吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (7): 2001-2015.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20210935
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
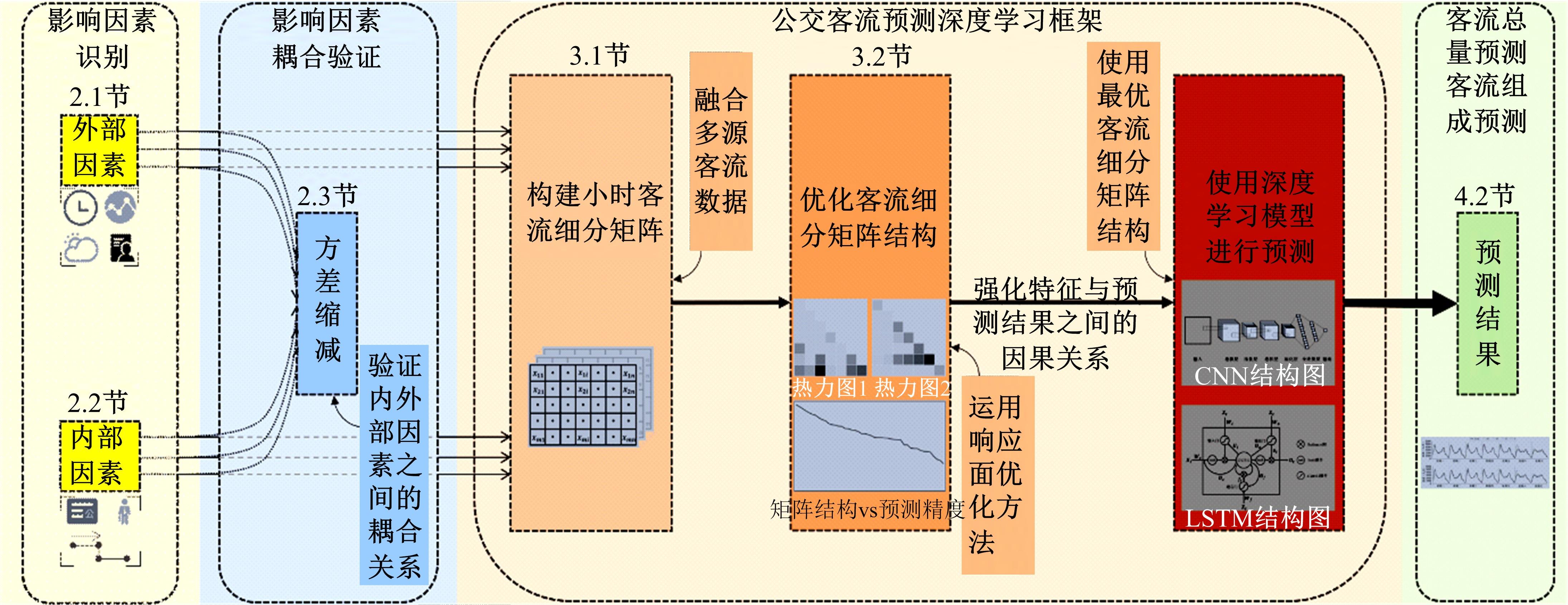
基于多源数据和响应面优化的公交客流预测深度学习方法
- 1.华南理工大学 土木与交通学院,广州 510641
2.深圳职业技术学院 汽车与交通学院,广东 深圳 518055
Deep learning method for bus passenger flow prediction based on multi-source data and surrogate-based optimization
Wei-tiao WU1( ),Kun ZENG1,Wei ZHOU1,Peng LI2(
),Kun ZENG1,Wei ZHOU1,Peng LI2( ),Wen-zhou JIN1
),Wen-zhou JIN1
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510641,China
2.School of Automotive and Transportation Engineering,Shenzhen Polytechnic,Shenzhen 518055,China
