吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (7): 1821-1830.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221193
• 车辆工程·机械工程 •
基于最小二乘的车速解耦路面辨识方法
- 1.青岛理工大学 机械与汽车工程学院,山东 青岛 266520
2.吉林大学 汽车仿真与控制国家重点实验室,长春 130022
Vehicle speed decoupling road identification method based on least squares
Jian-ze LIU1( ),Jiang LIU1,2(
),Jiang LIU1,2( ),Min LI1,Xin-jie ZHANG2
),Min LI1,Xin-jie ZHANG2
- 1.School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering,Qingdao University of Technology,Qingdao 266520,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
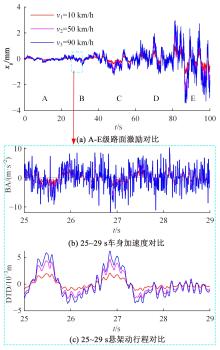
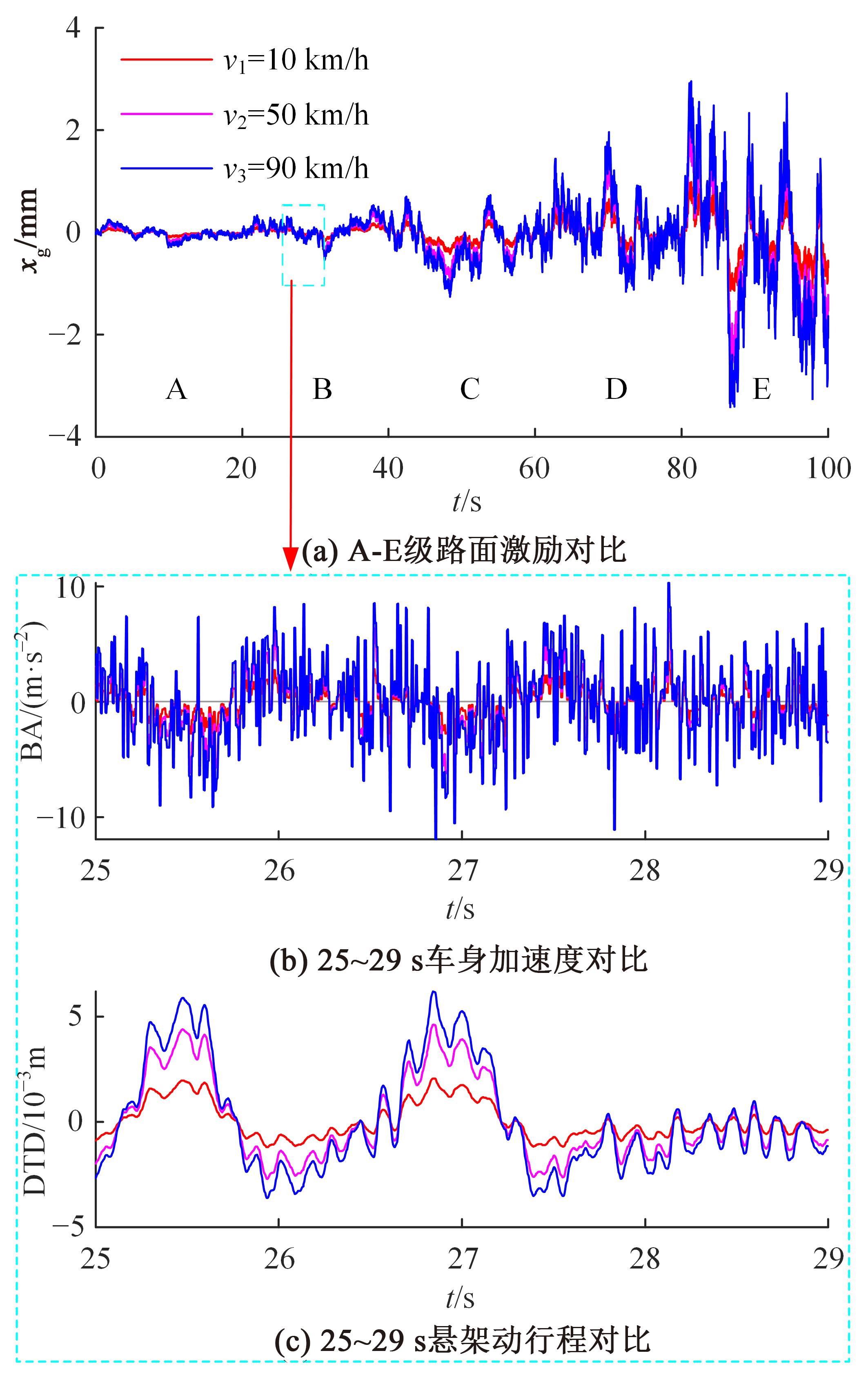
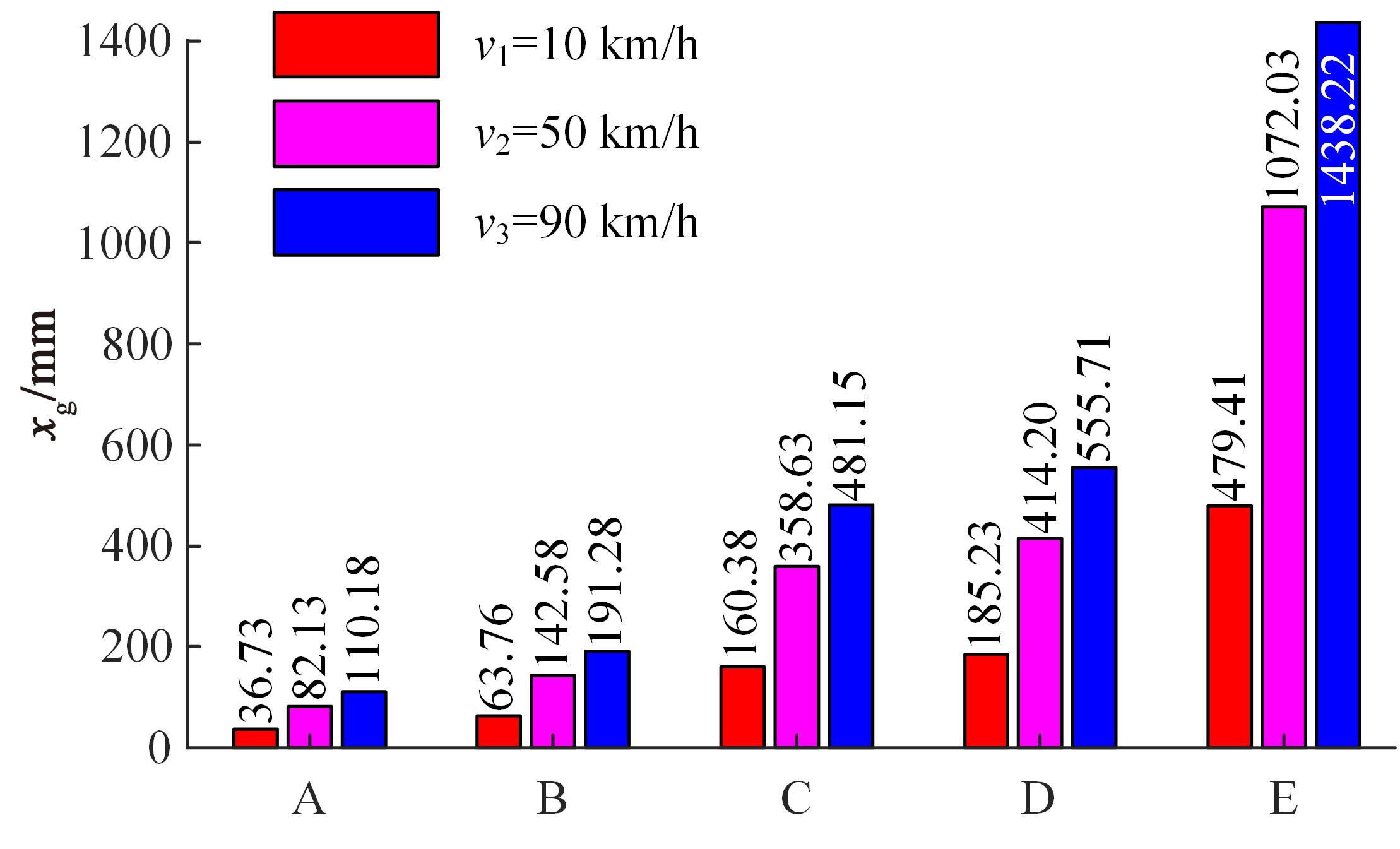
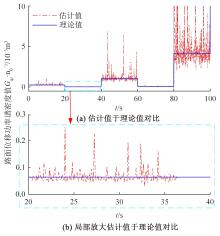
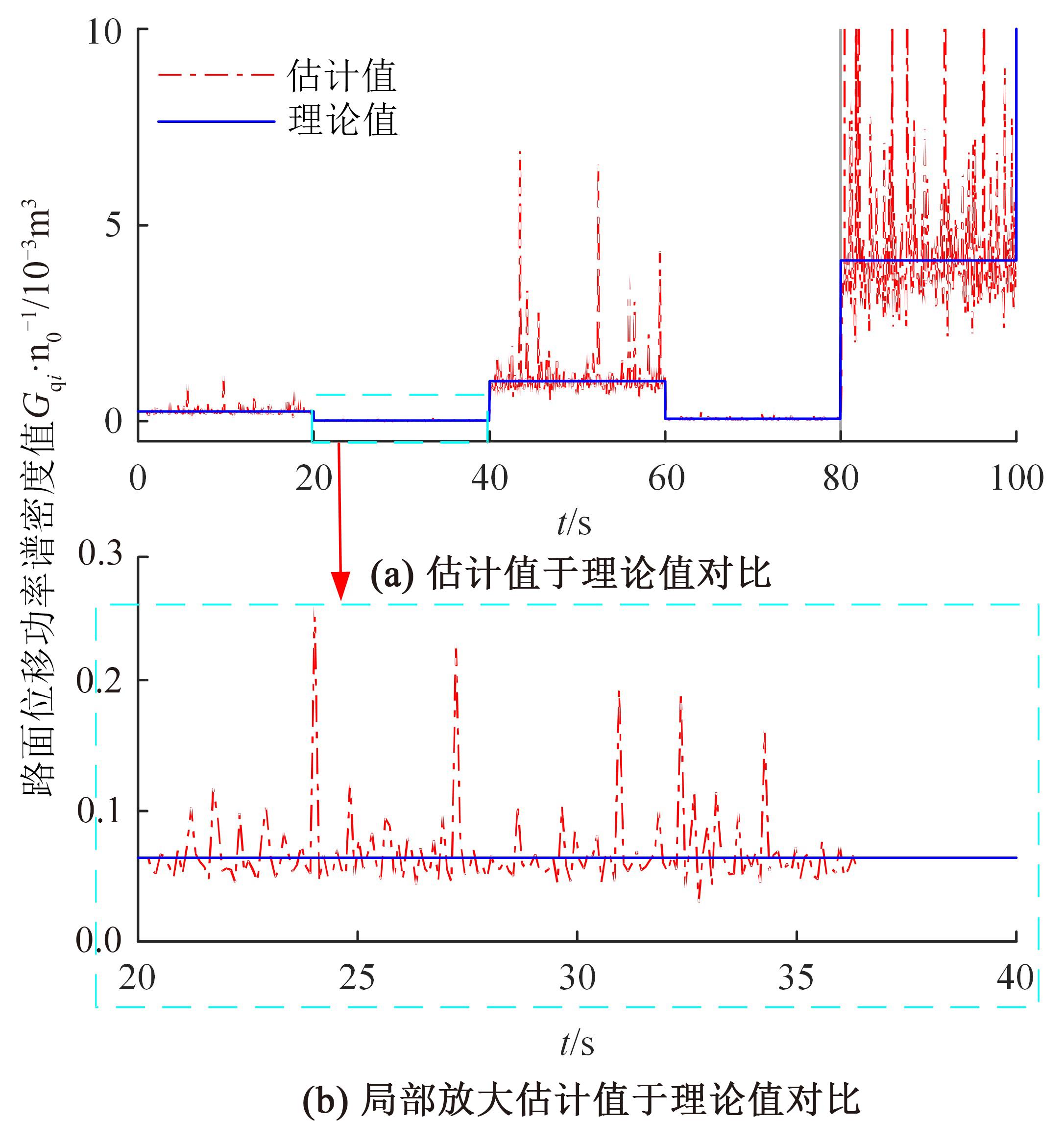
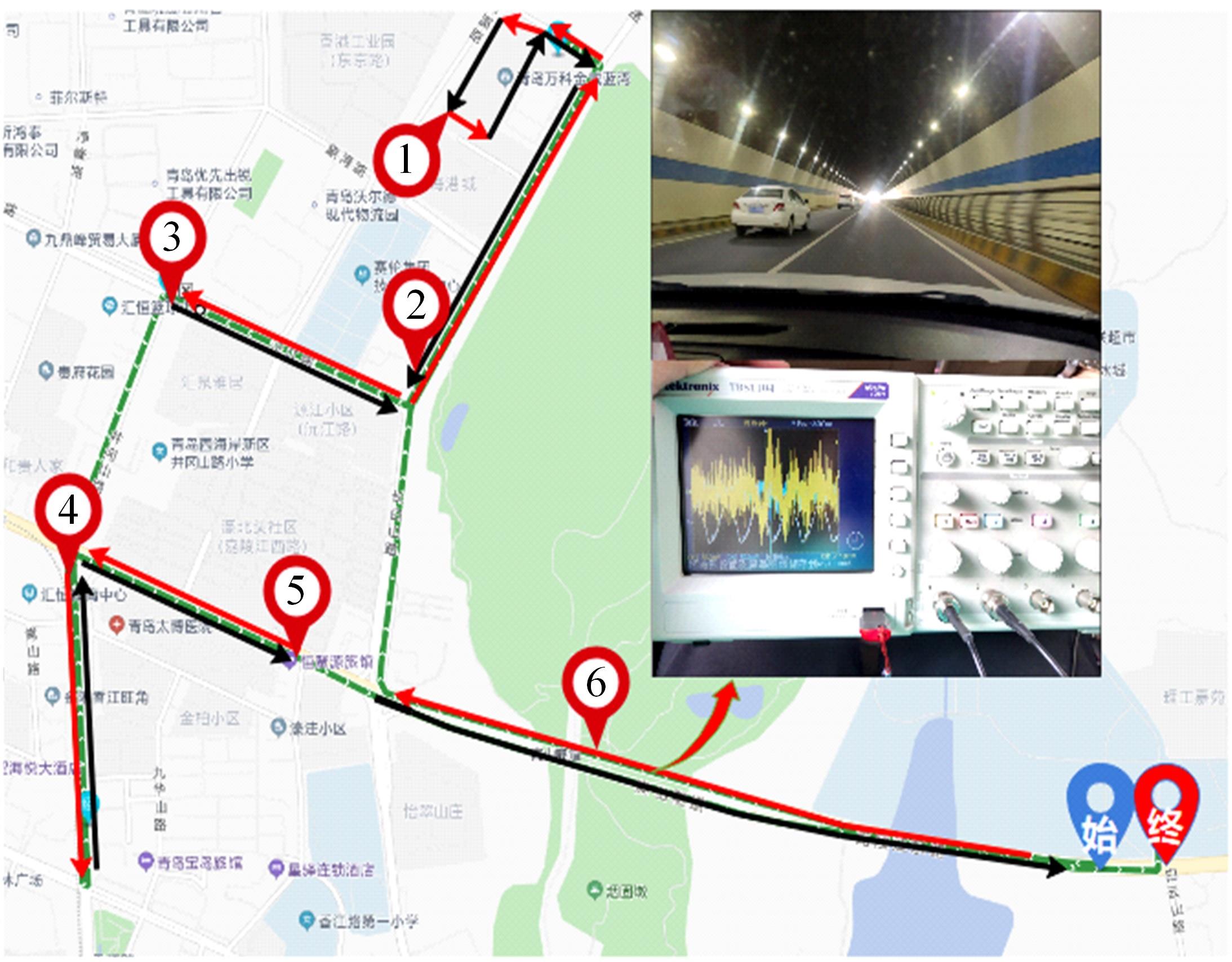
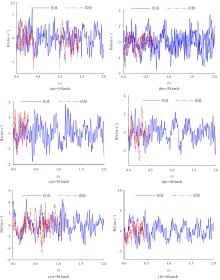
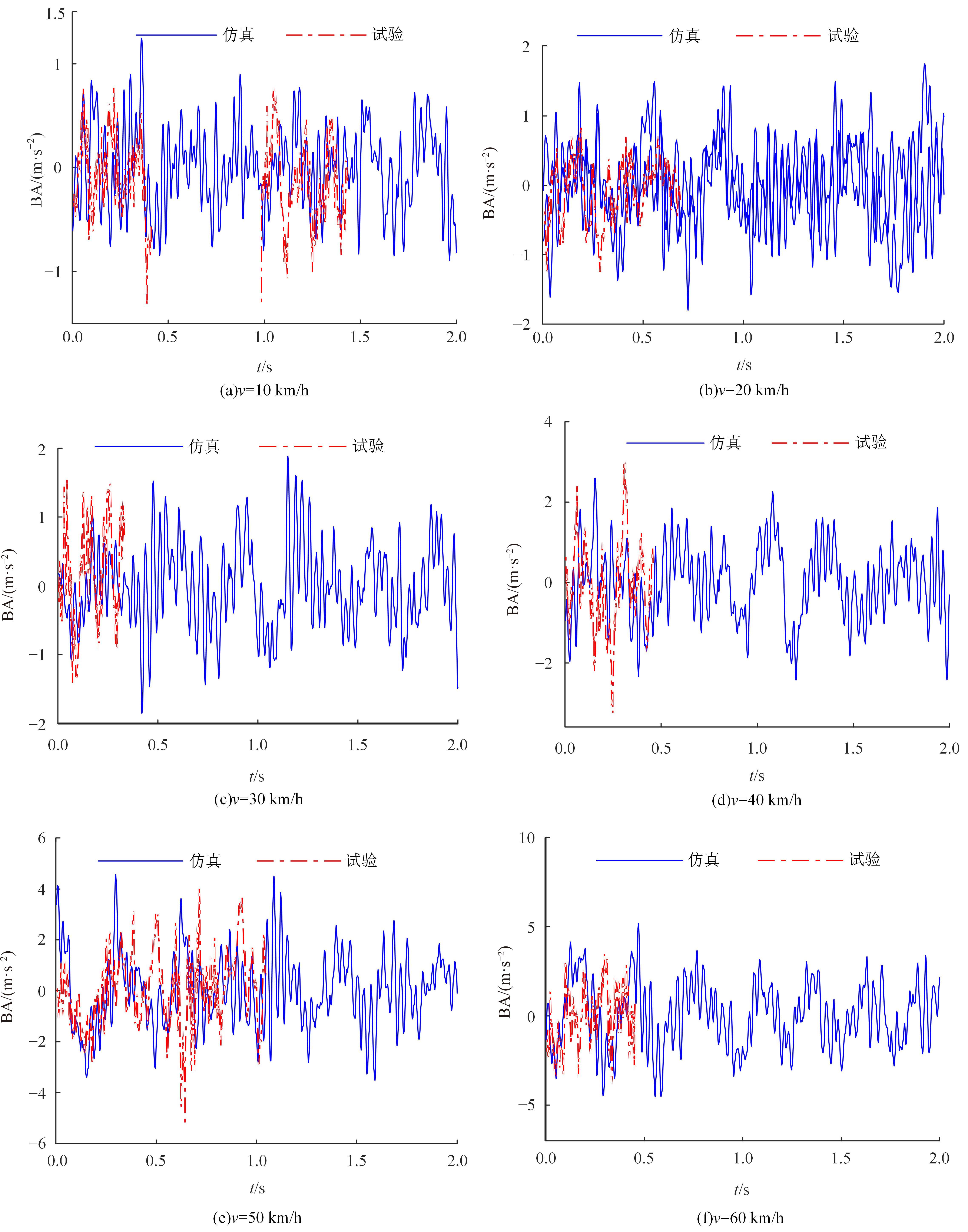
