吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (7): 2016-2028.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20210974
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于高精地图的超高速公路虚拟轨道系统
- 东北林业大学 交通学院,哈尔滨 150040
Superhighway virtual track system based on high precision map
Yong-ming HE( ),Shi-sheng CHEN,Jia FENG,Ya-nan WAN
),Shi-sheng CHEN,Jia FENG,Ya-nan WAN
- School of Traffic and Transportation,Northeast Forestry University,Harbin 150040,China
摘要:
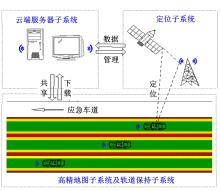
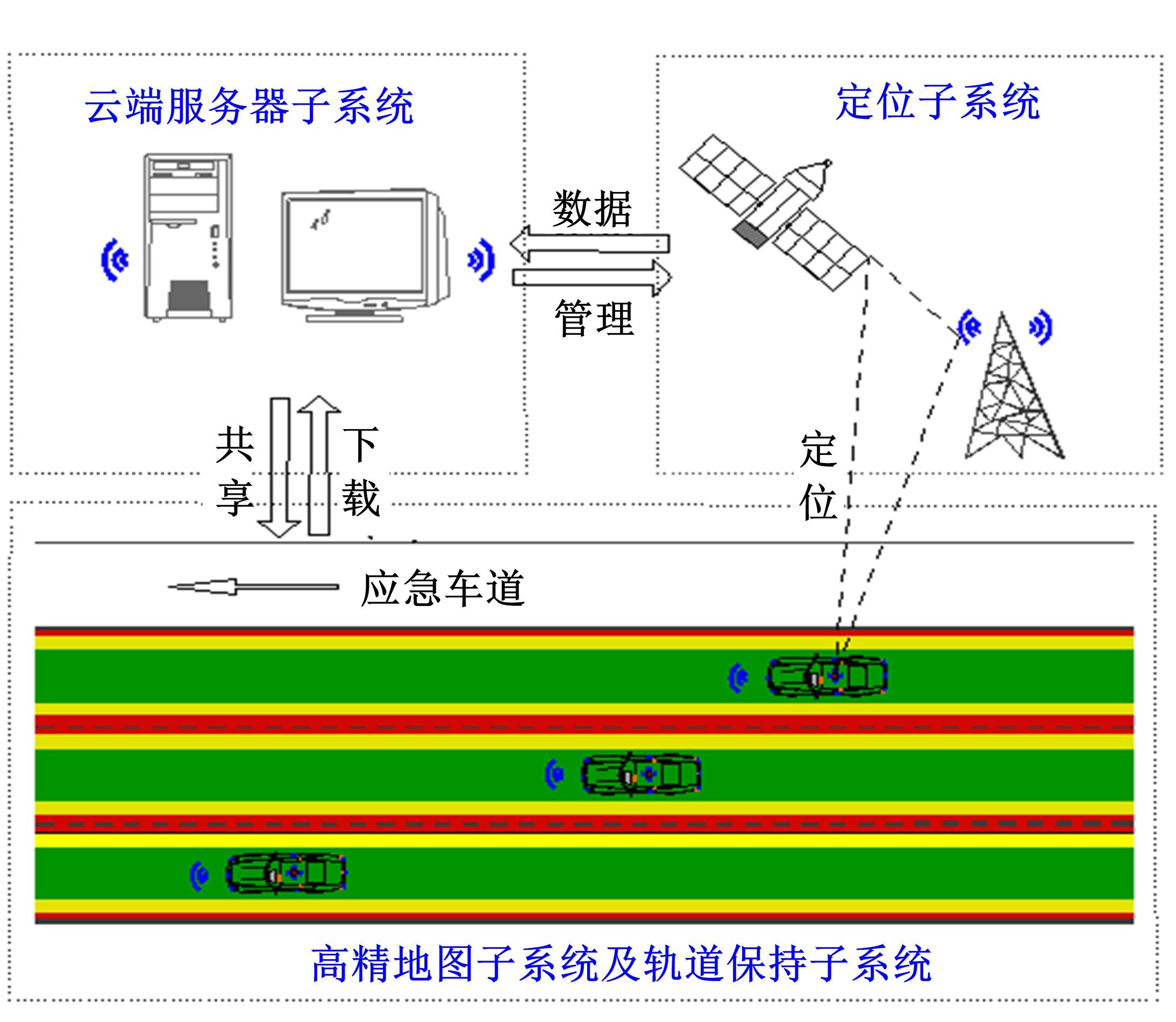
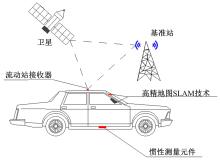
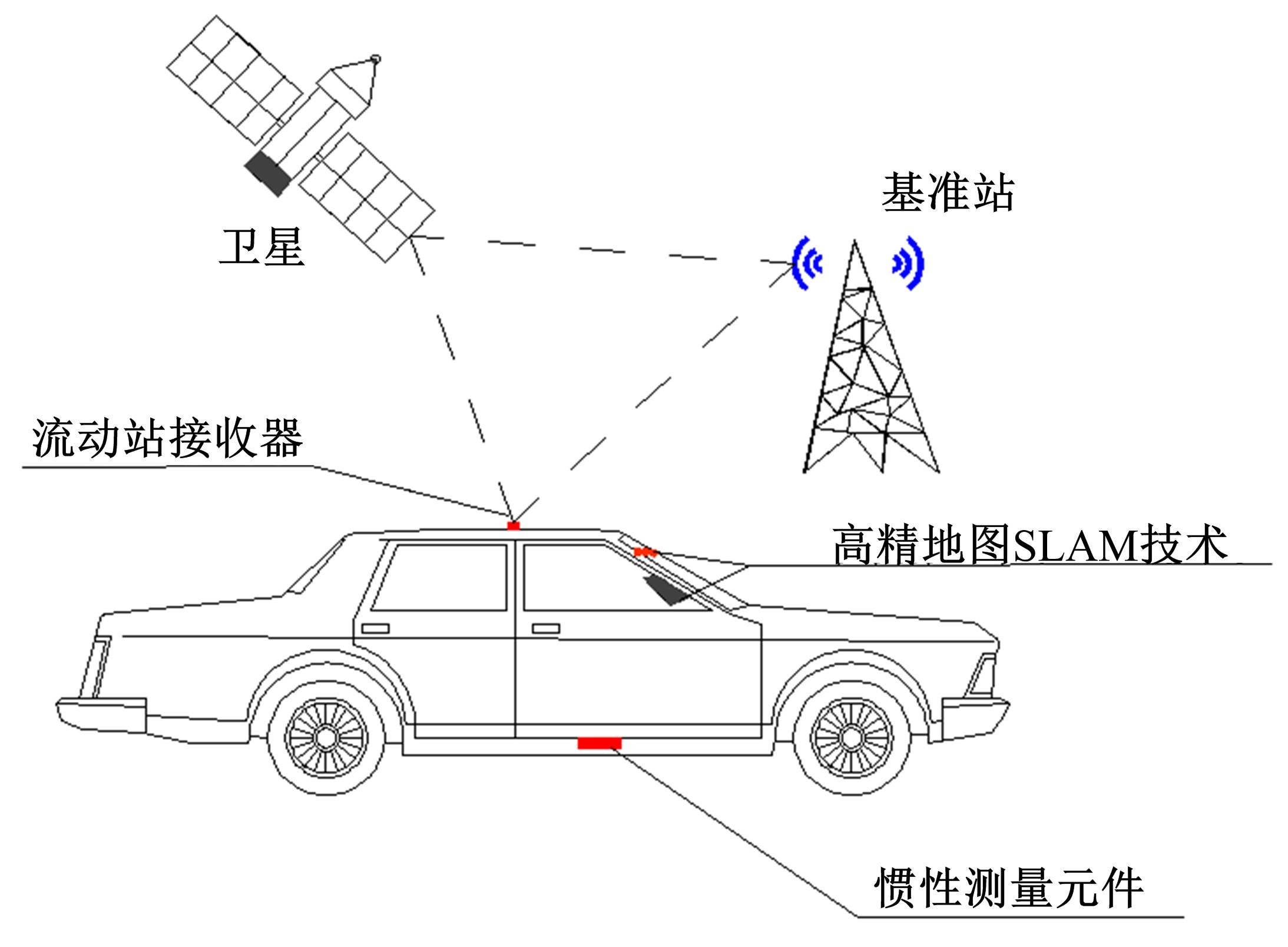
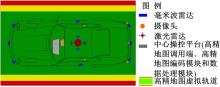
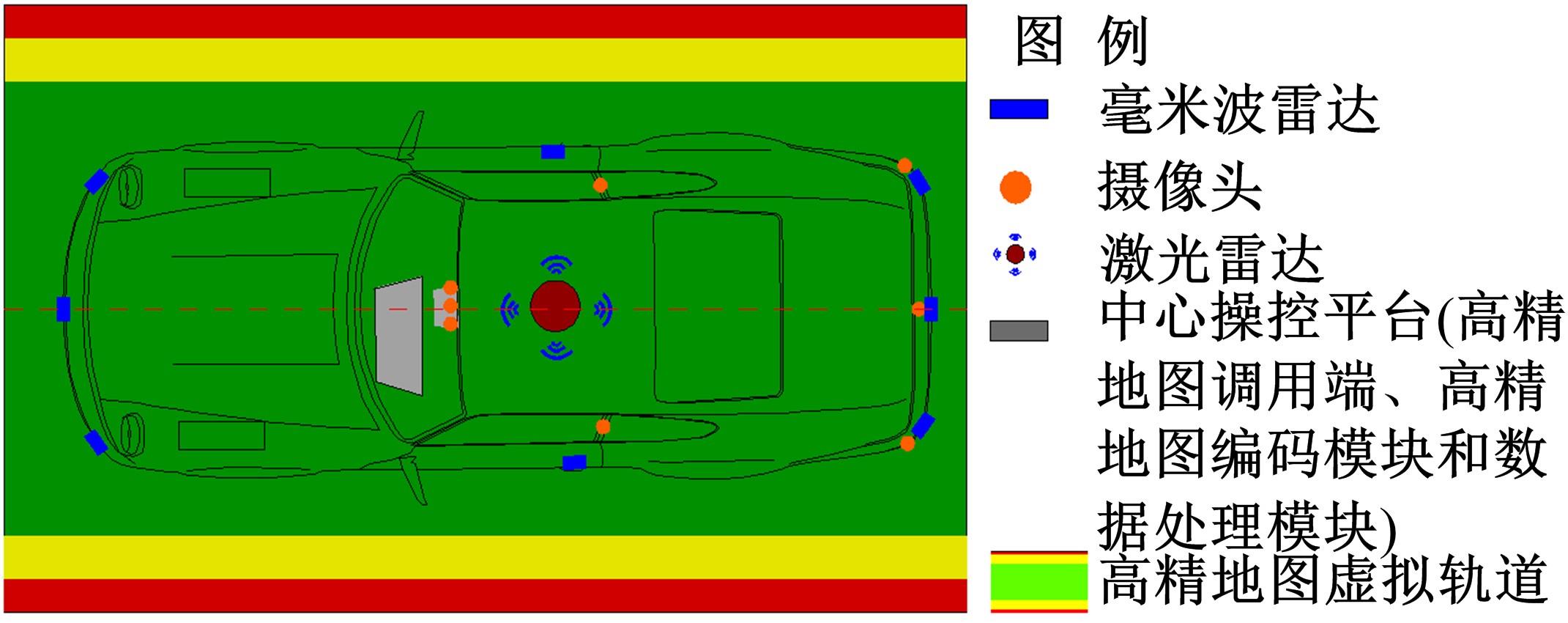
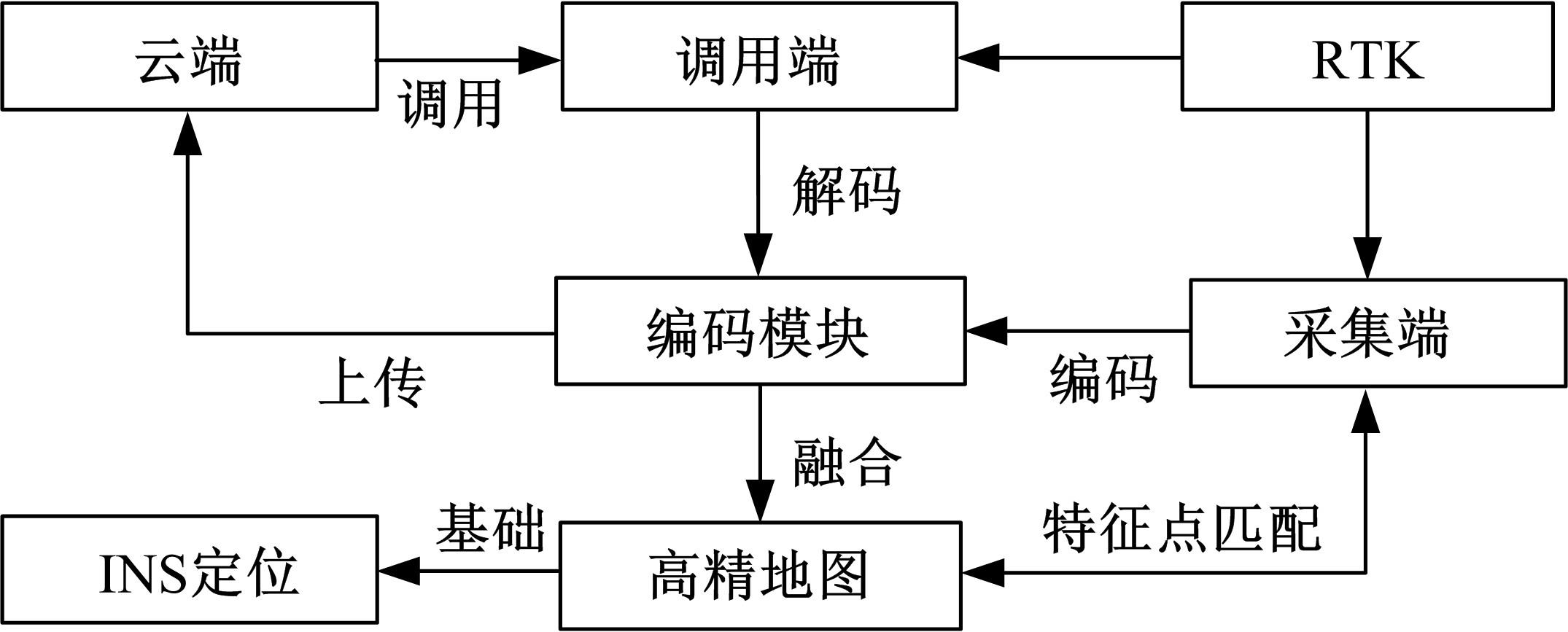
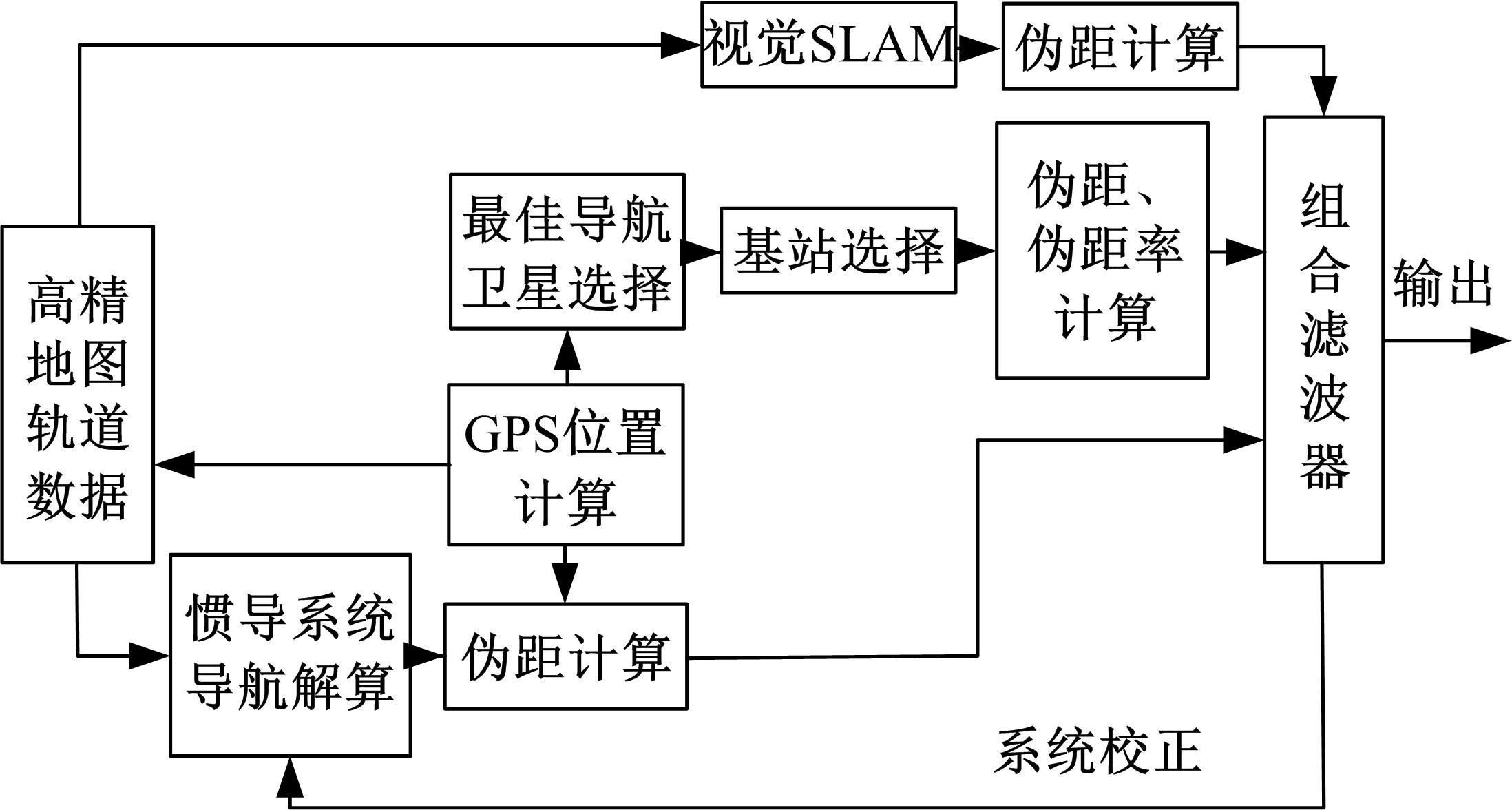
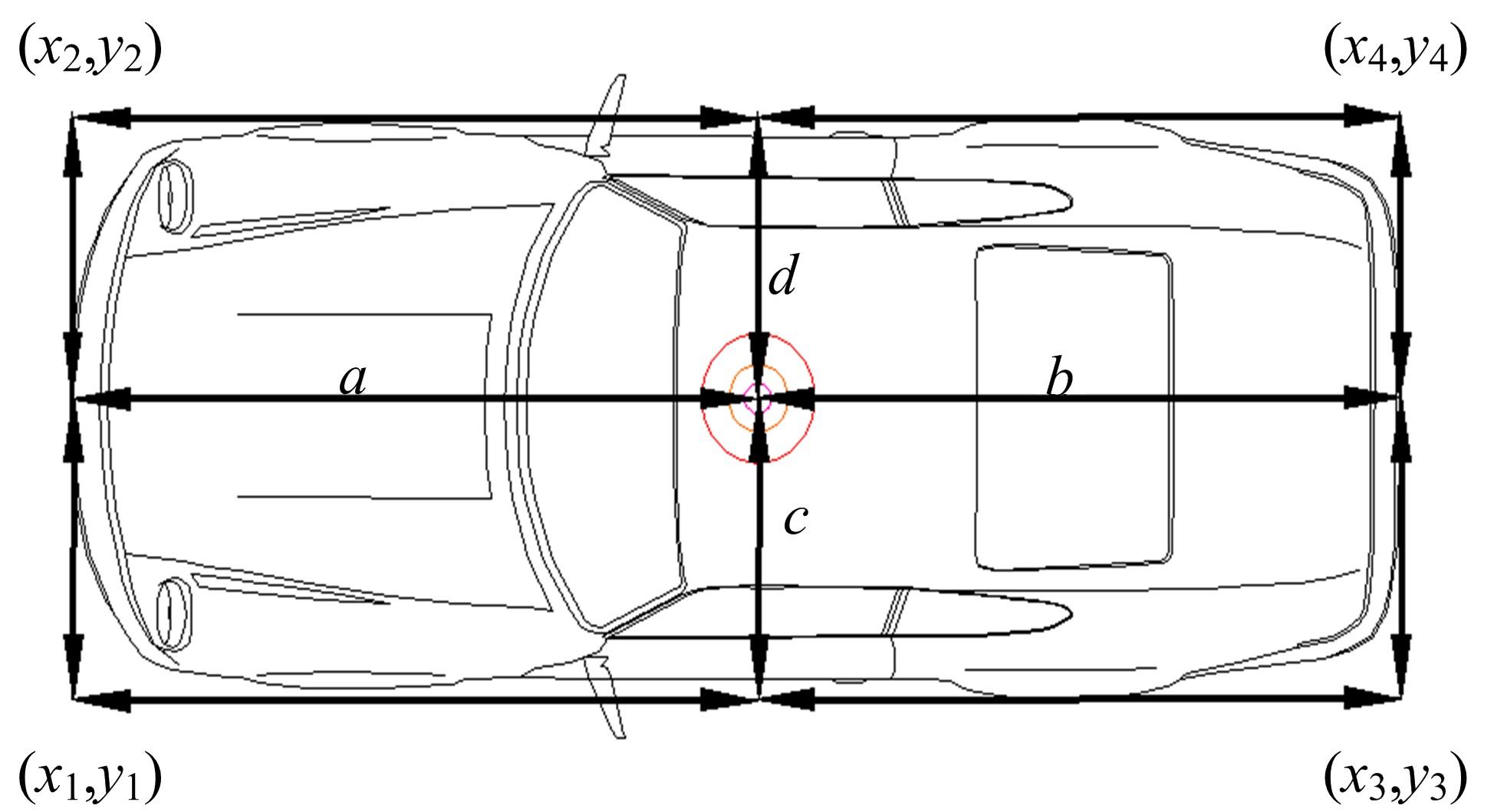
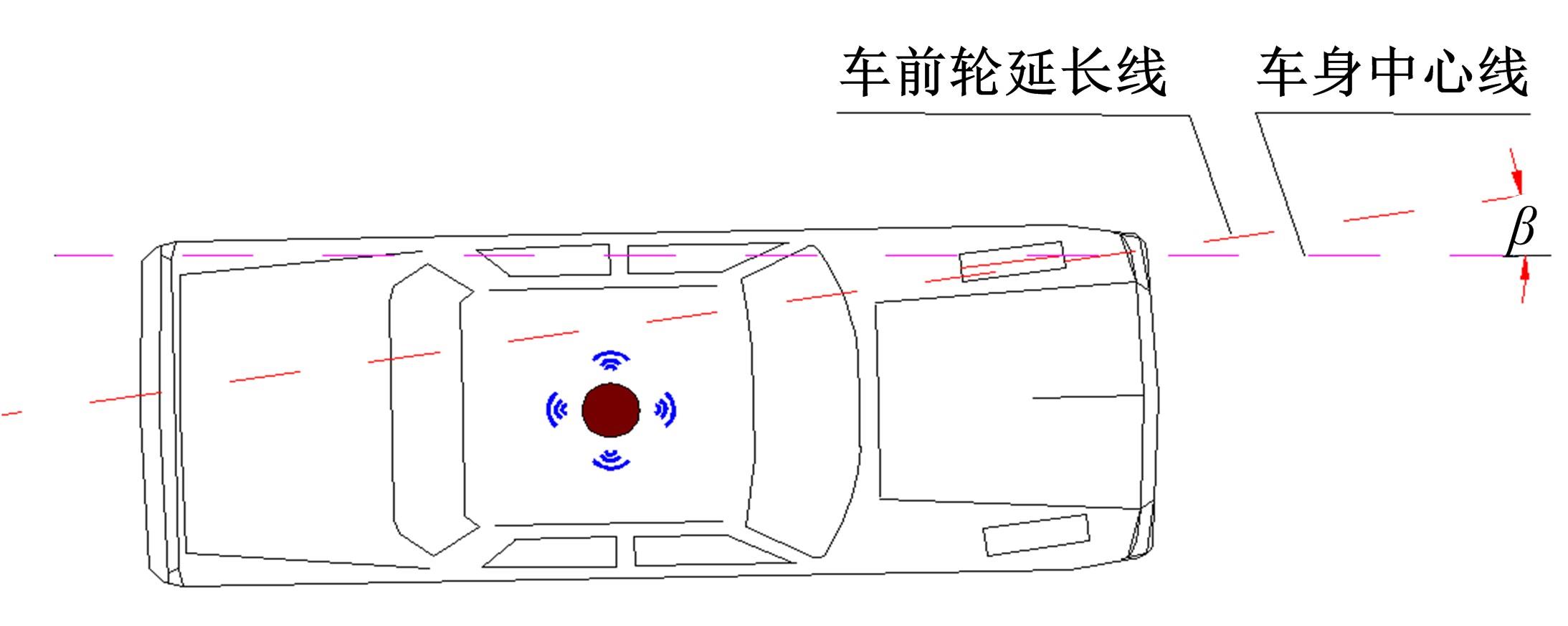
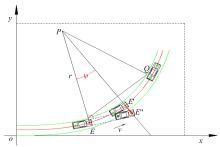
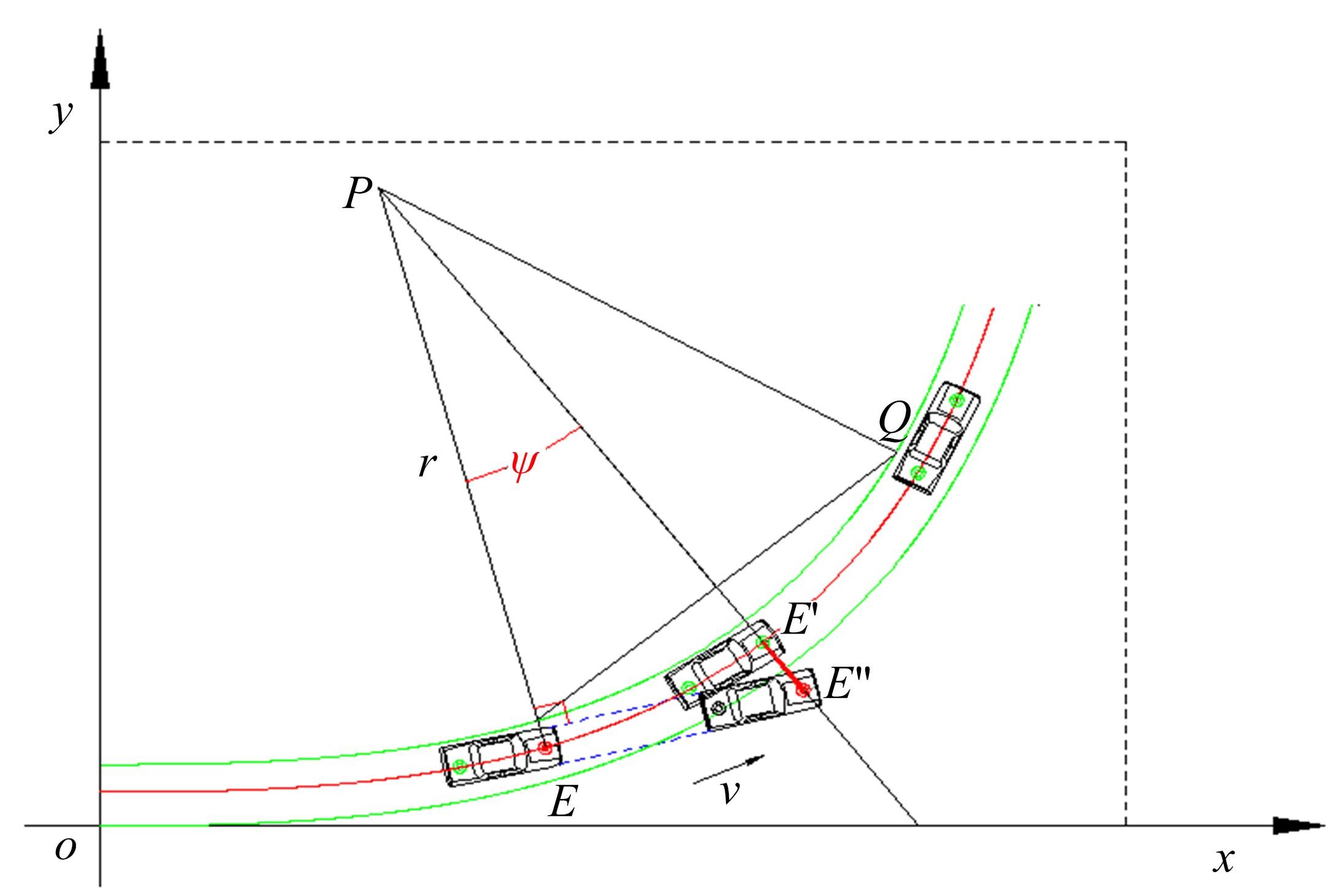
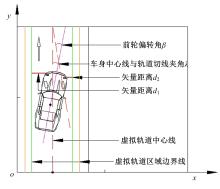
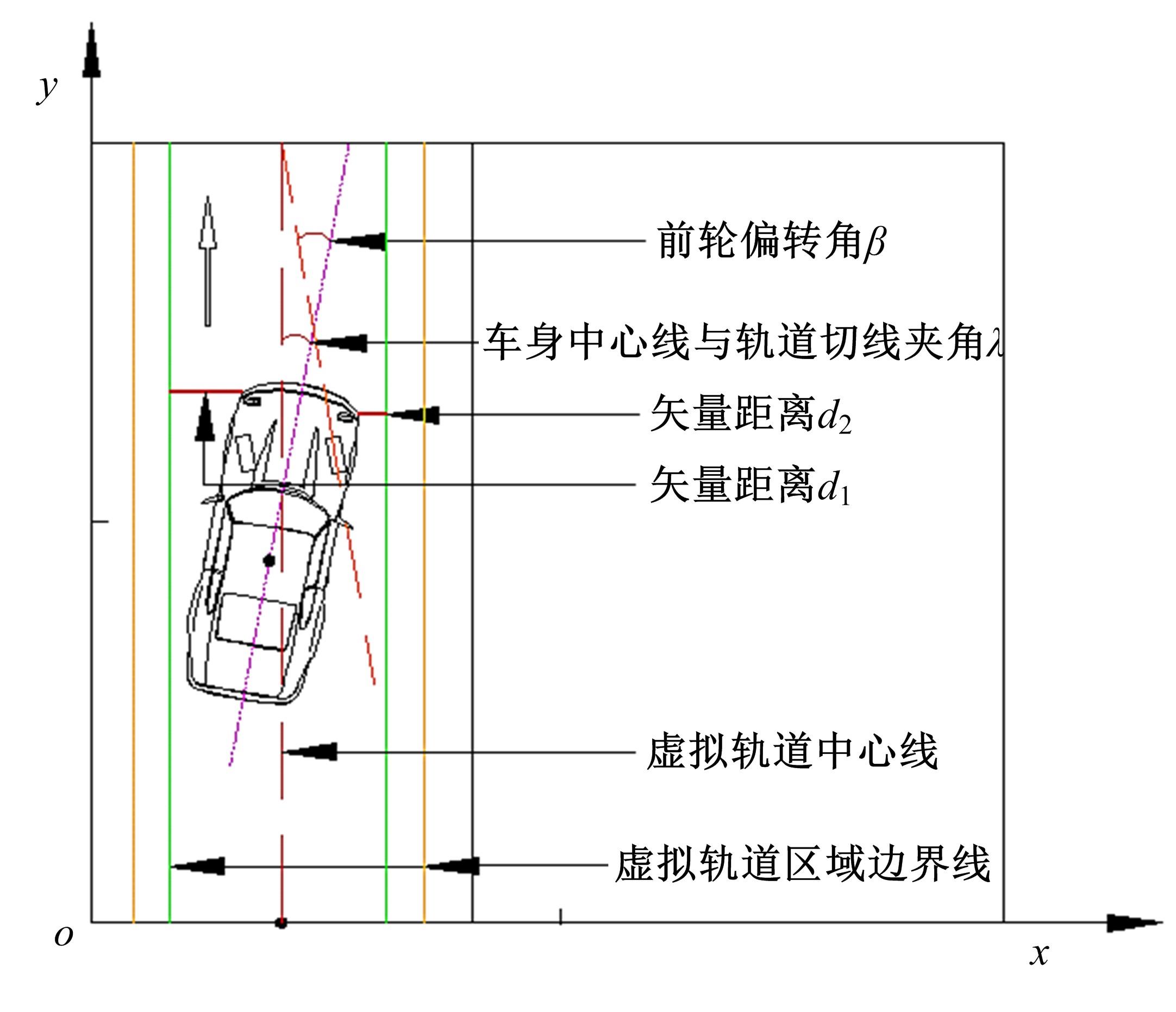
