吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 979-986.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220675
考虑个人偏好的观赛人群组合决策选择行为
- 1.北京交通大学 综合交通运输大数据应用技术交通运输行业重点实验室,北京 100044
2.浙江省交通运输科学研究院,杭州 310000
3.东南大学 交通学院,南京 211102
4.中交信有限责任公司,北京 100029
Combined decision-choice behavior of spectators considering personal preferences
Zhi-hua XIONG1( ),Dai-yue DONG2,Chun-jiao DONG1(
),Dai-yue DONG2,Chun-jiao DONG1( ),Yan ZHENG3,Chao XIE4
),Yan ZHENG3,Chao XIE4
- 1.Key Laboratory of Transport Industry of Big Data Application Technologies for Comprehensive Transport,Ministry of Transport,Beijing Jiaotong University,Beijing 100044,China
2.Zhejiang Scientific Research Institute of Transport,Hangzhou 310000,China
3.School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 211102,China
4.China Transport Information Co. ,Ltd. ,Beijing 100029,China
摘要:
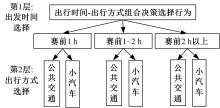
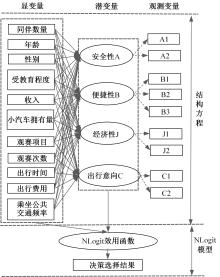
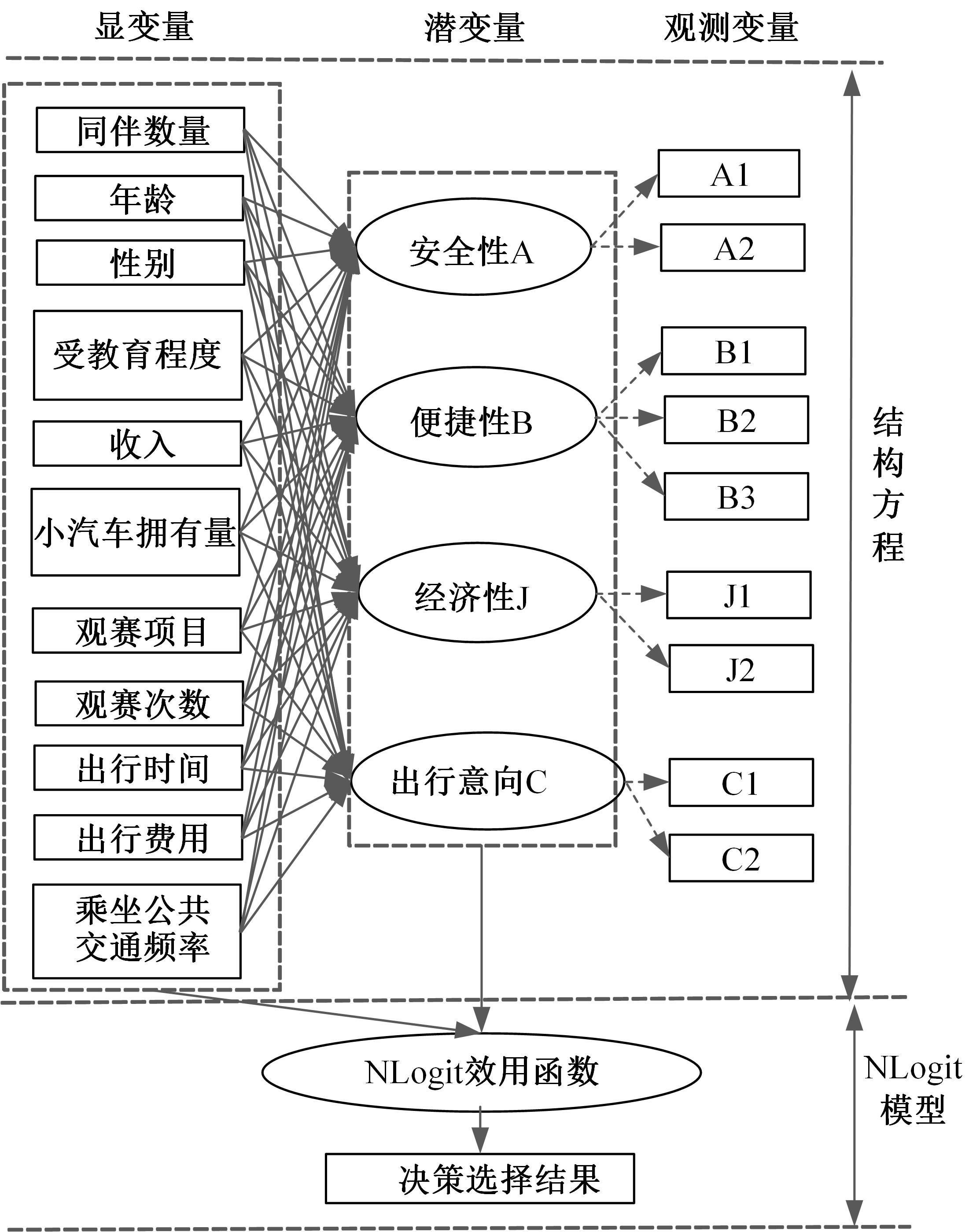
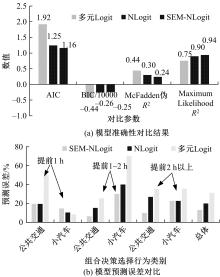
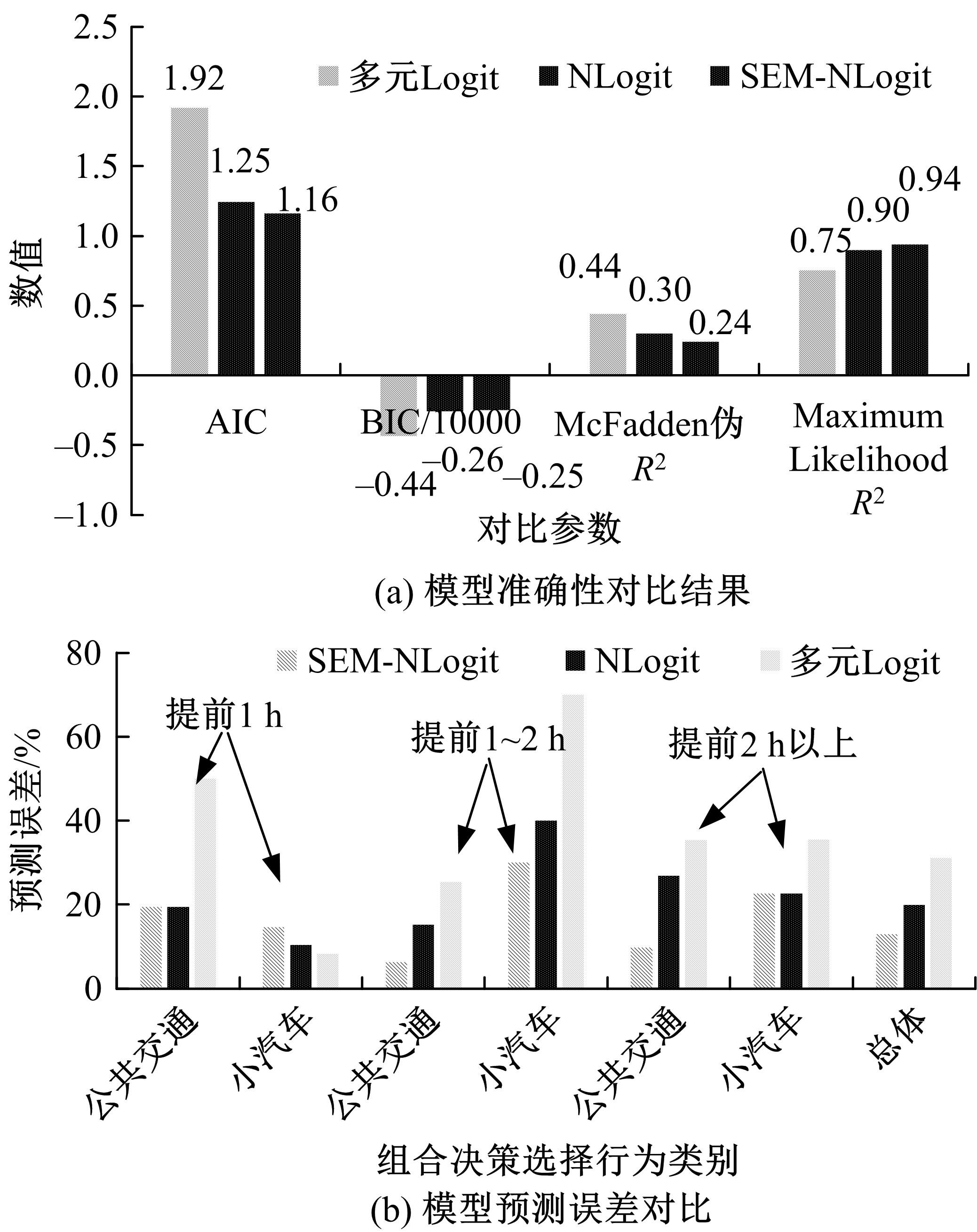
掌握观赛人群出行行为特征是应对赛事举办期间交通量激增、保障城市交通正常运行的关键。基于个人属性、出行特征、观赛特性和出行意愿的954份调查样本,引入结构方程刻画安全性、便捷性、经济性和出行意向4个潜变量与11个显变量的因果作用关系,考虑个人偏好对出发时间和出行方式组合决策选择行为的潜在影响,构建了基于SEM-NLogit的观赛人群组合决策选择行为模型。研究表明,模型预测精度为87.06%,与巢式Logit和多元Logit模型相比精度提高了6.99%和18.18%。本文模型更好地刻画了“观赛人群年龄越大,更倾向于提前出发;同伴数量越多、收入越高,越倾向于选择小汽车出行”的特征,并得到了出行时更注重安全性与经济性等巢式Logit模型无法得到但更符合实际出行规律的个人偏好的选择行为。
中图分类号:
- U491.1
| 1 | 谢陶,杨欢. 全球赛事影响力榜单公布:中国登顶榜首 成都首进全球前30城市[EB/OL]. [2009-04-30]. . |
