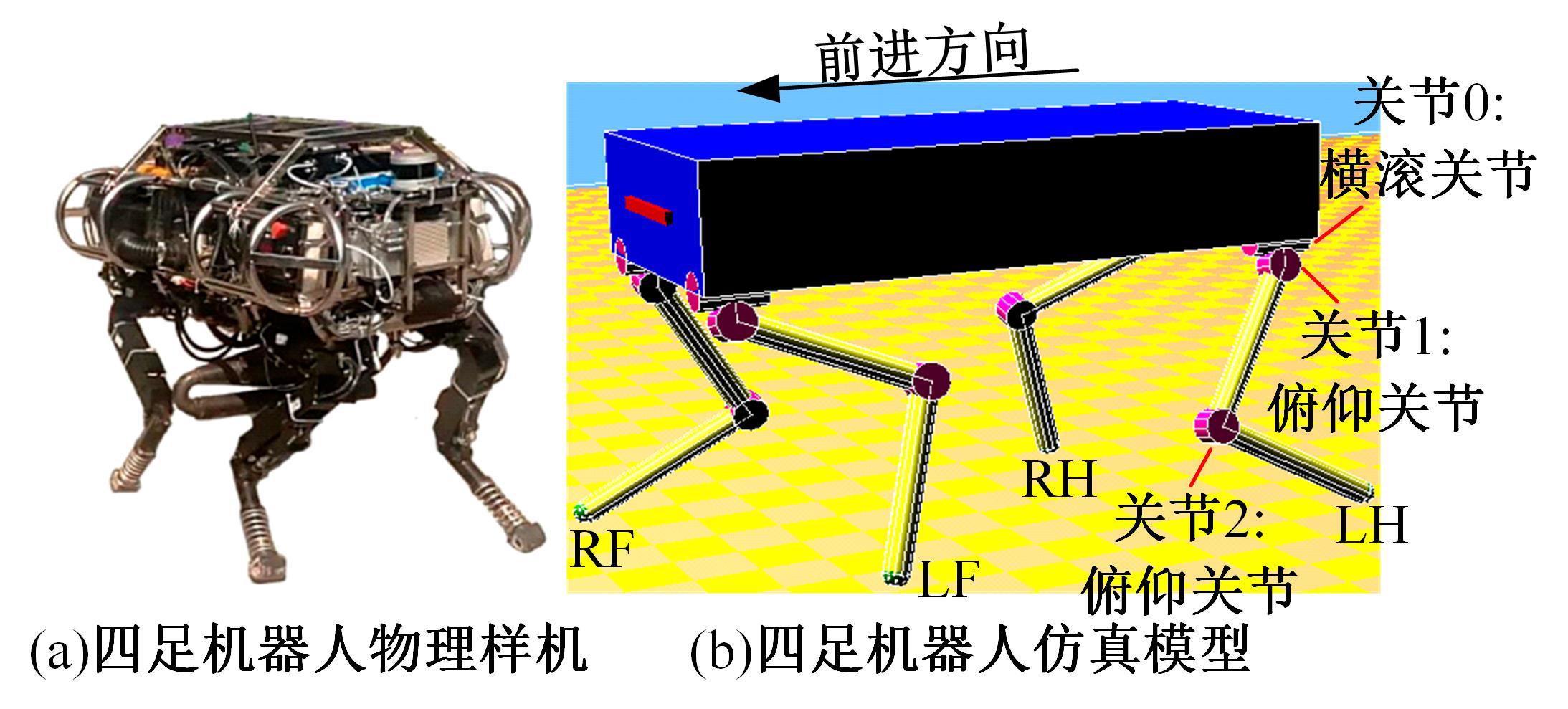
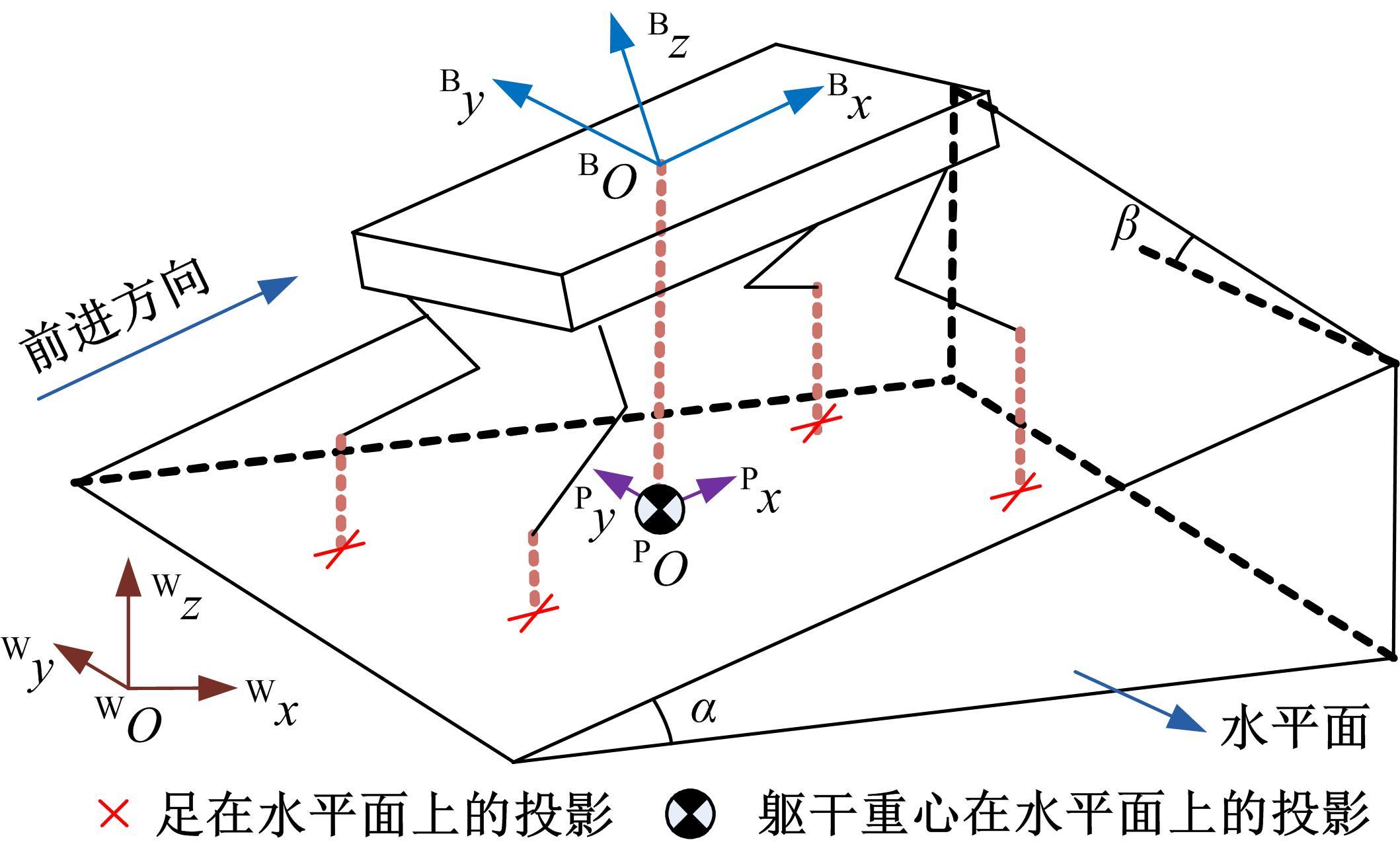
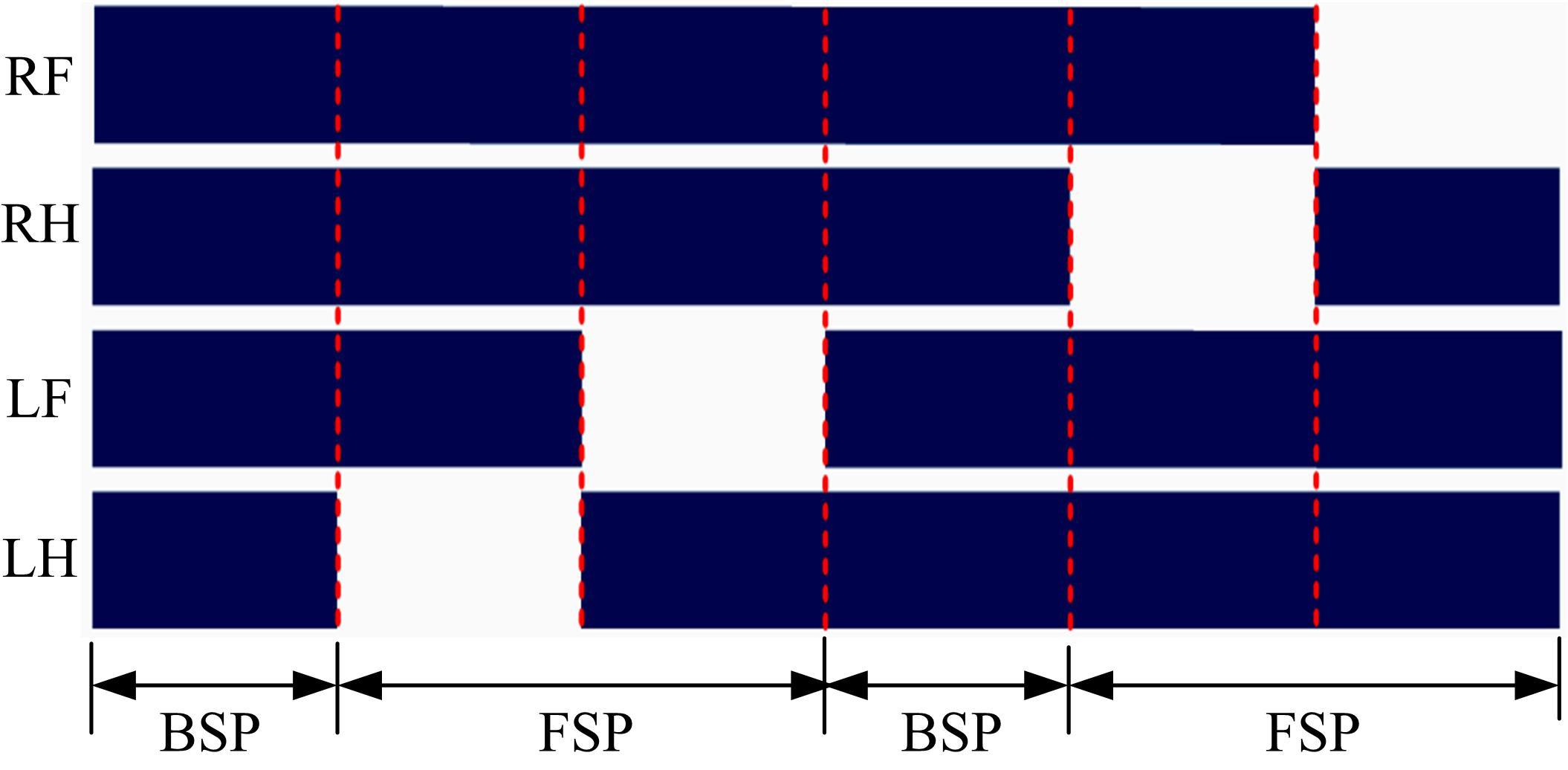
吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 902-912.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20221200
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
基于门控循环神经网络的四足机器人静步态规划方法
- 山东科技大学 电气信息系,济南 250031
Static gait planning method for quadruped robot based on gate recurrent neural network
Shuai-shuai ZHANG( ),Yan-fang YIN,Lin-jing XIAO,Shuai JIANG(
),Yan-fang YIN,Lin-jing XIAO,Shuai JIANG( )
)
- Department of Electrical and Information,Shandong University of Science and Technology,Jinan 250031,China
摘要:
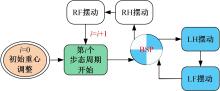
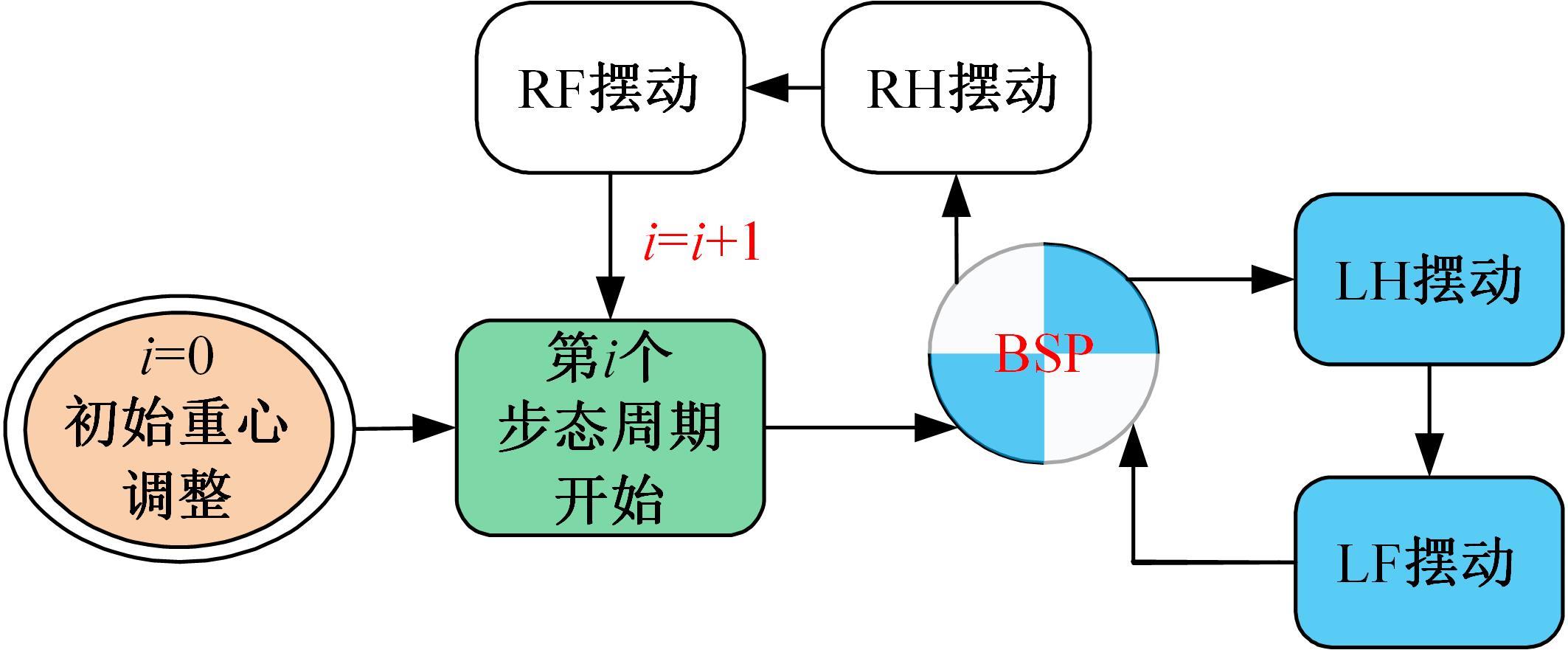
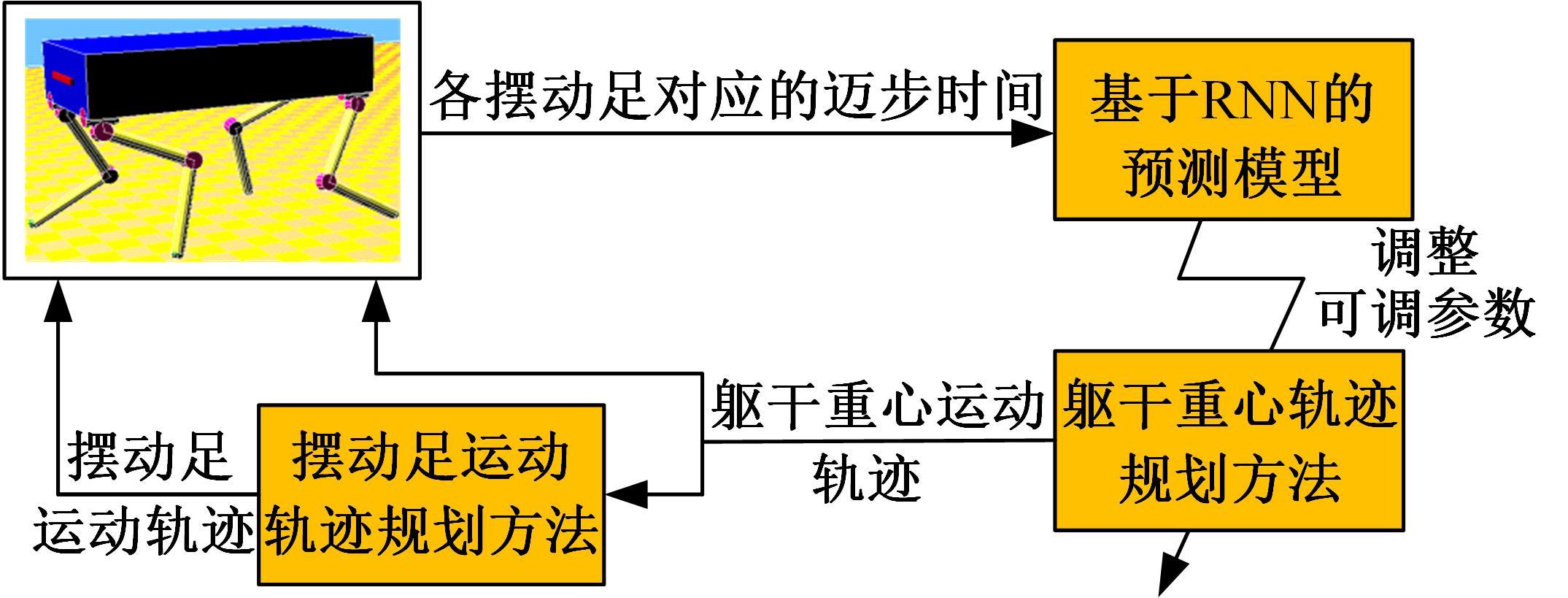
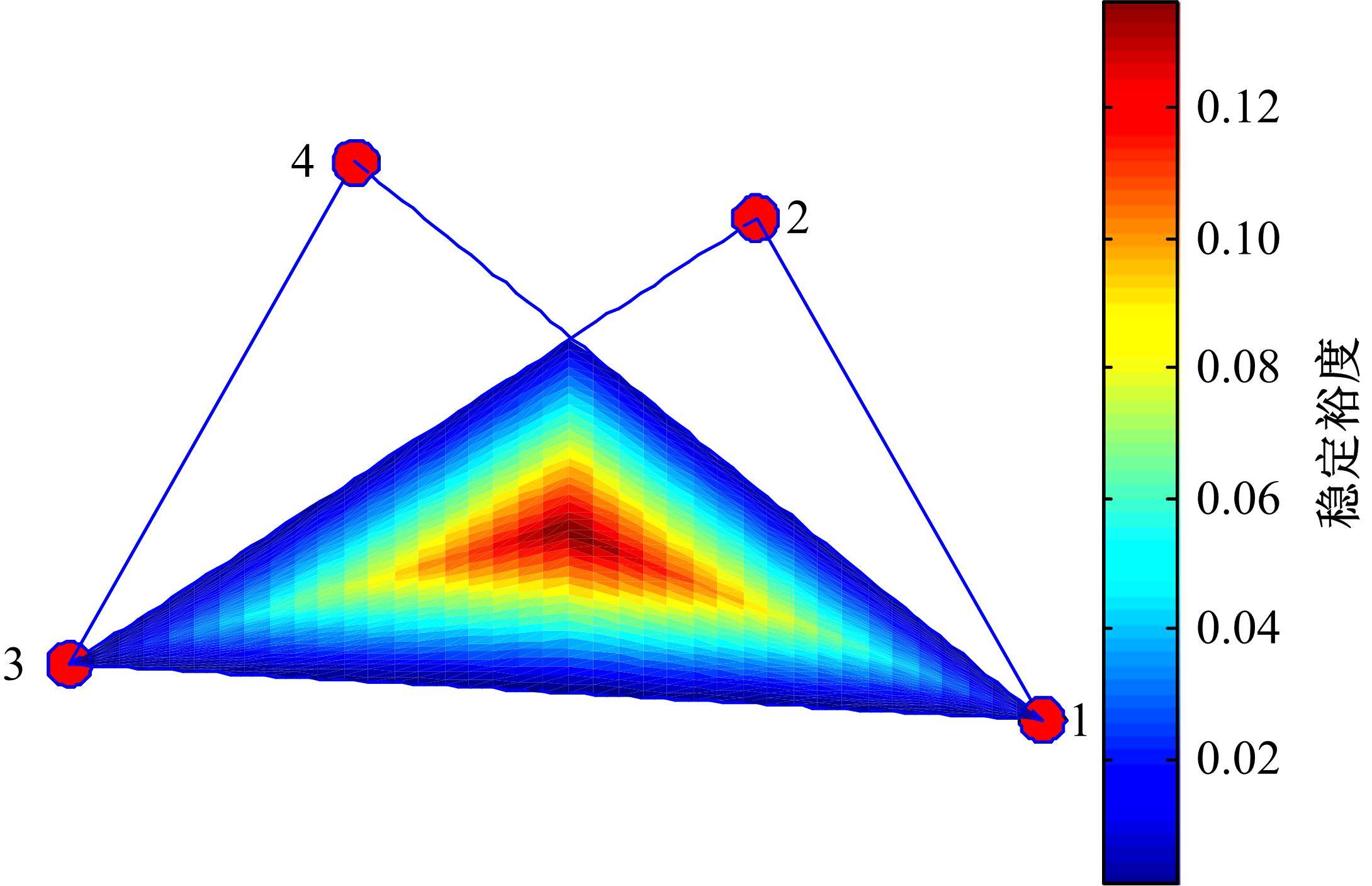
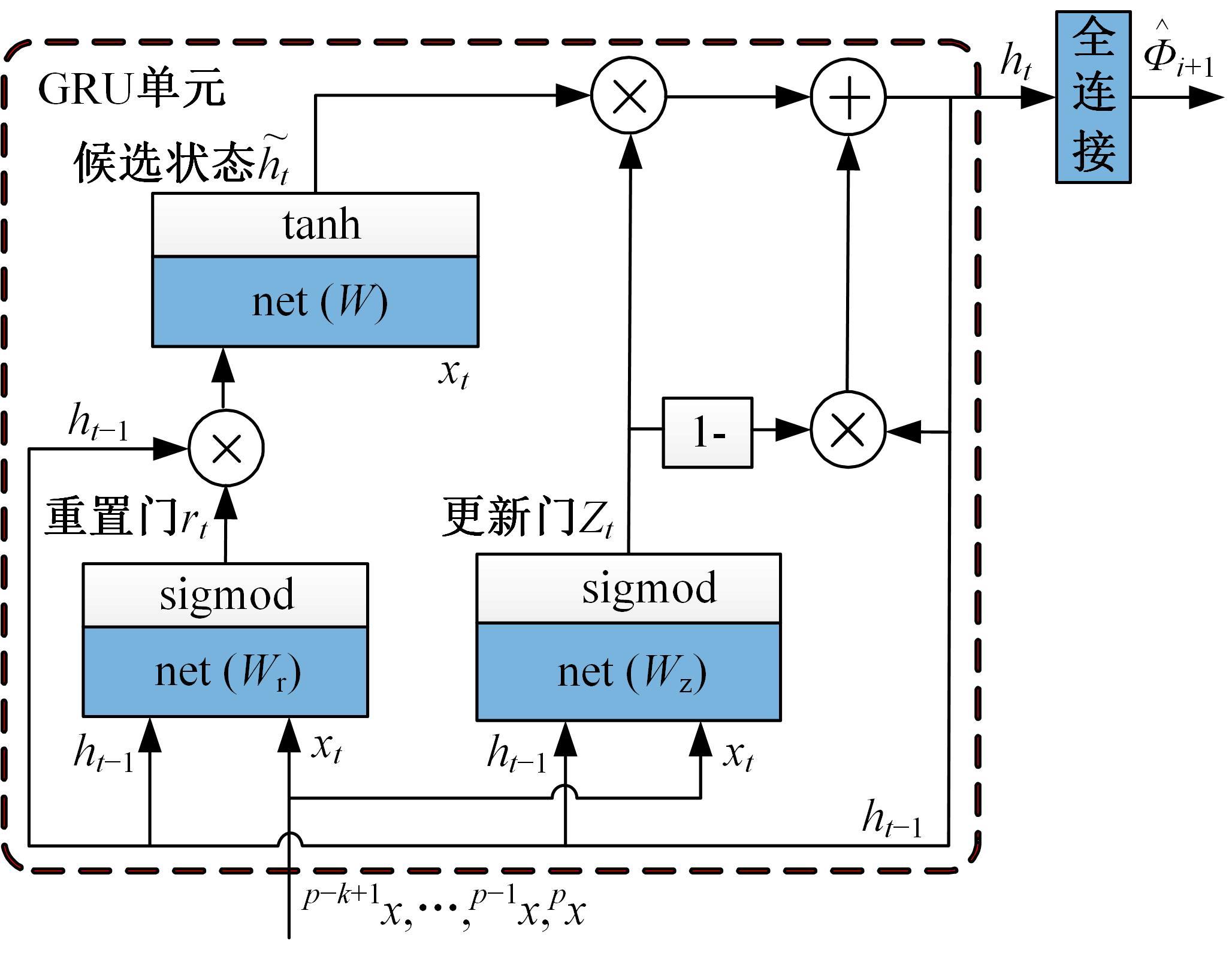
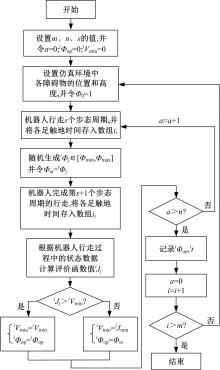
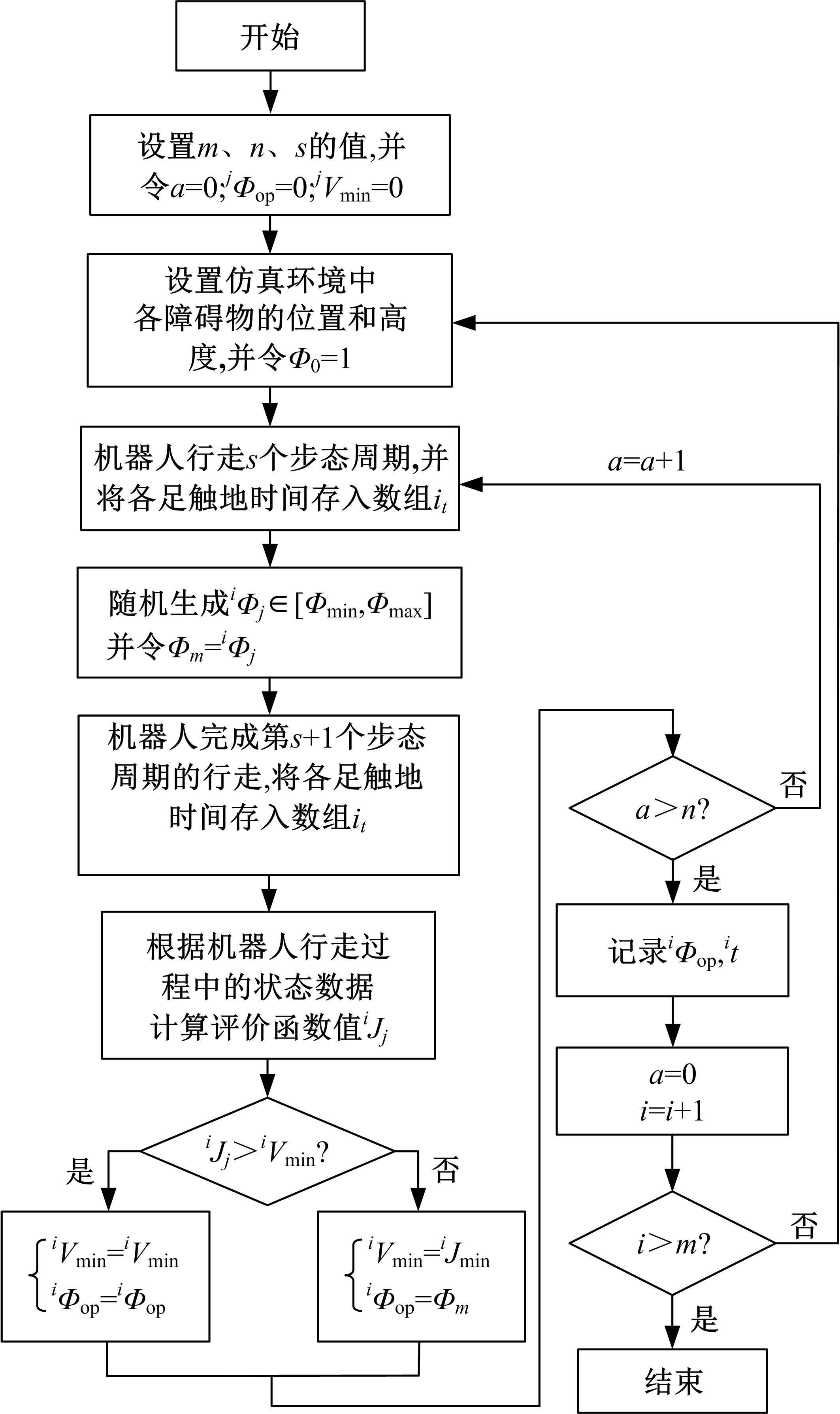
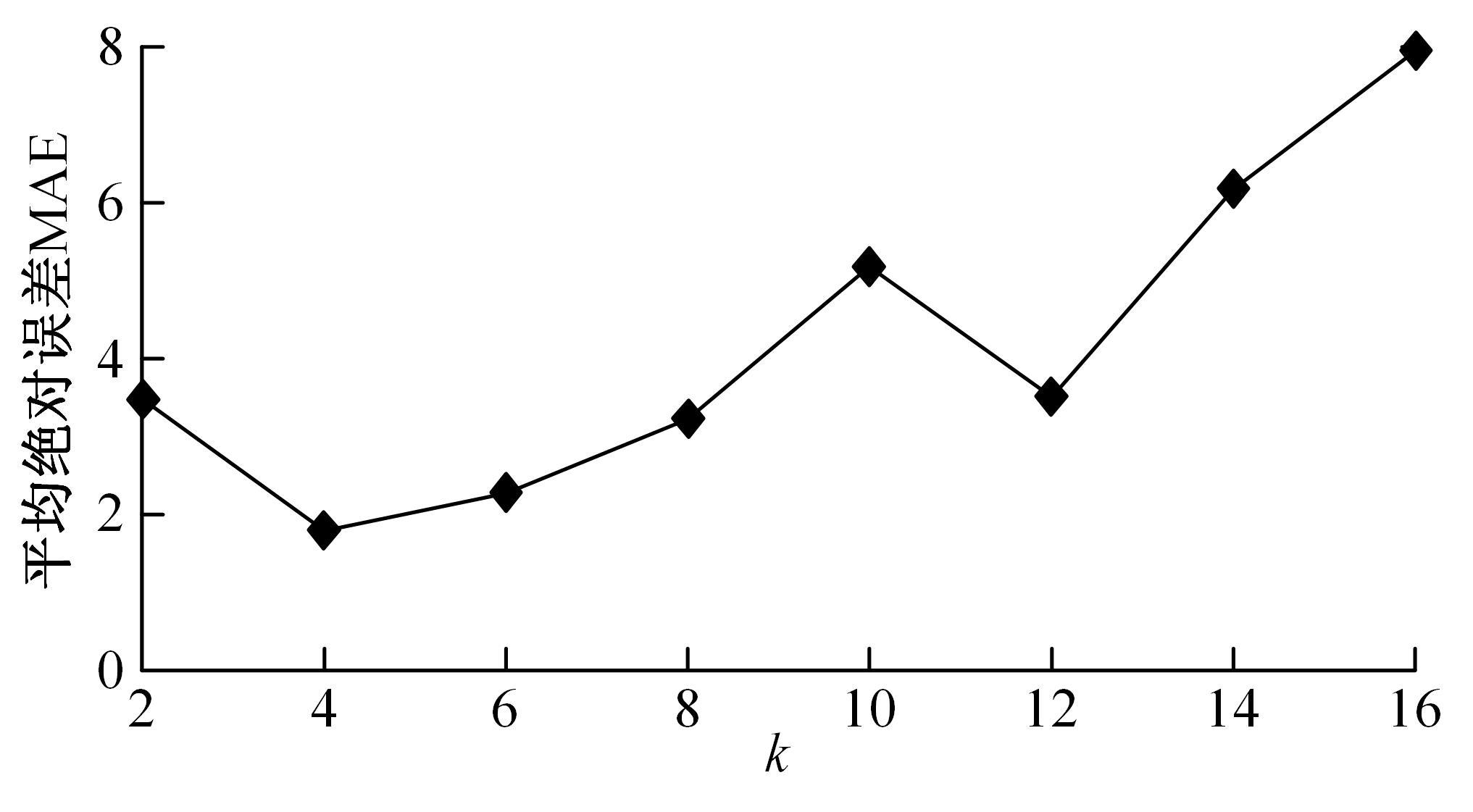
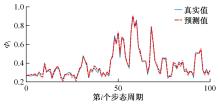
