吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 2007-2012.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200627
• 材料科学与工程 • 上一篇
烧结淬冷MnBi合金的相变和磁性
- 吉林师范大学 功能材料物理与化学教育部重点实验室,吉林 四平 136000
Phase transformation and magnetic properties of MnBi alloys by sintered and quenched
Yuan-long E( ),Hong-sheng JIA(
),Hong-sheng JIA( ),Xin-xuan YANG,Dong-fei LI,Mei LIU,Hai-bo LI
),Xin-xuan YANG,Dong-fei LI,Mei LIU,Hai-bo LI
- Key Laboratory of Functional Materials Physics and Chemistry,Ministry of Education,Jilin Normal University,Siping 136000,China
摘要:
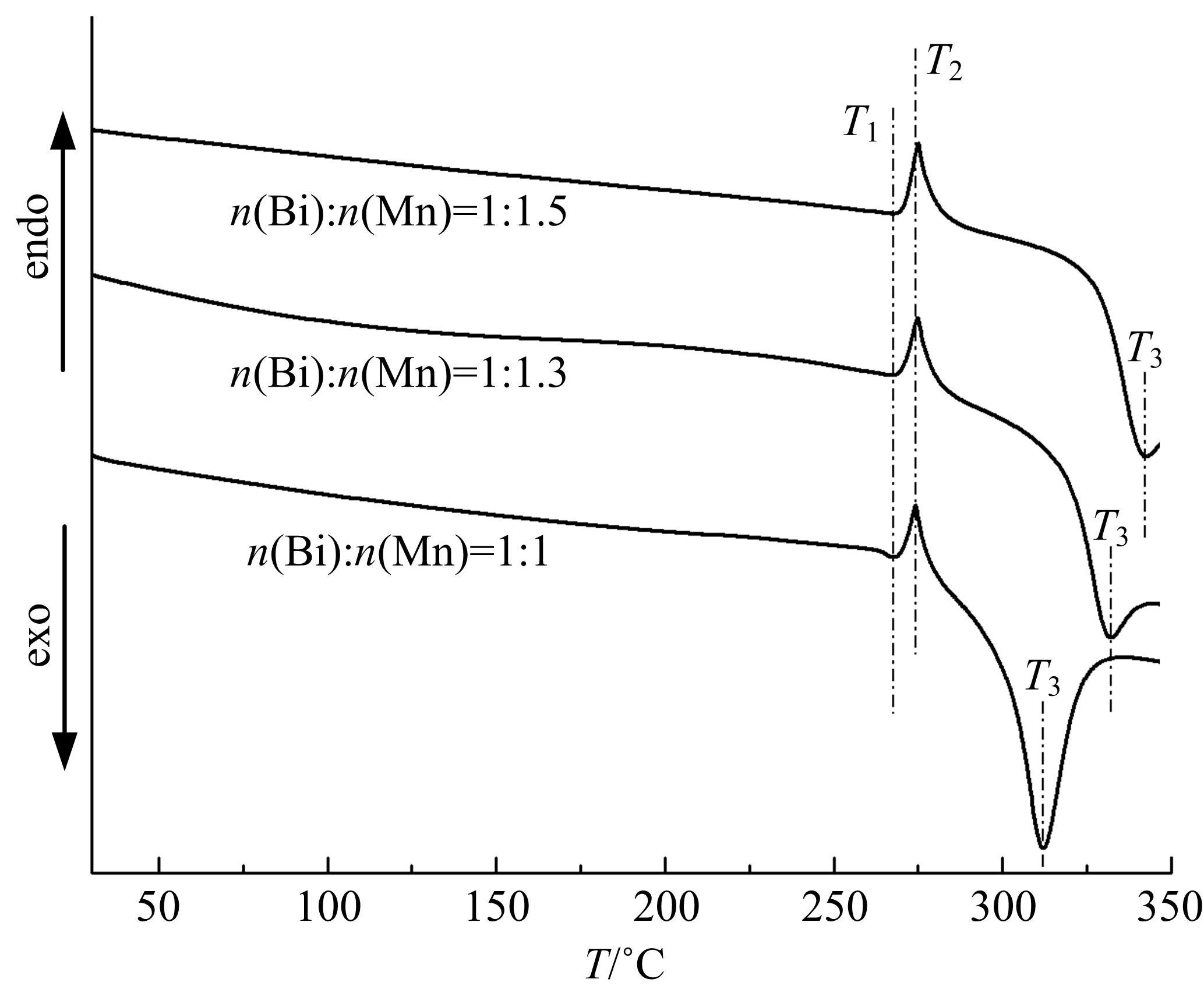
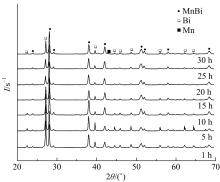
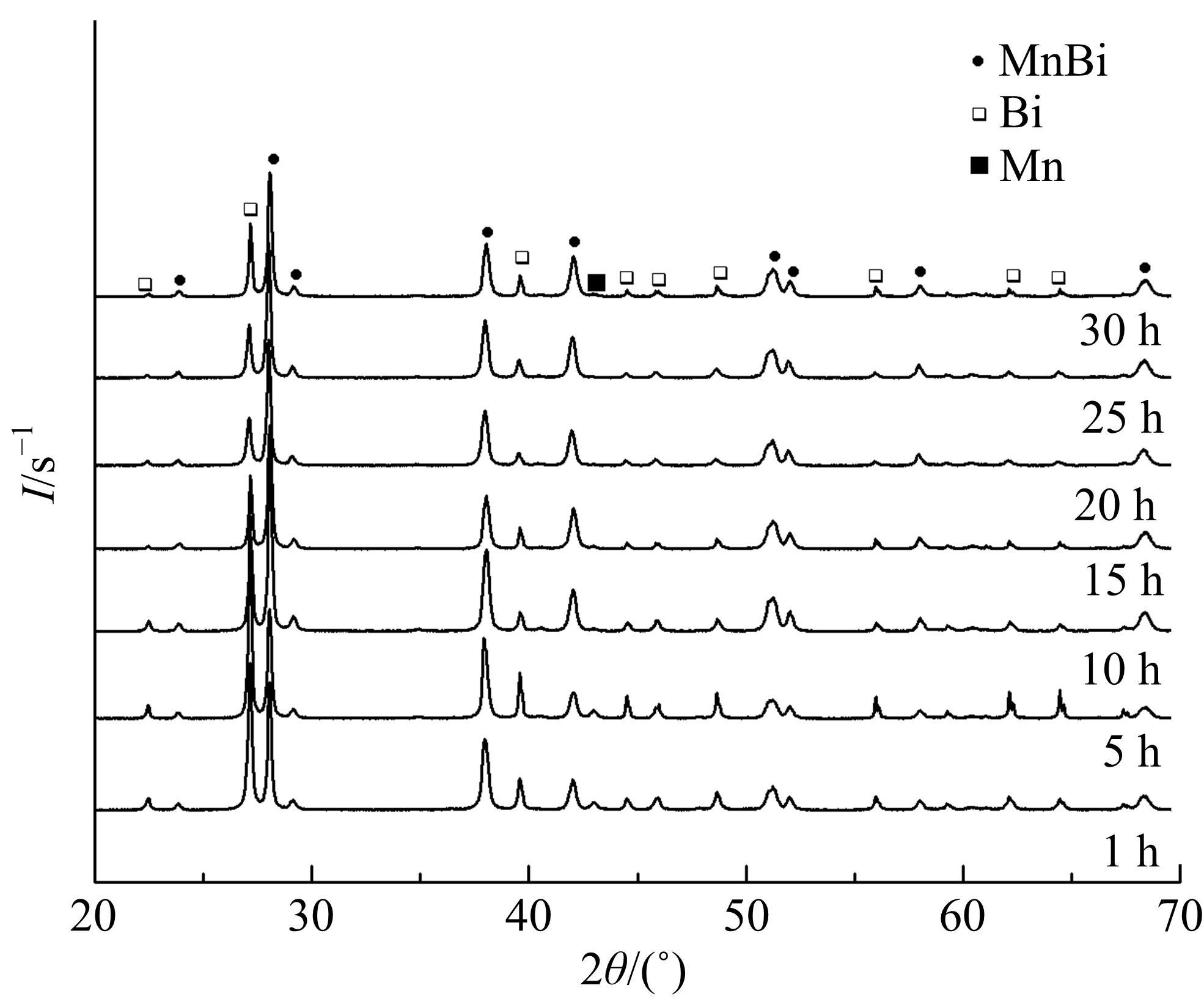
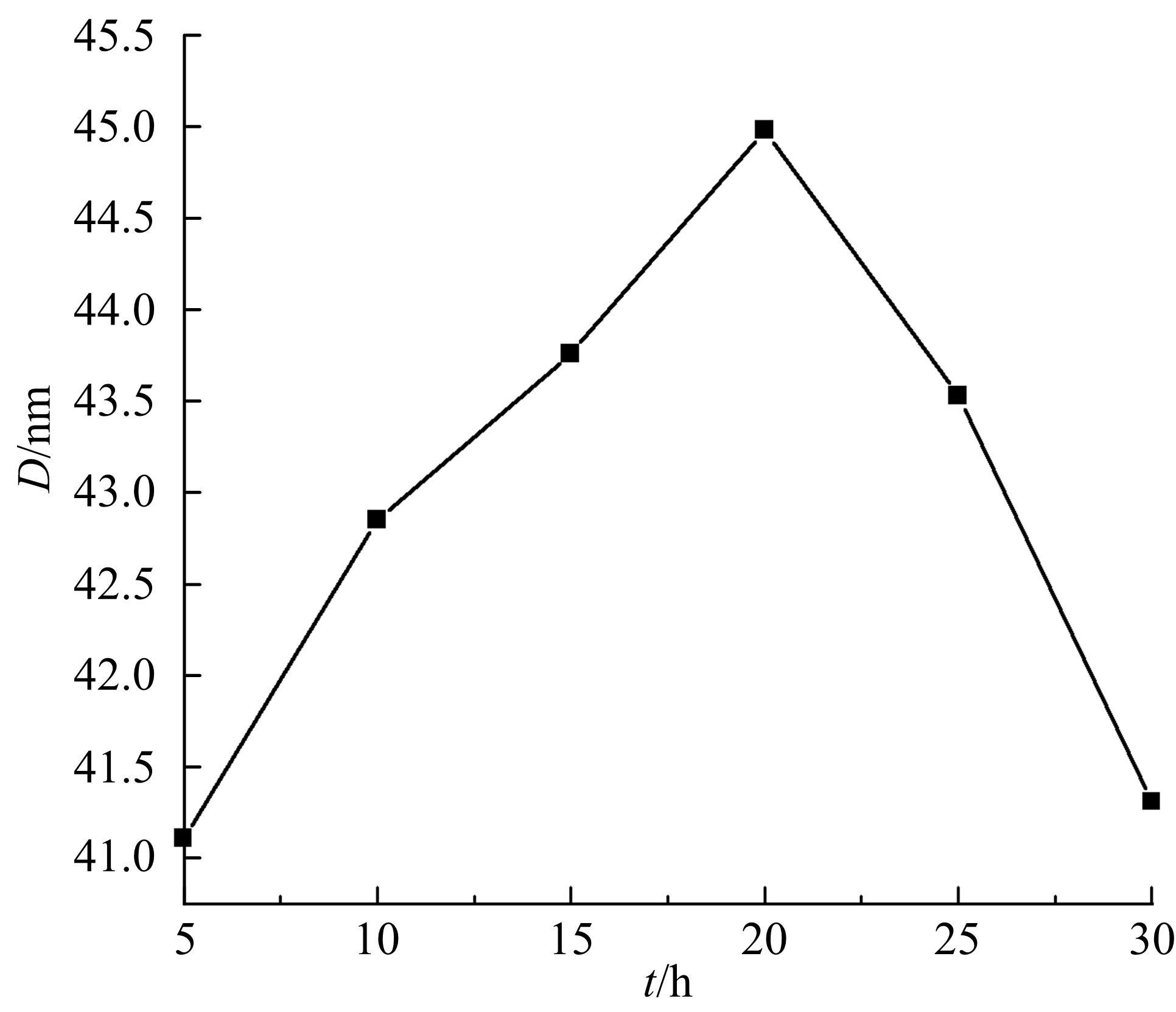
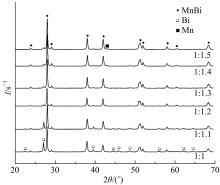
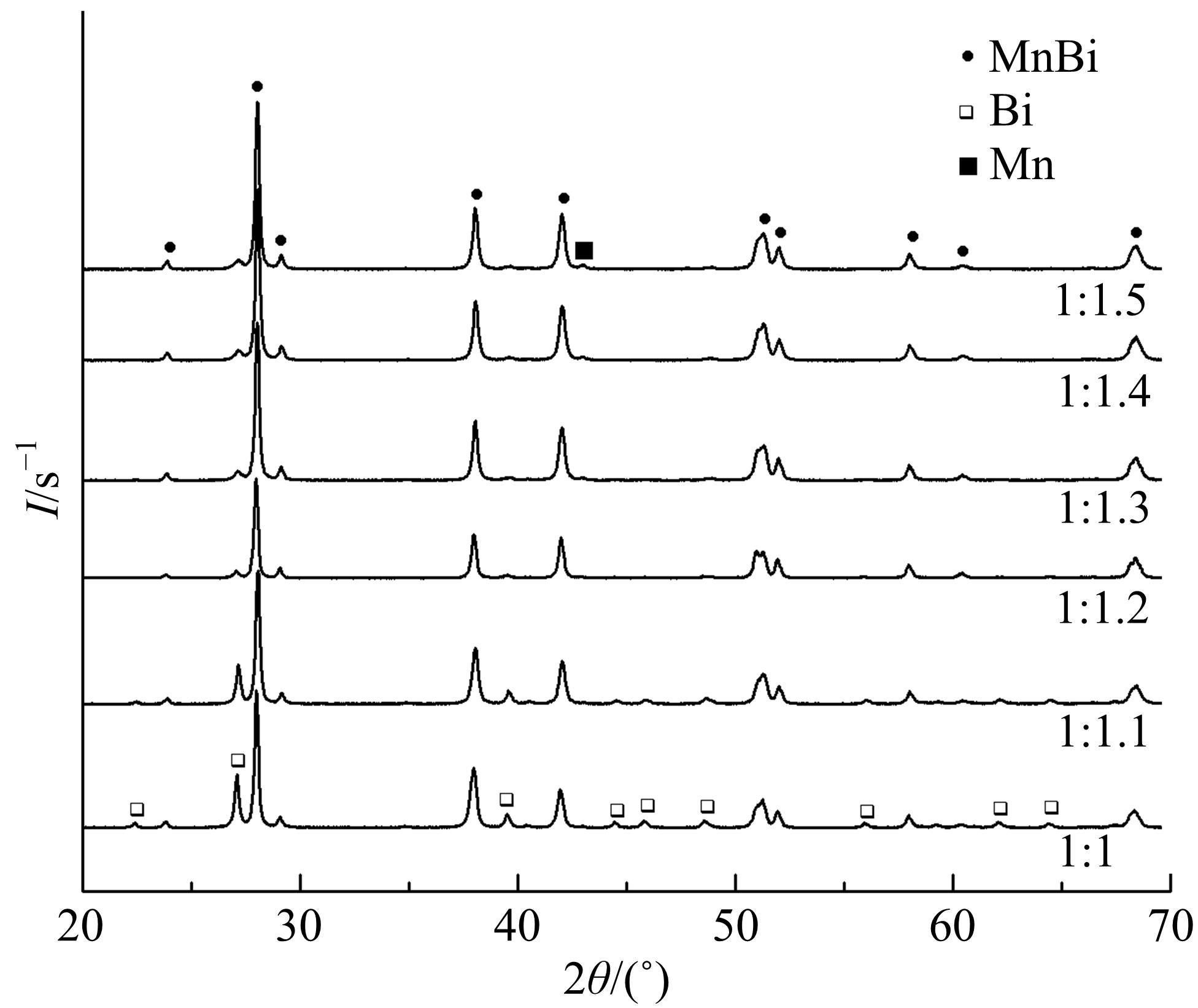
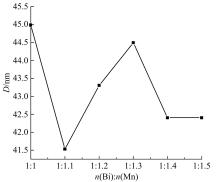
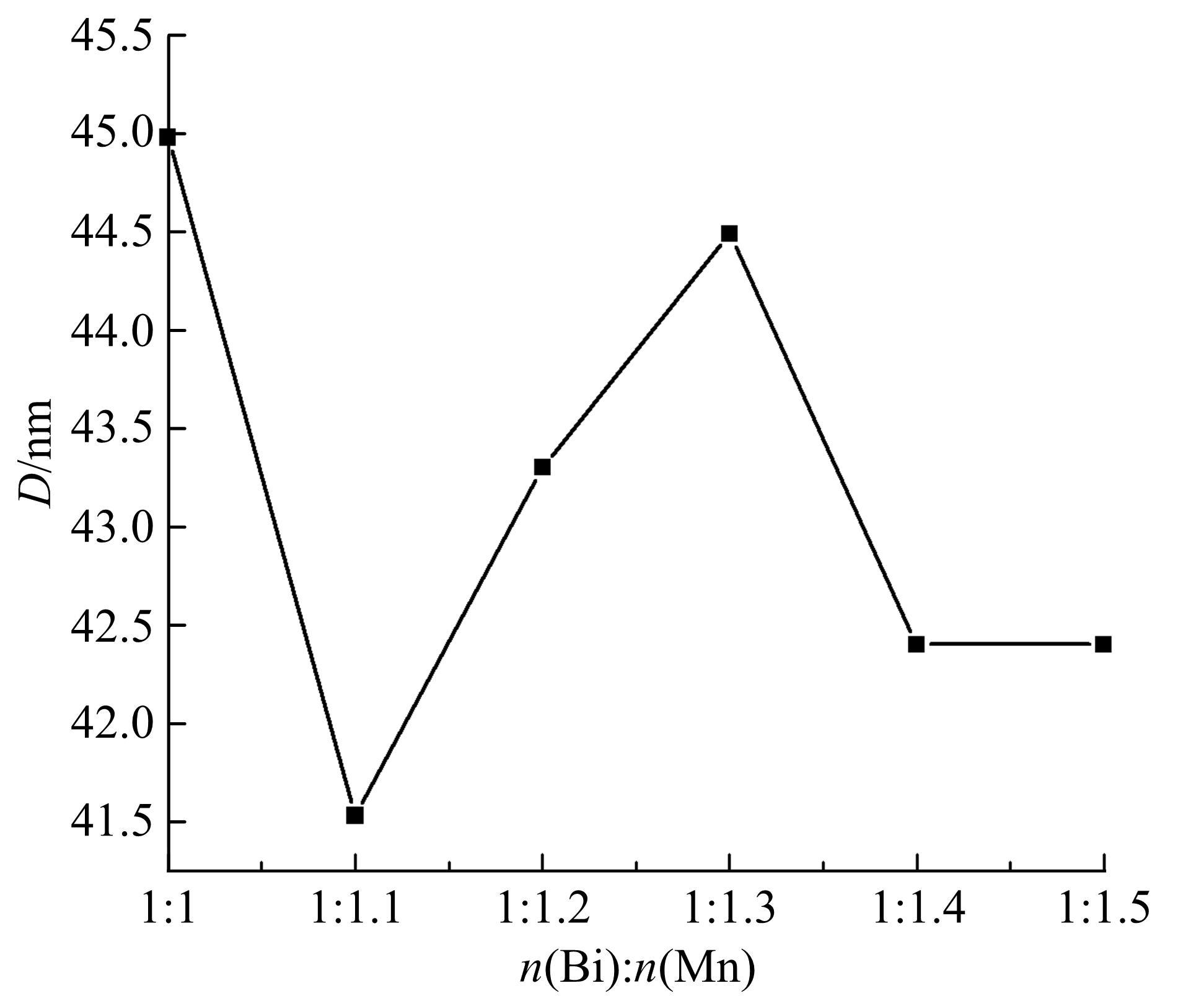
