吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (12): 3432-3445.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220078
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
山区公路回头曲线小客车纵向行驶特性及运行速度模型
- 1.重庆交通大学 交通运输学院,重庆 400074
2.重庆交通大学 山区复杂道路环境“人-车-路”协同与安全重庆市重点实验室,重庆 400074
3.浙江江南工程管理股份有限公司深圳分公司,广东 深圳 518000
4.中铁第四勘察设计院集团有限公司,武汉 430063
Longitudinal driving characteristics and operating speed prediction model of cars on hairpin curves of mountainous roads
Jin XU1,2( ),Yan-peng WANG1,Hai-yuan CHEN3,Xiao-bo ZHANG4,Cun-shu PAN1
),Yan-peng WANG1,Hai-yuan CHEN3,Xiao-bo ZHANG4,Cun-shu PAN1
- 1.College of Traffic and Transportation,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
2.Chongqing Key Laboratory of “Human-Vehicle-Road” Cooperation & Safety for Mountain Complex Environment,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
3.Zhejiang Jiangnan Engineering Management Co. ,Ltd. Shenzhen Branch,Shenzhen 518000,China
4.China Railway Siyuan Survey and Design Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Wuhan 430063,China
摘要:
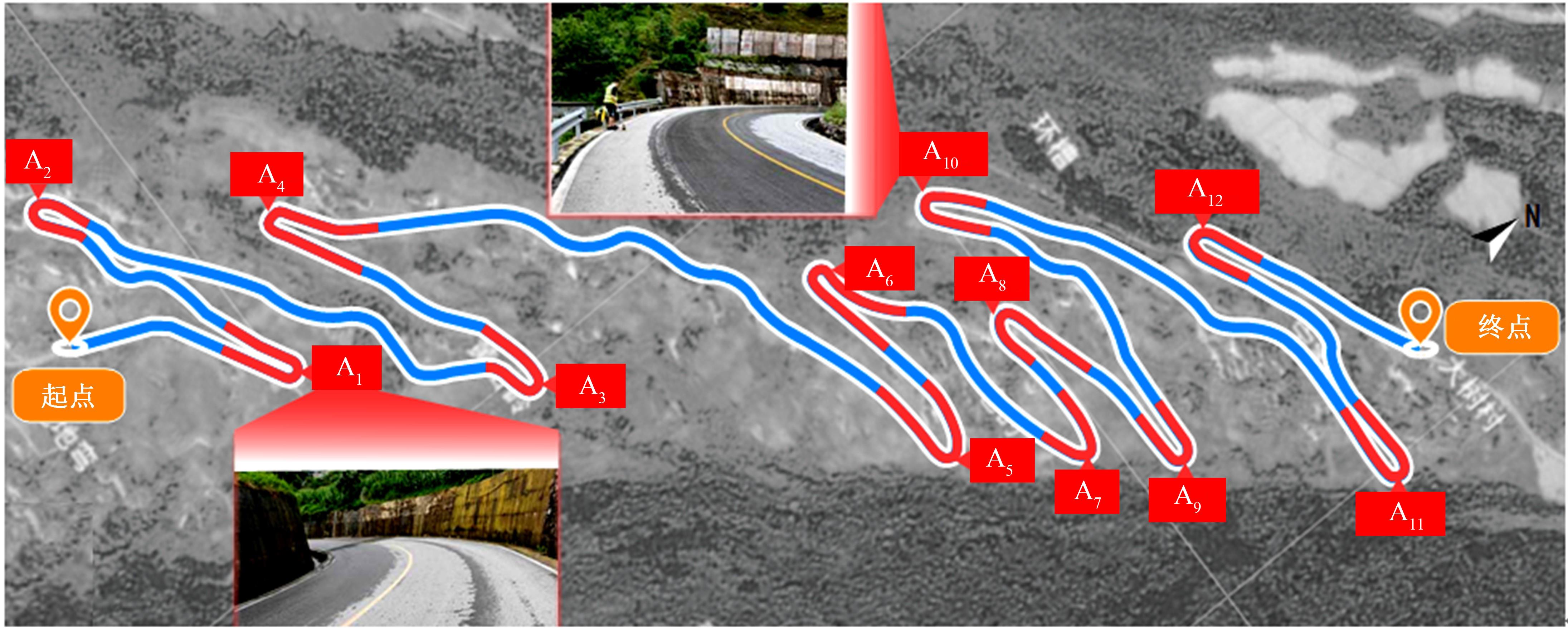
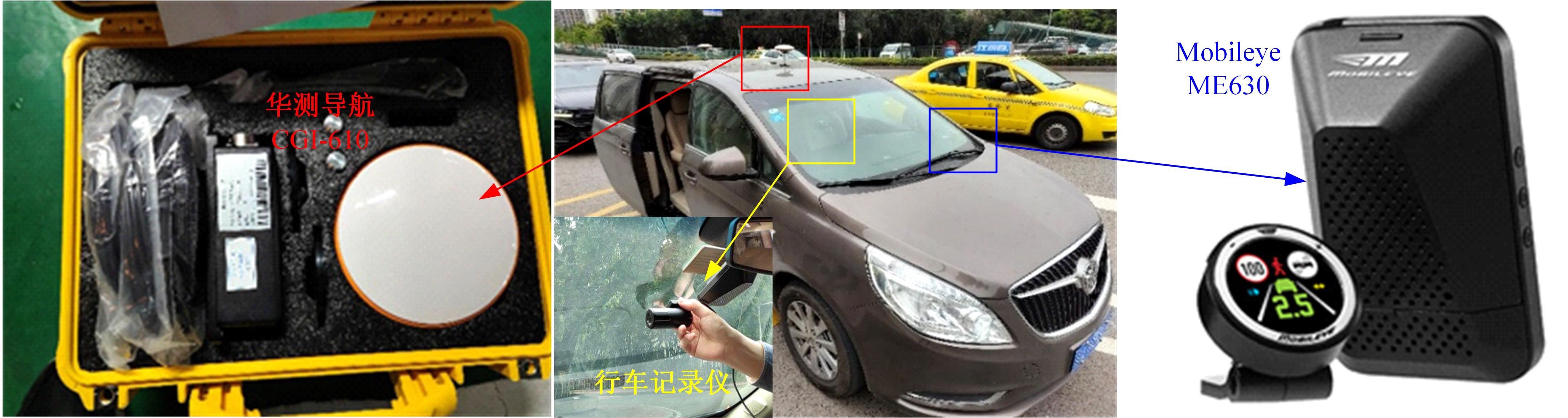
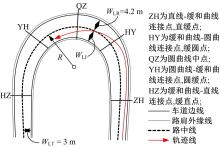
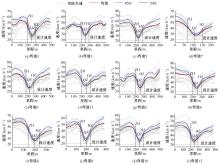
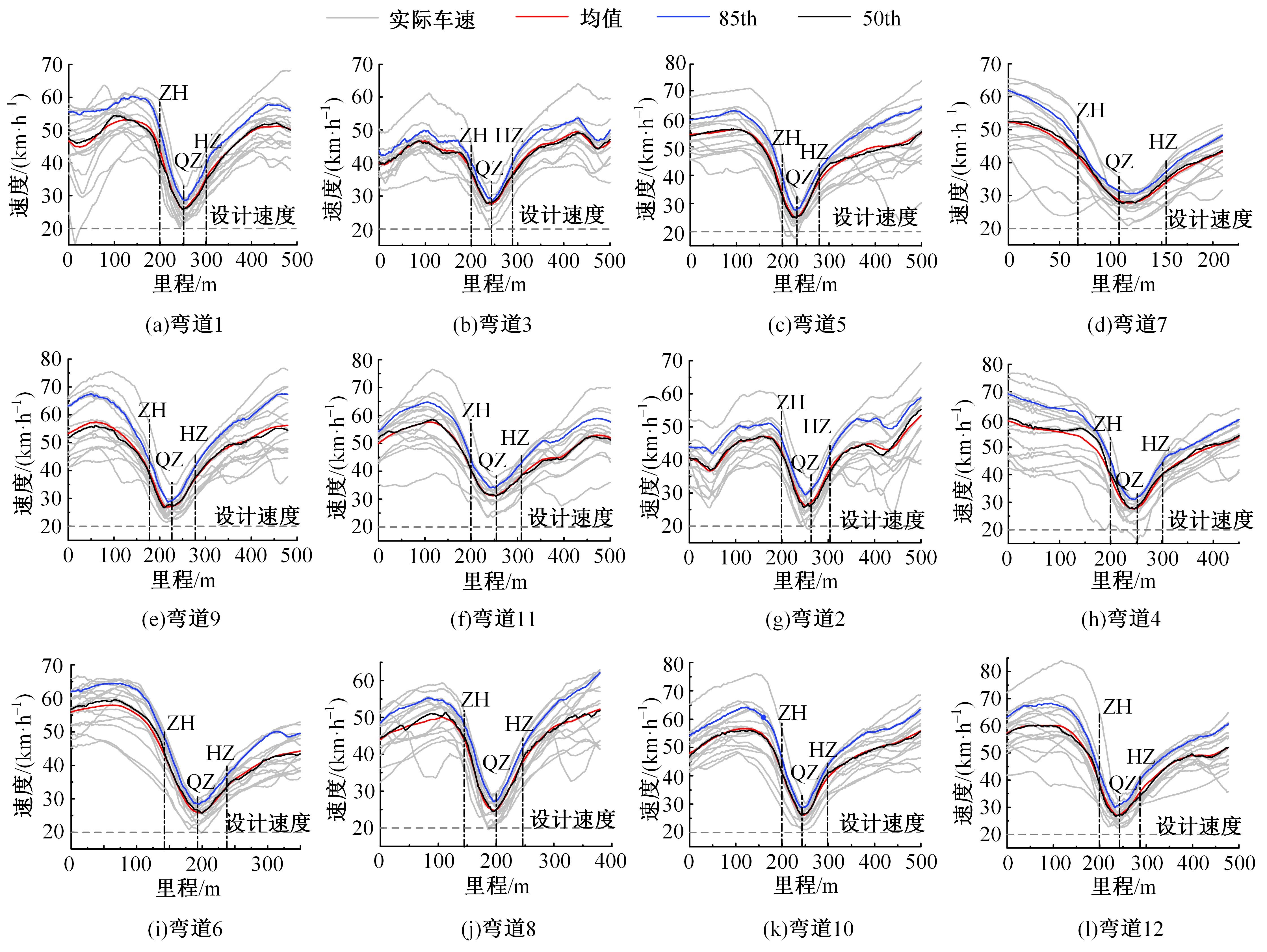
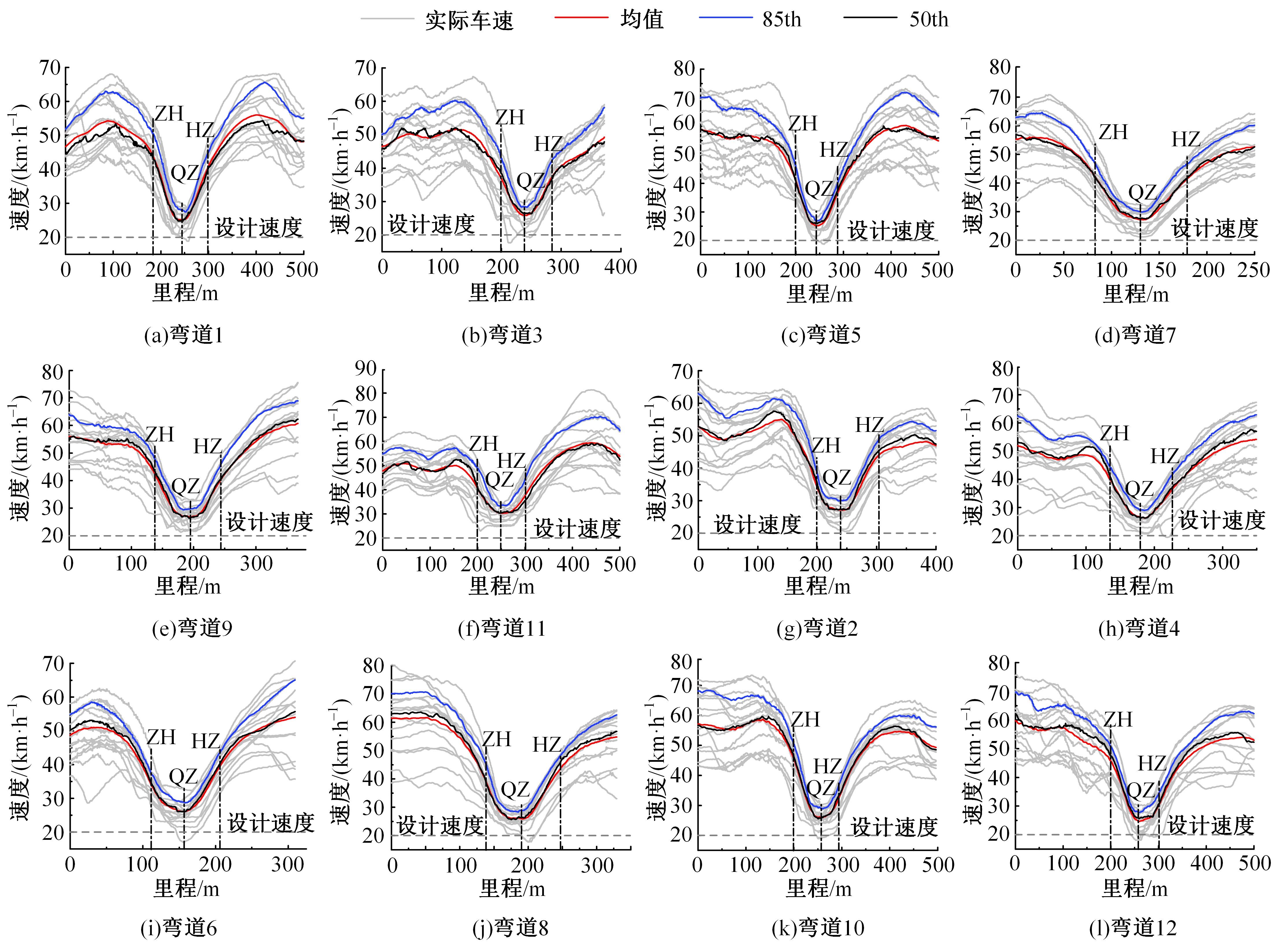