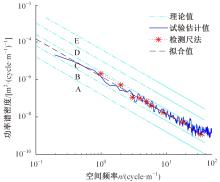
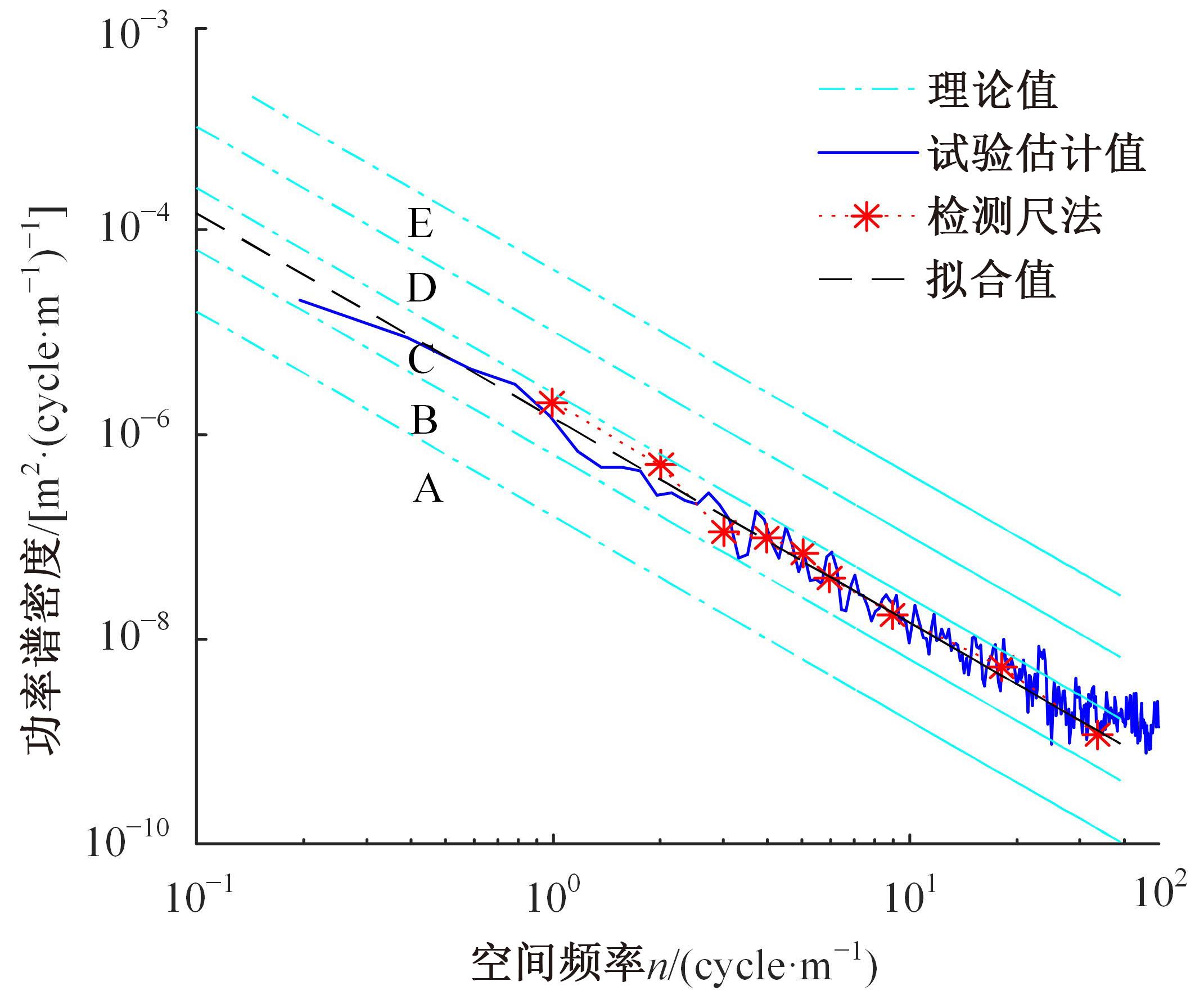
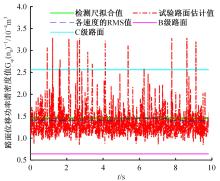
针对路面辨识方法需要大量训练集或高的算力支撑不利于驾乘感提升实现的问题,提出了一种改进的最小二乘估计方法,无需训练集,直接采集悬架响应来辨识路面激励及路面等级变化。在建立的路面等级系数和车速为变参数模型的基础上,探讨路面激励数据的取样处理规则,通过解耦行驶速度的影响,得到了实时的路面不平度系数。仿真结果表明,A-E级路面综合估值准确度在97%以上,对路面等级突变的响应时间少于0.15 s,对路面输入的跟随性能良好。采集不同路段不同车速下的实车动力学参数进行辨识,试验结果表明,该工况下估计值准确度为98.2%,与三米尺检测法所得实际路面等级相符,验证了这种车速解耦路面辨识方法的可行性及准确性。
中图分类号:
- U461.4
| 1 | 郭孔辉, 余五辉, 章新杰, 等. 自适应半主动悬架系统控制策略[J]. 湖南大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 40(2):39-44. |
| Guo Kong-hui, Yu Wu-hui, Zhang Xin-jie, et al. Semi-active suspension adaptive control strategy[J]. Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences), 2013, 40(2):39-44. | |
| 2 | Yang Y A, Hl A, Xt A, et al. Fundamental mode shape estimation and element stiffness evaluation of girder bridges by using passing tractor-trailers[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 169:No.108746. |
