吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 1296-1305.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200387
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
大跨桥梁主梁失效概率分析的最优R-Vine Copula
- 1.兰州大学 西部灾害与环境力学教育部重点实验室,兰州 730030
2.兰州大学 土木工程与力学学院,兰州 730030
3.华南理工大学 土木与交通学院,广州 510641
Optimal R-vine copula information fusion for failure probability analysis of long-span bridge girder
Xue-ping FAN1,2( ),Guang-hong YANG2,Qing-kai XIAO3,Yue-fei LIU1,2
),Guang-hong YANG2,Qing-kai XIAO3,Yue-fei LIU1,2
- 1.Key Laboratory of Mechanics on Disaster and Environment in Western China of the Ministry of Education,Lanzhou University,Lanzhou 730030,China
2.School of Civil Engineering and Mechanics,Lanzhou University,Lanzhou 730030,China
3.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China university of Technology,Guangzhou 510641,China
摘要:
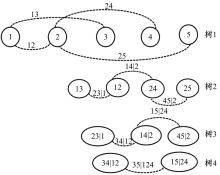
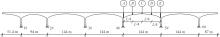
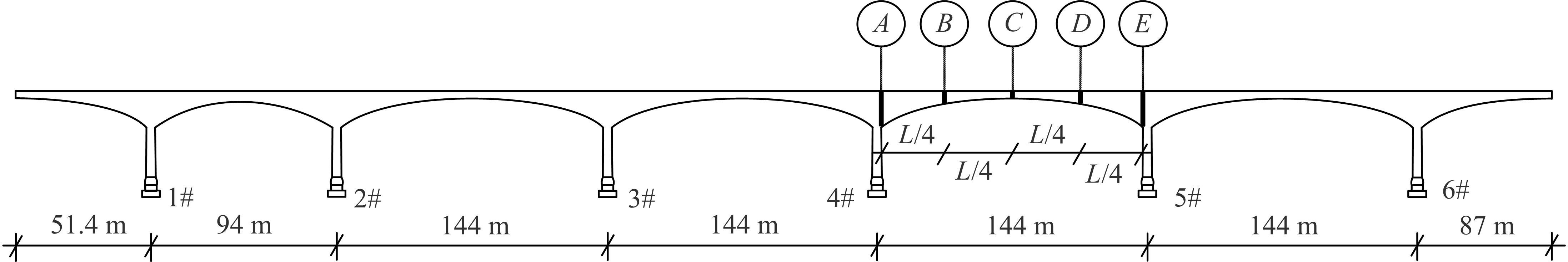
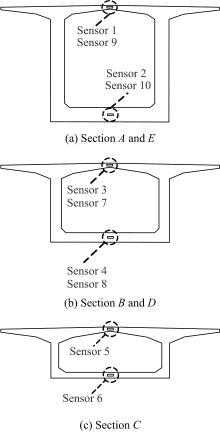
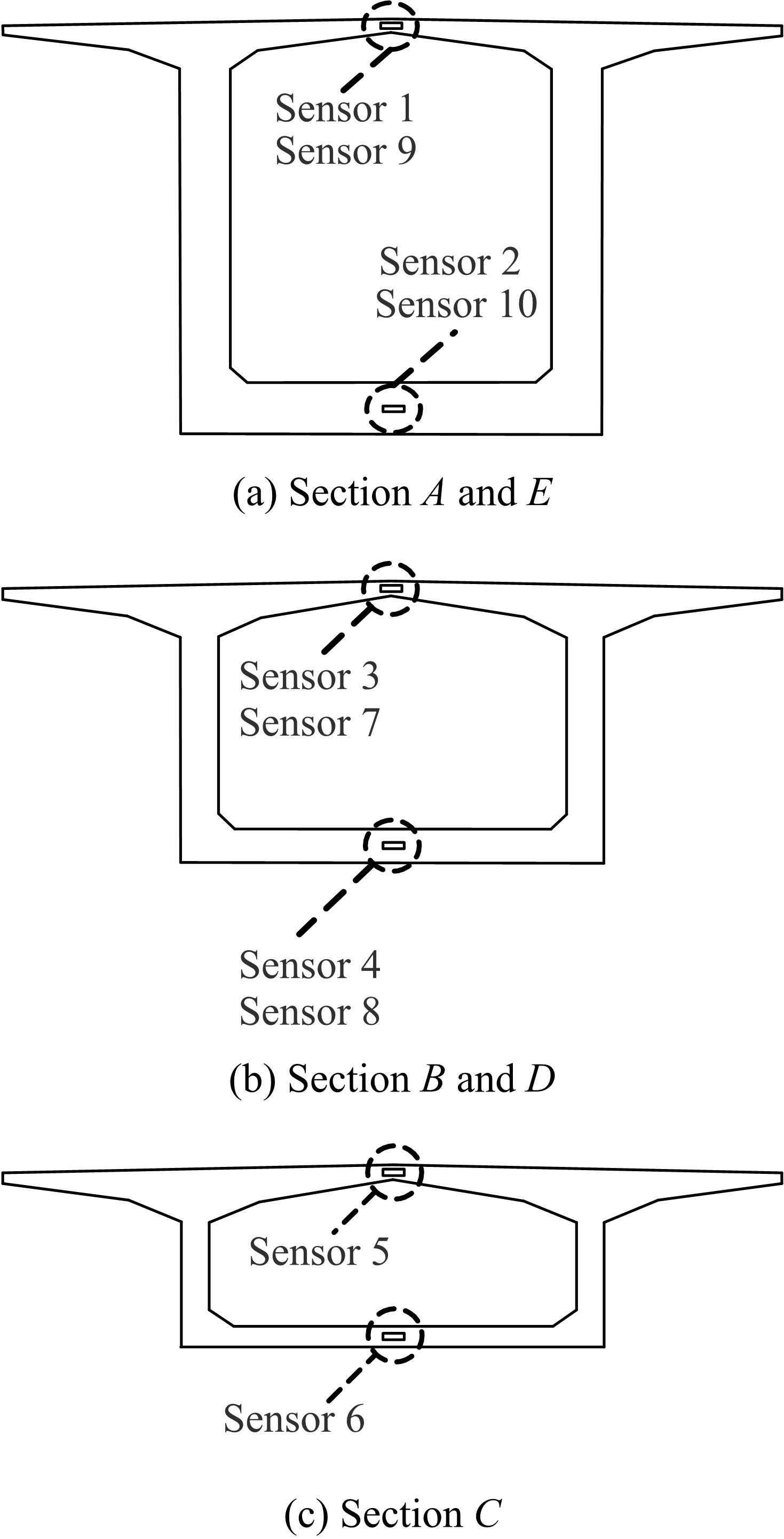
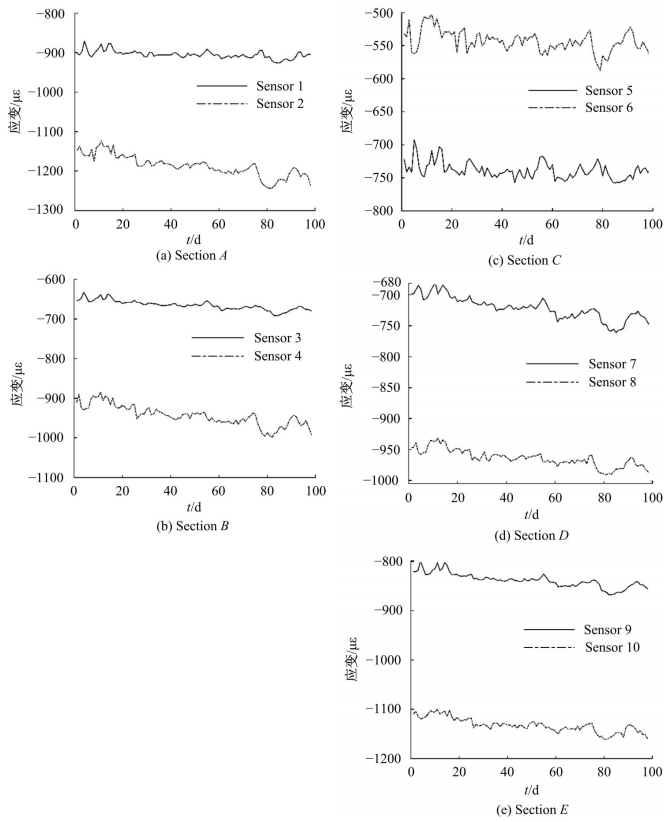
为合理分析大跨桥梁主梁的失效概率,考虑到多个控制监测点失效模式的相关性,提出了大跨桥梁主梁失效概率分析的信息融合新方法。利用极值应变信息,引入双变量Pair-Copula模型和R-Vine模型,结合多个控制监测点的功能函数,对监测点失效模式相关性进行最优Regular vine copula(R-Vine Copula)建模分析,融合一次二阶矩(FOSM)方法,进行失效模式相关的大跨桥梁主梁失效概率分析,通过在役桥梁监测数据对本文方法的合理性进行验证,并与其他分析方法进行比较。结果表明,考虑控制监测点失效模式相关性的大跨桥梁主梁失效概率分析的最优R-Vine Copula信息融合方法较为合理。
中图分类号:
- TU391
| 1 | 刘月飞, 樊学平. 失效非线性相关的桥梁截面可靠性Vine-Copula数据融合[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2019. 47(3): 315-321. |
| Liu Yue-fei, Fan Xue-ping. Data fusion about Vine-Copula for bridge section reliability considering nonlinear correlation of failure modes[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2019, 47(3): 315-321. | |
| 2 | Fan X P, Liu Y F. Time-variant reliability prediction of bridge system based on BDGCM and SHM data[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2018, 25(7): 1-16. |
| 3 | Liu Y F, Fan X P. Gaussian Copula-Bayesian dynamic linear model-based time-dependent reliability prediction of bridge structures considering nonlinear correlation between failure modes[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 8(11): 1-15. |
| 4 | 刘月飞. 考虑失效模式和验证模式相关性的桥梁结构体系可靠度分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学航天学院, 2015. |