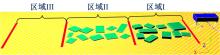
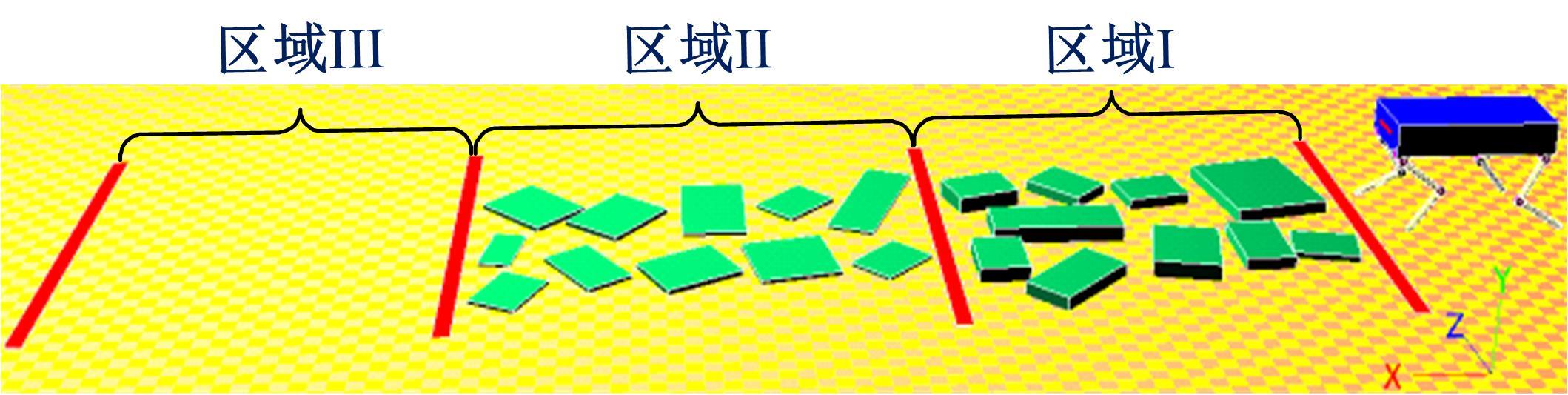
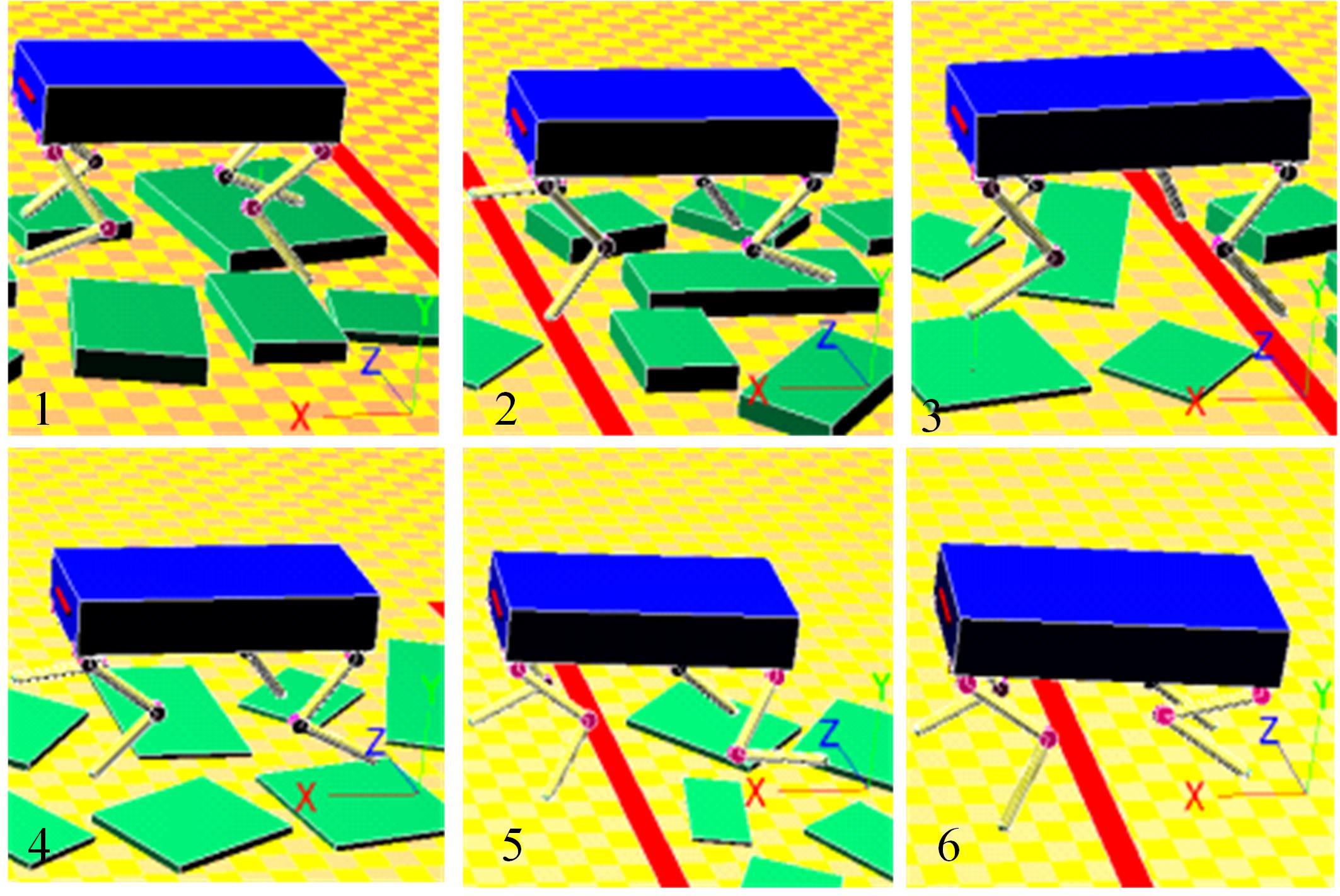
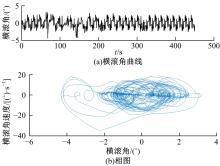
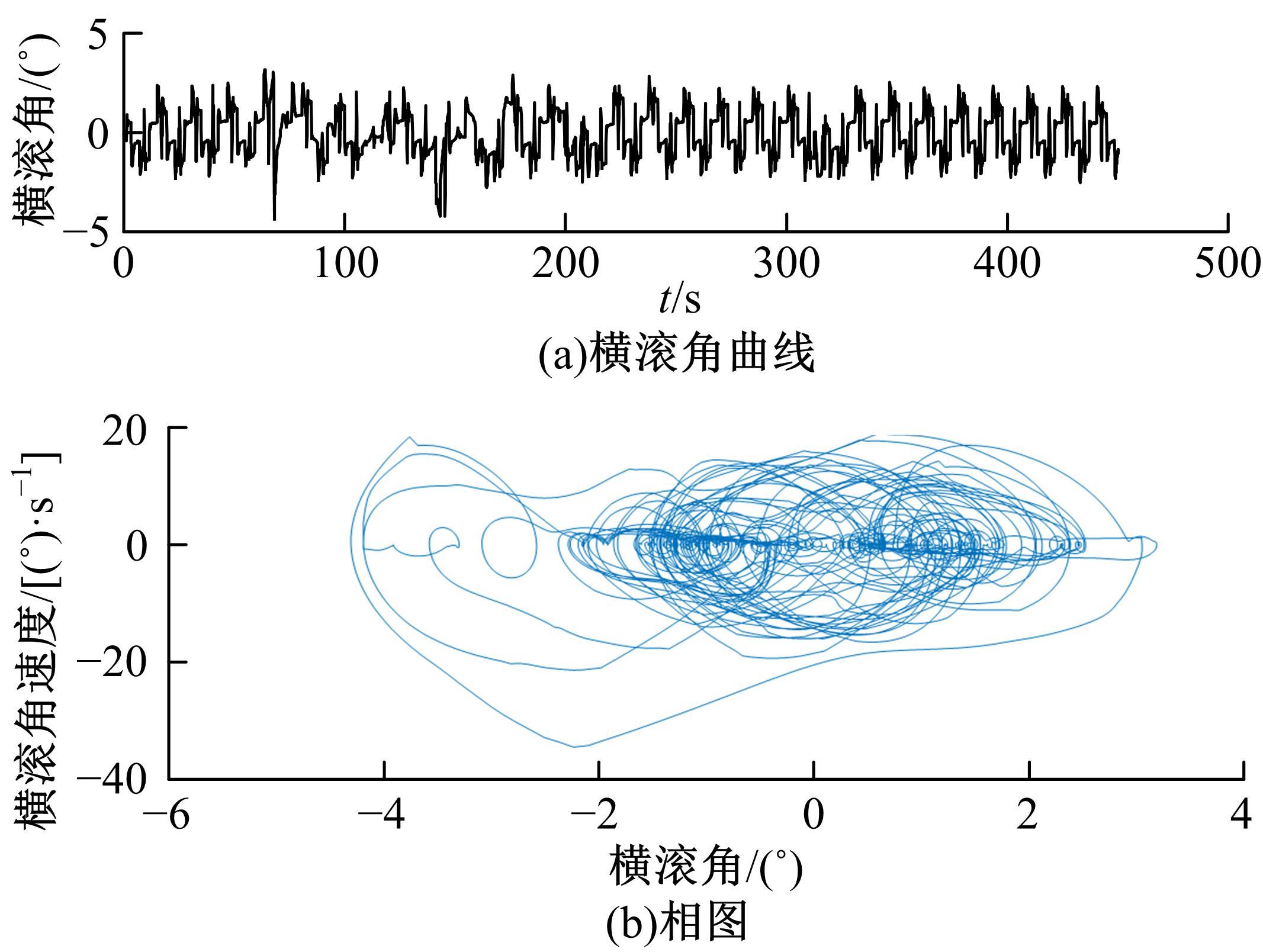
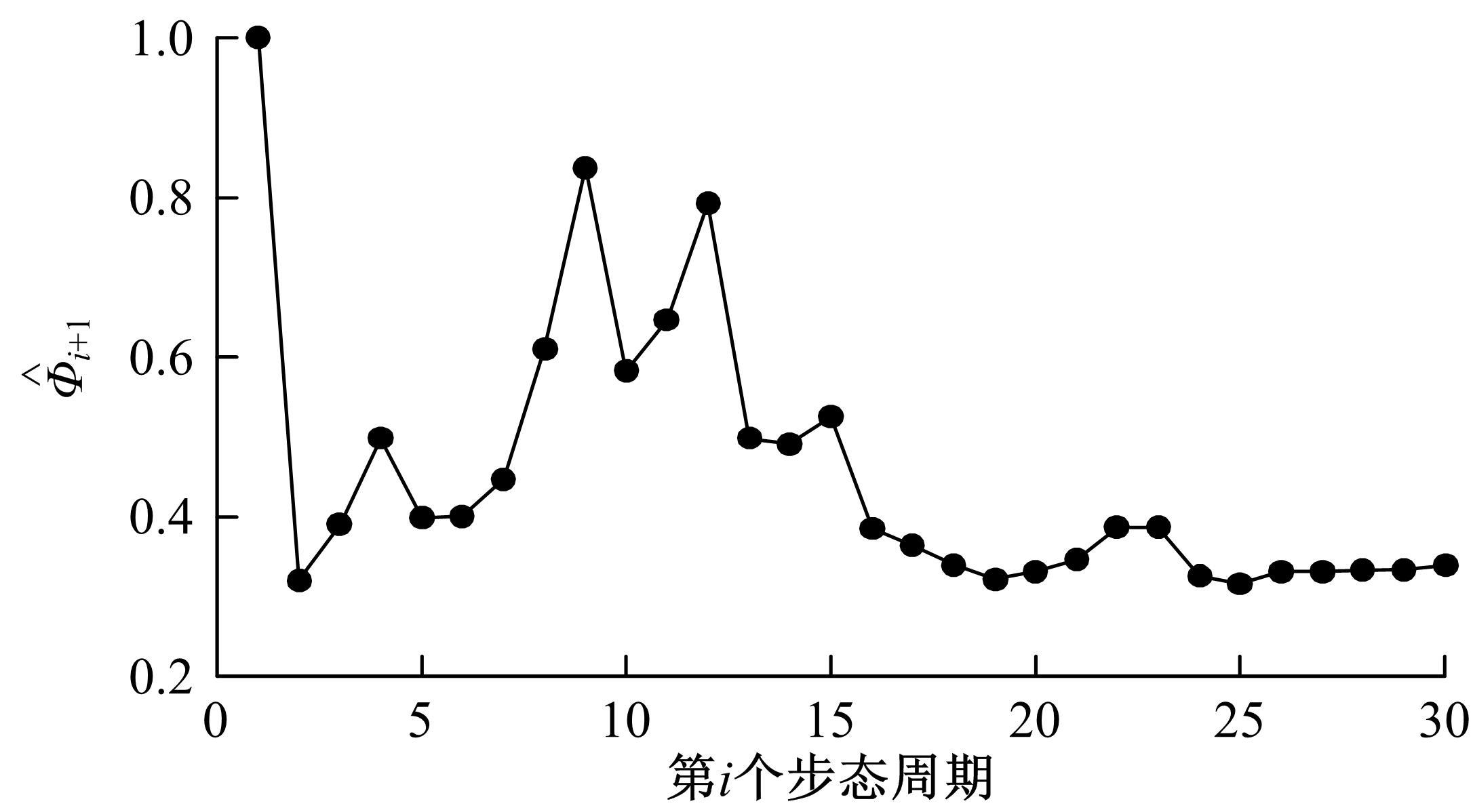
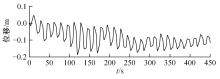
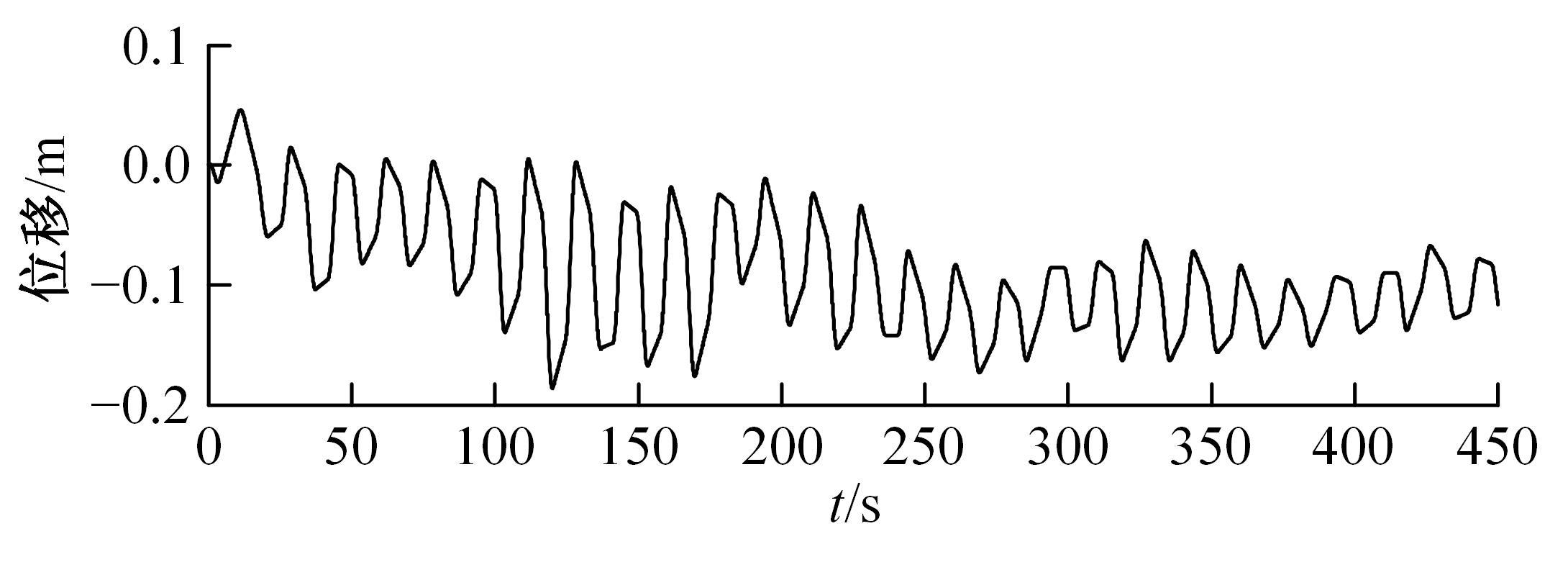
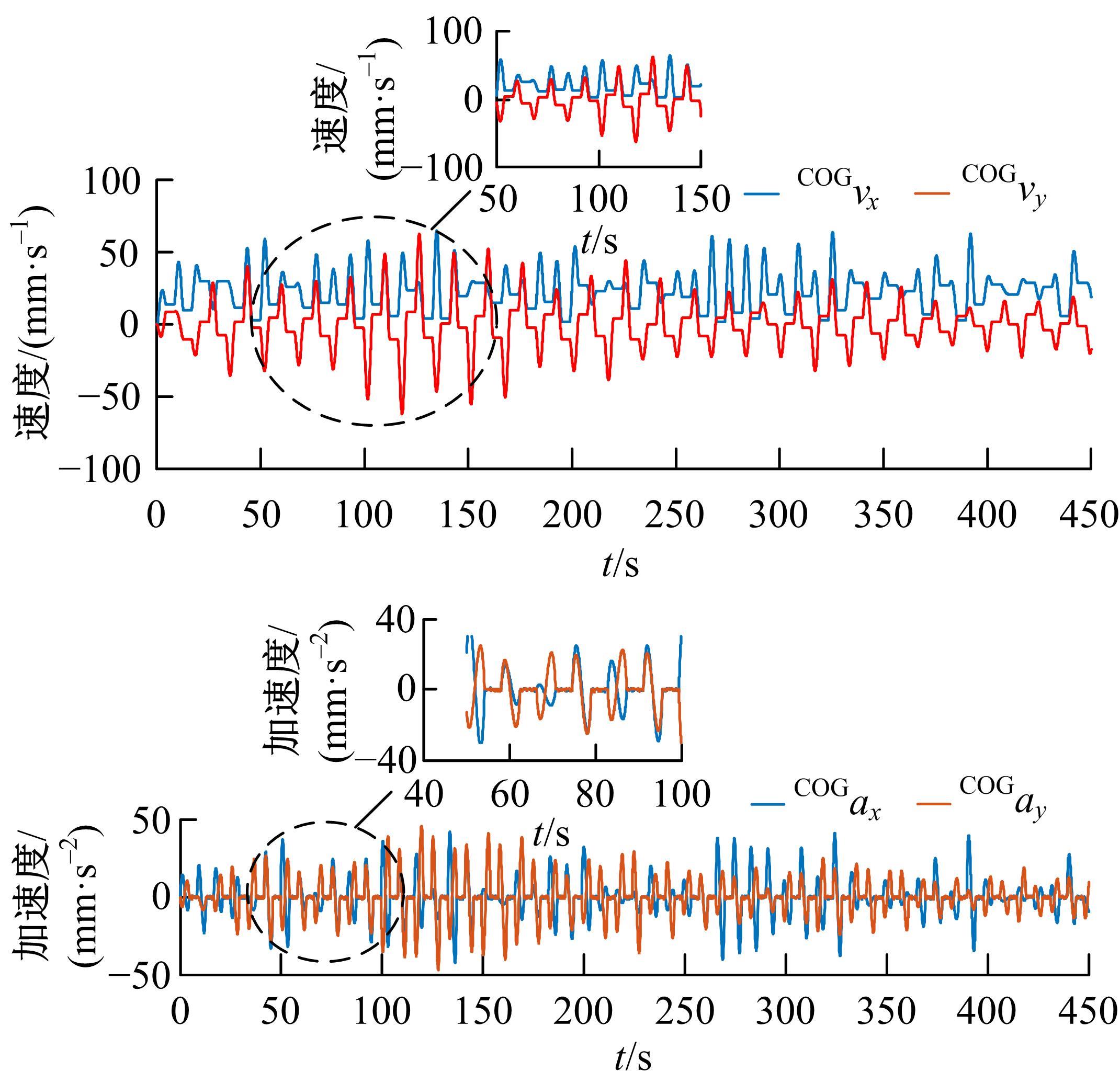
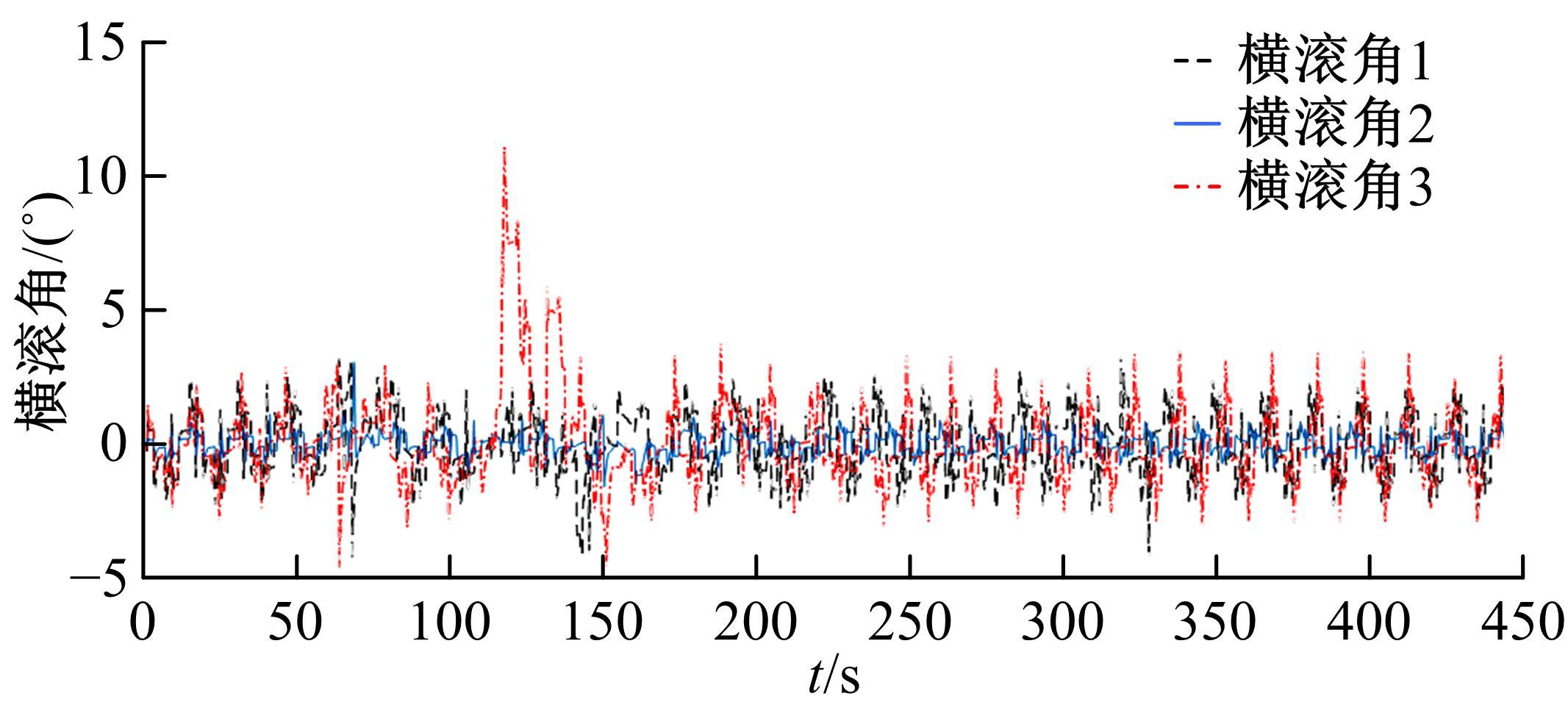
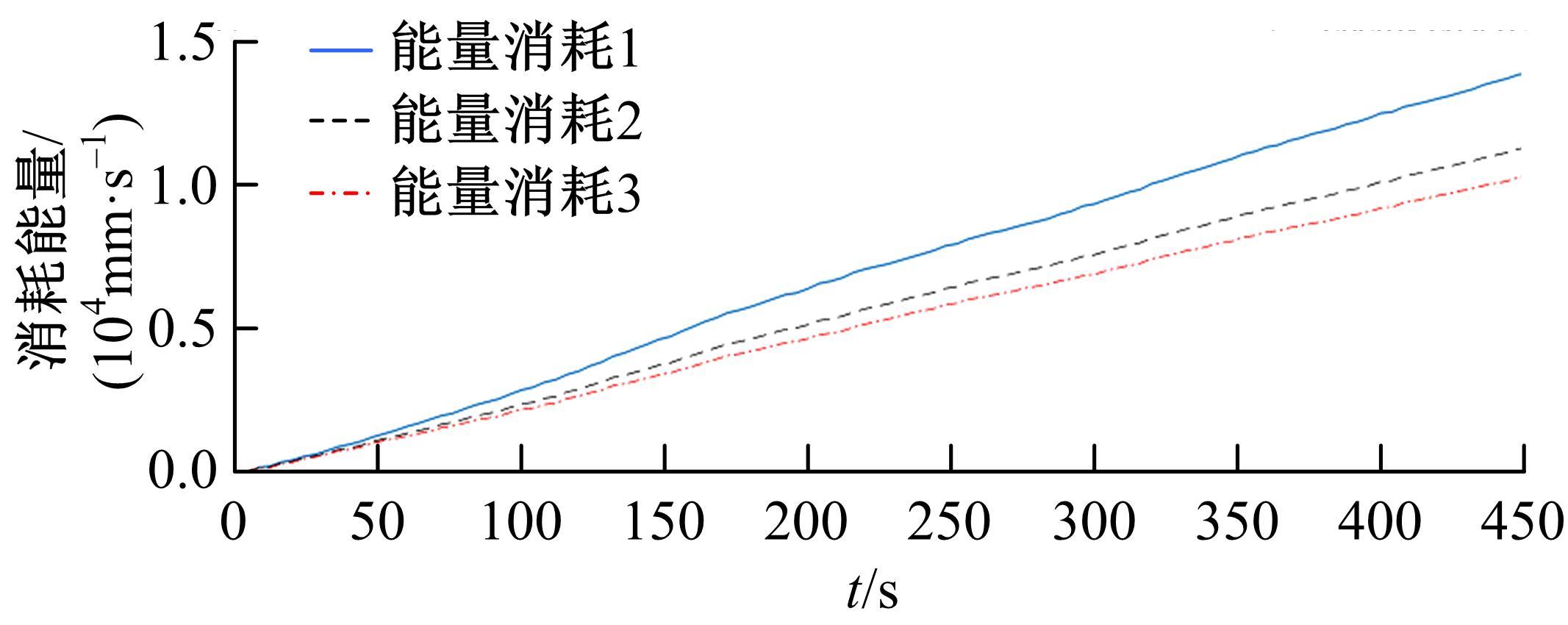
为使四足机器人在不配备地形感知设备的情况下,依然能够根据地形崎岖度变化自主调整自身步态规划参数,以提高其在复杂未知地形中的稳定性和适应性,提出了基于门控循环单元(GRU)模型的静步态规划方法。首先,给出了一种连续矩形迈步轨迹生成方法,能够保证机器人的摆动足在未知地形上顺利摆动至目标落足点且整个迈步过程连续。然后,提出了可通过调整参数改变躯干运动轨迹的规划方法。最后,利用GRU模型及各摆动足迈步时间实现对躯干运动轨迹规划中可调整参数的预测,以使四足机器人生成与地形崎岖度变化相适应的运动,且运动过程中能够兼顾能量消耗和自身稳定性。实验结果表明了本文方法的正确性和有效性。
中图分类号:
- TP242
| 1 | 付博. 四足机器人动态稳定性分析及运动控制研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学机电工程学院, 2010. |
| Fu Bo. Research on the analysis of quadruped robot dynamic stability and control[D]. Harbin: School of Mechatronics Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010. | |