| 3 | Abulizi N, Kawamura A, Tomiyama K, et al. Measuring and evaluating of road roughness conditions with a compact road profiler and ArcGIS[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering (English Edition), 2016, 3(5): 398-411. |
| 4 | Ori T R, Kone N M, Traore S. Development of a virtual environment for simulation of a 3D road profile using OpenCRG and MATLAB GUI[J]. Engineering, 2021,13(12):677-689. |
| 5 | 李杰, 郭文翠, 赵旗, 等. 基于车辆响应的路面不平度识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019,49(6):1810-1817. |
| Li Jie, Guo Wen-cui, Zhao Qi, et al. Road roughness identification based on vehicle responses[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1810-1817. | |
| 6 | 管欣, 金号, 段春光, 等. 汽车行驶道路侧向坡度估计[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(6): 1802-1809. |
| Guan Xin, Jin Hao, Duan Chun-guang, et al. Estimation of lateral slope of vehicle driving road[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1802-1809. | |
| 7 | 巩明德, 颜鑫. 采用路面识别方法的重型救援车辆主动悬架控制策略[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2019, 53(2): 32-39. |
| Gong Ming-de, Yan Xin.A control strategy for active suspension of heavy rescue vehicles based on road level estimation[J]. Journal of Xi´an Jiaotong University, 2019, 53(2): 32-39. | |
| 8 | Liu W, Wang R, Ding R, et al. On-line estimation of road profile in semi-active suspension based on unsprung mass acceleration[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2020, 135:No.106370. |
| 9 | Ding R, Wang R, Meng X, et al. Intelligent switching control of hybrid electromagnetic active suspension based on road identification - ScienceDirect[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2021,152: No.107355. |