| 2 | 赵丹,邵春福,王军利,等. 多方式诱导下通勤出行链交通方式组合选择行为模型[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2015,45(6):1763-1770. |
| Zhao dan, Shao chun-fu, Wang jun-li, et al. Modelling combined mode choice behavior of commute trip chain under multi-modal guidance[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015,45(6):1763-1770. | |
| 3 | 王月,姚恩建,郝赫. 低碳导向的多模式交通出行服务定价策略[J]. 清华大学学报:自然科学版,2023,63(11):1741-1749. |
| Wang Yue, Yao En-jian, Hao He. Low-carbon-oriented pricing strategy of multi-mode transportation service[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2023, 63(11):1741-1749. | |
| 4 | 于晓桦,刘欣萍,毕亚茹,等. 基于出行效用无差异阈值的组合交通客流分配模型[J]. 交通运输工程与信息学报,2023,21(4):25-34. |
| Yu Xiao-hua, Liu Xin-ping, Bi Ya-ru, et al. Passenger flow distribution model for combined transportation modes based on travel utility indifference threshold[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2023, 21(4):25-34. | |
| 5 | Jou R. Modeling the impact of pre-trip information on commuter departure time and route choice[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2001, 35(10): 887-902. |
| 6 | Jong G, Daily A, Pieters M, et al. A model for time of day and mode choice using error components logit[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2003, 39(3): 245-268. |
| 7 | 张波,隽志才,林徐勋. 基于累积前景理论的出发时间选择SDUO模型[J].管理工程学报, 2013,27(1):68-76. |