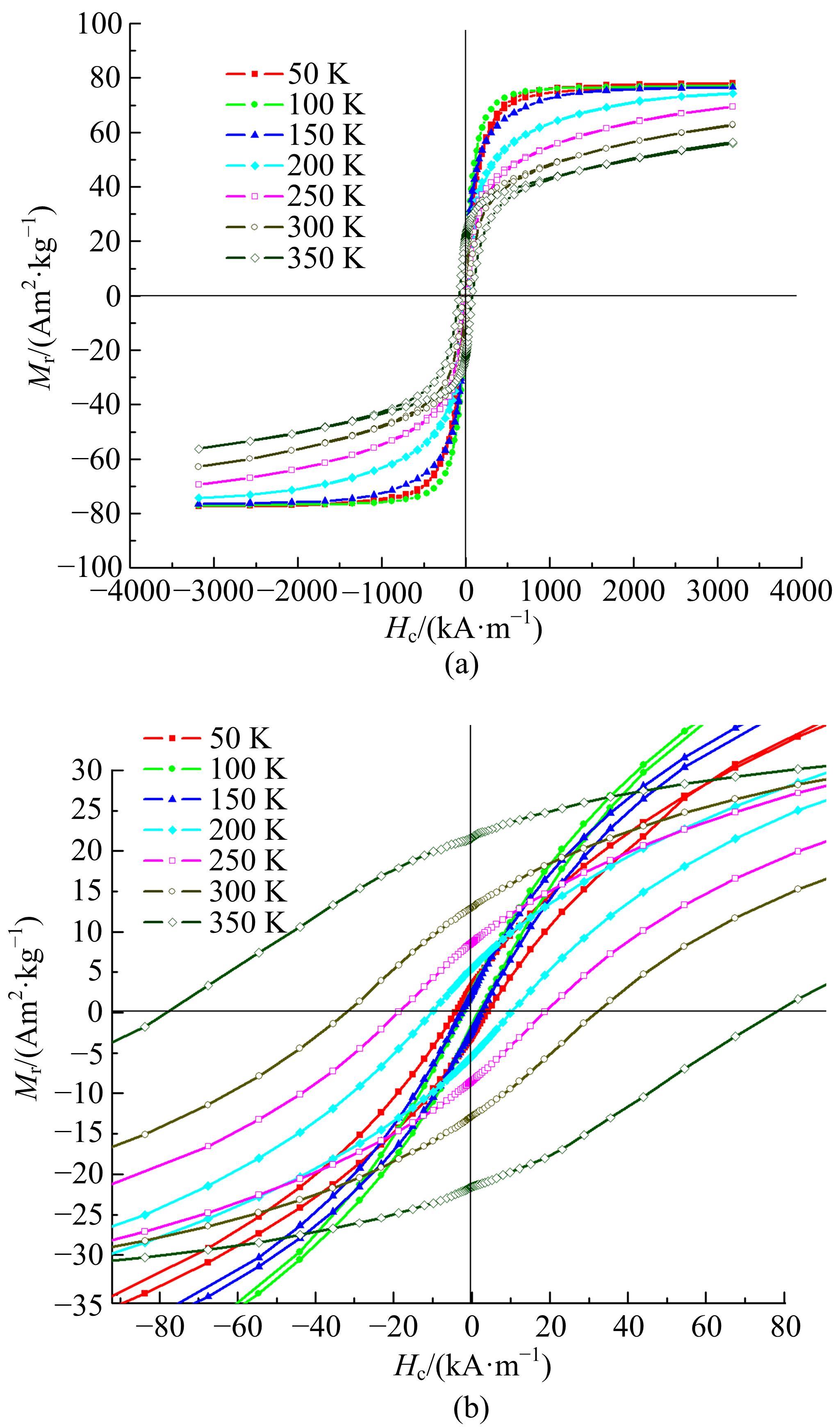
采用密封低温烧结再淬冷的方法制备了高纯度MnBi合金。利用差热分析仪(DTA)分析烧结过程中Mn-Bi的相变。利用X射线衍射仪(XRD)和振动样品磁强计(VSM)分析了烧结样品的物相和磁性。结果表明:n(Bi)∶n(Mn)为1∶1.3,275 ℃下烧结20 h后淬冷可获得高纯度的低温相MnBi合金块体材料;温度为50~350 K时,磁化强度随温度的升高而减小,矫顽力Hc和剩余磁化强度Mr先减小后增大;温度低于200 K时,随着温度的降低,样品趋近饱和;温度为50 K时,样品的饱和磁化强度为78.0 Am2/kg。本文制备工艺简单且可实现该合金的批量生产,对制备新型合金材料具有重要的参考价值。
中图分类号:
- TM273
| 1 | 李海波,张玉梅,刘梅,等. FePt/Ag薄膜的结构和磁性[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2010, 40(6):1572-1576. |
| Li Hai-bo, Zhang Yu-mei, Liu Mei, et al. Structure and magnetic properties of FePt/Ag thin film[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2010, 40(6):1572-1576. | |
| 2 | Nguyen T X, Vuong O K T, Nguyen H T, et al. Preparation and magnetic properties of MnBi/Co nanocomposite magnets[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2017, 46(6):3359-3366. |
