吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1570-1581.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20231280
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
考虑舒适度的智能汽车人工蜂群轨迹规划方法
谢宪毅1,2( ),张明君3(
),张明君3( ),金立生1,周彬4,胡涛1,白宇飞1
),金立生1,周彬4,胡涛1,白宇飞1
- 1.燕山大学 车辆与能源学院,河北 秦皇岛 066004
2.清华大学 汽车安全与节能国家重点实验室,北京 100084
3.中国汽车技术研究中心有限公司 中汽研汽车检验中心(天津)有限公司,天津 300300
4.北京航空航天大学 车路一体智能交通全国重点实验室,北京 102206
Artificial bee colony trajectory planning algorithm for intelligent vehicles considering comfortable
Xian-yi XIE1,2( ),Ming-jun ZHANG3(
),Ming-jun ZHANG3( ),Li-sheng JIN1,Bin ZHOU4,Tao HU1,Yu-fei BAI1
),Li-sheng JIN1,Bin ZHOU4,Tao HU1,Yu-fei BAI1
- 1.School of Vehicles and Energy,Yanshan University,Qinhuangdao 066004,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Automotive Safety and Energy,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China
3.CATARC Automotive Inspection Center (Tianjin) Co. ,Ltd. ,China Automotive Technology and Research Center Co. ,Ltd. ,Tianjin 300300,China
4.State Key Laboratory of Vehicle Road Integrated Intelligent Transportation System,Beihang University,Beijing 102206,China
摘要:
