吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 1085-1093.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20210843
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
车联网环境下考虑遵从程度的混合流量逐日均衡
- 1.江苏大学 汽车与交通工程学院,江苏 镇江 212013
2.东南大学 城市智能交通江苏省重点实验室,南京 211189
Day⁃to⁃day equilibrium of hybrid traffic considering obedience degree under internet of vehicles environment
Yu-lin CHANG1,2( ),Wen-qian XU1,Chao SUN1(
),Wen-qian XU1,Chao SUN1( ),Peng ZHANG1
),Peng ZHANG1
- 1.School of Automobile and Traffic Engineering,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang 212013,China
2.Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Intelligent Traffic System,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
摘要:
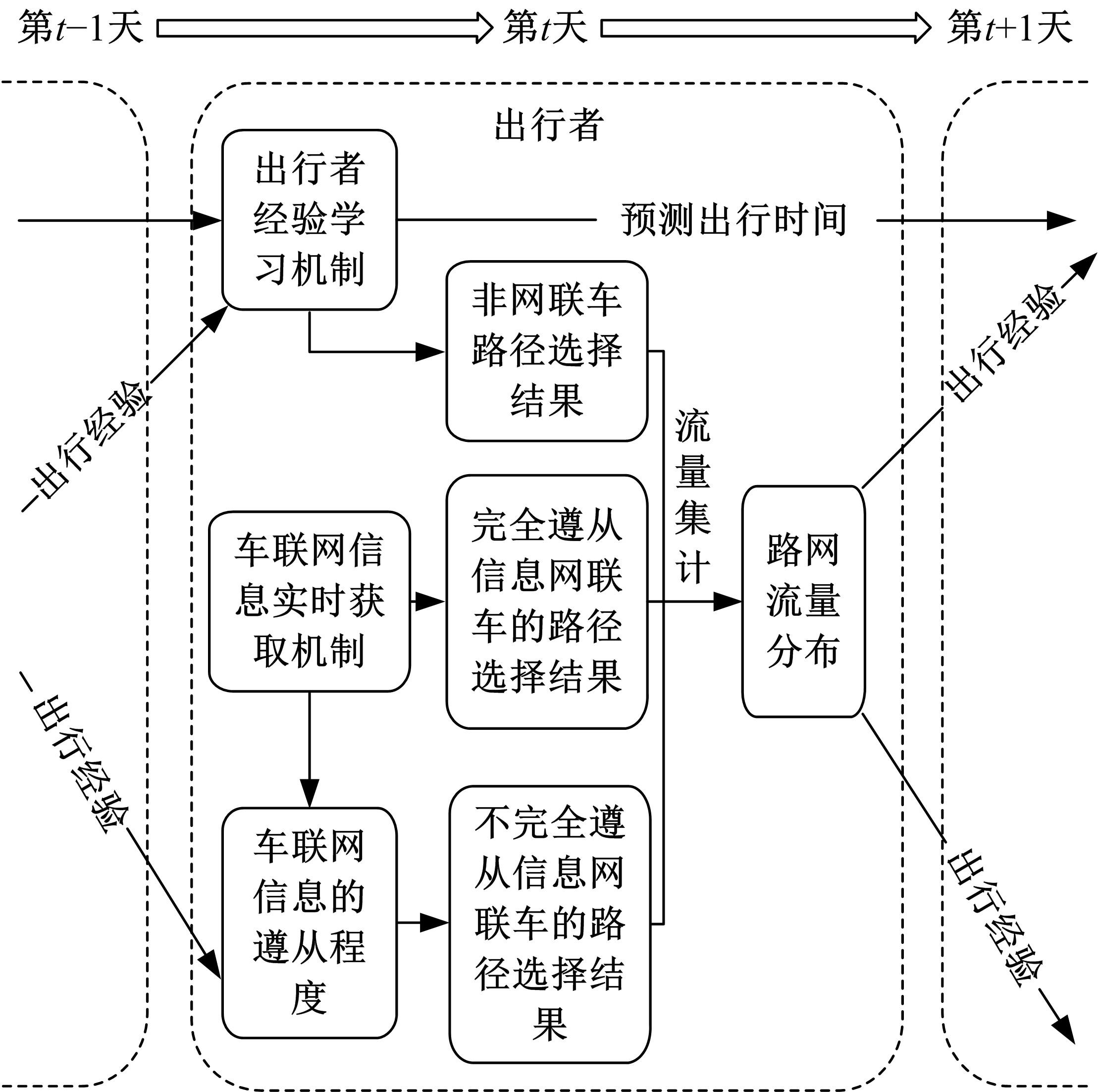
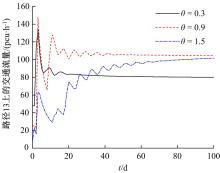
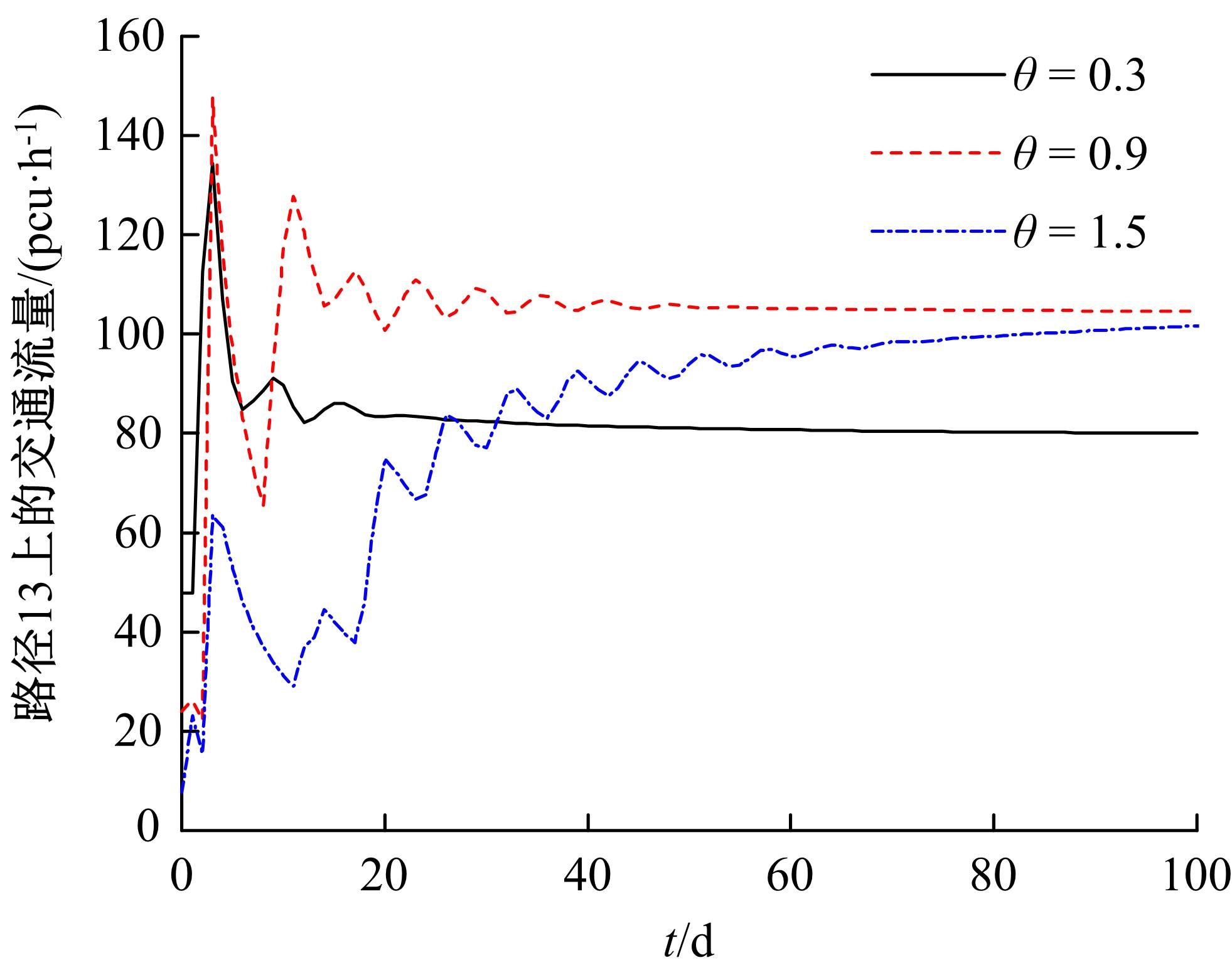