为提高车辆在超高速公路上行驶的安全性,建立了基于高精地图的超高速公路虚拟轨道系统模型,并对模型进行了分析验证。虚拟轨道系统由高精地图子系统、定位子系统、云端服务器子系统和轨道保持子系统组成。自动驾驶车辆在虚拟轨道上行驶时,车辆定位信息回传的频率影响车辆反应速度,以车辆不偏离虚拟轨道和换道安全为约束,计算得出最小定位回传频率。若车身中心线和轨道切线的夹角与前轮偏转角之和或横向偏移距离超过阈值,车辆可能偏离轨道,会触发轨道偏离预警系统,车辆则会以前轮最大安全偏转角度为参考修正的行驶轨迹。研究结果表明,车速分别为100、120、140、160、180 km/h时,系统定位回传频率保持在49、58、68、78、87 Hz以上就能够保证车辆在虚拟轨道内行驶。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | 何永明, 裴玉龙. 超高速公路发展可行性论证与必要性研究[J]. 公路, 2016, 61(1): 158-162. |
| He Yong-ming, Pei Yu-long. Feasibility demonstration and necessity analysis on superhighway[J]. Highway, 2016, 61(1): 158-162. | |
| 2 | 蒋勇, 马广才, 刁仁群. 浅谈高速公路限速问题[J]. 交通标准化, 2006 (12): 124-127. |
| Jiang Yong, Ma Guang-cai, Diao Ren-qun. Discussion on speed limitation of freeway[J]. Communications Standardization, 2006 (12): 124-127. | |
| 3 | 王涛, 陈艳丽, 贾双成. 简述高精地图的特点[J]. 软件, 2018, 39(9): 183-187. |
| Wang Tao, Chen Yan-li, Jia Shuang-cheng. Brief description of the characteristics of high precision map[J]. Computer Engineering & Software, 2018, 39(9): 183-187. | |
| 4 | 侯凯文. 基于虚拟轨道的自动驾驶车辆管控方法和系统研究[D]. 北京:北京交通大学交通运输学院, 2020. |