| 2 | McGhee R B, Frank A A. On the stability properties of quadruped creeping gaits[J]. Mathematical Biosciences, 1968, 3: 331-351. |
| 3 | Hwang H, Youm Y. Steady crawl gait generation algorithm for quadruped robots[J]. Advanced Robotics, 2008, 22(13/14):1539-1558. |
| 4 | Santos C P, Matos V. CPG modulation for navigation and omnidirectional quadruped locomotion[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2012, 60(6): 912-927. |
| 5 | Loc V G, Koo I M, Tran D T, et al. Improving travers ability of quadruped walking robots using body movement in 3D rough terrains[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2011, 59(12): 1036-1048. |
| 6 | 郝仁剑, 王军政, 史大威, 等. 基于速度矢量的四足机器人间歇步态规划方法[J]. 机器人, 2016, 38(5):540-549. |
| Hao Ren-jian, Wang Jun-zheng, Shi Da-wei, et al. Intermittent gait planning method of quadruped robot based on velocity vector[J].Robot,2016,38(5):540-549. | |
| 7 | 孟健, 李贻斌, 柴汇, 等. 连续不规则台阶环境四足机器人步态规划与控制[J]. 机器人, 2015, 37(1): 85-93. |
| Meng Jian, Li Yi-bin, Chai Hui, et al. Gait planning and control of quadruped robots in continuous irregular steps environment[J]. Robot, 2015, 37(1):85-93. | |
| 8 | 黄博,赵建文,孙立宁.基于静平衡的四足机器人直行与楼梯爬越步态[J]. 机器人, 2010, 32(2): 226-232. |
| Huang Bo, Zhao Jian-wen, Sun Li-ning. Straight walking and stair climbing gait of quadruped robot based on static balance[J]. Robot, 2010, 32 (2): 226-232. | |
| 9 | 冯华山, 王润孝, 赵国斌, 等.四足机器人坡面静步态平衡方法研究[J]. 机械科学与技术,2009,28(4):436-441. |
| Feng Hua-shan, Wang Run-xiao, Zhao Guo-bin,et al. A balance method for the static gait of a quadruped robot over a slope[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering,2009,28(4): 436-441. | |
| 10 | 汪山人. 仿生恐龙机器人的步态仿真及系统实现[D]. 成都:电子科技大学自动化工程学院, 2018. |
| Wang Shan-ren. Gait simulation and system realization of bionic dinosaur robot[D]. Chengdu: School of Automation Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2018. | |
| 11 | 张帅帅, 荣学文, 李贻斌, 等.崎岖地形环境下四足机器人的静步态规划方法[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 46(4): 1287-1296. |