| 3 | Ito M, Tanaka Y, Satoh T, et al. Magnetic properties and structure of low temperature phase MnBi with island structure[J]. AIP Advances, 2017, 7(5):No.056226. |
| 4 | Kim S, Moon H, Jung H, et al. Magnetic properties of large-scaled MnBi bulk magnets[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 708:1245-1249. |
| 5 | Cao S, Yue M, Yang Y X, et al. Magnetic properties and thermal stability of MnBi/NdFeB hybrid bonded magnets[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 109(7): No.07A740. |
| 6 | Jensen B A, Tang W, Liu X B, et al. Optimizing composition in MnBi permanent magnet alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2019, 181:595-602. |
| 7 | Huang Y L, Shi Z Q, Hou Y H, et al. Microstructure, improved magnetic properties, and recoil loops characteristics for MnBi alloys[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2019, 485:157-164. |
| 8 | Nguyen T X, Nguyen V V. Fabrication of MnBi alloys with high ferromagnetic phase content: effects of heat treatment regimes and dopants[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2019, 30: 6888-6894. |
| 9 | Cao J, Huang Y L, Hou Y H, et al. Microstructure and magnetic properties of MnBi alloys with high coercivity and significant anisotropy prepared by surfactant assisted ball milling[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2019, 473: 505-510. |
| 10 | Xiang Z, Wang T L, Ma S J, et al. Microstructural evolution and phase transformation kinetics of MnBi alloys[J], Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 741: 951-956. |
| 11 | 曹俊,黄有林,闫小童,等. MnBi合金的磁性能与回复曲线研究[J]. 功能材料,2018,49(6):6119-6123. |
| Cao Jun, Huang You-lin, Yan Xiao-tong, et al. Magnetic performance and recoil loops characteristics of MnBi alloy[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2018, 49(6): 6119-6123. | |