| 10 | Xue K, Nagayama T, Zhao B. Road profile estimation and half-car model identification through the automated processing of smartphone data[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2020, 142: No.106722. |
| 11 | Zhao B, Nagayama T, Xue K. Road profile estimation, and its numerical and experimental validation, by smartphone measurement of the dynamic responses of an ordinary vehicle[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2019, 457: 92-117. |
| 12 | Liu J, Liu J, Zhang X, et al. Transmission and energy-harvesting study for a novel active suspension with simplified 2-DOF multi-link mechanism[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2021, 160: No.104286. |
| 13 | 寇发荣, 高亚威, 景强强, 等. 基于路面等级自适应的主动悬架LQG控制[J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(23): 30-37. |
| Kou Fa-rong, Gao Ya-wei, Jing Qiang-qiang, et al. LQG control of active suspension based on adaptive road surface level[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(23): 30-37. | |
| 14 | Sun Y, Li L, Yan B J, et al. A hybrid algorithm combining EKF and RLS in synchronous estimation of road grade and vehicle' mass for a hybrid electric bus[J]. Mechanical Systems & Signal Processing, 2016, 68/69:416-430. |
| 15 | Li Z, Yu W, Cui X. Online classification of road roughness conditions with vehicle unsprung mass acceleration by sliding time window[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2018, 2018:1-13. |
| 16 | He Z, Yang Z, Cui X, et al. A method of state-of-charge estimation for EV power lithium-ion battery using a novel adaptive extended kalman filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(12):14618-14630. |