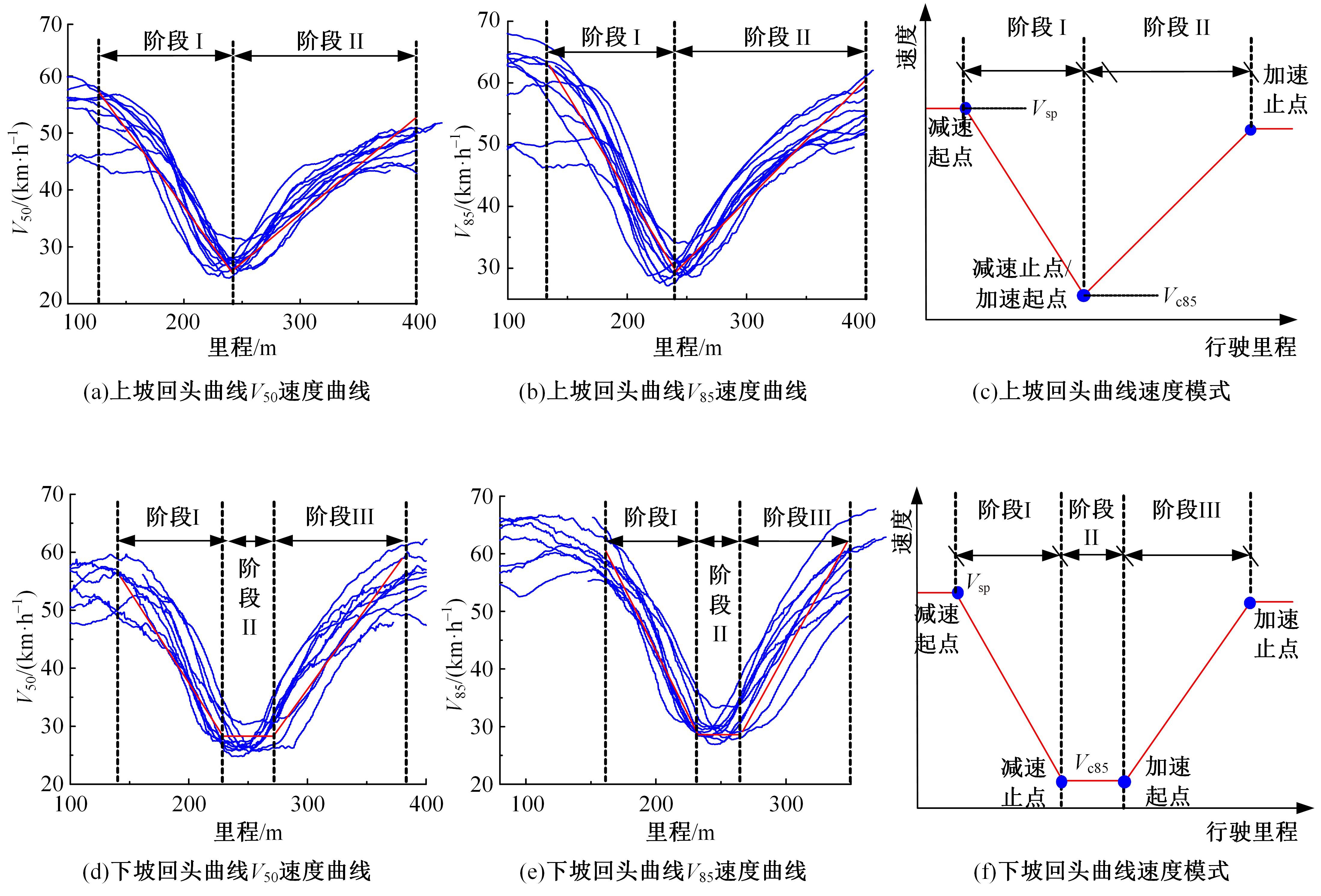
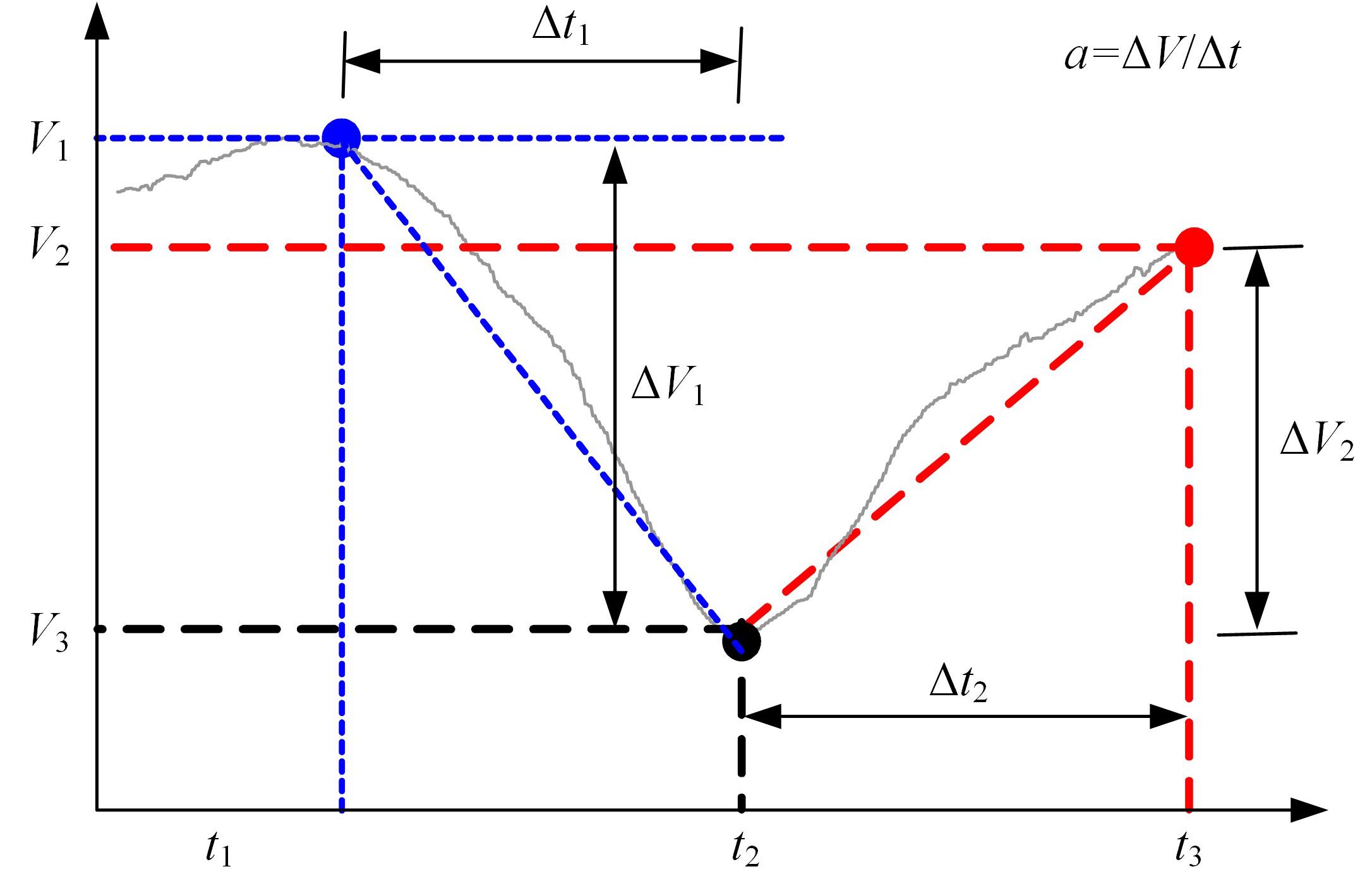
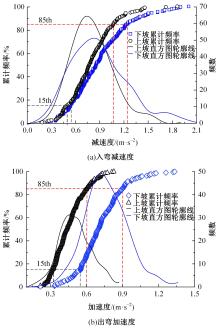
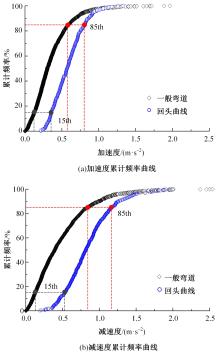
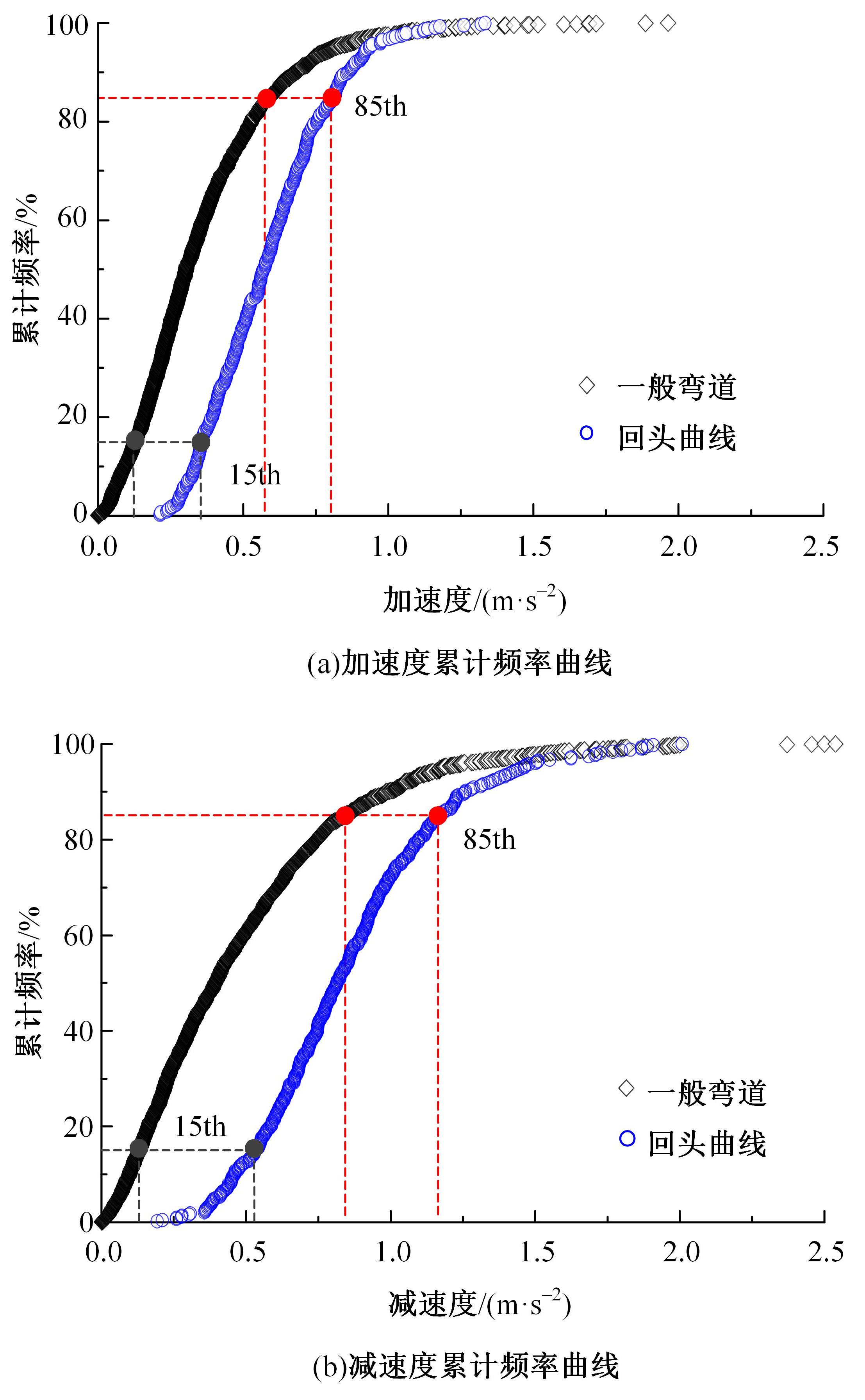
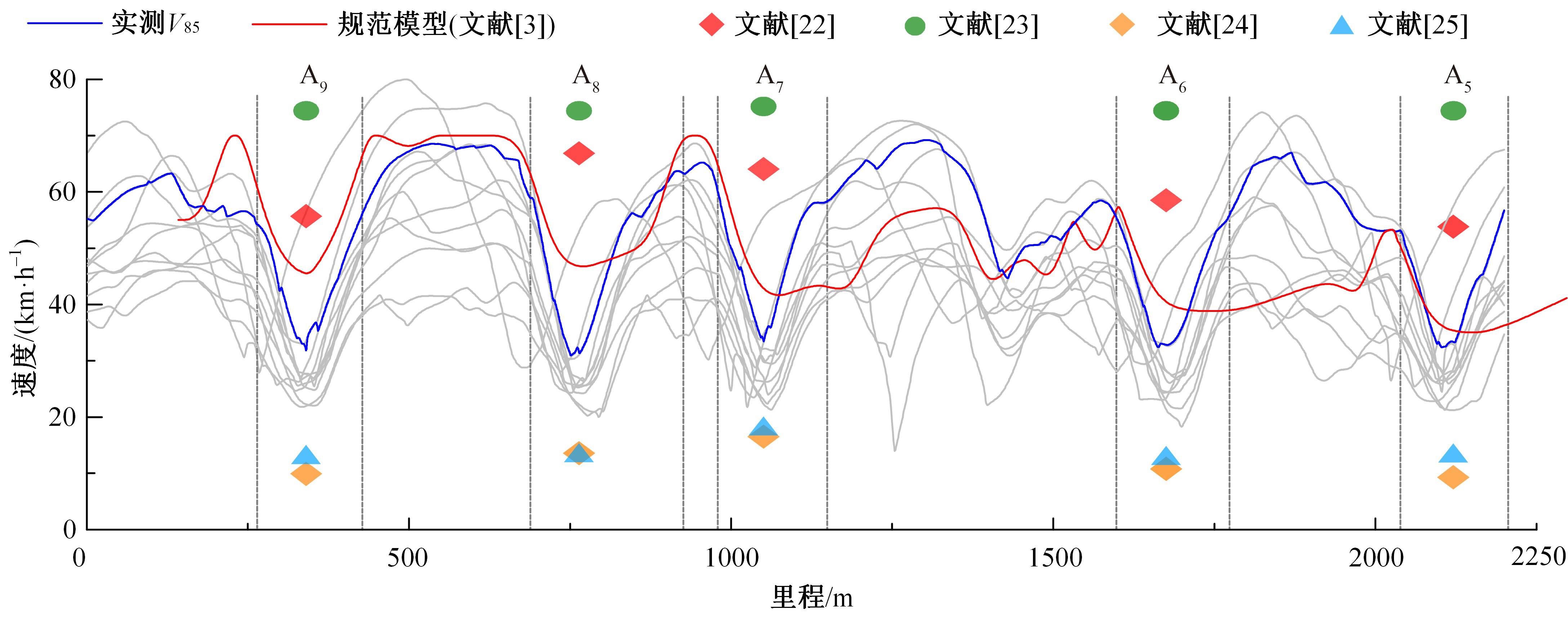
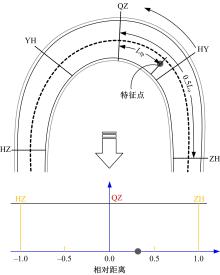
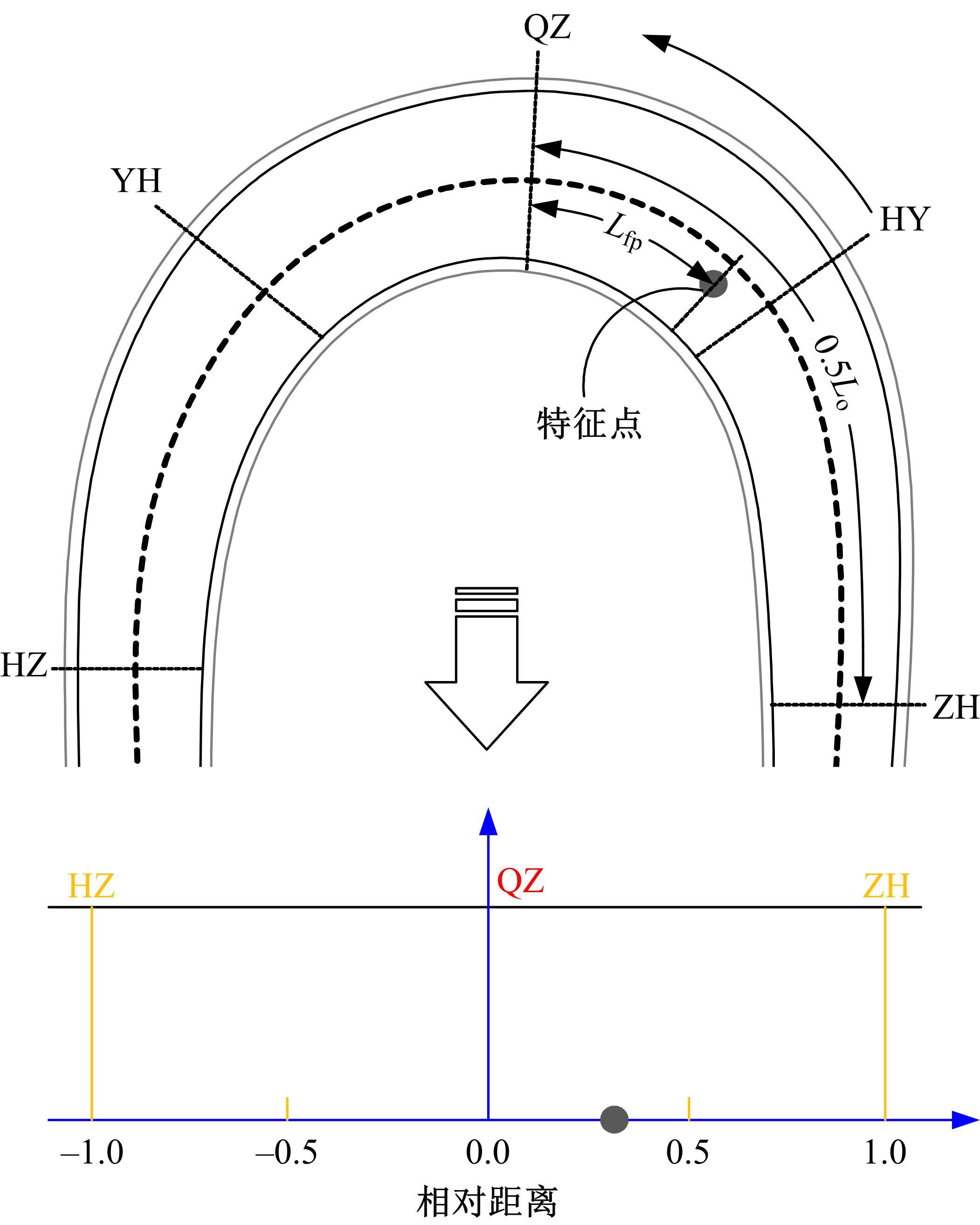
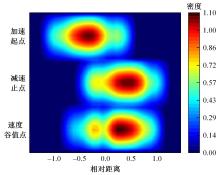
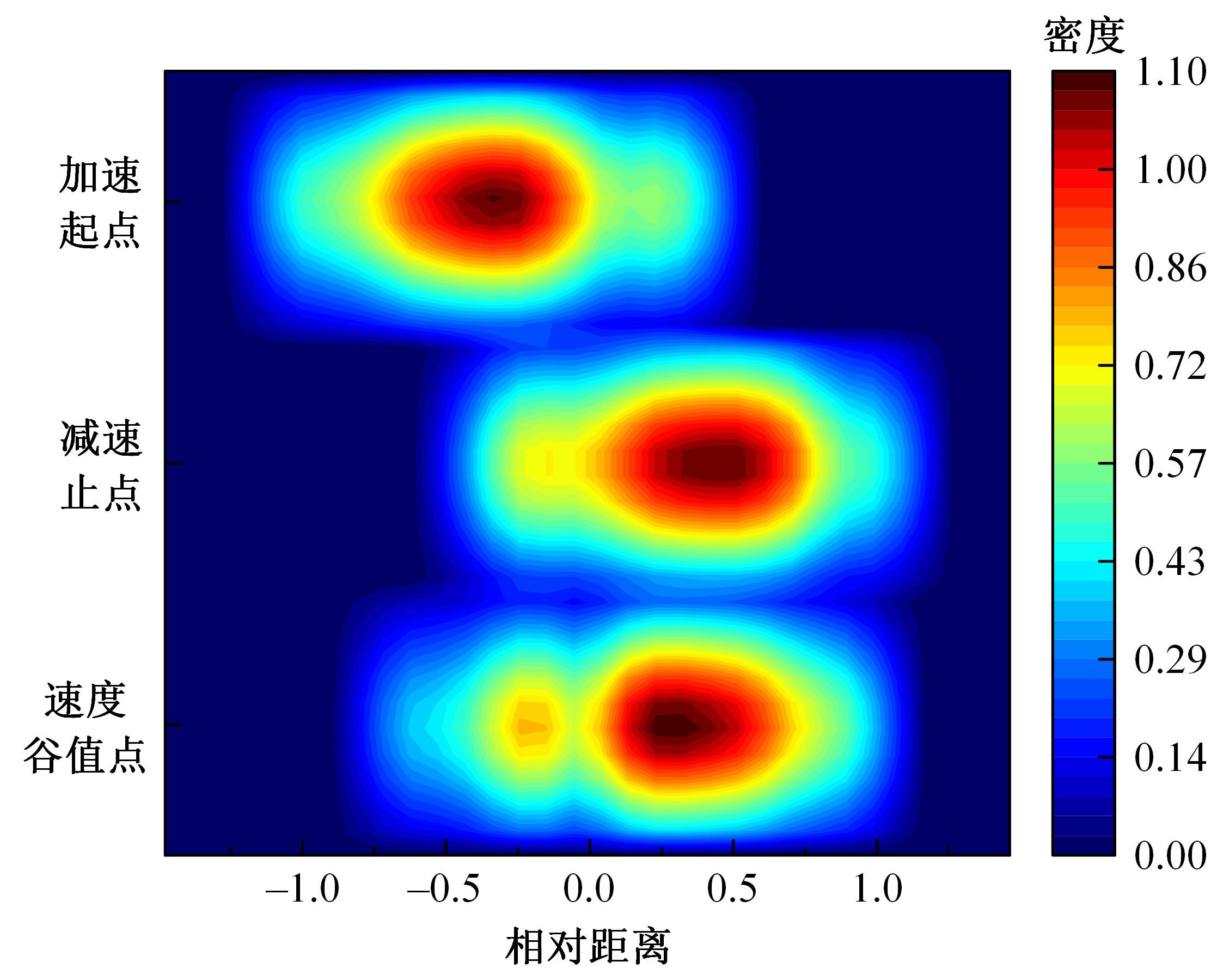
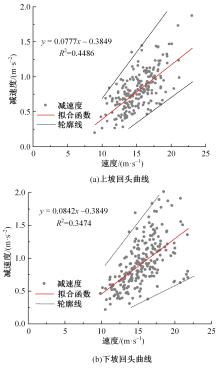
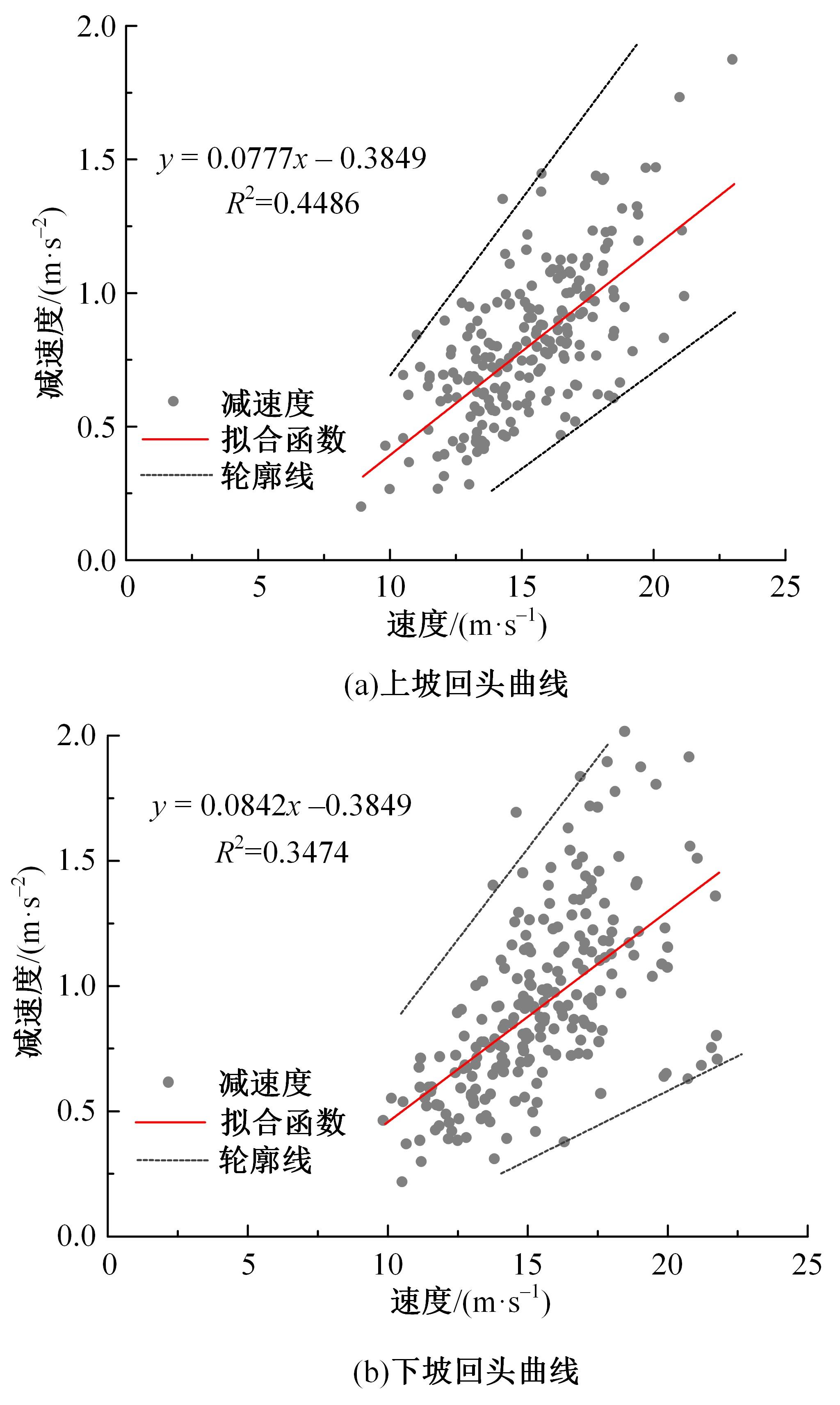
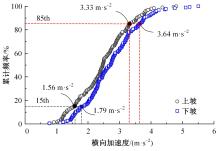
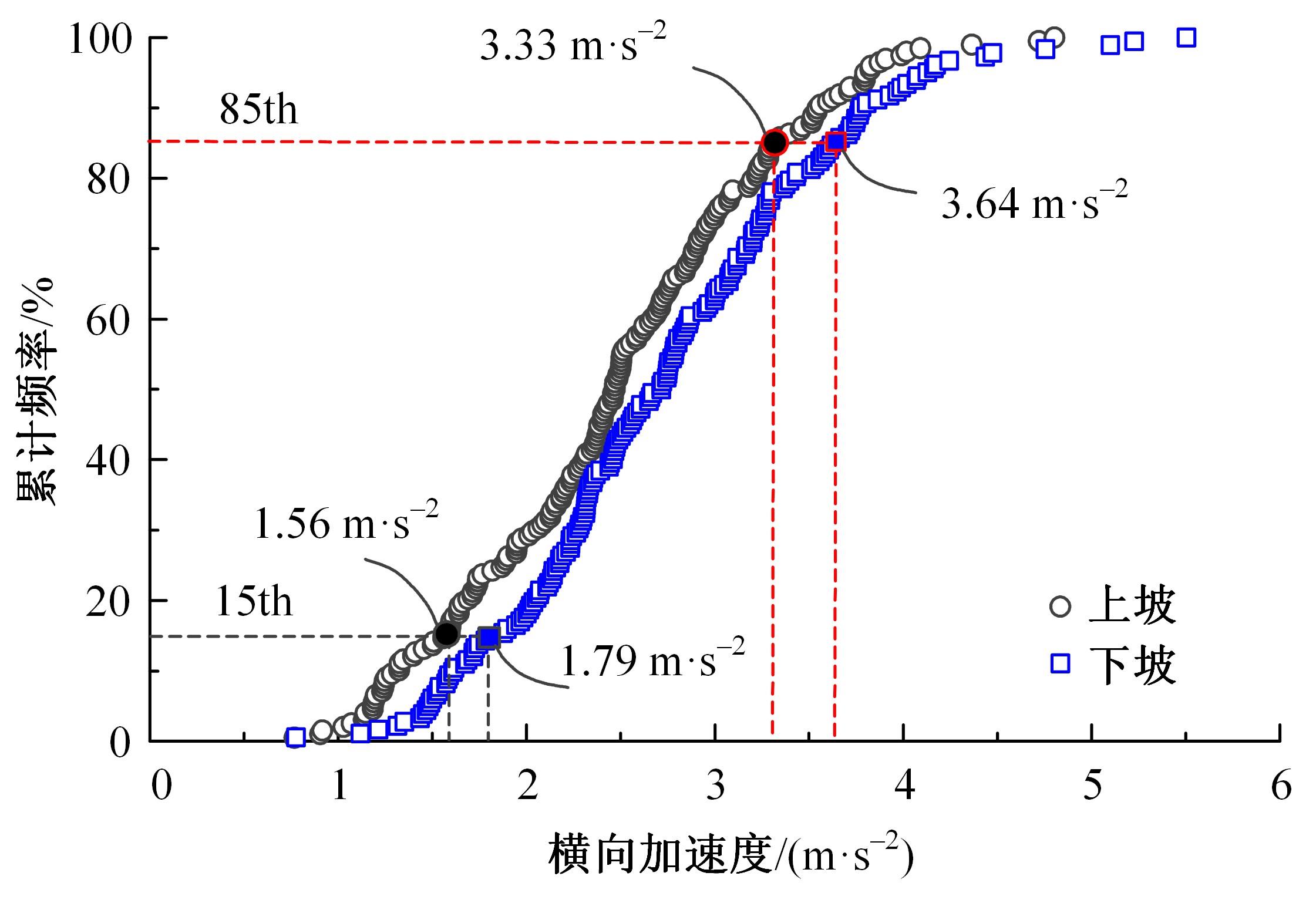
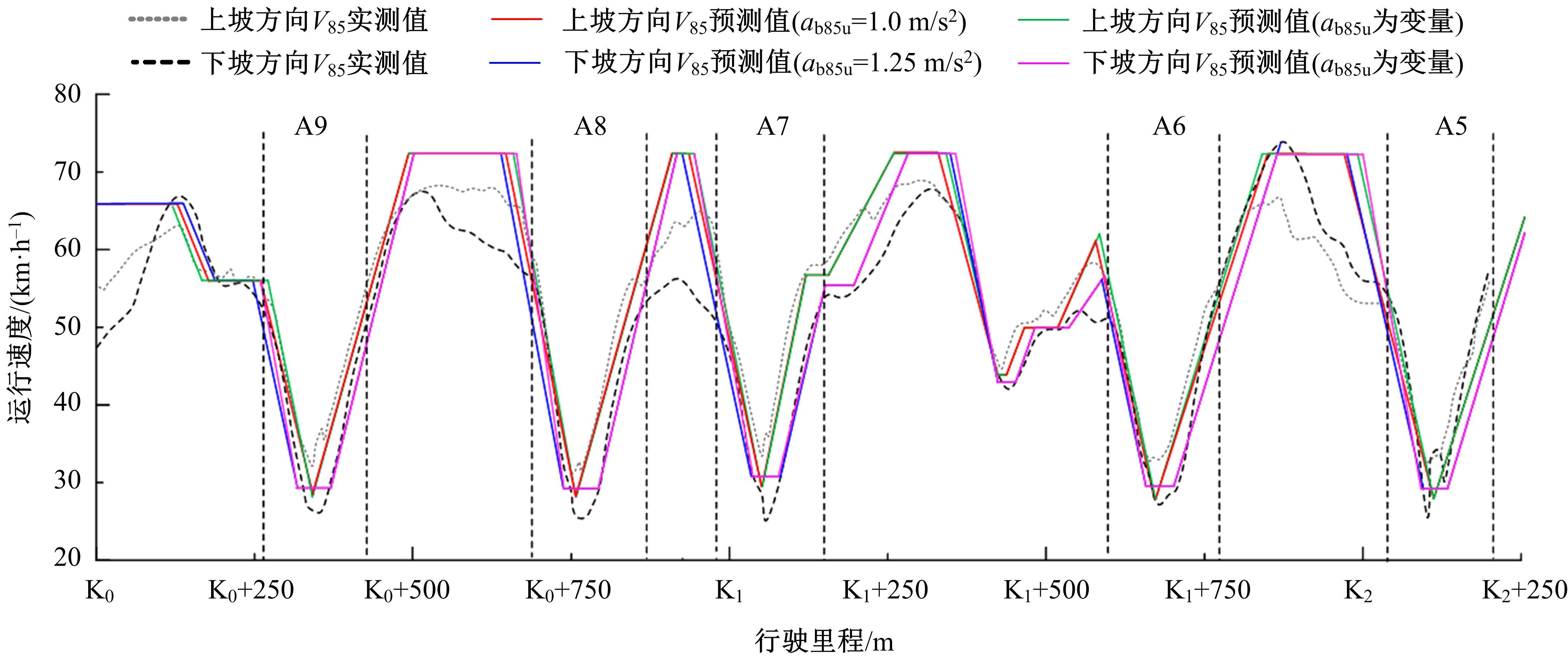
为明确山区公路回头曲线路段小客车的纵向驾驶行为特性,以国道G211线重庆市彭水县花地湾至宁家寨段为试验道路,开展了小客车实车驾驶试验。采集了自然驾驶状态下的车辆轨迹、速度、加速度等数据,分析了回头曲线路段的速度幅值特征;明确了上坡和下坡方向的速度行为模式,得到了速度变化特征点位置的分布规律;研究了入弯减速度和出弯加速度的幅值特征和影响因素。结果表明:回头曲线路段的车辆行驶速度明显高于道路设计速度和限速值,超速行为非常普遍;上坡方向为“减速-加速”两阶段速度模式,与一般弯道存在差异;下坡方向为“减速-匀速-加速”三阶段速度模式;速度特征点分布位置受到视距、坡度和曲线偏角等因素的影响,且与常规假设存在一定差异;上坡回头曲线的速度谷值点位置主要分布于圆曲线前半段;下坡方向减速止点主要集中在缓和曲线-圆曲线连接点与圆曲线中点附近,加速起点主要分布于圆曲线和第二缓和曲线范围内;回头曲线下坡方向和上坡方向的入弯减速度85分位值分别为1.25和1.0 m/s2,下坡方向和上坡方向的出弯加速度85分位值分别为0.9和0.6 m/s2,即坡向和坡度对加(减)速度存在显著影响。最后,建立了回头曲线路段入弯、弯中和出弯阶段的运行速度模型,并进行了验证。本文研究成果可为艰险山区复杂线形公路的安全性评价以及安全改善提供理论支撑和基础数据支持。
中图分类号:
- U491.2
| 1 | 徐进, 陈莹, 张晓波, 等. 回头曲线路段的轨迹曲率特性和汽车过弯方式[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2021, 56(6): 1143-1152. |