| Hou Kai-wen. Research on method and system of management and control for autonomous vehicles based on virtual track[D]. Beijing: School of Traffic and Transportation, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2020. | |
| 5 | 李运舵, 车进, 薛澄. 一种点线特征匹配的实时定位及地图重建方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2022,59(2):No.0210003. |
| Li Yun-duo, Che Jin, Xue Cheng. A method of simultaneous localization and mapping based on point and line feature matching[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress,2022,59(2):No.0210003. | |
| 6 | 何永明. 超高速公路安全保障与经济评价研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学交通学院, 2017. |
| He Yong-ming. Research safety support and economy evalution of superhighway[D]. Harbin: School of Traffic and Transportation, Northeast Foresty University, 2017. | |
| 7 | 何永明, 裴玉龙. 基于出行费用的超高速公路经济性评价[J]. 公路, 2018, 63(1): 117-123. |
| He Yong-ming, Pei Yu-long. Economic evaluation of superhighway based on travel cost[J]. Highway, 2018, 63(1): 117-123. | |
| 8 | 何永明, 裴玉龙, 冉斌. 基于智能路钮的超高速公路虚拟轨道系统研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2020, 20(2): 55-60, 75. |
| He Yong-ming, Pei Yu-long, Ran Bin. Superhighway virtual track system based on intelligent road Button [J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020, 20(2): 55-60, 75. | |
| 9 | Liu J, Zhan J, Guo C, et al. Data logic structure and key technologies on intelligent high-precision map[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geoinformation Science, 2020, 3(3): 1-17. |
| 10 | 王冕. 面向自动驾驶的高精度地图及其应用方法[J]. 地理信息世界, 2020, 27(4): 109-114. |
| Wang Mian. High definition map for autonomous driving: overview and analysis[J]. Geomatics World, 2020, 27(4): 109-114. | |
| 11 | 訾璐, 张江水, 杨振凯, 等. 高精地图交通要素对象化建模方法[J]. 测绘科学技术学报, 2020, 37(6): 636-642. |
| Zi Lu, Zhang Jiang-shui, Yang Zhen-kai, et al. Object modeling method of traffic elements in high-precision map[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2020, 37(6): 636-642. | |
| 12 | 张宁, 马文双. 自动驾驶对于高精地图的技术需求分析[J]. 物流技术与应用, 2020, 25(1): 135-137. |
| Zhang Ning, Ma Wen-shuang. Analysis on technical requirements of automatic driving for high-precision map[J]. Logistics & Material Handling, 2020, 25(1): 135-137. | |
| 13 | 张进明, 孙灿, 刘兆丹, 等. 智能网联汽车高精地图技术指标及标准化需求研究[J]. 中国汽车, 2019 (10): 49-52. |