| Zhang Bo, Zhi-cai Juan, Lin Xu-xun. Stochastic dynamic user optimum model with departure time choice based on cumulative prospect theory[J]. Journal of Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management, 2013,27(1):68-76. | |
| 8 | 诸葛承祥,邵春福,李霞,等.通勤者出行时间与出行方式选择行为研究[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2012,12(2):126-131. |
| Zhuge Cheng-xiang, Shao Chun-fu, Li Xia, et al. Commuter's choice behavior of travel time and travel mode[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2012,12(2):126-131. | |
| 9 | Zou M, Li M, Lin X, et al. An agent-based choice model for travel mode and departure time and its case study in Beijing[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2016(64): 133-147. |
| 10 | 杨励雅,李霞,邵春福.居住地、出行方式与出发时间联合选择的交叉巢式Logit模型[J].同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2012,40(11):1647-1653. |
| Yang Li-ya, Li Xia, Shao Chun-fu. Cross-nested Logit model for joint choice of residential location, travel mode and departure time[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2012,40(11):1647-1653. | |
| 11 | 杨励雅,李娟.居民出行链、出行方式与出发时间联合选择的交叉巢式Logit模型[J].北京大学学报:自然科学版,2017,53(4):722-730. |
| Yang Li-ya, Li Juan. Cross-nested Logit model for the joint choice of residential location, travel mode and departure time[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinens, 2017,53(4):722-730. |
| [1] | 吴娇蓉,林清凯,邓泳淇. 基于公交线路运行稳定性的潜在公交专用道需求识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 692-699. |