| Xu Jin, Chen Ying, Zhang Xiao-bo, et al. Study on trajectory curvature characteristics and bending modes of backward-curve sections[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(6): 1143-1152. | |
| 2 | 徐进, 陈莹, 陈海源, 等. 回头曲线路段的轨迹行为模式与事故风险[J]. 东南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 50(5): 973-982. |
| Xu Jin, Chen Ying, Chen Hai-yuan, et al. Track behavior pattern and accident risk of backward-curve sections[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 50(5): 973-982. | |
| 3 | . 公路项目安全性评价规范 [S]. |
| 4 | 本刊综合. 2020年公路成绩怎么样—《2020年交通运输行业发展统计公报》解读[J]. 中国公路, 2021(12): 18-19. |
| The Synthesis of this Journal. What is the performance of highway in 2020—an interpretation of the statistical bulletin on the development of transportation industry in 2020[J]. China Highway, 2021(12): 18-19. | |
| 5 | Cruzado I, Donnell E T. Factors affecting driver speed choice along two-lane rural highway transition zones[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2010, 136(8): 733-764. |
| 6 | Himes S C, Donnell E T. Speed prediction models for multilane highway: simultaneous equations approach[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2010, 136(10): 836-862. |
| 7 | Gibreel G M, Easa S M, El-dimecry L A. Prediction of operating speed on three dimensional highway alignments[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2001, 127(1): 21-30. |
| 8 | Himes S, Porter R J, Hamilton I, et al. Safety evaluation of geometric design criteria: horizontal curve radius and side friction demand on rural two-lane highways[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2019, 2673(3): 516-525. |
| 9 | Sil G, Nama S, Maji A, et al. Modeling 85th percentile speed using spatially evaluated free-flow vehicles for consistency-based geometric design[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering Part A: Systems, 2020, 146(2): 1-12. |
| 10 | Kim S, Choi J. Effects of preceding geometric conditions on operating speed consistency of multilane highways[J]. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 2013, 40(6): 528-536. |
| 11 | 徐进,罗庆,毛嘉川,等. 考虑弯道几何要素和交通量影响的汽车行驶速度预测模型[J]. 中国公路学报, 2012, 23(3): 47-57. |
| Xu Jin, Luo Qing, Mao Jia-chuan, et al. A vehicle speed prediction model considering the influence of curve geometry and traffic volume[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2012, 23(3): 47-57. | |
| 12 | 徐进, 邵毅明, 赵军, 等. 山区道路弯坡组合路段重载车辆行驶速度模型[J]. 长安大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 33(2): 67-74. |