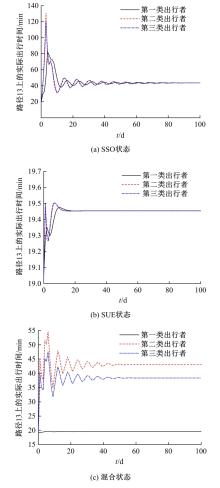
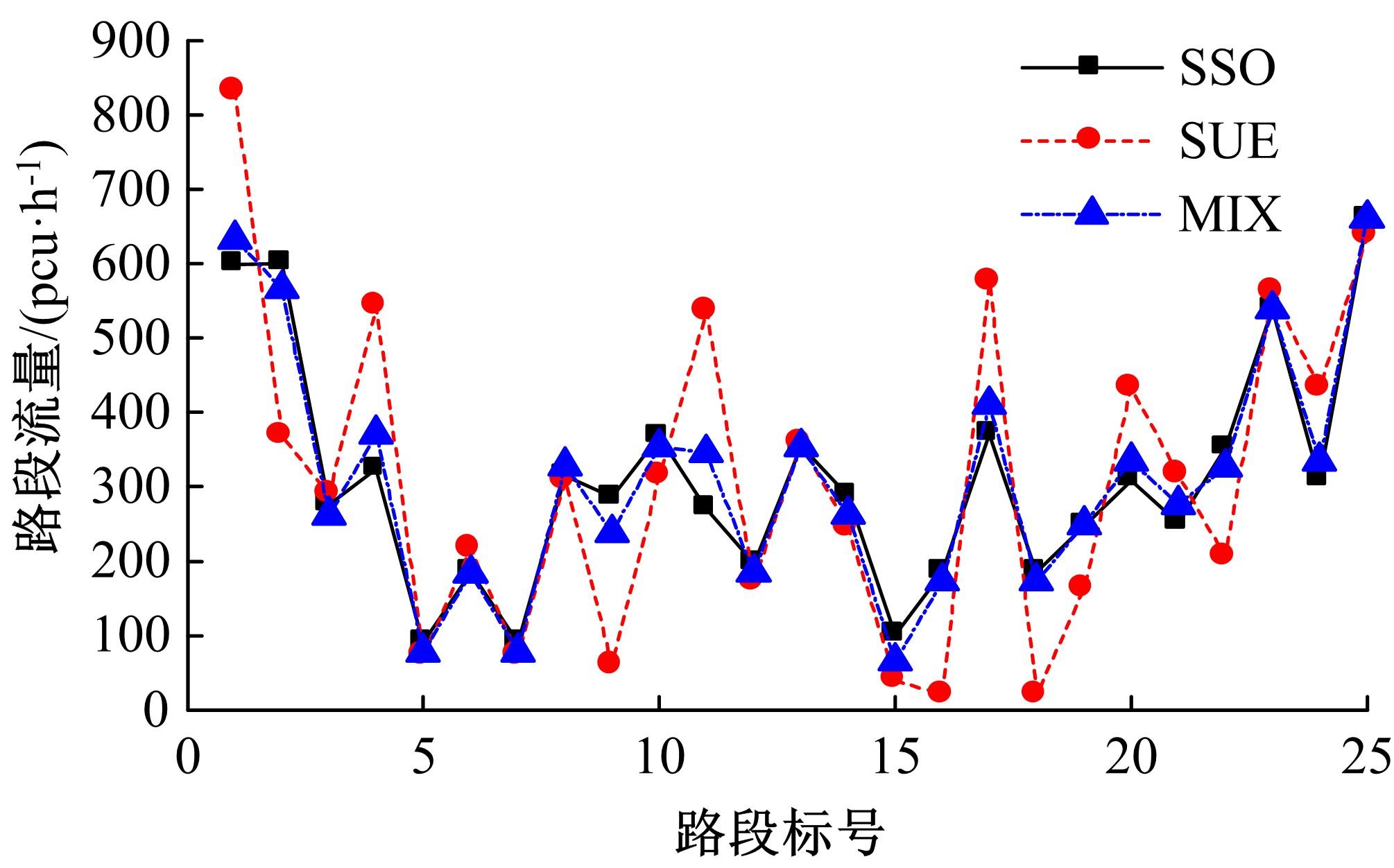
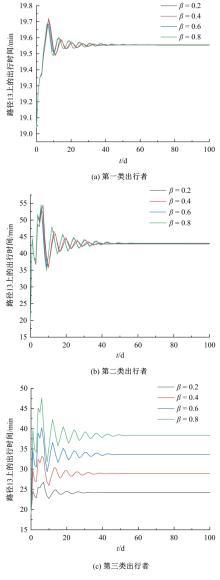
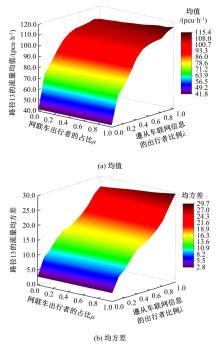
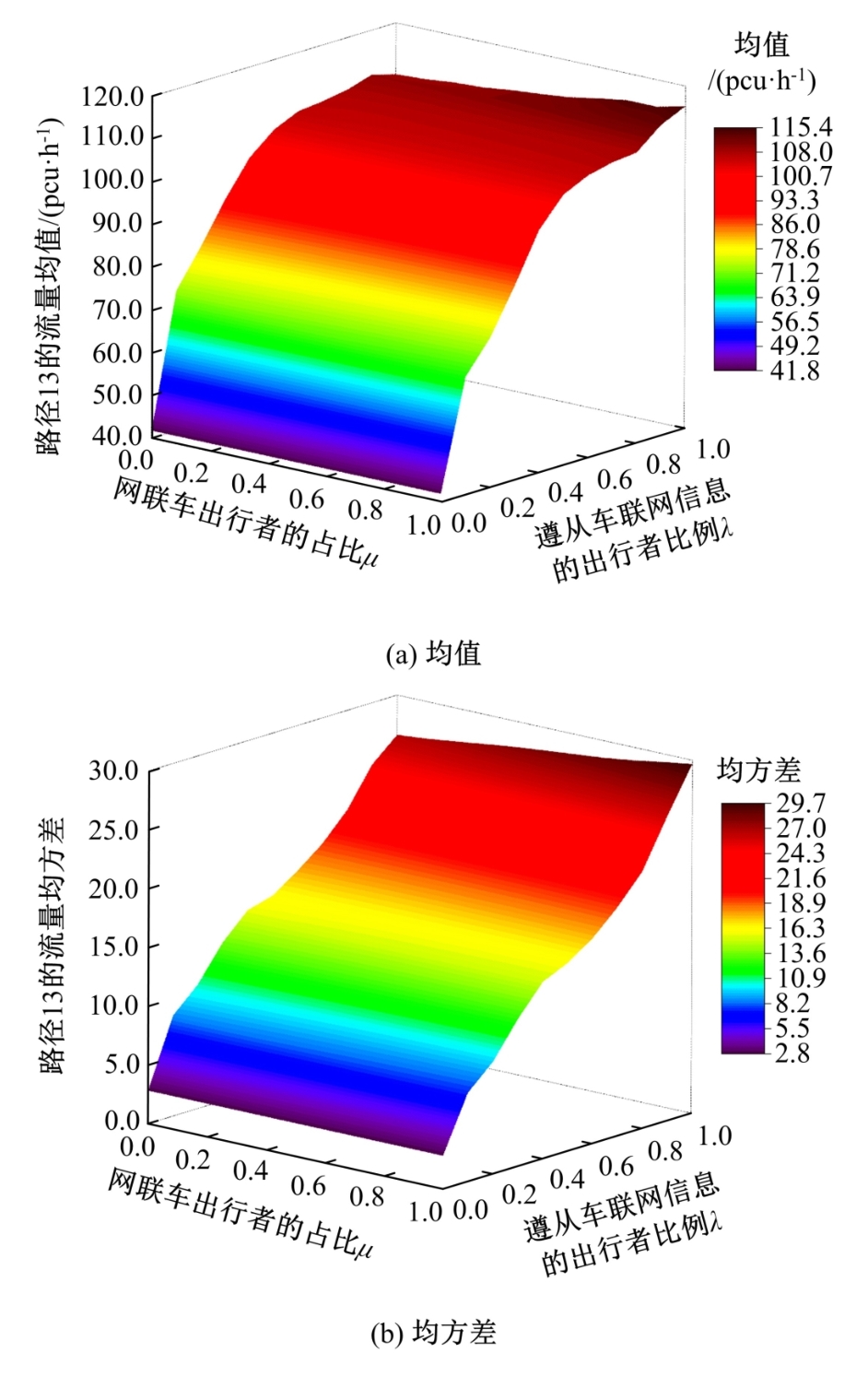
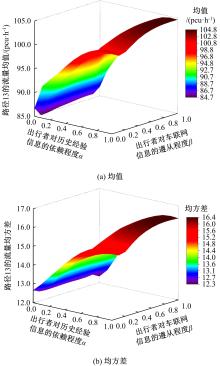
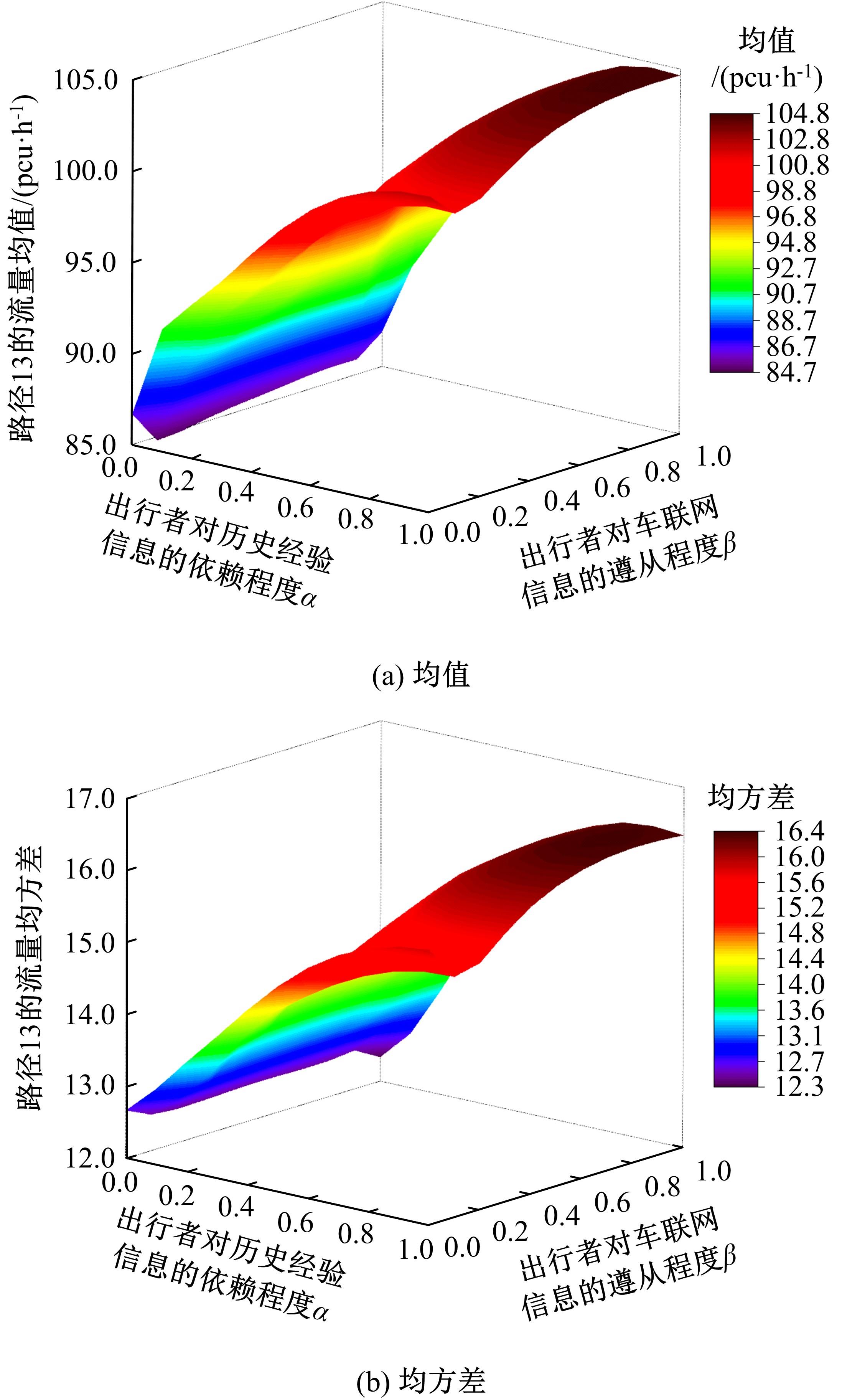
为研究网联车与非网联车混合交通中出行者的路径选择行为,根据出行者是否为网联车用户以及对车联网信息的遵从程度将出行者分为非网联车出行者、完全遵从信息的网联车出行者和不完全遵从信息的网联车出行者。三类出行者分别按照历史经验信息、车联网实时信息以及前两种信息的结合来更新出行路径,进一步运用交通网络理论建立考虑车联网信息遵从程度的混合逐日演化模型。通过算例发现,混合出行流量均衡状态下的路网稳定性优于随机用户均衡(SUE)均衡状态下的路网稳定性,同时出行者的出行时间到达稳定的天数短于随机系统最优(SSO)均衡状态下出行时间到达稳定的天数。遵从车联网信息出行者占比和网联车出行者对车联网信息的遵从程度是网络流量演变的主要影响因素。模型最终演化至SUE和SSO的混合均衡状态。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | Cascetta E, Cantarella G E. A day-to-day and within-day dynamic stochastic assignment model[J]. Transportation Research Part A: General, 1991,25(5): 277-291. |
