吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 969-978.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220656
面向交通事故检测及预防的异质传感器布设方法
- 吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
Deployment of heterogeneous sensors for traffic accident detection and prevention
Qian CAO( ),Zhi-hui LI(
),Zhi-hui LI( ),Peng-fei TAO,Hai-tao LI,Yong-jian MA
),Peng-fei TAO,Hai-tao LI,Yong-jian MA
- College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
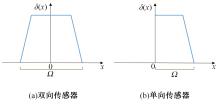
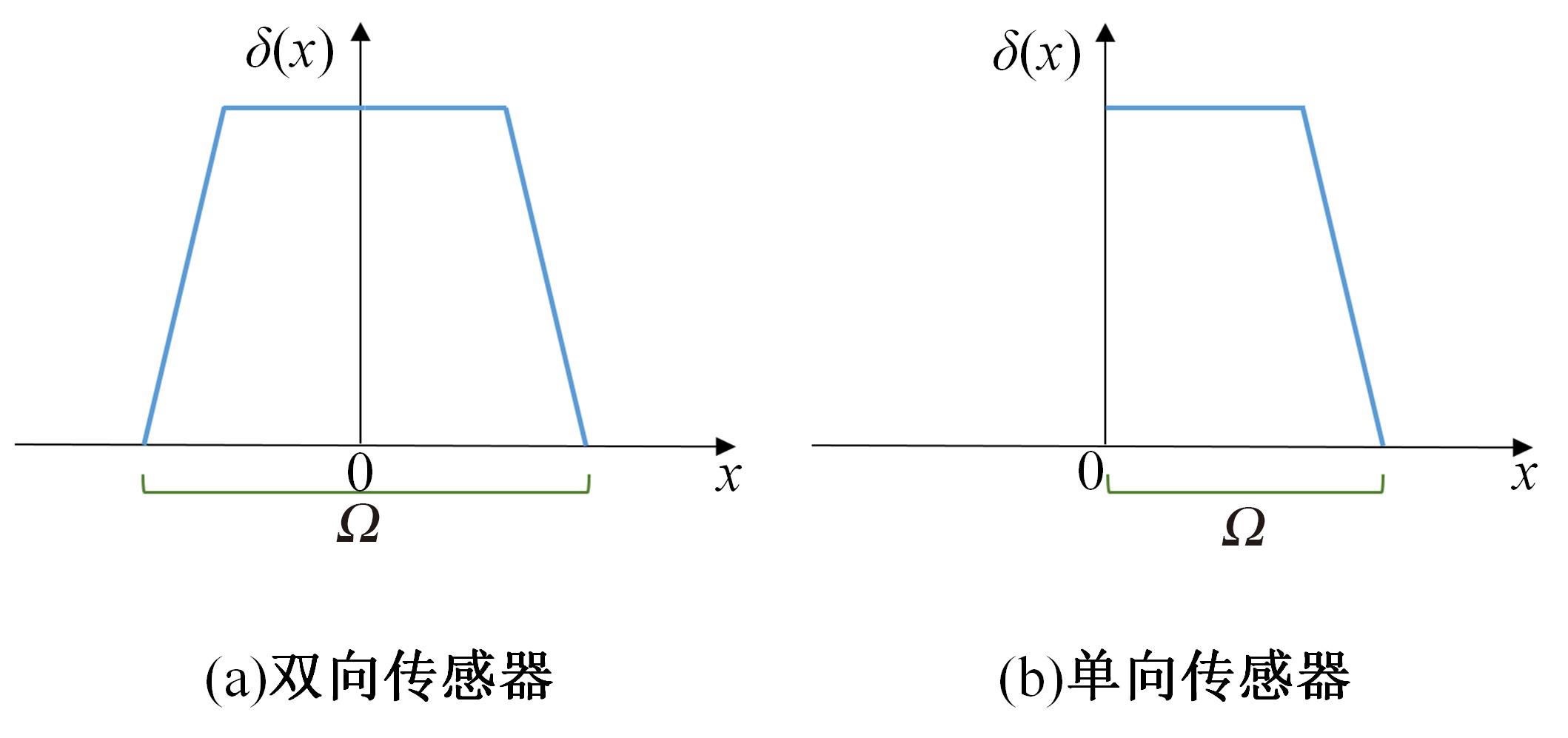
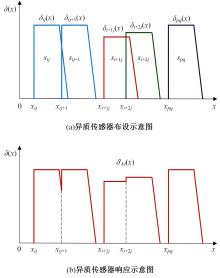
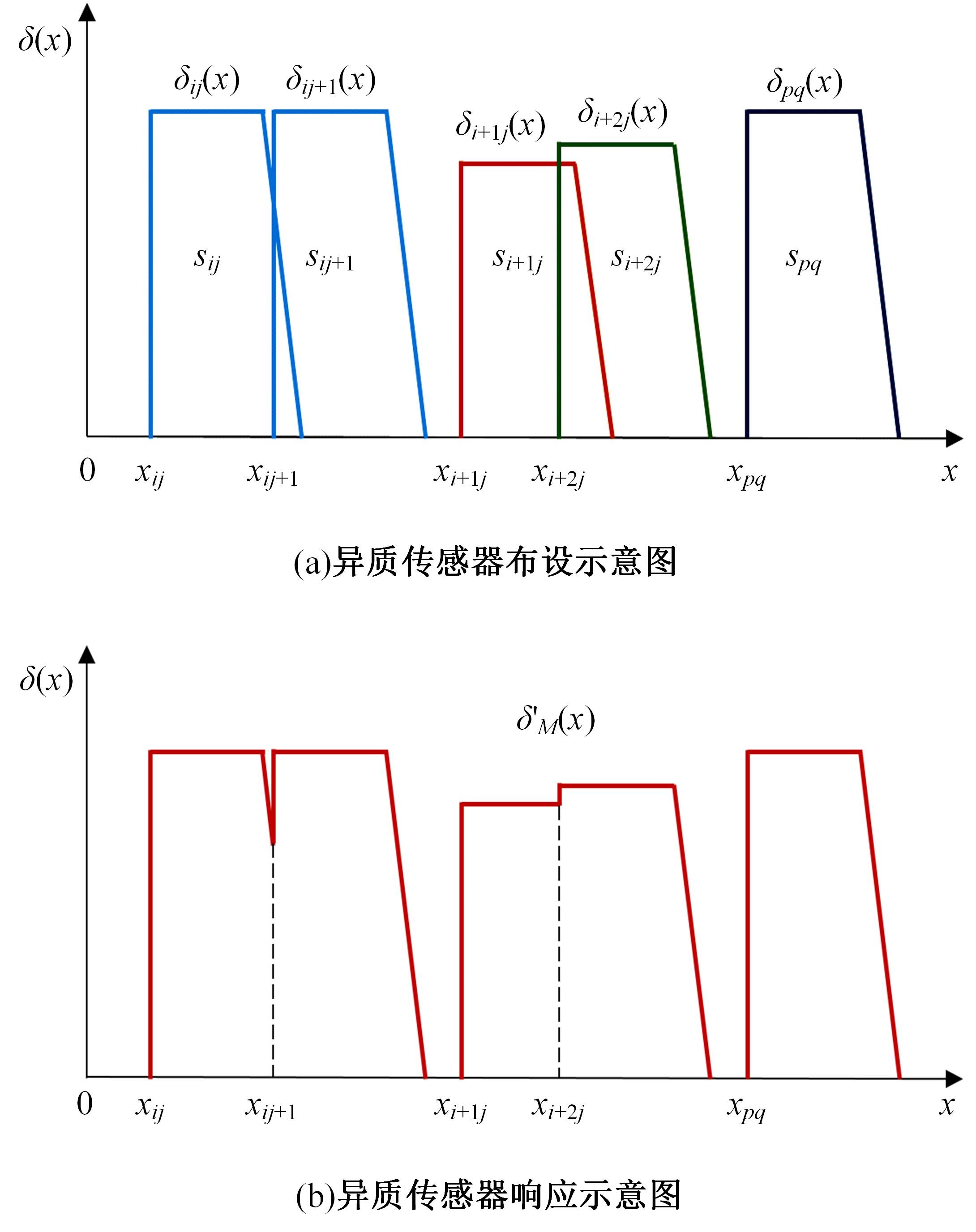
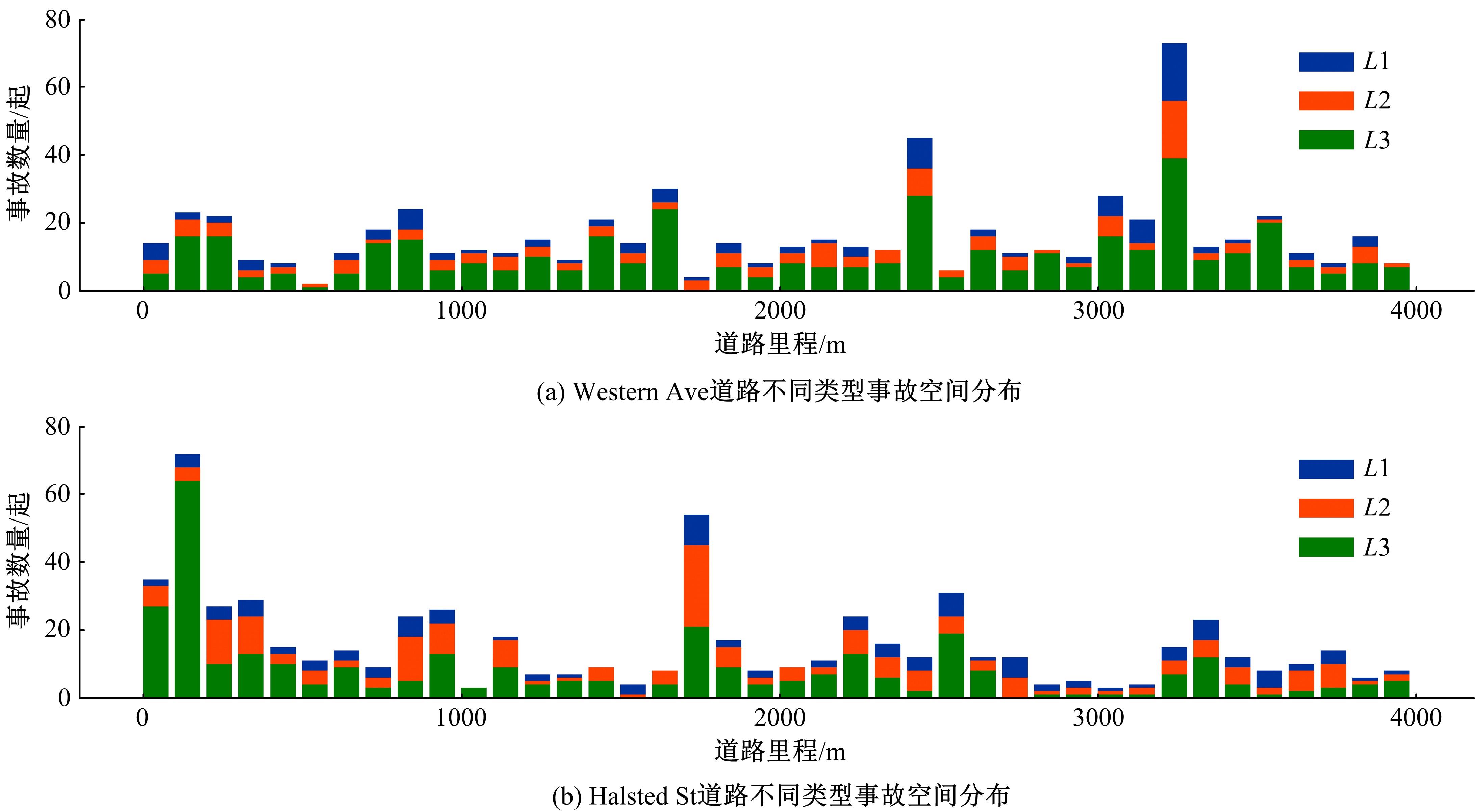
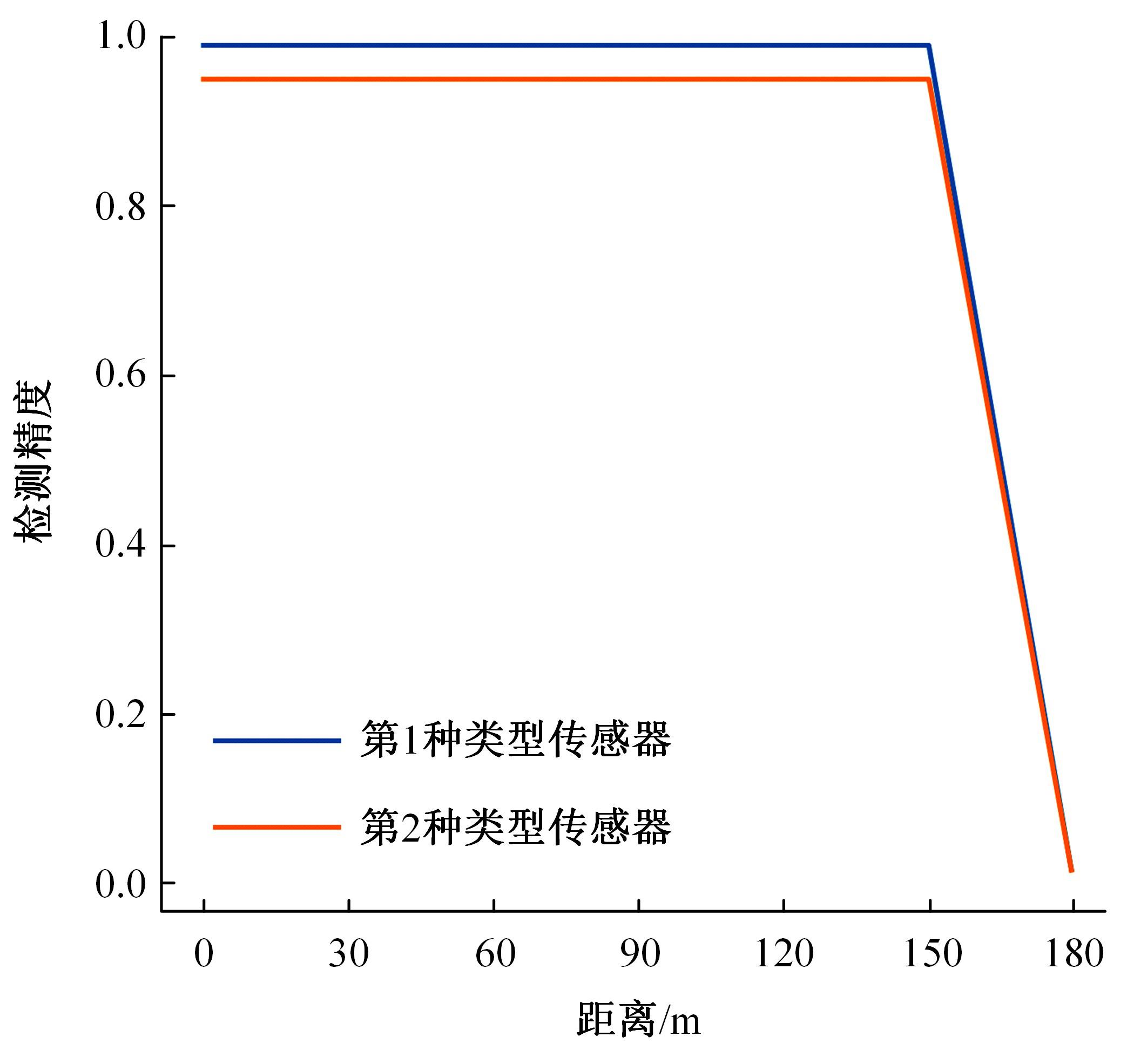
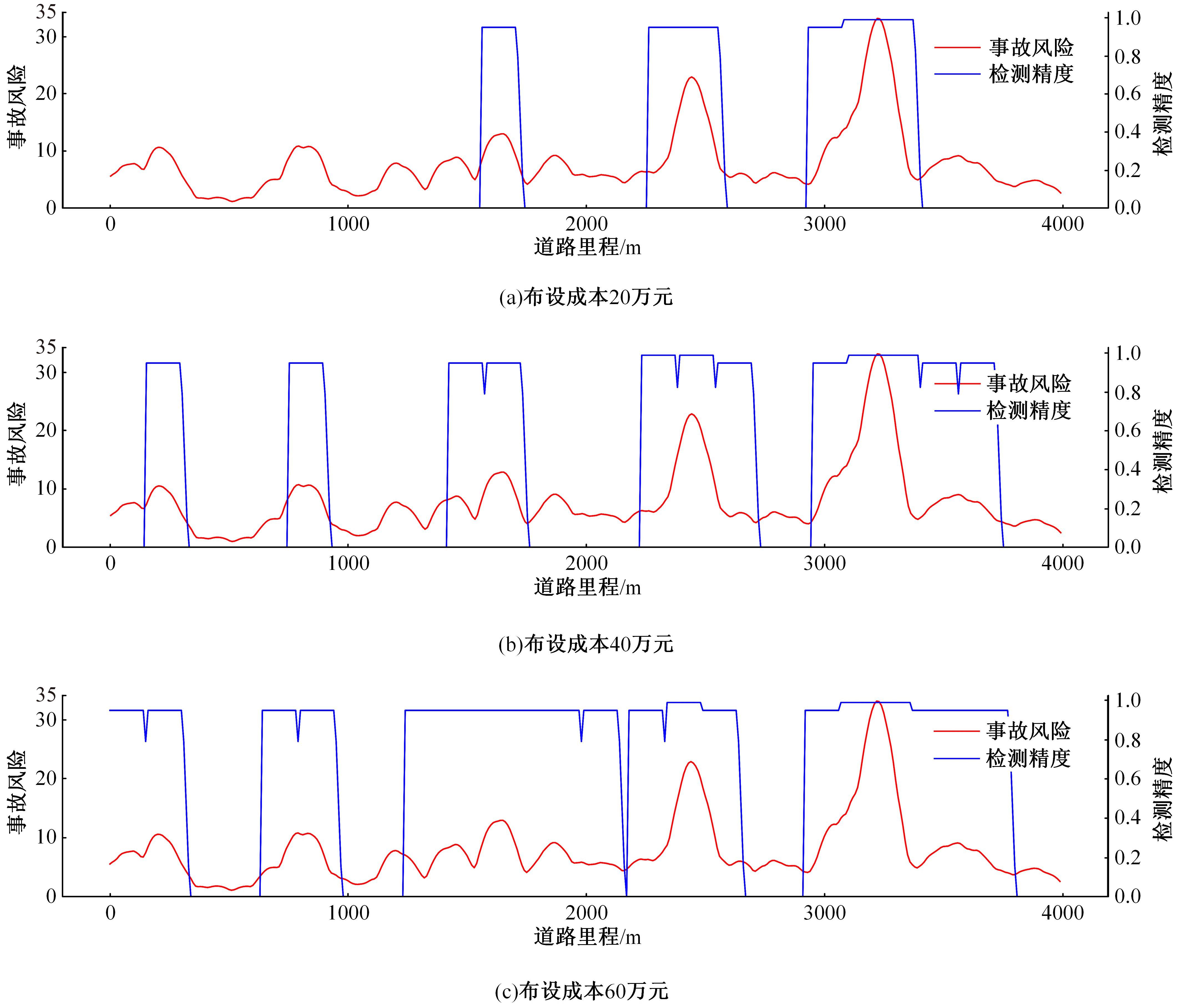
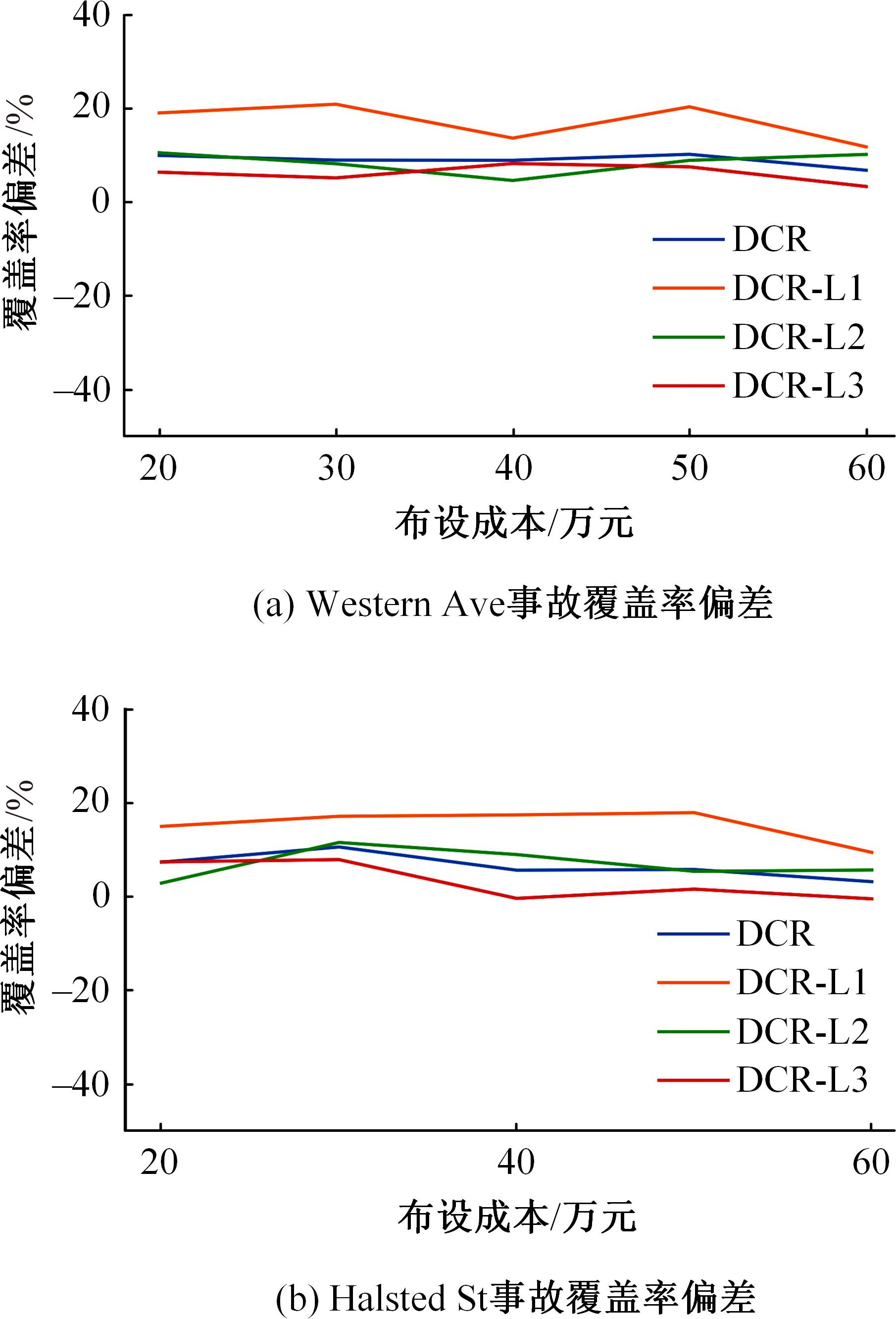