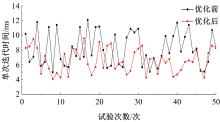
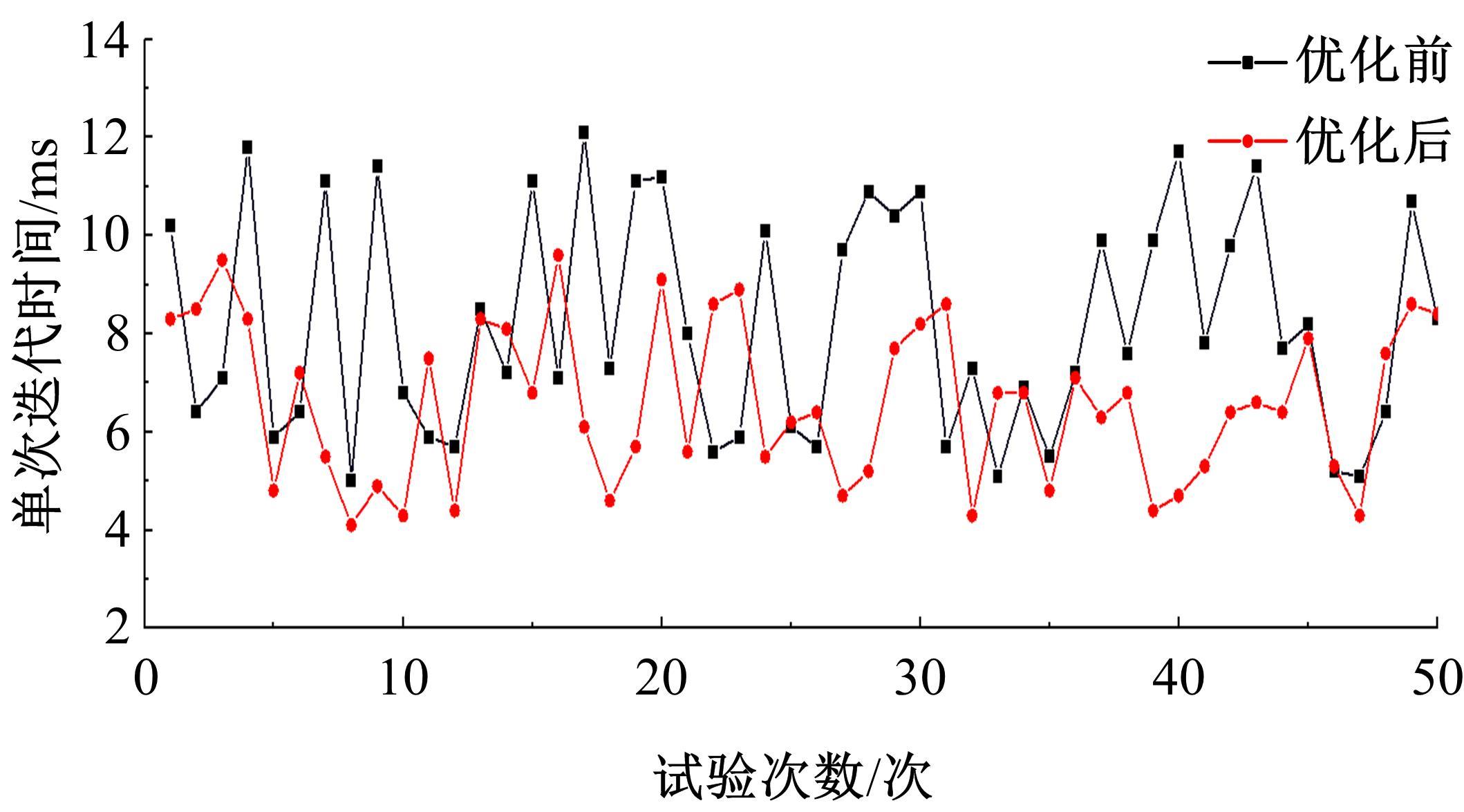
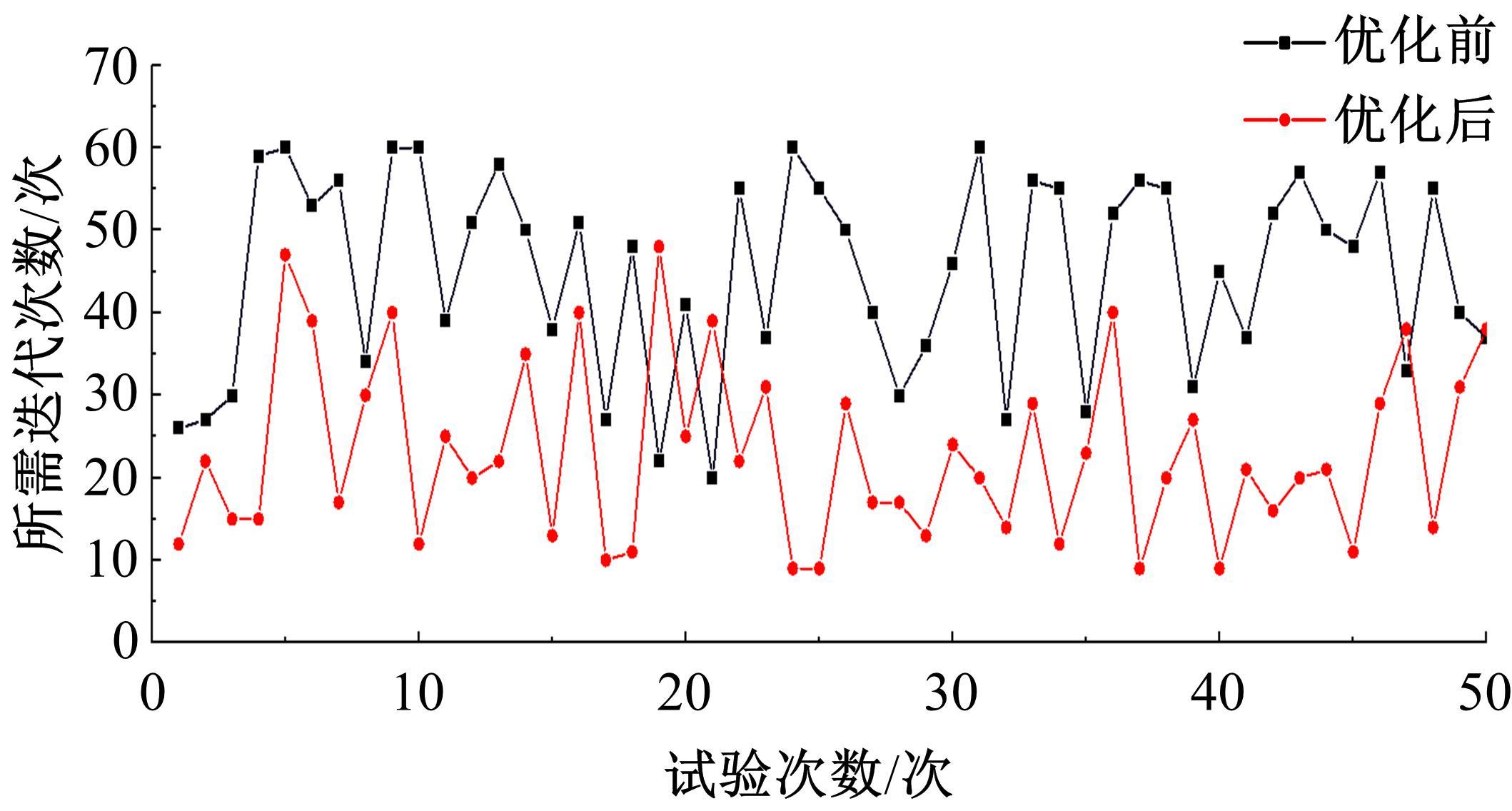
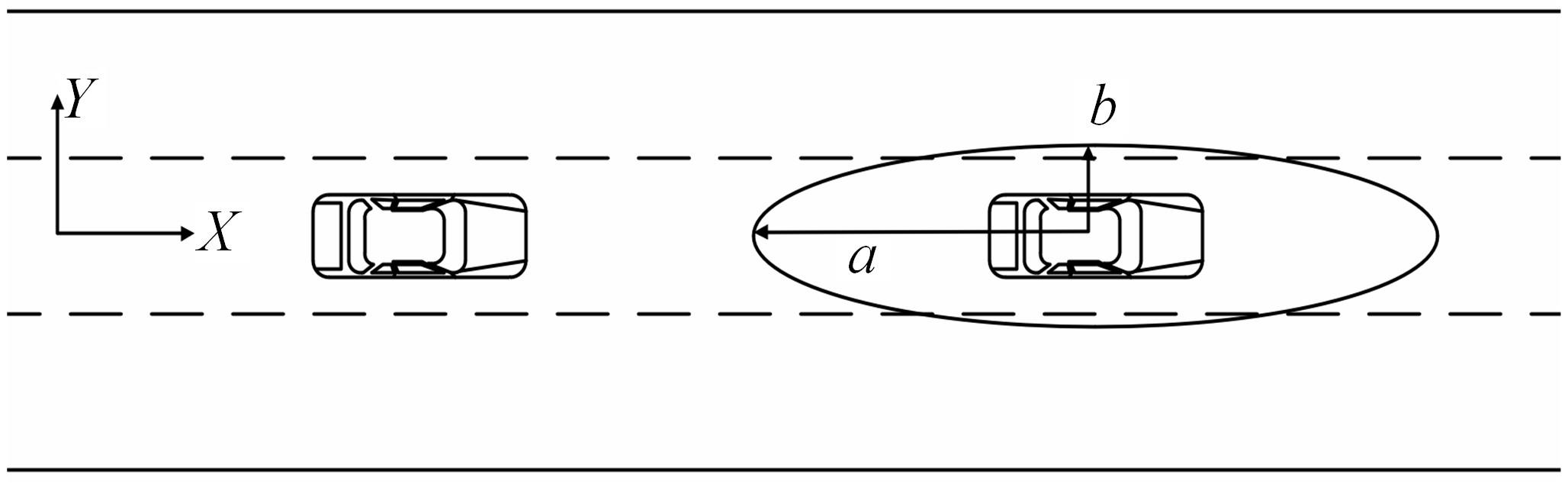
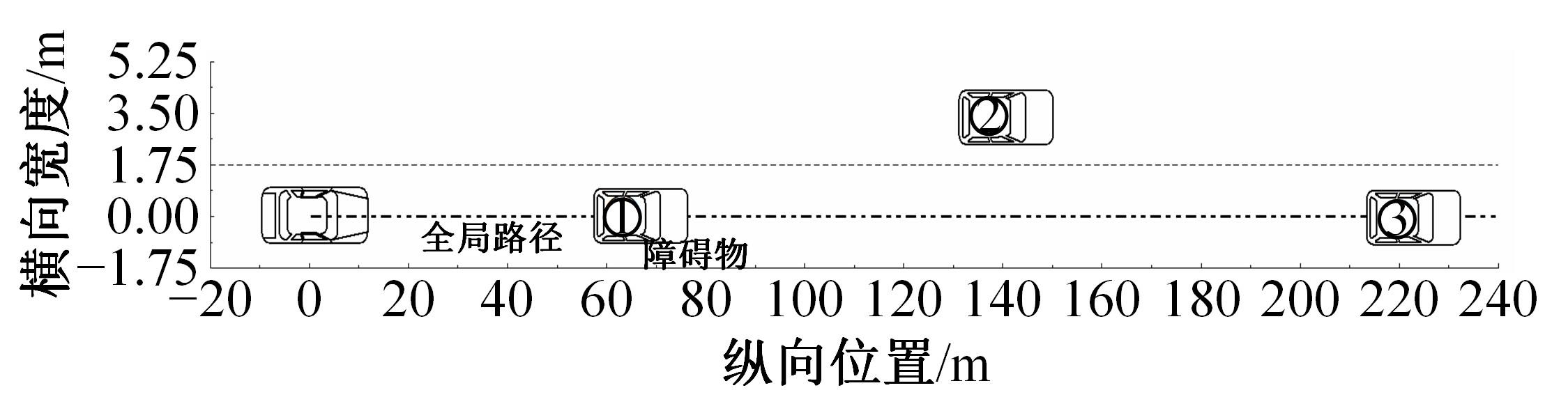
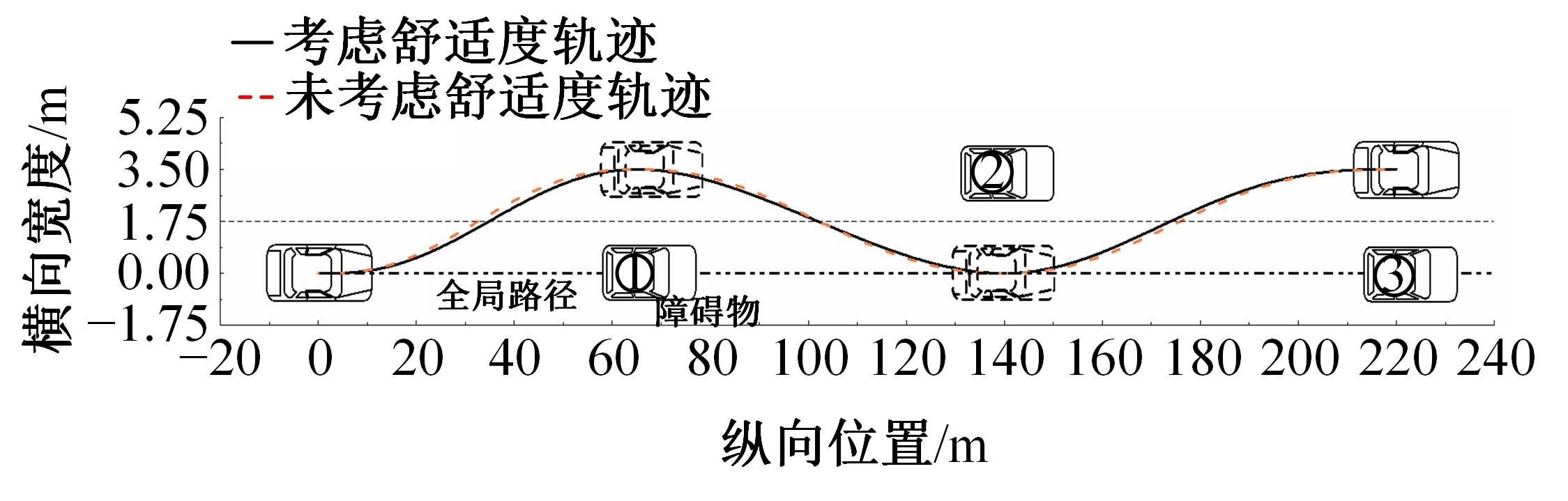
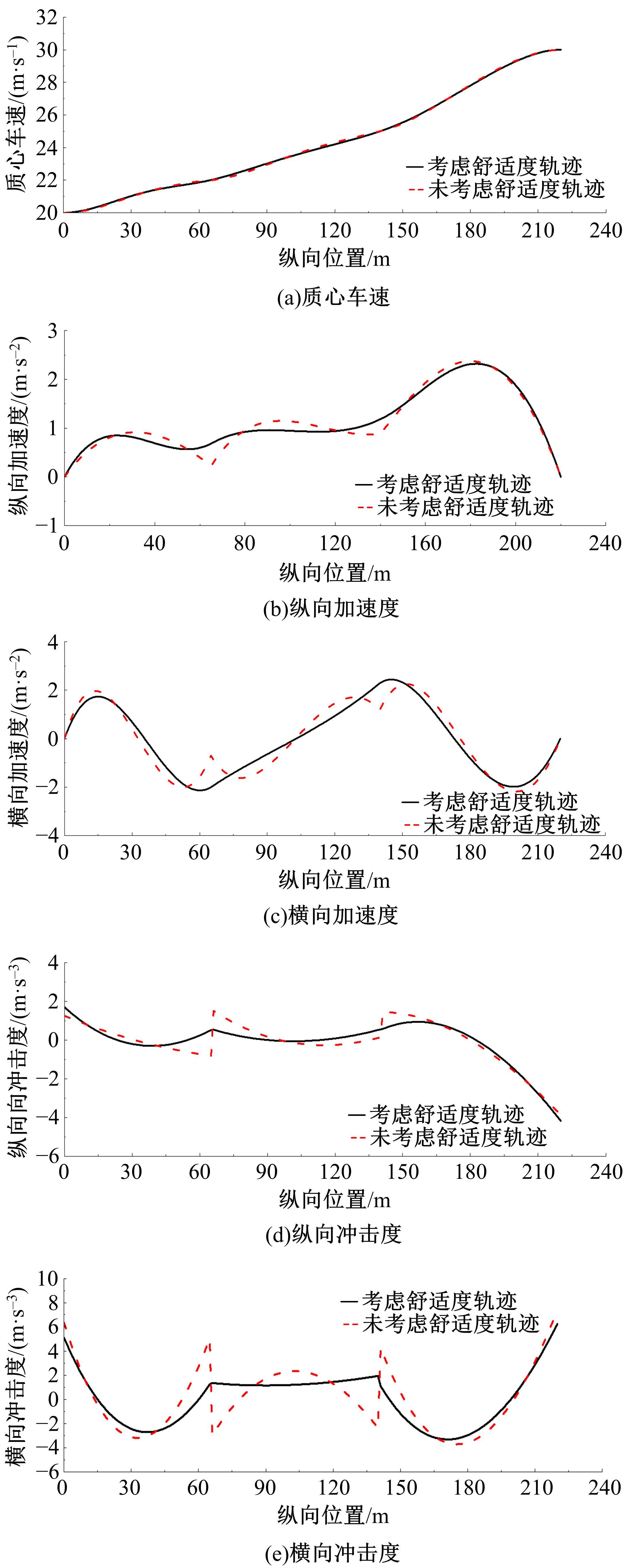
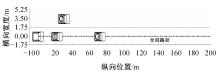
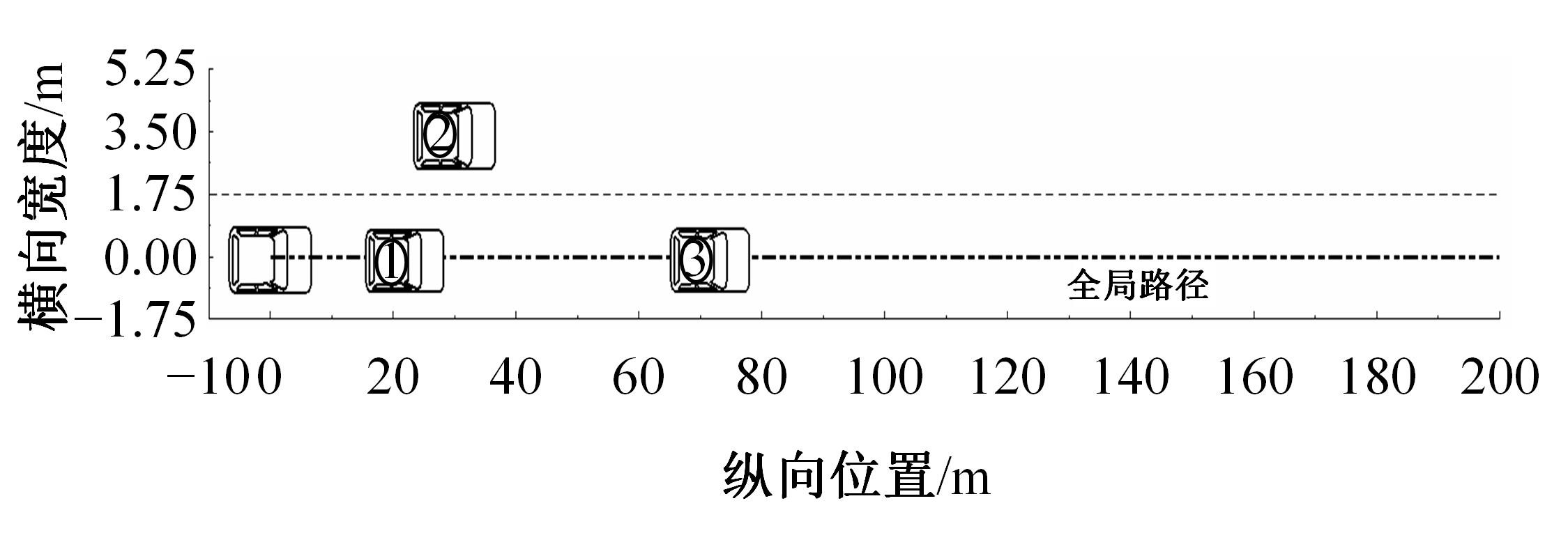
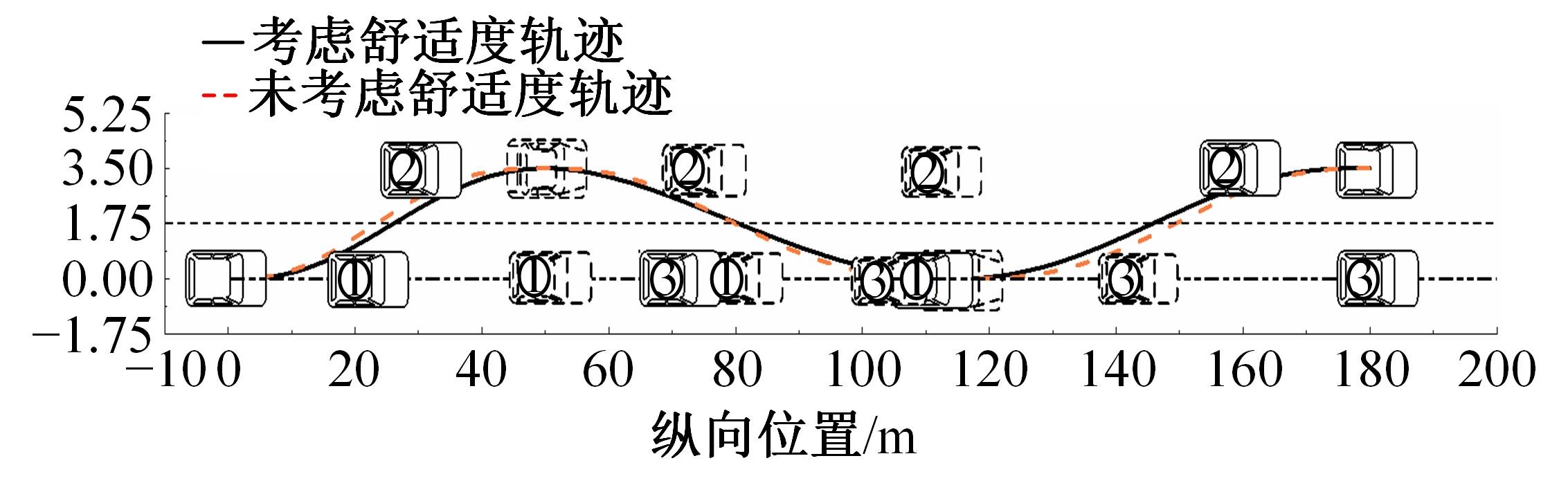
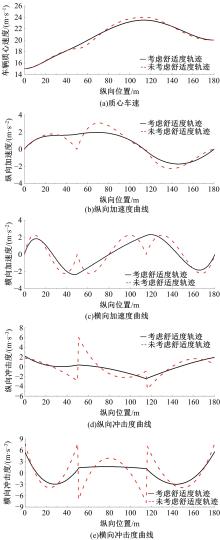
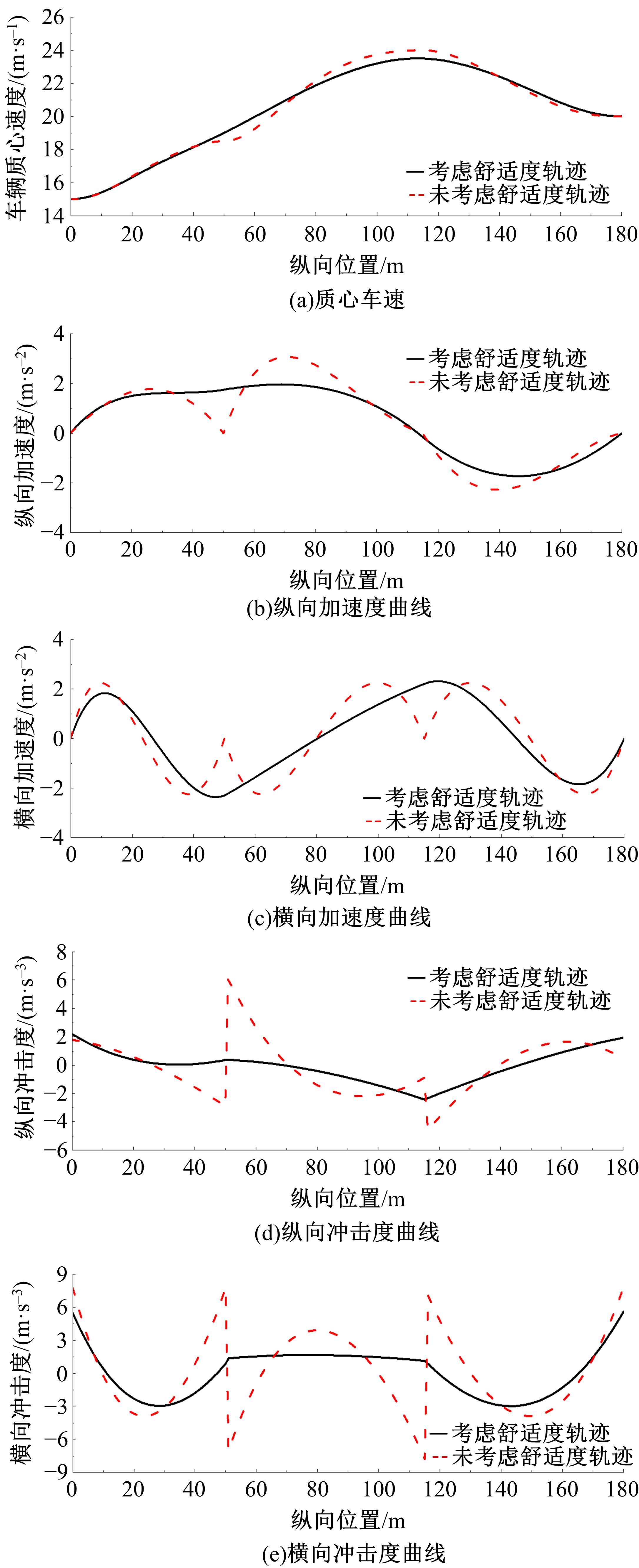
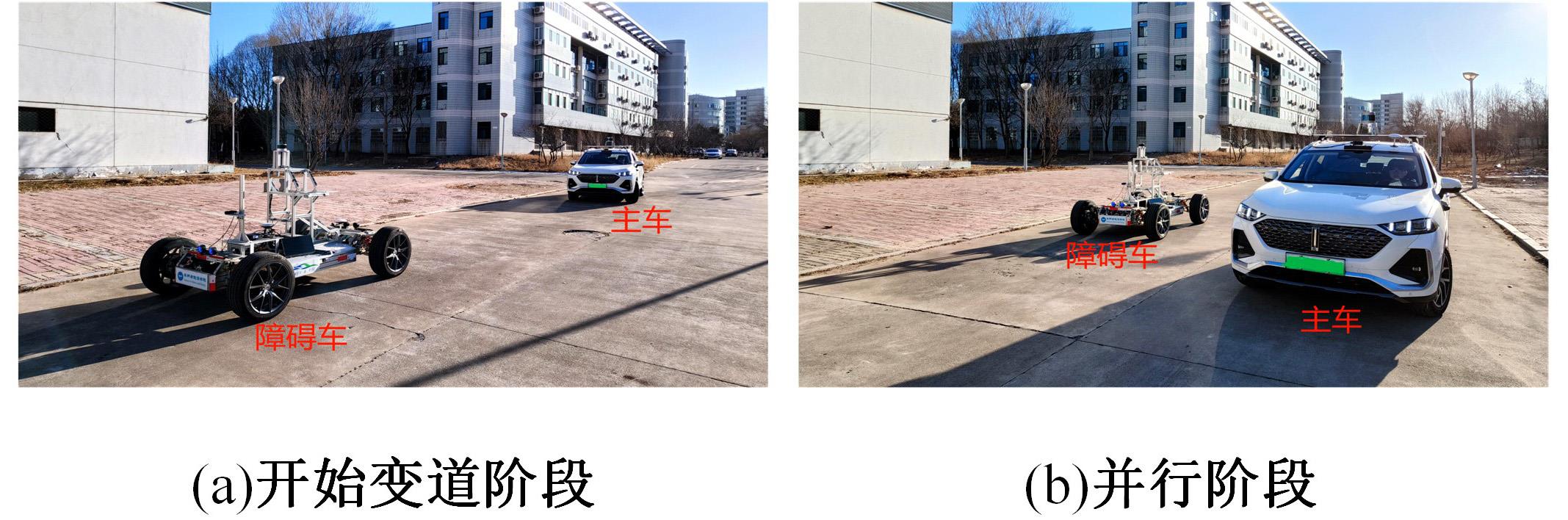
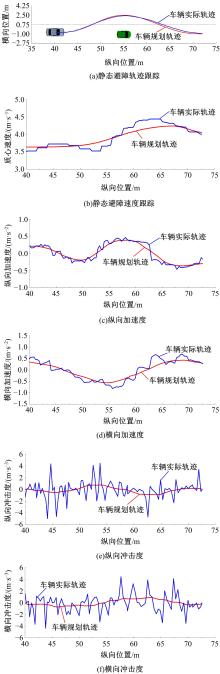
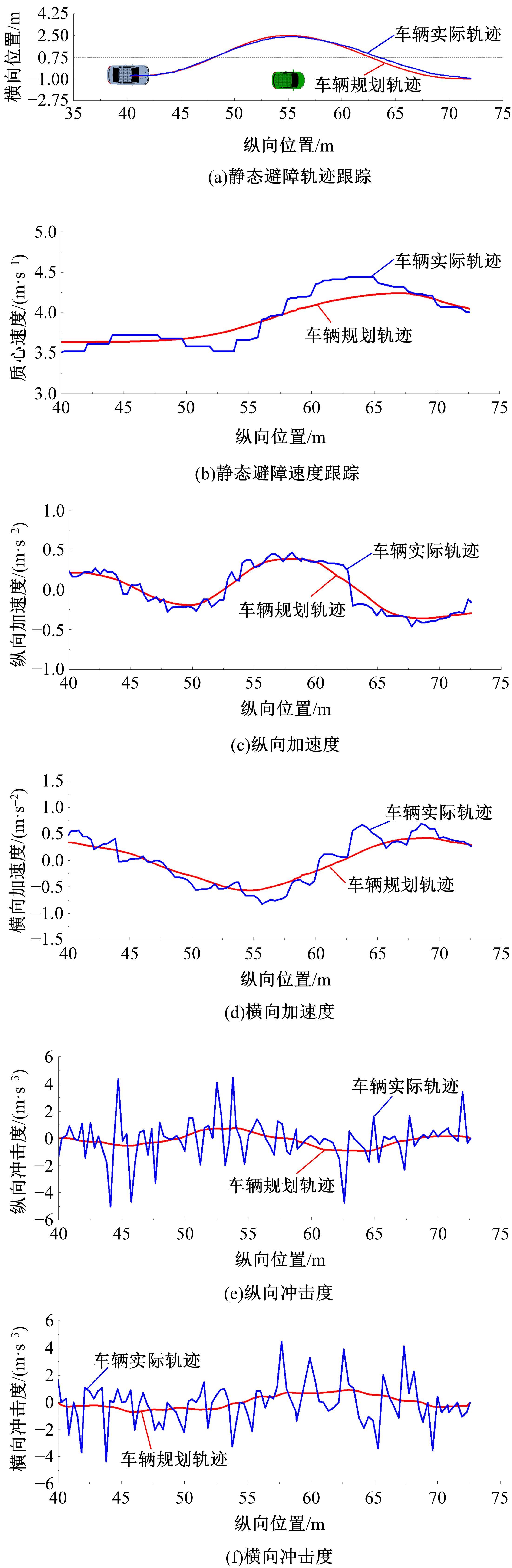
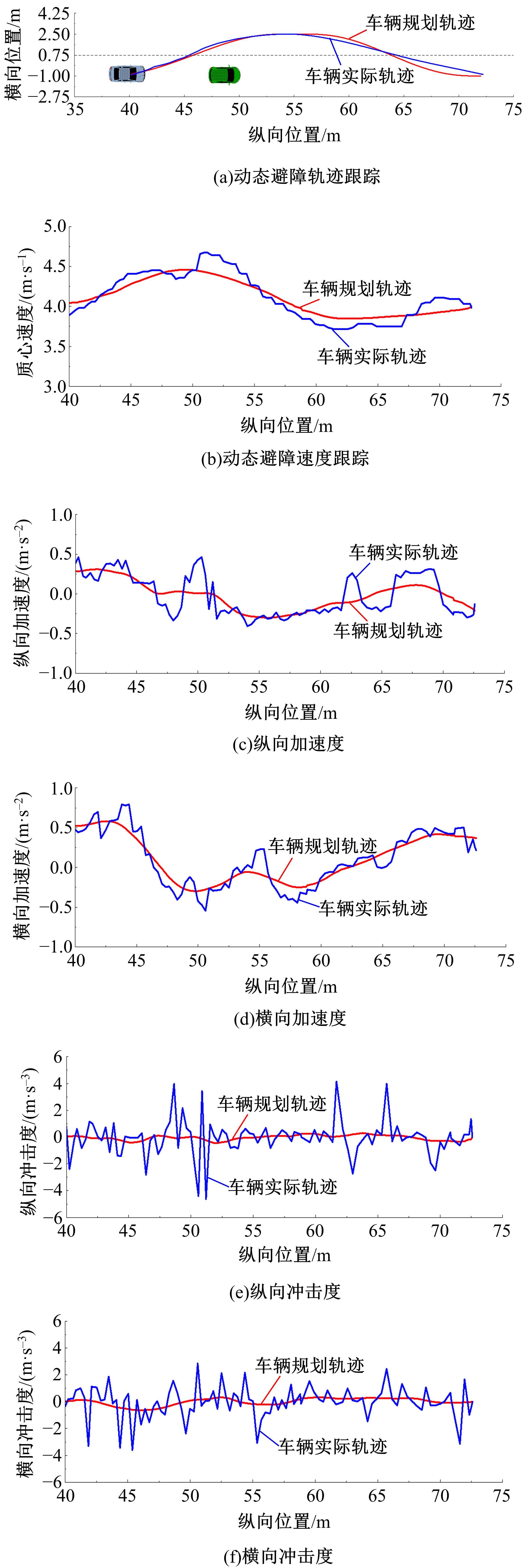
为提高智能汽车在避障换道过程中的舒适度与安全性,提出了一种考虑舒适度的智能汽车人工蜂群轨迹规划方法。通过采样法在速度-时间空间内进行位置采样,得到基于时间的速度序列,并设计新的蜜源搜索策略和蜜源更新策略以提高人工蜂群算法的搜索精度和收敛速度。结合五次多项式拟合速度序列与蜜源位置,得到换道轨迹。考虑车辆加速度和冲击度对舒适度的影响,设计轨迹舒适度评价函数并融合到适应度函数中,通过碰撞检测结果优化换道轨迹。基于Simulink-PreScan-CarSim联合仿真平台验证算法有效性。结果表明:面对不同工况,本文提出方法能够规划出符合加速度、冲击度最值约束的无碰撞安全换道轨迹,且规划结果优于未考虑舒适度的规划轨迹。在实车测试中,本文所提方法在低速场景下能够实现对静态障碍物、低速动态障碍物的避障轨迹规划,避障轨迹均符合舒适度要求,且表现出较好的可跟踪性。
中图分类号:
- U461.1
| 1 | 魏民祥, 滕德成, 吴树凡. 基于Frenet坐标系的自动驾驶轨迹规划与优化算法[J]. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(4): 815-824. |