摘要:
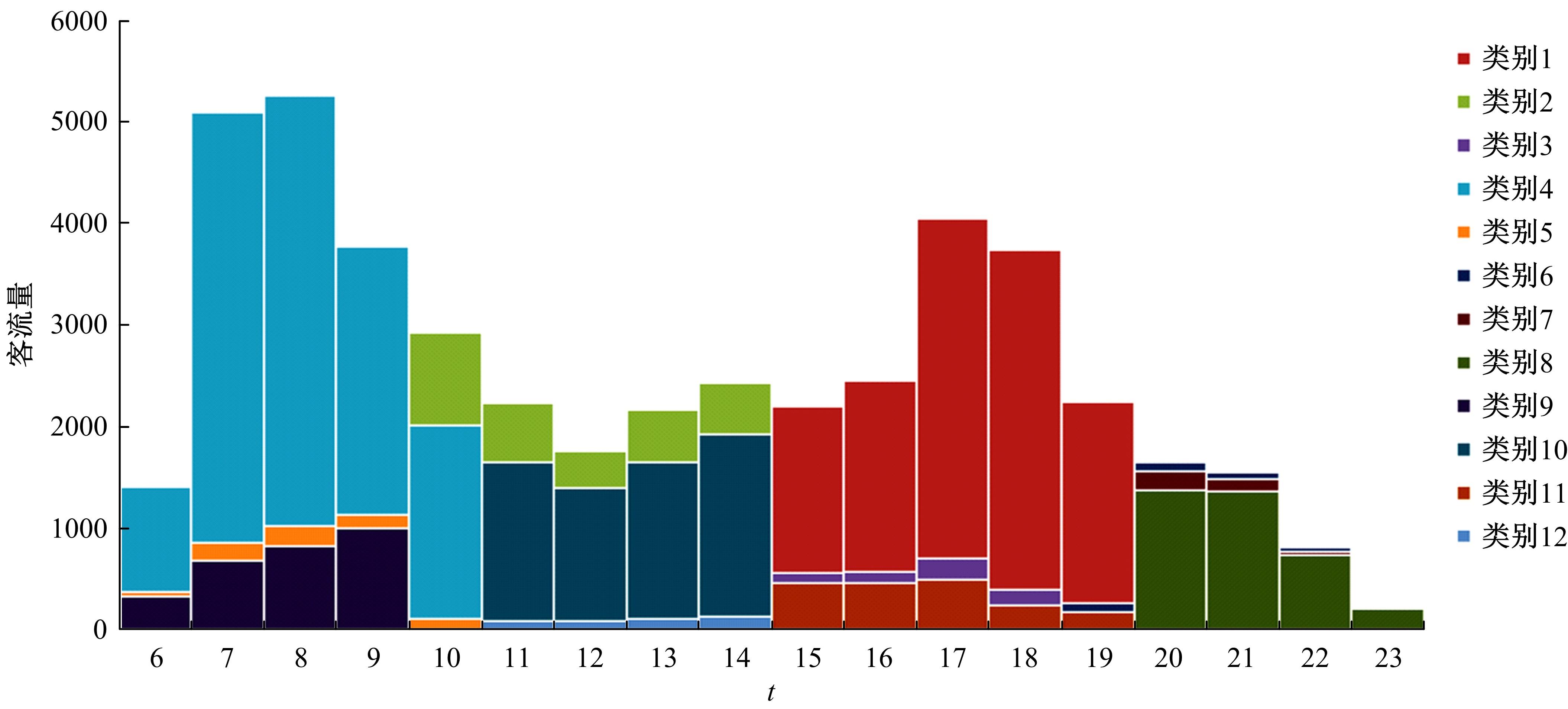
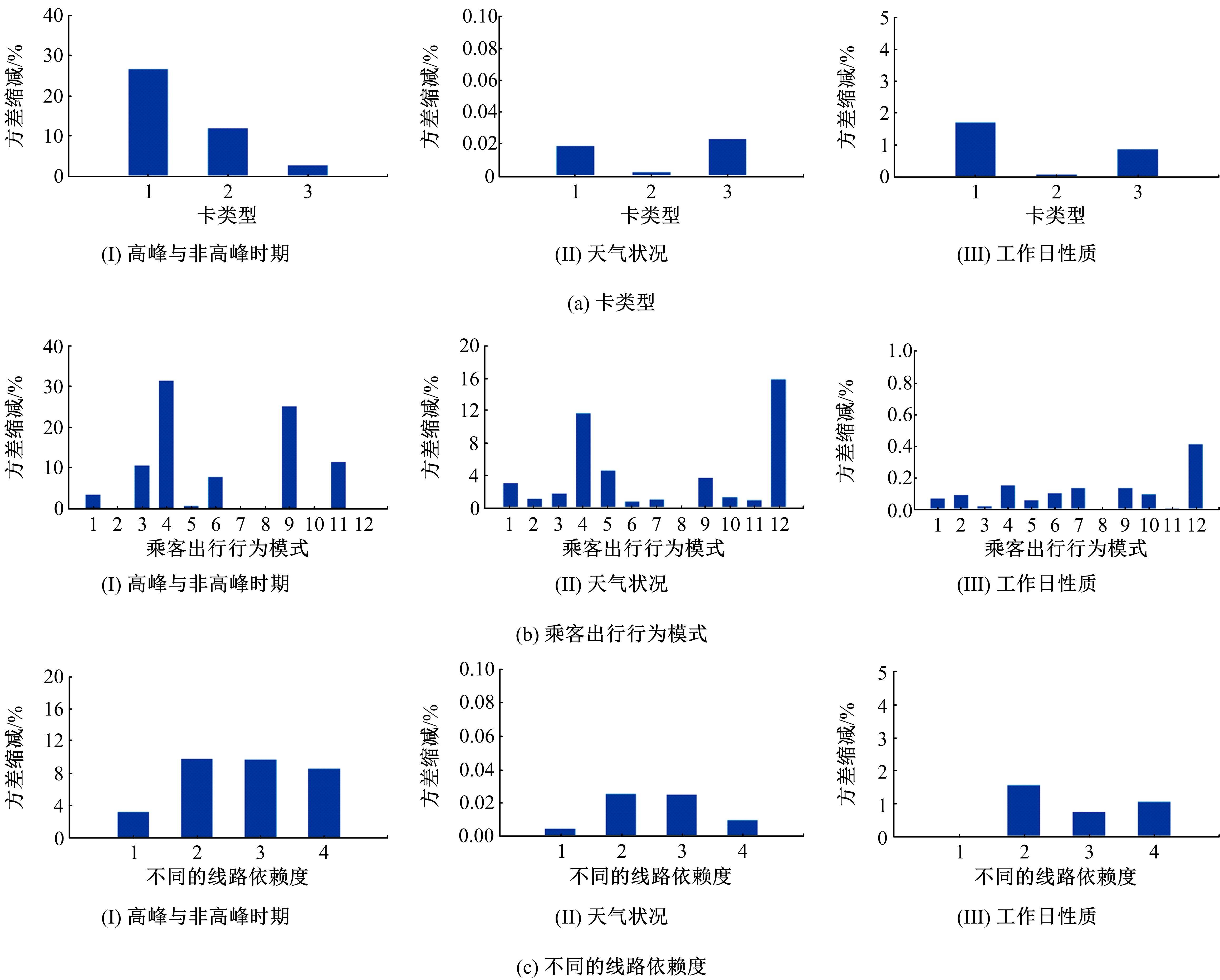
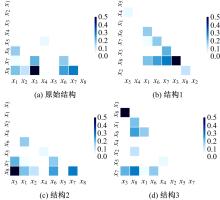
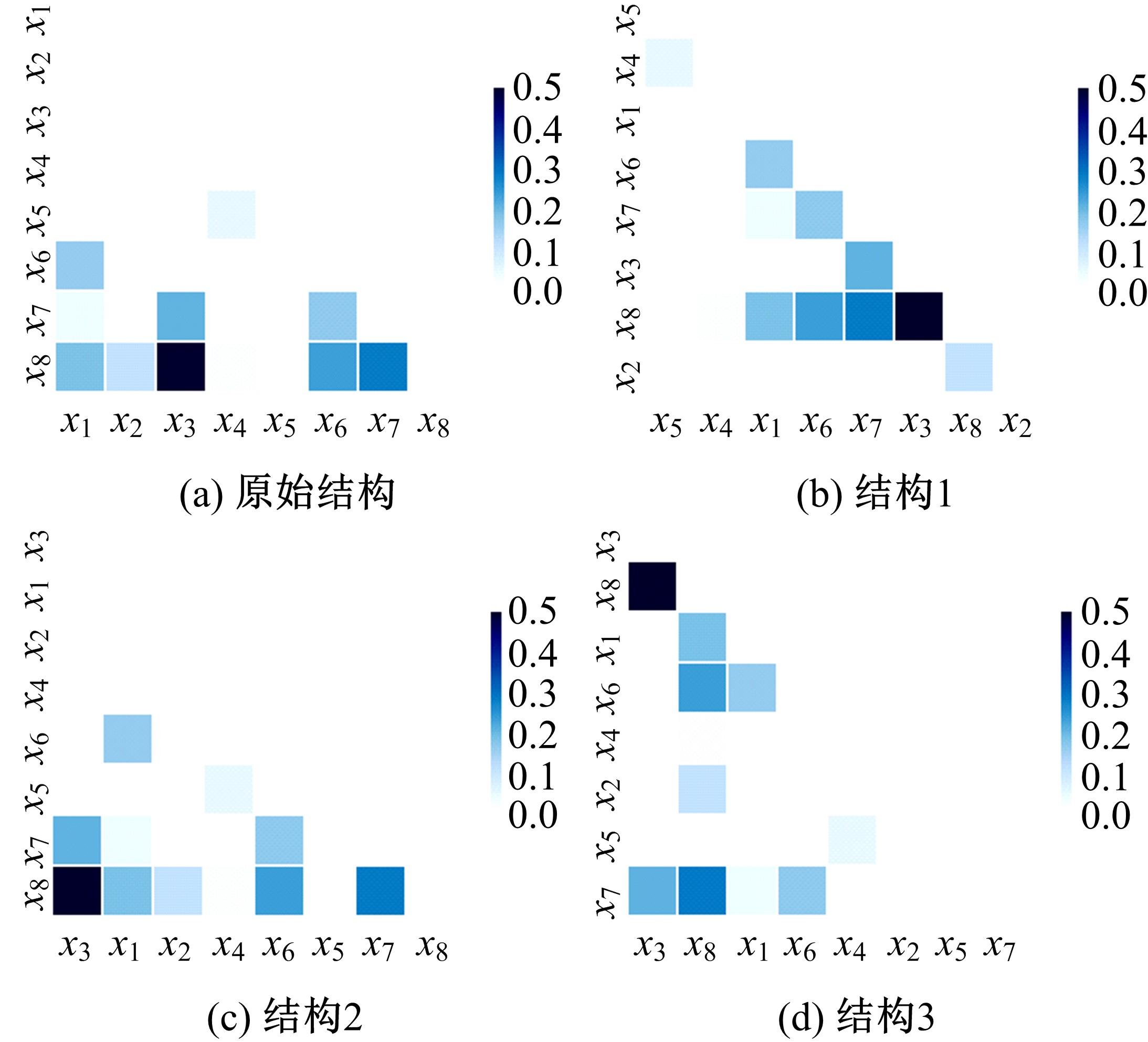
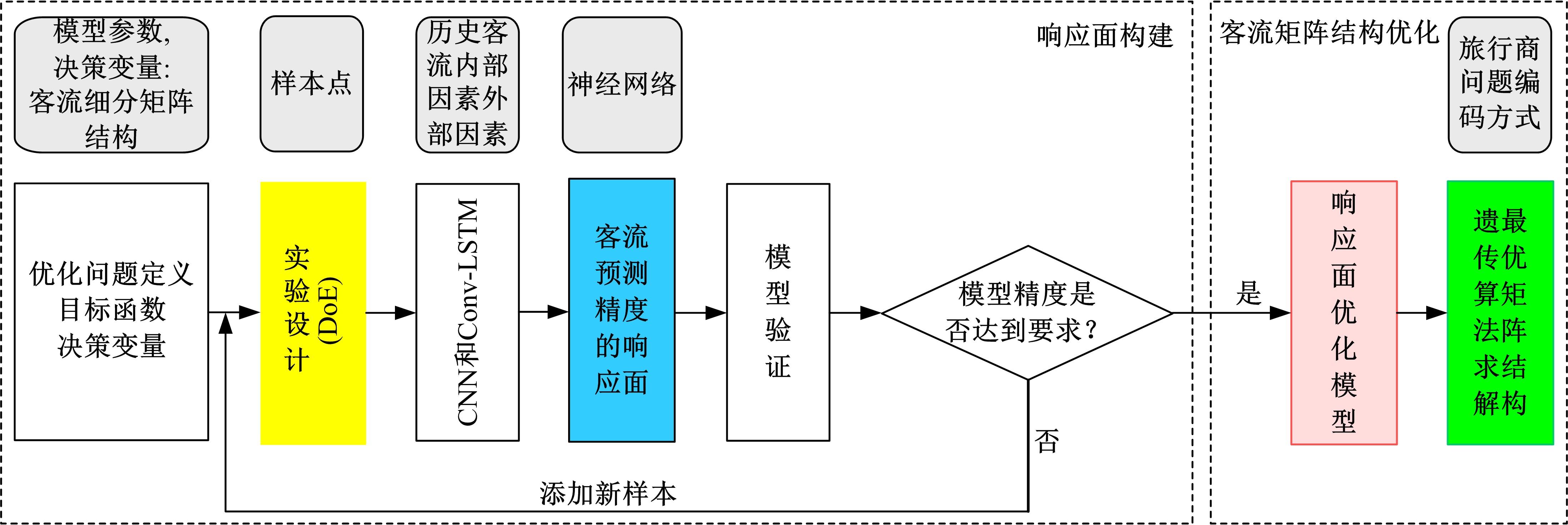
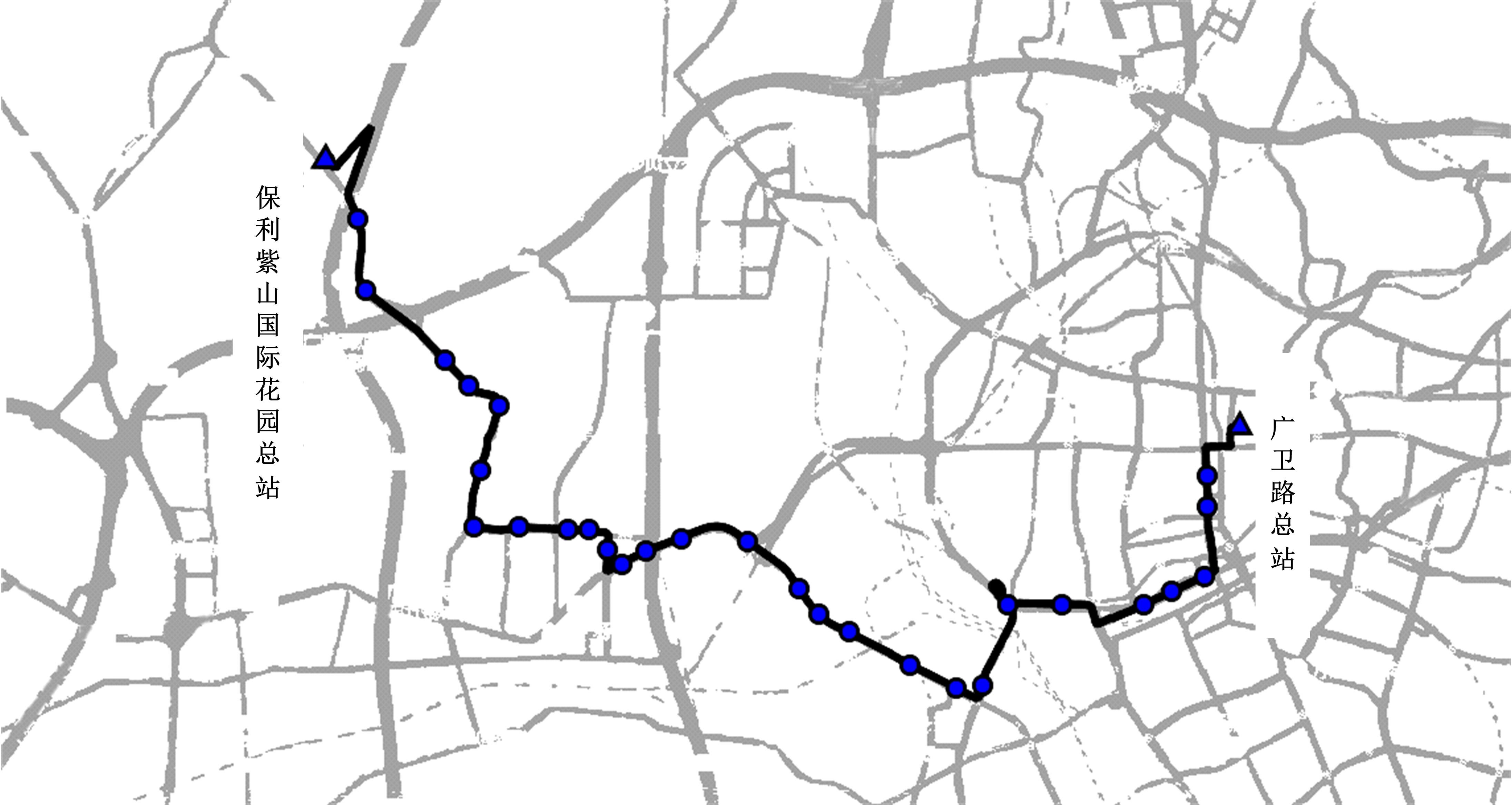
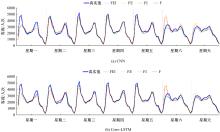
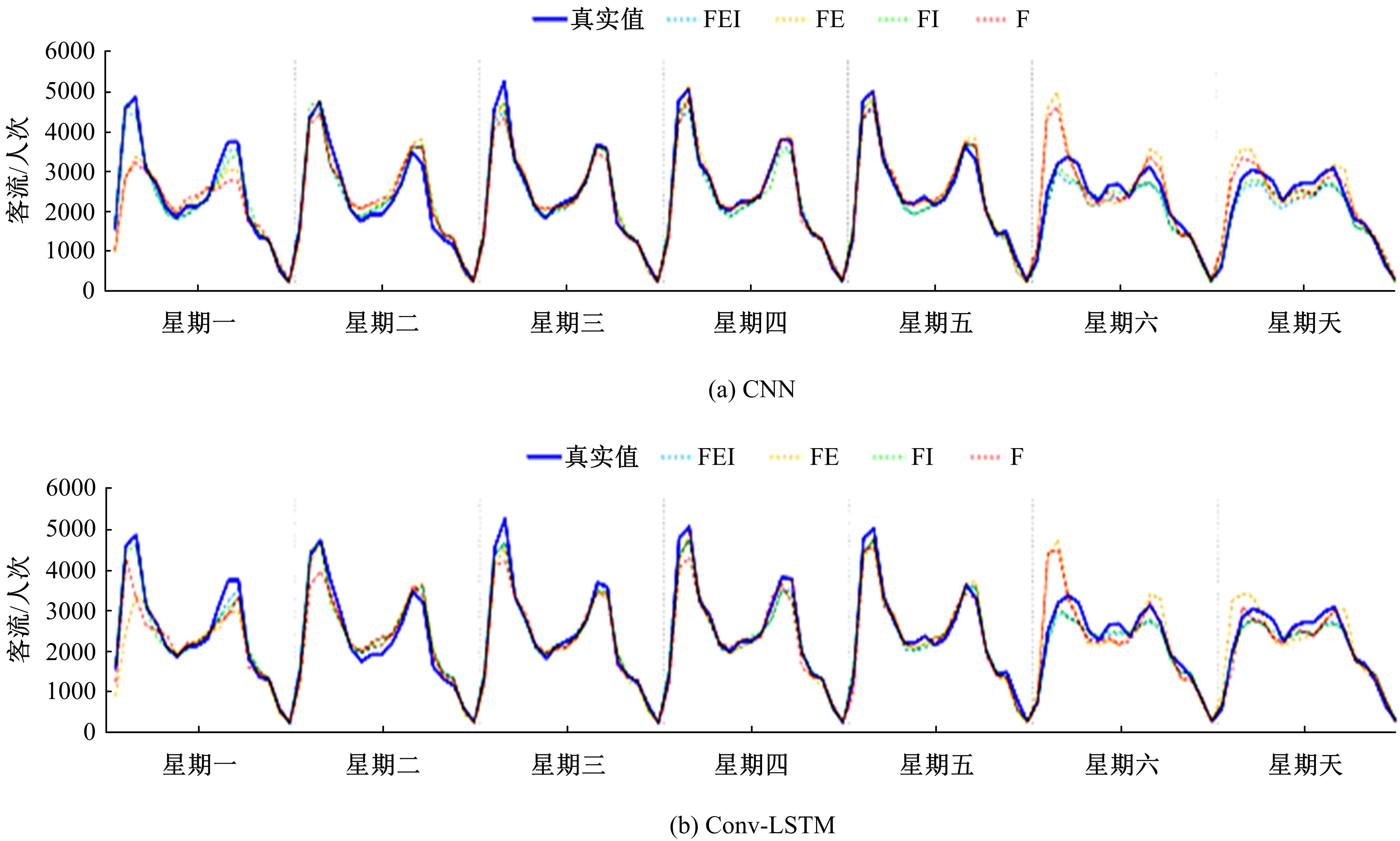
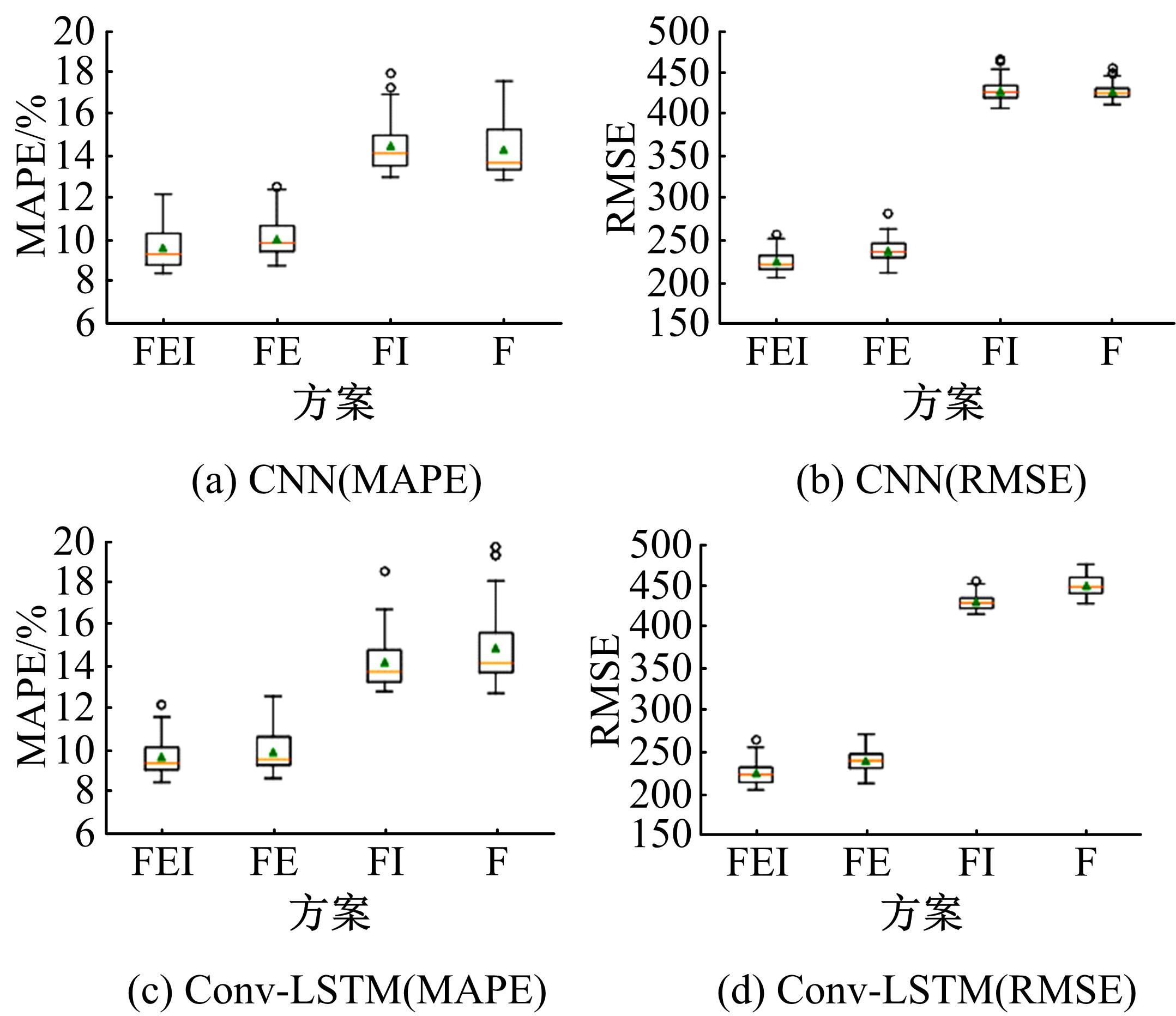
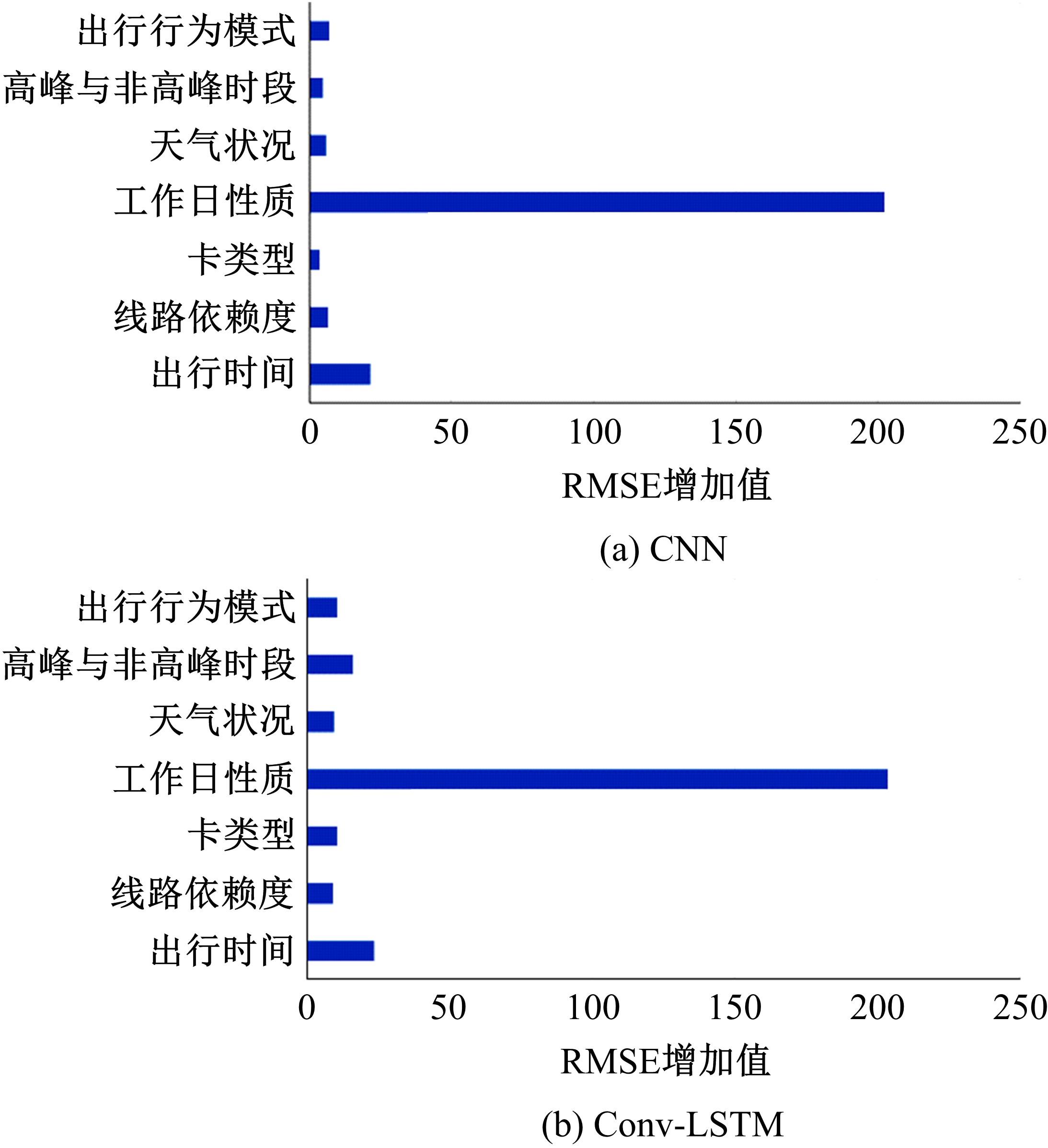
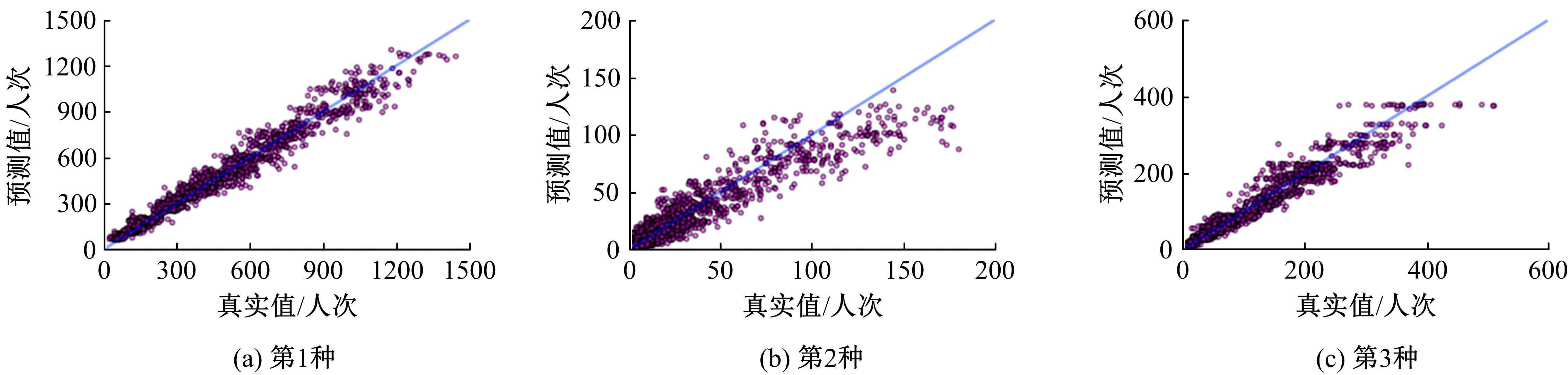
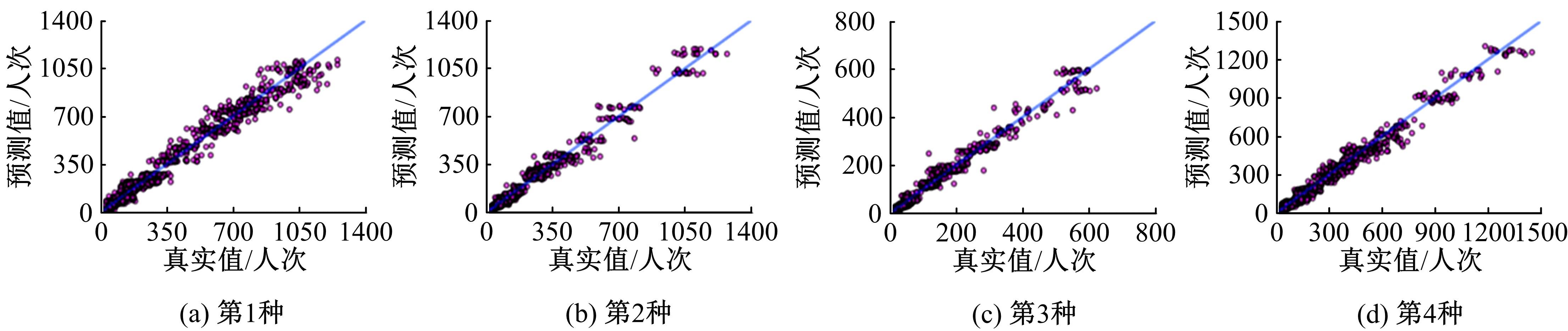
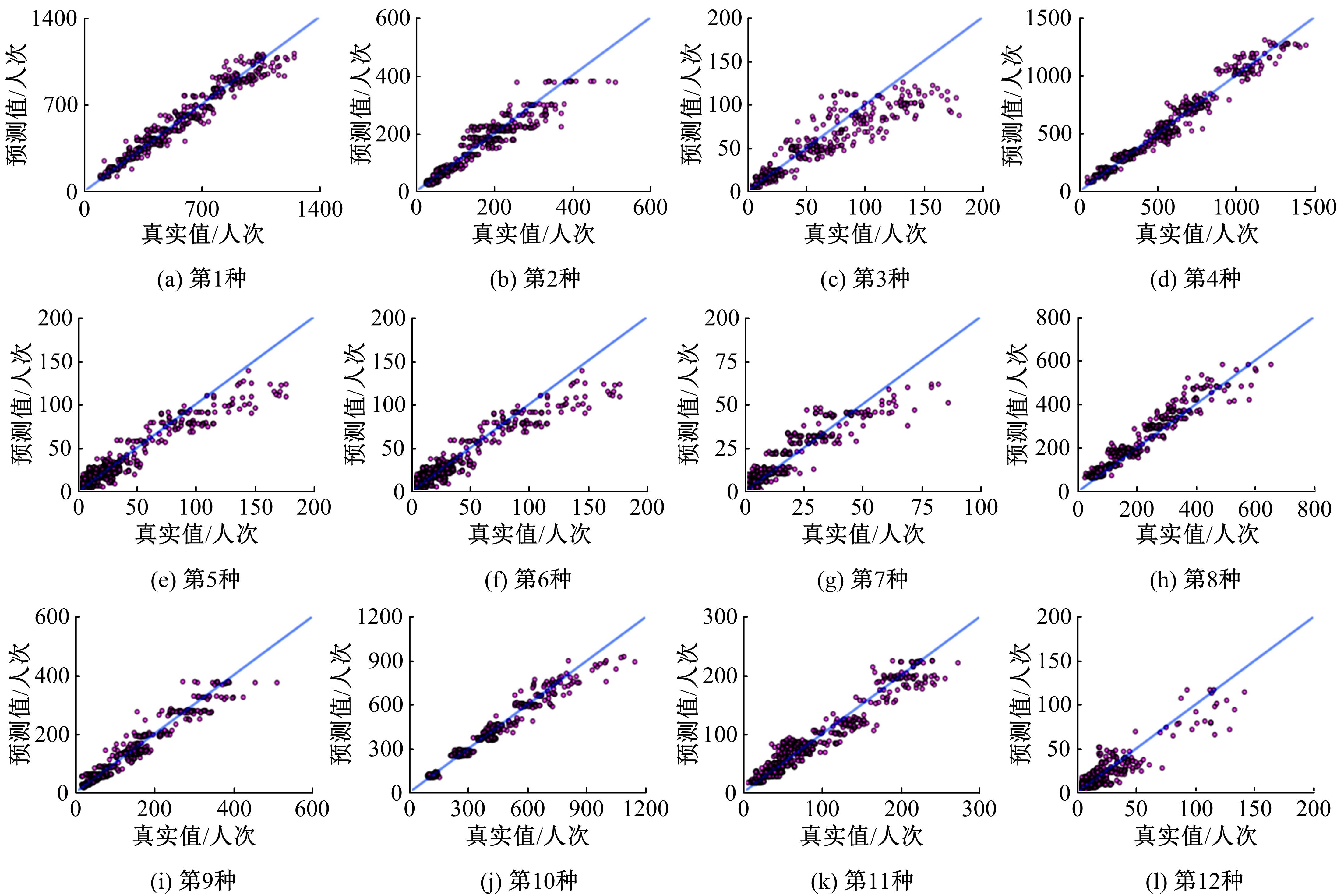