| Zhang Jin-ming, Sun Can, Liu Zhao-dan, et al. Intelligent and connected vehicle high precision map technologyindicator and standardization requirement research[J]. China Auto, 2019(10): 49-52. | |
| 14 | 陈萌, 黄旭. 日本自动驾驶产业发展现状分析[J]. 智能网联汽车, 2019(5): 60-65. |
| Chen Meng, Huang Xu. Analysis on the development status of automatic driving industry in Japan[J]. Intelligent Connected Vehicles, 2019(5): 60-65. | |
| 15 | 尹彤, 黄鹤, 郭迟, 等. 面向自动驾驶的高精地图生产技术及数据模型标准化探讨[J]. 中国标准化, 2021(4): 33-37. |
| Yin Tong, Huang He, Guo Chi, et al. Discussion on high-definition map production technology and data model standardization for autonomous driving[J]. China Standardization, 2021(4): 33-37. | |
| 16 | 梁宗正, 童杨. 高精度地图国内外发展现状及对策[J]. 科技中国, 2021(1): 13-16. |
| Liang Zong-zheng, Tong Yang. Development status and countermeasures of high-precision map at home and abroad[J]. Science and Technology of China, 2021(1): 13-16. | |
| 17 | 徐伟. 超级虚拟轨道快运系统(SRT)特点和适应性分析——以盐城市为例 [J]. 工程技术研究, 2021, 6(5): 40-41, 57. |