| Xu Jin, Shao Yi-ming, Zhao Jun, et al. Speed model of heavy vehicles on mountain road with curved slope[J]. Journal of Chang'an University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 33(2): 67-74. | |
| 13 | 郭腾峰, 刘建蓓, 汪双杰. 基于运行速度特征的公路平曲线设计半径推荐取值研究[J]. 中国公路学报,2010, 23(): 8-12. |
| Guo Teng-feng, Liu Jian-bei, Wang Shuang-jie. Track behavior pattern and accident risk of backward-curve sections[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2010, 23(Sup.2): 8-12. | |
| 14 | Echaveguren T, Henriquez C, Jimenez-Ramos G, et al. Longitudinal acceleration models for horizontal reverse curves of two-lane rural roads[J]. Baltic Journal of Road and Bridge Engineering, 2020, 15(1): 103-125. |
| 15 | Montella A, Galante F, Mauriello F, et al. Continuous speed profiles to investigate drivers' behavior on two-lane rural highways[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2015, 2521: 3-11. |
| 16 | Wen H, Eric T D. Models of acceleration and deceleration rates on a complex two-lane rural highway: Results from a nighttime driving experiment[J]. Transportation Research: Part F, 2010, 13(6): 397-408. |
| 17 | Dario B, Brijs T. Low-cost road marking measures for increasing safety in horizontal curves: a driving simulator study[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2021, 153: 1-10. |
| 18 | 徐进, 杨奎, 罗庆, 等. 公路客车横向加速度实验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2014, 49(3): 536-545. |