目前,道路交通事故检测及预防中缺乏异质传感器布设的相关技术标准和理论指导,为此本文提出了一种面向事故检测及预防的异质传感器布设方法。考虑到交通事故的不确定性,该方法利用历史交通事故数据,获取道路事故风险的稳定空间分布,从而将传感器布设问题转化为道路事故风险的最优覆盖问题。以覆盖质量最大为目标,以布设成本、事故检测误差等为约束,构建异质传感器布设的组合优化模型。通过国际公开事故数据与道路场景验证本文方法的有效性,结果显示不同成本约束下传感器布设方案均能够与道路事故风险有效匹配,且均能达到事故的预期覆盖效果。因此,本文方法能够满足事故不确定性下的传感器布设需求,实现异质传感器优化布设。
中图分类号:
- U491.5
| 1 | Koble H M, Anderson G, Goldblatt R. Formulation of guidelines for locating freeway sensors[R]. Washington: Federal Highway Admin, 1979. |
| 2 | 姜桂艳. 道路交通状态判别技术与应用[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2014. |
| 3 | 杨志清. 服务于安全运营管理的高速公路网信息系统[D]. 上海: 同济大学交通运输工程学院, 2008. |
| Yang Zhi-qing. The study on expressway network information system served for operating safety[D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, College of Transportation Engineering, 2008. | |
| 4 | Qin N N, Chen J L. An area coverage algorithm for wireless sensor networks based on differential evolution[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2018, 14(8): 1-11. |