| Liu Yue-fei. System reliability analysis of bridge structures considering correlation of failure modes and proof modes[D]. Harbin: Aerospace Academy,Harbin Institute of Technology, 2015. | |
| 5 | Liu Y F, Fan X P. Dynamic reliability prediction for the steel box girder based on multivariate Bayesian dynamic gaussian copula model and SHM extreme stress data[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2020,27(6): 1-17. |
| 6 | 樊学平, 杨光红, 肖青凯, 等. 考虑安全性的桥梁主梁体系可靠性动态藤Copula预测方法[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 48(2): 165-175. |
| Fan Xue-ping, Yang Guang-hong, Xiao Qing-kai, et al. Dynamic Vine-Copula prediction approach of bridge girder system reliability considering structural safety[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2020, 48(2): 165-175. | |
| 7 | Liu H B, Wang X R, Tan G J, et al. System reliability evaluation of a bridge structure based on multivariate copulas and the AHP-EW method that considers multiple failure criteria[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(4): 1-19. |
| 8 | Bedford T, Cooke R M. Probability density decomposition for conditionally dependent random variables modeled by vines[J]. Annals of Mathematics & Artificial Intelligence, 2001, 32(1-4): 245-268. |
| 9 | Bedford T, Cooke R M. Vines: a new graphical model for dependent random variables[J]. Annals of Statistics, 2002, 30(4): 1031-1068. |
| 10 | Nápoles O M, Cooke R M, Kurowicka D. About the number of vines and regular vines on n nodes [R/OL]. [2010-12-01]. . |
| 11 | Dissmann J, Brechmann E C, Czado C, et al. Selecting and estimating regular vine copulae and application to financial returns[J]. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 2013, 59(1): 52-69. |
| 12 | Pearson K. Mathematical contributions to the theory of evolution. III. regression, heredity, and panmixia[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London A, 1895, 186(4): 253-318. |
| 13 | Melchers R E, Beck A T. Structural Reliability Analysis and Prediction[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2018. |
| 14 | Ang A H S, Tang W H. Probability Concepts in Engineering Planning and Design (Vol. II) [M]. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1984. |