| Xu Jin, Yang Kui, Luo Qing, et al. Experimental study on lateral acceleration of highway bus[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(3): 536-545. | |
| 19 | Xu Jin, Lin Wei, Wang Xu, et al. Acceleration and deceleration calibration of operating speed prediction models for two-lane mountain highways[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering Part A: Systems, 2017, 143(7): 1-13. |
| 20 | 徐进, 李建兴, 林伟, 等. 螺旋匝道(桥)小客车横向行驶特性实测研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2019, 54(6): 1129-1138. |
| Xu Jin, Li Jian-xing, Lin Wei, et al. Experimental study on lateral driving characteristics of spiral ramp passenger car[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(6): 1129-1138. | |
| 21 | 徐进, 周佳, 汪旭, 等. 山区复杂线形公路小客车纵向加速度特性[J]. 中国公路学报,2017, 30(4): 115-126. |
| Xu Jin, Zhou Jia, Wang Xu, et al. Longitudinal acceleration characteristics of small buses on complex linear highway in mountainous areas[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(4): 115-126. | |
| 22 | 宋涛, 张永生, 郭彩香. 山区公路平曲线运行速度预测模型研究[J]. 交通运输工程与信息学报,2007, 5(1): 118-124. |
| Song Tao, Zhang Yong-sheng, Guo Cai-xiang. Study on prediction model of running speed of mountain highway flat curve[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2007, 5(1): 118-124. | |