| [2] | 庄焱,董春娇,米雪玉,张小雨,王菁. 基于随机参数Logit的中小城市居民出行方式选择建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 461-468. |
| [3] | 张文会,伊静. 考虑通行能力和排队延误的公交停靠系统优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 146-154. |
| [4] | 贺宜,孙昌鑫,彭建华,吴超仲,江亮,马明. 电动载货三轮车风险行为及影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 413-420. |
| [5] | 邝先验,陈自如. 基于CA的无信号灯控制路段行人过街横道处动态博弈礼让行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 837-846. |
| [6] | 李兴华,冯飞宇,成诚,王洧,唐鹏程. 网约拼车服务选择偏好分析及建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 578-584. |
| [7] | 贾洪飞,邵子函,杨丽丽. 终点不确定条件下网约车合乘匹配模型及算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 564-571. |
| [8] | 董春娇,董黛悦,诸葛承祥,甄理. 电动自行车出行特性及骑行决策行为建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2618-2625. |
| [9] | 杨世军,裴玉龙,潘恒彦,程国柱,张文会. 城市公交车辆驻站时间特征分析及预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2031-2039. |
| [10] | 马莹莹,陆思园,张晓明,魏文术. 考虑个体风险偏好差异的高速公路出行选择模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1673-1683. |
| [11] | 孙宝凤,姜源,郑黎黎,崔万坤,任欣欣. 变覆盖半径下城市轨道交通维护保障网络设计模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 526-534. |
| [12] | 陈磊,王江锋,谷远利,闫学东. 基于思维进化优化的多源交通数据融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 705-713. |
| [13] | 侯现耀, 陈学武. 基于态度的公交出行信息使用市场细分[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 98-104. |
| [14] | 于德新,杨兆升,高鹏. 动态限制搜索区域的带约束K则最优路径算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 172-0176. |
| [15] | 杨兆升,于悦,杨薇. 基于固定型检测器和浮动车的路段行程时间获取技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 168-0171. |
|
||