| 5 | Chauhan N, Chauhan S. A novel area coverage technique for maximizing the wireless sensor network lifetime[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2021, 46(4): 3329-3343. |
| 6 | 刘志敏, 贾维嘉, 王国军. 有向传感器网络覆盖预测模型与数量估计[J]. 软件学报, 2016, 27(12): 3120-3130. |
| Liu Zhi-min, Jia Wei-jia, Wang Guo-jun. Coverage prediction model and number estimation for directional sensor networks[J]. Journal of Software, 2016, 27(12): 3120-3130. | |
| 7 | 刘志敏, 贾维嘉, 王国军. 视觉传感器网络边界部署k-覆盖数量估计[J]. 计算机学报, 2019, 42(2): 79-92. |
| Liu Zhi-min, Jia Wei-jia, Wang Guo-jun. k-Coverage estimation in visual sensor networks based on boundary deployment[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2019, 42(2): 79-92. | |
| 8 | 范兴刚, 王恒, 蒿翔. 有向传感器网络的覆盖增强算法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2017, 38(2): 368-377. |
| Fan Xing-gang, Wang Heng, Hao Xiang. Algorithm for enhancing coverage ratio in directional sensor networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2017, 38(2): 368-377. | |
| 9 | 卢毅, 周杰, 万连城. 一种无线传感器网络二维目标覆盖的改进方法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2019, 46(2): 101-106. |
| Lu Yi, Zhou Jie, Wan Lian-cheng. Improved method for 2D target coverage in wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2019, 46(2): 101-106. | |
| 10 | Zhao H T, Wang H J, Wu W Y, et al. Deployment algorithms for UAV airborne networks toward on-demand coverage[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2018, 36(9): 2015-2031. |
| 11 | Wang H J, Zhao H T, Wu W Y, et al. Deployment algorithms of flying base stations: 5G and beyond with UAVs[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(6): 10009-10027. |
| 12 | Savkin A V, Huang H L. Deployment of unmanned aerial vehicle base stations for optimal quality of coverage[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(1): 321-324. |