| 23 | 王晓安, 李志中, 计斌, 等. 山区双车道公路平曲线路段运行速度预测模型研究[J]. 黑龙江交通科技,2015, 38(7): 4-6. |
| Wang Xiao-an, Li Zhi-zhong, Ji Bin, et al. Study on running speed prediction model of flat curve section of two-lane highway in mountainous area[J]. Heilongjiang Transportation Technology, 2015, 38(7): 4-6. | |
| 24 | Jacob A, Anjaneyulu M V L R. Operating speed of different classes of vehicles at horizontal curves on two-lane rural highways[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2013, 139(3): 287-294. |
| 25 | Abbas S, Adnan M A, Endut I R. Exploration of 85th percentile operating speed model on horizontal urve: a case study for two-lane rural highways[J]. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2011, 16: 352-363. |
| 26 | Shao Yi-ming, Xu Jin, Li Ben-wang, et al. Modeling the speed choice behaviors of drivers on mountainous roads with complicated shapes[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 7(2): No. 862610. |
| [1] | 张健,李青扬,李丹,姜夏,雷艳红,季亚平. 基于深度强化学习的自动驾驶车辆专用道汇入引导[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2508-2518. |
| [2] | 郑植,袁佩,金轩慧,魏思斯,耿波. 桥墩复合材料柔性防撞护舷试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2581-2590. |
| [3] | 李建华,王泽鼎. 考虑路径耗时的城市汽车分布式充电桩选点规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2298-2303. |