| Wei Min-xiang, Teng De-cheng, Wu Shu-fan. Trajectory planning and optimization algorithm for automated driving based on Frenet coordinate system[J]. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(4): 815-824. | |
| 2 | 张玮,张树培,罗崇恩,等.智能汽车紧急工况避撞轨迹规划[J].吉林大学学报:工学版,2022,52(7):1515-1523. |
| Zhang Wei, Zhang Shu-pei, Luo Chong-en,et al. Collision avoidance trajectory planning of intelligent vehicle under emergency conditions[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2022,52(7):1515-1523. | |
| 3 | 张琳,章新杰,郭孔辉,等.未知环境下智能汽车轨迹规划滚动窗口优化[J].吉林大学学报:工学版, 2018,48(3):652-660. |
| Zhang Lin, Zhang Xin-jie, Guo Kong-hui,et al. Optimization of rolling window of intelligent vehicle trajectory planning in unknown environment[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2018,48(3) :652-660. | |
| 4 | Ferguson D, Stentz A. Using interpolation to improve path planning: the field D* algorithm[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2010, 23(2): 79-101. |
| 5 | Zuo Z, Yang X, Li Z, et al. MPC-based cooperative control strategy of path planning and trajectory tracking for intelligent vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2021, 6(3): 513-522. |