| 12 | 刘泽民,张素银,邵诚,等. 无稀土MnBi永磁合金的研究进展[J]. 科技咨询,2016,14(34):80-84. |
| Liu Ze-min, Zhang Su-yin, Shao Cheng, et al. The research progress of rare-earth free permanent magnetic alloy in MnBi[J]. Science & Technology Information, 2016,14(34): 80-84. | |
| 13 | 张素银,刘泽民,邵成,等. 稀土元素Gd对MnBi合金的微结构与磁性能的影响[J]. 功能材料,2017,48(1):1221-1224, 1229. |
| Zhang Su-yin, Liu Ze-min, Shao Cheng, et al. Effect of rare earth elements Gd doping on microstructure and magnetic properties of MnBi alloy[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2017, 48(1): 1221-1224, 1229. | |
| 14 | Kang K, Moodenbaugh A R, Lewis L H. MnBi nanostructures: size dependence of magnetostructural transition and matrix templating[J].Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 90(15):No.153112. |
| 15 | Yang J B, Kamarju K, Yelon W B, et al. Magnetic properties of the MnBi intermetallic compound[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2001, 79(12): 1846-1848. |
| 16 | Yang J B, Yang Y B, Chen X G, et al. Anisotropic nanocrystalline MnBi with high coercivity at high temperature[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 99(8):No.082505. |
| 17 | 黄潇,李传健,李卫. 粉末混合烧结法制备MnBi永磁合金的研究[J]. 金属功能材料,2006,13(2):14-16. |
| Huang Xiao, Li Chuan-jian, Li Wei. Preparation of MnBi permanent alloy using powder technique[J]. Metallic Functional Materials, 2016, 13(2): 14-16. | |
| 18 | 蒋欢畅,张朋越,葛洪亮,等. 熔淬法制备MnxBi100-x永磁合金的成相过程和磁性能[J]. 磁性材料及器件,2014,45(2):6-8. |
| Jiang Huan-chang, Zhang Peng-yue, Ge Hong-liang, et al. Phase formation behavior and magnetic properties of MnxBi100-x permanent magnetic alloys prepared by melt-spinning[J]. Journal of Magnetic Materials and Devices, 2014, 45(2): 6-8. | |
| 19 | 钟文定,杨正. 锰铋合金在不同热处理后的磁性研究[J]. 物理学报,1962,18(4):188-193. |