| Zhang Shuai-shuai, Rong Xue-wen, Li Yi-bin, et al. Static gait planning method for quadruped robots on rough terrains[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016,46(4):1287-1296. | |
| 12 | Fankhauser P, Bjelonic M, Bellicoso C D, et al. Robust rough-terrain locomotion with a quadrupedal robot[C]∥2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 2018: 1-8. |
| 13 | Bazeille S, Barasuol V, Focchi M, et al. Vision enhanced reactive locomotion control for trotting on rough terrain[C]∥2013 IEEE Conference on Technologies for Practical Robot Applications (TePRA), Woburn, MA, USA, 2013: 1-6. |
| 14 | Buchli J, Kalakrishnan M, Mistry M, et al. Compliant quadruped locomotion over rough terrain[C]∥2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, USA, 2009: 814-820. |
| 15 | Kalakrishnan M, Buchli J, Pastor P, et al. Fast, robust quadruped locomotion over challenging terrain[C]∥2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, USA,2010: 2665-2670. |
| 16 | Kalakrishnan M, Buchli J, Pastor P, et al. Learning, planning, and control for quadruped locomotion over challenging terrain[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2011, 30(2): 236-258. |
| 17 | Zico K J, Ng A Y. The stanford littledog: a learning and rapid replanning approach to quadruped locomotion [J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2011, 30(2): 150-174. |
| 18 | Zucker M, Ratliff N, Stolle M, et al. Optimization and learning for rough terrain legged locomotion [J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2011, 30(2): 175-191. |
| 19 | Shao X, Yang Y, Wang W. Obstacle crossing with stereo vision for a quadruped robot[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Chengdu, China, 2012: 1738-1743. |
| 20 | Havoutis I, Ortiz J, Bazeille S, et al. Onboard perception-based trotting and crawling with the hydraulic quadruped robot (HyQ)[C]∥2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 2013: 6052-6057. |