| 6 | 赵树恩,王金祥,李玉玲.基于多目标优化的智能车辆换道轨迹规划[J].交通运输工程学报,2021,21(2):232-242. |
| Zhao Shu-en, Wang Jin-xiang, Li Yu-ling. Lane change trajectory planning for intelligent vehicle based on multi-objective optimization[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering,2021,21(2):232-242. | |
| 7 | Bae I, Moon J, Park H, et al. Path generation and tracking based on a Bezier curve for a steering rate controller of autonomous vehicles[C]∥16th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Hague, Netherlands, 2013: 436-441. |
| 8 | Guo B, Kuang Z, Guan J, et al. An improved a-star algorithm for complete coverage path planning of unmanned ships[J]. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 36(3): 1-10. |
| 9 | Qi J, Yang H, Sun H. MOD-RRT*: a sampling-based algorithm for robot path planning in dynamic environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 68(8): 7244-7251. |
| 10 | 徐胜,邢强,王浩. 解决势场法路径规划中局部极小问题的角度累积法[J]. 控制与决策, 2022, 37(8): 1997-2007. |
| Xu Sheng, Xing Qiang, Wang Hao. Angle accumulation method for solving local minimum problem in path planning with potential field method[J]. Control and Decision, 2022, 37(8): 1997-2007. | |
| 11 | Keller M, Hoffmann F, Hass C, et al. Planning of optimal collision avoidance trajectories with timed elastic bands[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2014, 47(3): 9822-9827. |
| 12 | Rasekhipour Y, Khajepour A, Chen S K, et al. A potential field-based model predictive path-planning controller for autonomous road vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(5):1255-1267. |
| 13 | Dixit S, Montanaro U, Dianati M, et al. Trajectory planning for autonomous high-speed overtaking in structured environments using robust MPC[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 21(6): 2310-2323. |
| 14 | 彭浩楠,唐明环,查奇文,等.自动驾驶汽车双车道换道最优轨迹规划方法[J].吉林大学学报:工学版,2022,52(12):2852-2863. |
| Peng Hao-nan, Tang Ming-huan, Zha Qi-wen, et al. Optimal trajectory planning method for two-lane lane change of autonomous vehicle[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2022,52(12):2852-2863. | |
| 15 | Ji Y, Ni L, Zhao C, et al. TriPField: a 3D potential field model and its applications to local path planning of autonomous vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(3): 3541-3554. |