| [4] | 李洪涛,王琳虹,李俊达. 公路交叉口照明和限速对视觉搜索能力的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2287-2297. |
| [5] | 巫威眺,曾坤,周伟,李鹏,靳文舟. 基于多源数据和响应面优化的公交客流预测深度学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| [6] | 程国柱,盛林,赵浩,冯天军. 基于危险度分析的信号交叉口专用相位设置条件[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1962-1969. |
| [7] | 何永明,陈世升,冯佳,万亚楠. 基于高精地图的超高速公路虚拟轨道系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2016-2028. |
| [8] | 张雅丽,付锐,袁伟,郭应时. 考虑能耗的进出站驾驶风格分类及识别模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2029-2042. |
| [9] | 薛志佳,王召阳,张久鹏,晏长根,许子凯,张英立,黄晓明,马涛. 泥石流作用下道路结构韧性分析及提升[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1773-1781. |
| [10] | 刘振亮,赵存宝,吴云鹏,马迷娜,马龙双. 数据驱动的公路桥梁网络全寿命抗震韧性评估[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1695-1701. |
| [11] | 宋灿灿,荆迪菲,谢俊峰,康可心. 设置广告牌的高速公路平曲线路段驾驶行为分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1345-1354. |
| [12] | 贾洪飞,徐英俊,杨丽丽,王楠. 商品车多式联运联盟成员选择及利益分配[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1060-1069. |
| [13] | 孙超,尹浩为,汤文蕴,褚昭明. 交通需求估计下的检测器布局和手机数据扩样推断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1070-1077. |
| [14] | 常玉林,徐文倩,孙超,张鹏. 车联网环境下考虑遵从程度的混合流量逐日均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1085-1093. |
| [15] | 姚荣涵,徐文韬,郭伟伟. 基于因子长短期记忆的驾驶人接管行为及意图识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 758-771. |
|
||