提出一种可扩展的深度学习框架实现多源数据预测公交客流。首先,在4个外部因素的基础上,引入3个内部因素作为公交线路客流的解释变量;其次,利用方差缩减法验证了内外部因素之间的耦合关系以及捕获多源数据耦合关系的必要性;然后,利用卷积神经网络中卷积运算处理二维数据的优势,将客流影响因素图像化,构建出小时客流细分矩阵适应其卷积运算,捕获多源数据之间的耦合性。为进一步提高预测性能,将矩阵结构优化问题转化为旅行商问题,运用响应面优化方法对客流细分矩阵结构进行高效优化。最后,以广州市281路公交线路实际数据为例进行验证,结果表明:通过优化小时客流细分矩阵结构,可以有效提高公交客流预测精度,实现数据资源的最优化利用;内部因素的独立效应不显著,而外部因素和内部因素的联合效应却作用显著;在预测精度上,与仅考虑外部因素的结果和其他深度学习模型相比存在一定优势。
中图分类号:
- U491.1
| 1 | Wei Y, Chen M C. Forecasting the short-term metro passenger flow with empirical mode decomposition and neural networks[J]. Transportation Research Part C, 2012, 21:148-162. |
| 2 | Liu Y, Liu Z Y, Jia R. DeepPF: a deep learning based architecture for metro passenger flow prediction[J]. Transportation Research Part C, 2019, 101: 18-34. |