| 16 | Guo H, Shen C, Zhang H, et al. Simultaneous trajectory planning and tracking using an MPC method for cyber-physical systems: a case study of obstacle avoidance for an intelligent vehicle[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(9): 4273-4283. |
| 17 | Yang H, Qi J, Miao Y, et al. A new robot navigation algorithm based on a double-layer ant algorithm and trajectory optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(11):8557-8566. |
| 18 | Ma Y N, Gong Y J, Xiao C F, et al. Path planning for autonomous underwater vehicles: an ant colony algorithm incorporating alarm pheromone[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(1): 141-154. |
| 19 | Zong C, Yao X, Fu X. Path planning of mobile robot based on improved ant colony algorithm[C]∥2022 IEEE 10th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference, Chongqing, China, 2022: 1106-1110. |
| 20 | Xu F, Li H, Pun C M, et al. A new global best guided artificial bee colony algorithm with application in robot path planning[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 88: 1-13. |
| 21 | Contreras-Cruz M A, Ayala-Ramirez V, Hernandez Belmonte U H. Mobile robot path planning using artificial bee colony and evolutionary programming[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 30: 319-328. |
| 22 | 刘志强, 张春雷, 张爱红, 等. 基于驾驶行为的追尾避撞控制策略研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2017, 39(9): 1068-1073, 1080. |
| Liu Zhi-qiang, Zhang Chun-lei, Zhang Ai-hong, et al. A study on the control strategy for rear-end collision avoidance based on drivers' behavior[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2017, 39(9): 1068-1073, 1080. |
| [1] | 刘从臻,陈高,刘洪柱,马强,徐成伟,孟辉,王国林. 湿滑路面轮胎接地力学特性模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1501-1511. |
| [2] | 黄玲,崔躜,游峰,洪佩鑫,钟浩川,曾译萱. 适用于多车交互场景的车辆轨迹预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1188-1195. |
| [3] | 郭洪艳,王连冰,赵旭,戴启坤. 考虑侧向运动的整车质量与道路坡度估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1175-1187. |
| [4] | 陆玉凯,袁帅科,熊树生,朱绍鹏,张宁. 汽车漆面缺陷高精度检测系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1205-1213. |
| [5] | 汪少华,张启睿,施德华,殷春芳,李春. 双行星排式混合动力传动系统非线性振动响应特性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 890-901. |