| 15 | 李英华. 基于长期健康监测的连续刚构梁桥的性能分析与演化规律研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学土木与交通学院, 2012. |
| Li Ying-hua. Performance analysis and evolution of continuous rigid frame bridge based on long-term health monitoring[D]. Guangzhou: School of Civil Engineering and Transportation, South China University of Technology, 2012. | |
| 16 | 王震. 基于桥梁长期健康监测的数据特征分析与可靠度计算[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学机械与汽车工程学院, 2014. |
| Wang Zhen. Characteristics analysis and reliability calculation based on long-term bridge health monitoring data[D]. Guangzhou: School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, South China University of Technology, 2014. |
| [1] | 于江,赵志浩,秦拥军. 基于声发射和分形的钢筋混凝土受剪梁损伤[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 620-630. |
| [2] | 熊二刚,徐涵,谭赐,王婧,丁若愚. 基于弹塑性应力场理论的钢筋混凝土梁受剪承载力[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 259-267. |
| [3] | 樊学平,屈广,刘月飞. 应用新数据同化算法的桥梁极值应力预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 572-580. |
| [4] | 杨德磊,童乐为. 支管受轴向受拉工况下CHS-CFSHS T型节点应力集中系数计算公式[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1891-1899. |
| [5] | 白伦华,沈锐利,张兴标,王路. 自锚式悬索桥的面内稳定性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1500-1508. |
| [6] | 戴岩, 聂少锋, 周天华. 带环梁的方钢管约束钢骨混凝土柱-钢梁节点滞回性能有限元分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1426-1435. |
| [7] | 刘杰, 张平, 高万夫. 基于条件相关的特征选择方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 874-881. |
| [8] | 冯建鑫. 具有测量时滞的不确定系统的递推鲁棒滤波[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1561-1567. |
| [9] | 杨昕卉, 薛伟, 郭楠. 钢板增强胶合木梁的抗弯性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 468-477. |
| [10] | 孟广伟, 冯昕宇, 周立明, 李锋. 基于降维算法的结构可靠性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 174-179. |
| [11] | 陈鑫, 胡翠松, 宁厚于, 吴元强, 汪硕, 杨昌海. SUV白车身隐式参数化建模及多性能优化轻量化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1780-1785. |
| [12] | 王少杰, 徐赵东, 李舒, 王凯洋,Dyke Shirley J. 基于应变监测的连续梁支承差异沉降识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1090-1096. |
| [13] | 朱义君, 付红双, 蔡文炳. 可见光通信中低复杂度自适应广义空间调制算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 2080-2084. |
| [14] | 张艳, 梁栋, 鲍文霞, 朱明, 孙怡宁. 基于相关性度量的触觉步态特征优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1608-1614. |
| [15] | 敬明, 王昊, 王文静. 基于跟驰数据采集分析的各异性跟驰模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 761-768. |
|
||