吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 1798-1805.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230891
基于分层强化学习的自动驾驶决策控制算法
- 1.大连理工大学 汽车工程学院,辽宁 大连 116024
2.华电煤业集团数智技术有限公司,北京 102488
An automatic driving decision control algorithm based on hierarchical reinforcement learning
Wei-dong LI1( ),Cao-yuan MA1,Hao SHI2,Heng CAO2
),Cao-yuan MA1,Hao SHI2,Heng CAO2
- 1.School of Automotive Engineering,Dalian University of Technology,Dalian 116024,China
2.Huadian Coal Industry Group Digital Intelligence Technology Co. ,Ltd. ,Beijing 102488,China
摘要:
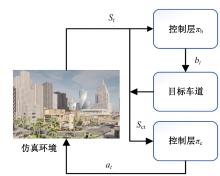
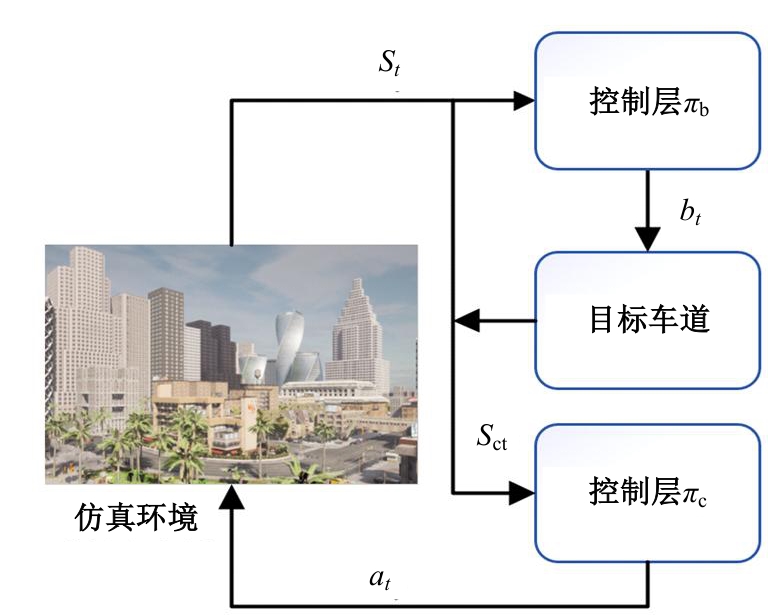
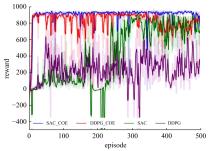
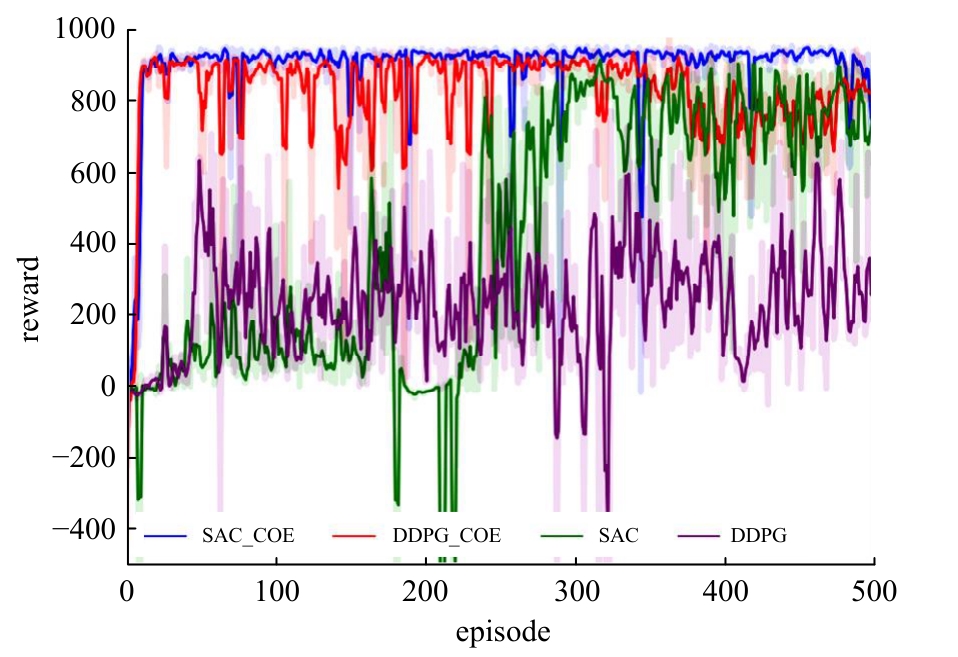
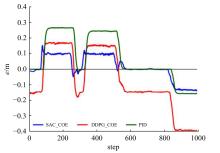
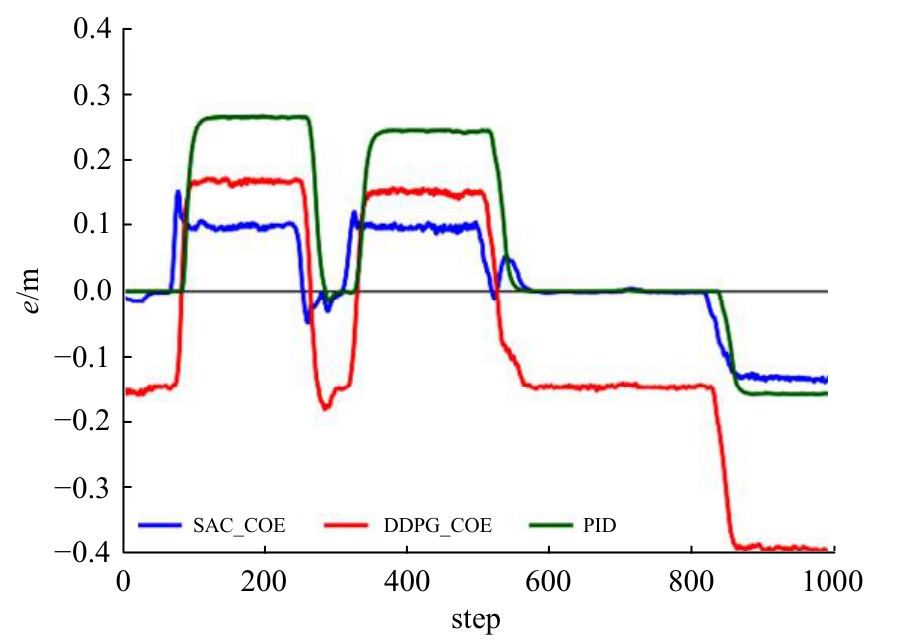
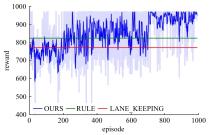
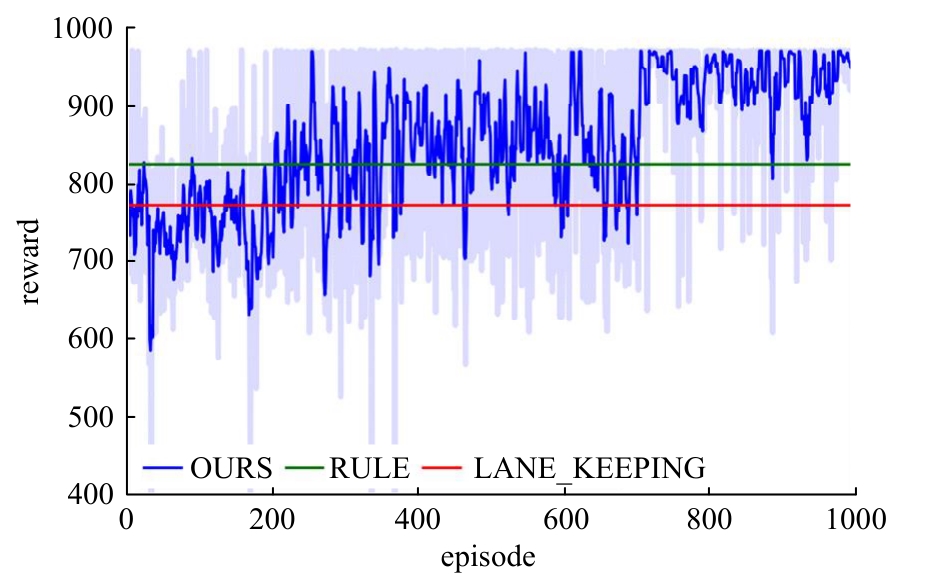
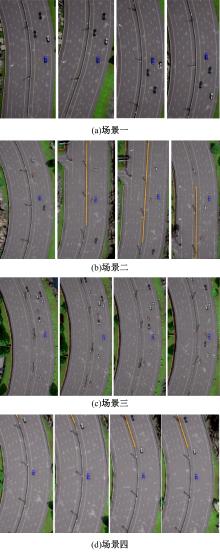
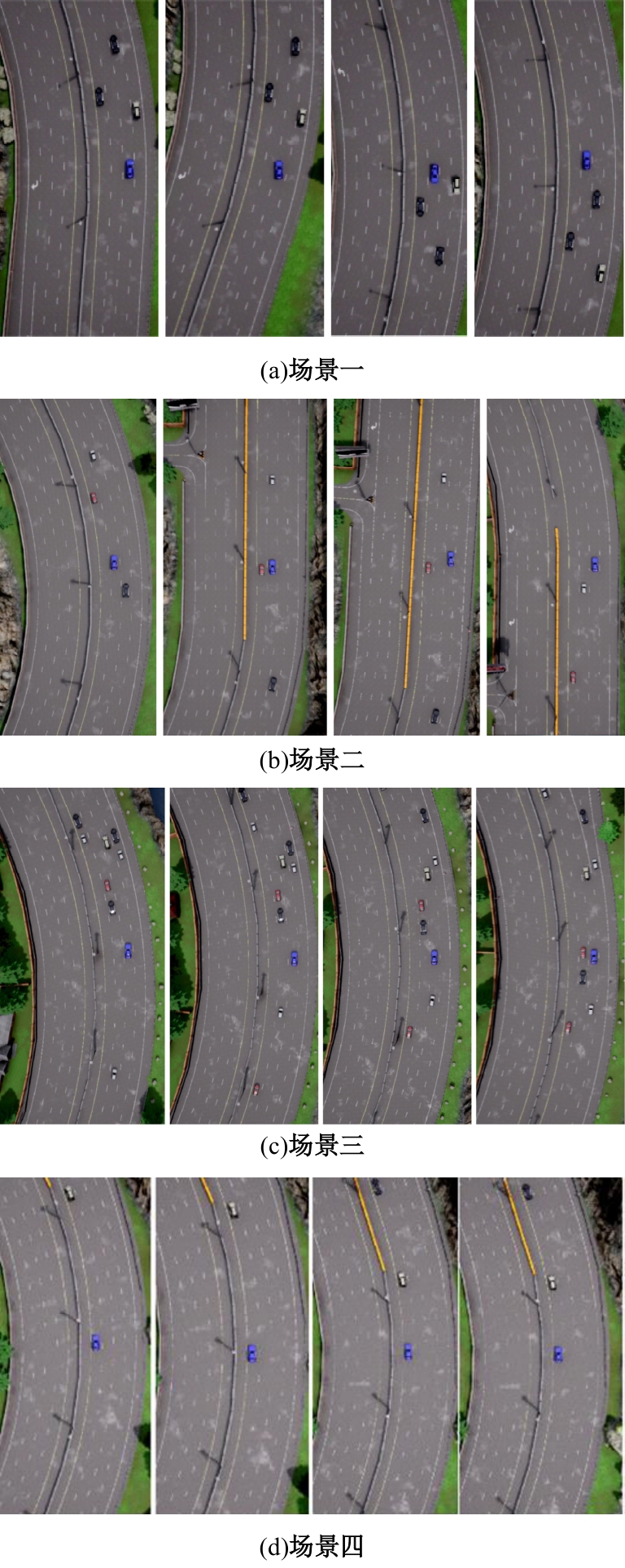
针对强化学习模型在自动驾驶任务中存在收敛速度慢和应用场景单一的问题,提出了一种两层的强化学习框架来替代传统的决策层与控制层。决策层将驾驶行为分为车道保持、左变道和右变道,决策层选择对应的行为后,通过改变控制层输入的方式完成该行为。然后,结合强化学习和在线专家提出了一种训练控制层的新方法RL_COE。最后,在Carla中搭建了高速公路仿真环境对本文算法进行验证,并与强化学习基线算法进行比较,结果表明:该方法大大提高了算法的收敛速度和稳定性,可以更好地完成驾驶任务。
中图分类号:
- U495
| [1] | 张羽翔. 基于知识与机理增强强化学习的智能车辆决策与控制[D]. 长春: 吉林大学汽车工程学院, 2022. |
| Zhang Yu-xiang. Domain knowledge and physical-enhanced reinforcement learning for intelligent vehicles decision-making and control[D]. Changchun: School of Transportation, Jilin University, 2022. | |
| [2] | Schwarting W, Alonso M J, Rus D. Planning and decision-making for autonomous vehicles[J]. Annual Review of Control, Robotics, and Autonomous Systems, 2018, 1: 187-210. |