| [6] | 高镇海,蔡荣贵,孙天骏,于桐,赵浩源,班浩. 人机共驾下的驾驶行为数据滤波方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 589-599. |
| [7] | 谢宪毅,王禹涵,金立生,赵鑫,郭柏苍,廖亚萍,周彬,李克强. 基于改变控制时域时间步长的智能车轨迹跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 620-630. |
| [8] | 邓小林,杨馥模,覃善甘. 新型仿竹六边形梯度层级多胞管耐撞性对比分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 333-345. |
| [9] | 王毅刚,王玉鹏,张昊,赵思安. 高速列车转向架区域气动噪声源识别与分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 346-355. |
| [10] | 聂建军,侯军凯,解晓琳,鄢鸿桢. 新型巡检机器人移动底盘设计及越障性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 356-364. |
| [11] | 胡宏宇,张慧珺,姚荣涵,陈国迎,高菲. L3级自动驾驶接管过程驾驶员情景意识研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 410-418. |
| [12] | 吴骁,史文库,郭年程,赵燕燕,陈志勇,李鑫鹏,孙卓,刘健. 基于Ease off的准双曲面齿轮多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 76-85. |
| [13] | 王铁,李旭东,田程,赵宏伟. 基于多轴载荷投影构建轮辋双轴疲劳损伤模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 99-104. |
| [14] | 李旭东,王新宇,田程,张新峰,牛治慧,赵志强. 基于用户关联的车辆耐久性载荷谱编制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 66-75. |
| [15] | 陈兆玮,蒲前华. 弹性车轮对大跨斜拉桥车桥耦合振动的抑制特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2519-2532. |
|
||