| 2 | Iryo T. Day-to-day dynamical model incorporating an explicit description of individuals' information collection behaviour[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2016, 92(A): 88-103. |
| 3 | 尹子坤, 关宏志, 李涛. 逐日路径演化中出行者信息偏好的实验分析[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2017, 17(4): 234-240. |
| Yin Zi-kun, Guan Hong-zhi, Li Tao. Experimental analysis of diver's information preference under day-to-day traffic dynamics[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2017, 17(4): 234-240. | |
| 4 | Peque G, Miyagi T, Kurauchi F. Adaptive learning algorithms for simulation-based dynamic traffic user equilibrium[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems Research, 2018, 16(3): 215-226. |
| 5 | Yang Y, Ke H, Ochieng W. Day-to-day dynamic traffic assignment with imperfect information, bounded rationality and information sharing[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2020, 114: 59-83. |
| 6 | Bagloee S A, Sarvi M, Patriksson M, et al. A mixed user-equilibrium and system-optimal traffic flow for connected vehicles stated as a complementarity problem[J]. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2017, 32(7): 562-580. |
| 7 | Lou X M, Cheng L, Chu Z M. Modelling travellers' en-route path switching in a day-to-day dynamical system[J]. Transportmetrica B: Transport Dynamics, 2017, 5(1): 15-37. |
| 8 | Zhou B J, Xu M, Meng Q, et al. A day-to-day route flow evolution process towards the mixed equilibria[J]. Transportation Research Part C, 2017, 82: 210-228. |
| 9 | 黄中祥, 陈思臣. 考虑服从率的道路网络交通流逐日演化博弈模型[J]. 长沙理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 17(1): 8-15. |
| Huang Zhong-xiang, Chen Si-chen. Day-to-day evolutionary game model of road network traffic flow considering traveler's compliant rate[J]. Journal of Changsha University of Science and Technology(Natural Science), 2020, 17(1): 8-15. |