| [3] | Paden B, Čáp M, Yong S Z, et al. A survey of motion planning and control techniques for self-driving urban vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2016, 1(1): 33-55. |
| [4] | 王景珂. 基于学习的自动驾驶行为决策研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学控制科学与工程学院, 2021. |
| Wang Jing-ke. Research on autonomous driving behavior decison-making based on learning[D]. Hangzhou: College of Control Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, 2021. | |
| [5] | Sutton R S, Barto A G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2018. |
| [6] | Kendall A, Hawke J, Janz D, et al. Learning to drive in a day[C]∥International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Montreal, Canada, 2019: 8248-8254. |
| [7] | Wurman P R, Barrett S, Kawamoto K, et al. Outracing champion gran turismo drivers with deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2022, 602: 223-228. |
| [8] | 李文礼, 邱凡珂, 廖达明, 等. 基于深度强化学习的高速公路换道跟踪控制模型[J]. 汽车安全与节能学报, 2022, 13(4): 750-759. |
| Li Wen-li, Qiu Fan-ke, Liao Da-ming, et al. Highway lane change decision control model based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy, 2022, 13(4): 750-759. | |
| [9] | Kiran B R, Sobh I, Talpaert V, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for autonomous driving: a survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 23(6): 4909-4926. |
| [10] | Zhu M, Wang Y, Pu Z, et al. Safe, efficient, and comfortable velocity control based on reinforcement learning for autonomous driving[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2020, 117: 102662. |