| Xu Wei. Characteristics and adaptability analysis of super virtual rail express system (SRT) -- a case study of Yancheng City[J]. Engineering and Technological Research, 2021, 6(5): 40-41, 57. | |
| 18 | 薄纯玉. 中国中车成功研发全球首列虚拟轨道列车[J] . 城市轨道交通, 2017(2): 38-39. |
| Bo Chuan-yu. CRRC successfully developed the world's first virtual rail train[J]. China Metros, 2017(2): 38-39. | |
| 19 | 罗毅. 城市新型轨道交通发展的适应性研究——以四川省宜宾市为例[J]. 城市管理与科技, 2019, 21(2): 38-41. |
| Luo Yi. Study on the adaptability of urban new rail transit development -- a case study of Yibin City, Sichuan Province[J]. Urban Management and Science & Technology, 2019, 21(2):38-41. | |
| 20 | 韩鹏. 基于虚拟轨道的自导向有轨电车控制策略研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学牵引动力国家重点实验室, 2017. |
| Han Peng. The comtrol strategy of self-guiding tramcar based on virtual track[D]. Chengdu:State Key Laboratory of Traction Power of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017. | |
| 21 | 刘建平, 郑阳, 郑望晓. 高精度地图的应用和更新方案[J]. 汽车实用技术, 2021, 46(12): 27-29. |
| Liu Jian-ping, Zheng Yang, Zheng Wang-xiao. Application and update solution of high definition map[J]. Automobile Applyied Technology, 2021, 46(12): 27-29. | |