| 3 | 张春辉, 宋瑞, 孙杨. 基于卡尔曼滤波的公交站点短时客流预测[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2011, 11(4):154-159. |
| Zhang Chun-hui, Song Rui, Sun Yang. Kalman filter-based short-term passenger flow forecasting on bus stop[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2011, 11(4): 154-159. | |
| 4 | 王庆荣, 张秋余. 基于随机灰色蚁群神经网络的近期公交客流预测[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2012, 29(6): 2078-2080. |
| Wang Qing-rong, Zhang Qiu-yu. Forecasting of short-term urban public transit volume based on random gray ant colony neural network[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2012, 29(6):2078-2080. | |
| 5 | 王立政, 朱从坤. 基于LM-BP算法的轨道交通客流短时预测[J]. 价值工程, 2018(3):154-156. |
| Wang Li-zheng, Zhu Cong-kun. Short-term prediction research on urban rail transit passenger flow based on LM-BP algorithm[J]. Value Engineering, 2018(3):154-156. | |
| 6 | Ma X L, Wu Y J, Wang Y H, et al. Mining smart card data for transit riders' travel patterns[J]. Transportation Research Part C, 2013, 36:1-12. |
| 7 | Chen X Q, Xiong C F, He X, et al. Time-of-day vehicle mileage fees for congestion mitigation and revenue generation: a simulation-based optimization method and its real-world application[J]. Transportation Research Part C, 2016, 63: 71-95. |