| [11] | Huang Z, Wu J, Lyu C. Efficient deep reinforcement learning with imitative expert priors for autonomous driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(10): 7391-7403. |
| [12] | Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 518: 529-533. |
| [13] | Haarnoja T, Zhou A, Abbeel P, et al. Soft actor-critic: off-policy maximum entropy deep reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor[C]∥International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 1861-1870. |
| [14] | Liang X, Wang T, Yang L, et al. Cirl: controllable imitative reinforcement learning for vision-based self-driving[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munichi, Germany, 2018: 584-599. |
| [15] | Hester T, Vecerik M, Pietquin O, et al. Deep q-learning from demonstrations[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 3223-3230. |
| [16] | Elallid B B, Benamar N, Hafid A S, et al. A comprehensive survey on the application of deep and reinforcement learning approaches in autonomous driving[J]. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, 2022, 34(9): 7366-7390. |
| [17] | Kulkarni T D, Narasimhan K, Saeedi A, et al. Hierarchical deep reinforcement learning: integrating temporal abstraction and intrinsic motivation[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2016, 29: 990-998. |
| [18] | Duan J, Eben L S, Guan Y, et al. Hierarchical reinforcement learning for self‐driving decision‐making without reliance on labelled driving data[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2020, 14(5): 297-305. |
| [19] | Dosovitskiy A, Ros G, Codevilla F, et al. CARLA: an open urban driving simulator[C]∥Conference on Robot Learning, Mountain View, USA, 2017: 1-16. |