| 22 | 姚可星. 高精度GNSS载波相位差分定位技术[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学机电工程学院, 2020. |
| Yao Ke-xing. GNSS high precision real time kinematic positioning technology[D]. Guangzhou: School of Electromechanical Engineering, Guangdong University of Technology, 2020. | |
| 23 | 郭楠. 基于GNSS/IMU的行人组合导航定位技术研究[D]. 北京:北京建筑大学测绘与城市空间信息学院, 2021. |
| Guo Nan. Research on pedestrian integrated navigation and positioning technology based on GNSS/IMU[D]. Beijing: School of Geomatics and Urban Upatial Informatics, Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 2021. |
| [1] | 巫威眺,曾坤,周伟,李鹏,靳文舟. 基于多源数据和响应面优化的公交客流预测深度学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| [2] | 程国柱,盛林,赵浩,冯天军. 基于危险度分析的信号交叉口专用相位设置条件[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1962-1969. |
| [3] | 常玉林,徐文倩,孙超,张鹏. 车联网环境下考虑遵从程度的混合流量逐日均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1085-1093. |
| [4] | 孙超,尹浩为,汤文蕴,褚昭明. 交通需求估计下的检测器布局和手机数据扩样推断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1070-1077. |
| [5] | 贾洪飞,徐英俊,杨丽丽,王楠. 商品车多式联运联盟成员选择及利益分配[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1060-1069. |