| [1] | 孙超,尹浩为,汤文蕴,褚昭明. 交通需求估计下的检测器布局和手机数据扩样推断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1070-1077. |
| [2] | 贾洪飞,徐英俊,杨丽丽,王楠. 商品车多式联运联盟成员选择及利益分配[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1060-1069. |
| [3] | 肖雪,李克平,彭博,昌满玮. 基于决策-规划迭代框架的智驾车换道行为建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 746-757. |
| [4] | 姚荣涵,徐文韬,郭伟伟. 基于因子长短期记忆的驾驶人接管行为及意图识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 758-771. |
| [5] | 王菁,万峰,董春娇,邵春福. 城市轨道交通站点吸引范围及强度建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 439-447. |
| [6] | 马敏,胡大伟,舒兰,马壮林. 城市轨道交通网络韧性评估及恢复策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 396-404. |
| [7] | 方松,马健霄,李根,沈玲宏,徐楚博. 城市快速路右侧车道移动作业区行车风险分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1786-1791. |
| [8] | 宋现敏,杨舒天,刘明鑫,李志慧. 站点间公交行程时间波动特性及预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1792-1799. |
| [9] | 张玮,张树培,罗崇恩,张生,王国林. 智能汽车紧急工况避撞轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1515-1523. |
| [10] | 郑植,耿波,王福敏,董俊宏,魏思斯. 既有低等级混凝土护栏防护能力提升[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1362-1374. |
| [11] | 吴文静,战勇斌,杨丽丽,陈润超. 考虑安全间距的合流区可变限速协调控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1315-1323. |
| [12] | 徐洪峰,陈虹瑾,张栋,陆千惠,安娜,耿现彩. 面向网联汽车环境的单点全感应式信号配时技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1324-1336. |
| [13] | 盖松雪,曾小清,岳晓园,袁子豪. 基于用户-系统双层优化算法的车位引导模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1344-1352. |
| [14] | 李先通,全威,王华,孙鹏程,安鹏进,满永兴. 基于时空特征深度学习模型的路径行程时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [15] | 冯天军,孙学路,黄家盛,田秀娟,宋现敏. 基于三种过街方式的两相位信号交叉口延误[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 550-556. |
|
||