| 13 | Sobouti M J, Rahimi Z, Mohajerzadeh A H, et al. Efficient deployment of small cell base stations mounted on unmanned aerial vehicles for the internet of things infrastructure[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(13): 7460-7471. |
| 14 | 李明, 胡江平, 曹晓莉. 异构传感网成本优化的节点部署策略 [J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2021, 48(4): 11-19, 49. |
| Li Ming, Hu Jiang-ping, Cao Xiao-li. Minimum cost of node deployment strategy for heterogeneous sensor networks[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2021, 48(4): 11-19, 49. | |
| 15 | Kashi S S. Area coverage of heterogeneous wireless sensor networks in support of Internet of Things demands[J]. Computing, 2019, 101(4): 363-385. |
| 16 | Al-Fuhaidi B, Mohsen A M, Ghazi A, et al. An efficient deployment model for maximizing coverage of heterogeneous wireless sensor network based on harmony search algorithm [J]. Journal of Sensors, 2020: No. 8818826. |
| 17 | Elma K J, Meenakshi S. Optimal coverage along with connectivity maintenance in heterogeneous wireless sensor network[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2021, 12(3): 3647-3658. |
| 18 | Hanh N T, Binh H T T, Hoai N X, et al. An efficient genetic algorithm for maximizing area coverage in wireless sensor networks [J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 488: 58-75. |
| 19 | 陈金林. 基于网络核密度估计城市路网事故黑点鉴别研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学交通学院, 2015. |
| Chen Jin-lin. Research on identifying hotspots in the urban road networks based on the network kernel density estimation method[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, School of Transportation, 2015. | |