| [6] | 朱冰,范天昕,赵健,张培兴,孙宇航. 基于危险边界搜索的自动驾驶系统加速测试方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 704-712. |
| [7] | 肖雪,李克平,彭博,昌满玮. 基于决策-规划迭代框架的智驾车换道行为建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 746-757. |
| [8] | 何科,丁海涛,赖宣淇,许男,郭孔辉. 基于Transformer的轮式里程计误差预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 653-662. |
| [9] | 刘嫣然,孟庆瑜,郭洪艳,李嘉霖. 图注意力模式下融合高精地图的周车轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 792-801. |
| [10] | 姚荣涵,徐文韬,郭伟伟. 基于因子长短期记忆的驾驶人接管行为及意图识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 758-771. |
| [11] | 陶博,颜伏伍,尹智帅,武冬梅. 基于高精度地图增强的三维目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 802-809. |
| [12] | 王菁,万峰,董春娇,邵春福. 城市轨道交通站点吸引范围及强度建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 439-447. |
| [13] | 马敏,胡大伟,舒兰,马壮林. 城市轨道交通网络韧性评估及恢复策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 396-404. |
| [14] | 方松,马健霄,李根,沈玲宏,徐楚博. 城市快速路右侧车道移动作业区行车风险分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1786-1791. |
| [15] | 宋现敏,杨舒天,刘明鑫,李志慧. 站点间公交行程时间波动特性及预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1792-1799. |
|
||