| 21 | Graves A, Mohamed A, Hinton G. Speech recognition with deep recurrent neural networks[C]∥2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2013: 6645-6649. |
| 22 | Cho K, van Merriënboer B, Bahdanau D, et al. On the properties of neural machine translation: encoder-decoder approaches[C]∥8th Workshop on Syntax, Semantics and Structure in Statistical Translation, Doha, Qatar, 2014: 103-111. |
| [1] | 祁贤雨,王巍,王琳,赵玉飞,董彦鹏. 基于物体语义栅格地图的语义拓扑地图构建方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 569-575. |
| [2] | 李昂,杨泓渊,雷小萌,宋凯文,千承辉. 基于等效连杆模型的六足机器人行进姿态闭环控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1696-1708. |
| [3] | 李学勇,赵仲秋,张春松,路长厚. 基于有限元的人体⁃机械手交互力计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1612-1619. |
| [4] | 刘明,荣学文,李贻斌,张帅帅,尹燕芳,阮久宏. 基于地形聚类分析的移动机器人速度自适应控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1496-1505. |
| [5] | 于树友,常欢,孟凌宇,郭洋,曲婷. 基于扰动观测器的轮式移动机器人滚动时域路径跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1097-1105. |
| [6] | 周挺,徐宇工,吴斌. 球形机器人的自适应分数阶PIλDμ滑模速度控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 728-737. |