| 8 | Wu W T, Li P, Liu R H, et al. Predicting peak load of bus routes with supply optimization and scaled Shepard interpolation: a newsvendor model[J]. Transportation Research Part E, 2020, 142:No.102041. |
| 9 | Yu B, Guo Z, Asian S, et al. Flight delay prediction for commercial air transport: a deep learning approach[J]. Transportation Research Part E, 2019, 125: 203-221. |
| [1] | 程国柱,盛林,赵浩,冯天军. 基于危险度分析的信号交叉口专用相位设置条件[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1962-1969. |
| [2] | 张振海,季坤,党建武. 基于桥梁裂缝识别模型的桥梁裂缝病害识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1418-1426. |
| [3] | 孙超,尹浩为,汤文蕴,褚昭明. 交通需求估计下的检测器布局和手机数据扩样推断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1070-1077. |
| [4] | 吴飞,农皓业,马晨浩. 基于粒子群优化算法⁃长短时记忆模型的刀具磨损预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 989-997. |
| [5] | 常玉林,徐文倩,孙超,张鹏. 车联网环境下考虑遵从程度的混合流量逐日均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1085-1093. |
| [6] | 贾洪飞,徐英俊,杨丽丽,王楠. 商品车多式联运联盟成员选择及利益分配[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1060-1069. |
| [7] | 肖雪,李克平,彭博,昌满玮. 基于决策-规划迭代框架的智驾车换道行为建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 746-757. |
| [8] | 何科,丁海涛,赖宣淇,许男,郭孔辉. 基于Transformer的轮式里程计误差预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 653-662. |
| [9] | 姚荣涵,徐文韬,郭伟伟. 基于因子长短期记忆的驾驶人接管行为及意图识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 758-771. |
| [10] | 王菁,万峰,董春娇,邵春福. 城市轨道交通站点吸引范围及强度建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 439-447. |
| [11] | 张惠臻,高正凯,李建强,王晨曦,潘玉彪,王成,王靖. 基于循环神经网络的城市轨道交通短时客流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 430-438. |
| [12] | 马敏,胡大伟,舒兰,马壮林. 城市轨道交通网络韧性评估及恢复策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 396-404. |
| [13] | 高金武,贾志桓,王向阳,邢浩. 基于PSO-LSTM的质子交换膜燃料电池退化趋势预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2192-2202. |
| [14] | 方松,马健霄,李根,沈玲宏,徐楚博. 城市快速路右侧车道移动作业区行车风险分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1786-1791. |
| [15] | 宋现敏,杨舒天,刘明鑫,李志慧. 站点间公交行程时间波动特性及预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1792-1799. |
|
||