杨玲. 矮寨特大桥融雪防冰电发热沥青混凝土试验研究[J]. 中外公路, 2011, 31(6): 29-32. |
| Zhang Yong-jian, Yuan Yu-qing, Yang Ling. Experimental study on snow-melting and anti-icing electric heating asphalt concrete for Aizhai Bridge[J]. Journal of China & Foreign Highway, 2011, 31(6): 29-32. | |
| 8 | Arabzadeh A, Notani M A, Zadeh A K, et al. Electrically conductive asphalt concrete: an alternative for automating the winter maintenance operations of transportation infrastructure[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 173: No. 106985. |
| 9 | Arabzadeh A, Ceylan H, Kim S, et al. Electrically-conductive asphalt mastic: temperature dependence and heating efficiency[J]. Materials and Design, 2018, 157: 303-313. |
| 10 | 刘志胜, 武胜兵, 刘鹏飞, 等. 导电沥青混凝土及其功能特性研究进展[J].材料导报, 2017, 31(): 374-378, 387. |
| Liu Zhi-sheng, Wu Sheng-bing, Liu Peng-fei, et al. review on functional features of conductive asphalt concrete[J]. Materials Review, 2017, 31(Sup.1): 374-378, 387. | |
| 11 | 姚占勇, 韩杰, 商庆森, 等. 碳纤维石墨导电沥青砂浆压敏性能研究[J]. 山东大学学报: 工学版, 2013, 43(1): 80-85. |
| Yao Zhan-yong, Han Jie, Shang Qing-sen, et al. Research on pressure sensitivity of the conductive asphalt mortar with carbon fiber and graphite powders[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Science), 2013, 43(1): 80-85. | |
| 12 | 匡希龙, 刘俊, 吴刚, 等. 嵌入式导电沥青混凝土路面结构热效应特性研究[J]. 公路工程, 2015, 40(2): 147-149, 154. |
| Kuang Xi-long, Liu Jun, Wu Gang, et al. Research of thermal effects on embedded electrically asphalt conductive concrete pavement[J]. Highway Engineering, 2015, 40(2): 147-149, 154. | |
| 13 | 谭忆秋, 刘凯, 王英园. 碳纤维/石墨烯导电沥青混凝土的非线性伏安特性[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2019, 22(2): 278-283. |
| Tan Yi-qiu, Liu Kai, Wang Ying-yuan. Nonlinear voltammetric characteristics of carbon fiber/graphene conductive asphalt concrete[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2019, 22(2): 278-283. | |
| 14 | 胡天文, 霍海峰, 张佩浩, 等. 碳纤维沥青混凝土导电特性研究[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2017, 44(10): 58-61, 80. |
| Hu Tian-wen, Huo Hai-feng, Zhang Pei-hao, et al. Conductive characteristic research of carbon fiber asphalt concrete[J]. New Building Materials, 2017, 44(10): 58-61, 80. | |
| 15 | 叶家军, 吴学伟, 丁庆军, 等. 导电沥青混合料导电机理及电热性能研究[J].武汉理工大学学报, 2009, 31(9): 16-20. |
| Ye Jia-jun, Wu Xue-wei, Ding Qing-jun, et al. Electrically conductive mechanism and electrothermal performance of conductive asphalt mixtures[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2009, 31(9): 16-20. | |
| 16 | . 公路沥青路面施工技术规范 [S]. |
| 17 | Al-Balbissi A H. A comparative analysis of the fracture and fatigue properties of asphalt concrete and sulphlex[D]. Texas: Texas A&M University, 1983. |
| [1] | 姚玉权,仰建岗,高杰,宋亮. 基于性能-费用模型的厂拌再生沥青混合料优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 585-595. |
| [2] | 夏全平,高江平,罗浩原,张其功,李志杰,杨飞. 用于高模量沥青砼的复合改性硬质沥青低温性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 541-549. |
| [3] | 冉武平,陈慧敏,李玲,冯立群. 干湿循环下粗粒土回弹模量演变规律及模型预估和修正[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2079-2086. |
| [4] | 董伟智,张爽,朱福. 基于可拓层次分析法的沥青混合料路用性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2137-2143. |
| [5] | 许哲谱,杨群. 基于实时路况地图的短期养护作业开始时间优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1763-1774. |
| [6] | 文畅平,任睆遐. 基于Lade模型的生物酶改良膨胀土双屈服面本构关系[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1716-1723. |
| [7] | 惠迎新,孙晓荣,王红雨,高晨. 预制T梁早期水化热温度效应及梁端开裂机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1734-1741. |
| [8] | 王元元,孙璐,刘卫东,薛金顺. 测量路面三维纹理双目重构算法的约束改进[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1342-1348. |
| [9] | 彭勇,杨汉铎,陆学元,李彦伟. 基于离散元法的空隙特征对沥青混合料虚拟剪切疲劳寿命的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 956-964. |
| [10] | 朱伟刚,朱超,张亚球,魏海斌. 基于卷积格网曲面拟合滤波算法的数字高程模型构建及质量评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1073-1080. |
| [11] | 程永春,李赫,李立顶,王海涛,白云硕,柴潮. 基于灰色关联度的矿料对沥青混合料力学性能的影响分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 925-935. |
| [12] | 宫亚峰,逄蕴泽,王博,谭国金,毕海鹏. 基于吉林省路况的新型预制装配式箱涵结构的力学性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 917-924. |
| [13] | 阳恩慧,徐加秋,唐由之,李奥,邱延峻. 温拌剂对沥青断裂和老化性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 604-610. |
| [14] | 孔庆雯,谭国金,王龙林,王勇,魏志刚,刘寒冰. 基于有限元方法的裂缝箱梁桥自振特性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 225-232. |
| [15] | 方宇,孙立军. 基于生存分析的城市桥梁使用性能衰变模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 557-564. |
|
||