| [7] | 周炳海,吴琼. 基于多目标的机器人装配线平衡算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 720-727. |
| [8] | 胡明伟,王洪光,潘新安. 基于正交设计的协作机器人全域结构优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 370-378. |
| [9] | 赵云伟,耿德旭,刘晓敏,刘齐. 气动柔性六足机器人定半径转弯实现方法与稳定性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 472-482. |
| [10] | 马芳武,倪利伟,吴量,聂家弘,徐广健. 轮腿式全地形移动机器人位姿闭环控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1745-1755. |
| [11] | 周炳海,吴琼. 考虑工具和空间约束的机器人装配线平衡优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2069-2075. |
| [12] | 温海营,任翔,徐卫良,丛明,秦文龙,胡书海. 咀嚼机器人颞下颌关节仿生设计及试验测试[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 943-952. |
| [13] | 顾万里,王萍,胡云峰,蔡硕,陈虹. 具有H∞性能的轮式移动机器人非线性控制器设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1811-1819. |
| [14] | 李战东,陶建国,罗阳,孙浩,丁亮,邓宗全. 核电水池推力附着机器人系统设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1820-1826. |
| [15] | 王林, 王洪光, 宋屹峰, 潘新安, 张宏志. 输电线路悬垂绝缘子清扫机器人行为规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 518-525. |
|
||