| [1] | 卢荡,索艳茹,孙宇航,吴海东. 基于无量纲格式的轮胎侧倾侧偏力学特性预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1516-1524. |
| [2] | 高镇海,郑程元,赵睿. 真实与虚拟场景下自动驾驶车辆的主动安全性验证与确认综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1142-1162. |
| [3] | 张涛,林黄达,余中军. 混合动力车辆换挡的实时滚动优化控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1215-1224. |
| [4] | 卢荡,王晓凡,吴海东. TWEEL轮胎接地压力均布特性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 811-819. |
| [5] | 曲俊龙,史文库,玄圣夷,陈志勇. 面向汽车传动系统多挡共振的多级吸振器参数设计方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 444-455. |
| [6] | 朱冰,范天昕,赵文博,李伟男,张培兴. 自动驾驶汽车连续测试场景复杂度评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 456-467. |
| [7] | 陈发城,鲁光泉,林庆峰,张浩东,马社强,刘德志,宋会军. 有条件自动驾驶下驾驶人接管行为综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 419-433. |
| [8] | 陈鑫,张祥源,武子涛,于贵申,杨立飞. 工艺顺序对车用铝薄板胶-PFSSW接头拉剪性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 468-475. |
| [9] | 王军年,曹宇靖,罗智仁,李凯旋,赵文伯,孟盈邑. 基于双目视觉的道路水深在线检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 175-184. |
| [10] | 谭草,任浩鑫,葛文庆,宋亚东,陆佳瑜. 直驱阀控液压振动平台改进自抗扰控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 84-92. |
| [11] | 胡宏宇,张争光,曲优,蔡沐雨,高菲,高镇海. 基于双分支和可变形卷积网络的驾驶员行为识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 93-104. |
| [12] | 王长帅,徐铖铖,任卫林,彭畅,佟昊. 自动驾驶接管过程中驾驶能力恢复状态对交通流振荡特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 150-161. |
| [13] | 李寿涛,杨路,屈如意,孙鹏鹏,于丁力. 基于模型预测控制的滑移率控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2687-2696. |
| [14] | 吴量,顾义凡,邢彪,马芳武,倪利伟,贾微微. 基于线性二次型调节器的四轮转向与分布式集成控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2414-2422. |
| [15] | 王玉海,李晓之,李兴坤. 面向高速工况的混合动力卡车预见性节能算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2121-2129. |
|