| 20 | Xie Z X, Jun Y. Kernel density estimation of traffic accidents in a network space[J]. Computers Environment and Urban Systems, 2008, 32(5): 396-406. |
| [1] | 张鑫,胡启洲,何君,吴啸宇. 考虑交通梗塞的合流区交通状况诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 478-484. |
| [2] | 张卫华,刘嘉茗,解立鹏,丁恒. 网联混合环境快速路交织区自动驾驶车辆换道模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 469-477. |
| [3] | 岳昊,张琦悦,杨子玉,任孟杰,张旭. 拥堵空间排队的静态交通流分配迭代加权算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 136-145. |
| [4] | 杜筱婧,姚荣涵. 智能网联公交车出站强制换道的演化博弈机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 124-135. |
| [5] | 马壮林,崔姗姗,胡大伟,王晋. 限行政策下传统小汽车出行者出行方式选择[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1981-1993. |
| [6] | 张雅丽,付锐,袁伟,郭应时. 考虑能耗的进出站驾驶风格分类及识别模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2029-2042. |
| [7] | 尹超英,陆颖,邵春福,马健霄,许得杰. 考虑空间自相关的建成环境对通勤方式选择的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1994-2000. |
| [8] | 潘恒彦,王永岗,李德林,陈俊先,宋杰,杨钰泉. 基于交通冲突的长纵坡路段追尾风险评估及预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1355-1363. |
| [9] | 宋灿灿,荆迪菲,谢俊峰,康可心. 设置广告牌的高速公路平曲线路段驾驶行为分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1345-1354. |
| [10] | 卢凯,徐广辉,叶志宏,林永杰. 考虑清空时间的双向队首绿波协调控制数解算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 421-429. |
| [11] | 曹倩,李志慧,陶鹏飞,马永建,杨晨曦. 考虑风险异质特性的路网交通事故风险评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2817-2825. |
| [12] | 张鑫,张卫华. 快速路合流区主线不同交通状态下的安全性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1308-1314. |
| [13] | 曲大义,赵梓旭,贾彦峰,王韬,刘琼辉. 基于Lennard-Jones势的车辆跟驰动力学特性及模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2549-2557. |
| [14] | 董春娇,董黛悦,诸葛承祥,甄理. 电动自行车出行特性及骑行决策行为建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2618-2625. |
| [15] | 曲大义,黑凯先,郭海兵,贾彦峰,王韬. 车联网环境下车辆换道博弈行为及模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 101-109. |
|
||