| Zhong Wen-ding, Yang Zheng. Magnetic properties of MnBi alloys after different heat treatments[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 1962, 18(4):188-193. |
| [1] | 陈奕颖,金敬福,丛茜,陈廷坤,任露泉. 不同冰点介质对冰黏附强度的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1926-1932. |
| [2] | 杨帆,张旭东,赵蒙,折波,邓俊楷. 基于有限元计算的形状记忆合金⁃金属玻璃复合材料变形行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 172-180. |
| [3] | 段春争,张方圆,寇文能,魏斌. 高速硬切削表面白层马氏体相变[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1575-1583. |
| [4] | 姚海洋, 王海燕, 张之琛, 申晓红. 双Duffing振子逆向联合信号检测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1282-1290. |
| [5] | 孙正, 黄钰期, 俞小莉. 径向滑动轴承润滑油膜流动-传热过程仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 744-751. |
| [6] | 张仰鹏, 魏海斌, 贾江坤, 陈昭. 季冻区组合冷阻层应用表现的数值评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 121-126. |
| [7] | 万成彪, 潘孟春, 张琦, 庞鸿锋, 朱学军. 基于张量特征值和特征向量的磁性目标定位[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 655-660. |
| [8] | 杨悦, 李雪, 徐晓丹. Ti-B-C-N粉末烧结的微观组织及其性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 552-556. |
| [9] | 金敬福, 韩丽曼, 曹敏, 李杨, 齐迎春, 丛茜. 水滴结冰相变体积膨胀规律[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1546-1551. |
| [10] | 张家陶, 赵宇光, 谭娟. 初始组织对电脉冲处理逆变奥氏体晶粒细化效果的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 193-198. |
| [11] | 庄蔚敏, 解东旋, 余天明, 于皖东. 基于损伤-相变本构模型的高强钢热成形数值模拟分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1206-1212. |
| [12] | 马云海, 尚文博, 范雪莹, 高知辉, 佟金, 闫志峰, 常志勇. 仿骨β相磷酸三钙多孔生物陶瓷制备及降解[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1367-1374. |
| [13] | 曹敏, 陈廷坤, 丛茜, 金敬福. 表面形态对结冰附着强度的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(05): 1314-1319. |
| [14] | 朱丽娟, 谷诤巍, 吕义, 徐虹. 超高强钢热冲压硬化机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(02): 376-379. |
| [15] | 万云霞, 程德福, 卢浩, 王言章. 混场源电磁探测仪器发射天线设计[J]. , 2012, (06): 1432-1436. |
|
||