| 17 | 隗海林, 包翠竹, 李洪雪, 等. 基于最小二乘支持向量机的怠速时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2018, 48(5): 1360-1365. |
| Kui Hai-lin, Bao Cui-zhu, Li Hong-xue, et al. Idling time prediction method based on least square support vector machine[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1360-1365. | |
| 18 | Güneş H. Design and manufacture of tube type nonhollow linear generators for suspension systems of electric and hybrid cars[J]. Journal of Process Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 235(5): 1420-1428. |
| [1] | 刘从臻,陈高,刘洪柱,马强,徐成伟,孟辉,王国林. 湿滑路面轮胎接地力学特性模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1501-1511. |
| [2] | 谢宪毅,张明君,金立生,周彬,胡涛,白宇飞. 考虑舒适度的智能汽车人工蜂群轨迹规划方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1570-1581. |
| [3] | 黄玲,崔躜,游峰,洪佩鑫,钟浩川,曾译萱. 适用于多车交互场景的车辆轨迹预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1188-1195. |
| [4] | 郭洪艳,王连冰,赵旭,戴启坤. 考虑侧向运动的整车质量与道路坡度估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1175-1187. |
| [5] | 陆玉凯,袁帅科,熊树生,朱绍鹏,张宁. 汽车漆面缺陷高精度检测系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1205-1213. |
| [6] | 汪少华,张启睿,施德华,殷春芳,李春. 双行星排式混合动力传动系统非线性振动响应特性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 890-901. |
| [7] | 高镇海,蔡荣贵,孙天骏,于桐,赵浩源,班浩. 人机共驾下的驾驶行为数据滤波方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 589-599. |
| [8] | 谢宪毅,王禹涵,金立生,赵鑫,郭柏苍,廖亚萍,周彬,李克强. 基于改变控制时域时间步长的智能车轨迹跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 620-630. |
| [9] | 邓小林,杨馥模,覃善甘. 新型仿竹六边形梯度层级多胞管耐撞性对比分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 333-345. |
| [10] | 王毅刚,王玉鹏,张昊,赵思安. 高速列车转向架区域气动噪声源识别与分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 346-355. |
| [11] | 聂建军,侯军凯,解晓琳,鄢鸿桢. 新型巡检机器人移动底盘设计及越障性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 356-364. |
| [12] | 胡宏宇,张慧珺,姚荣涵,陈国迎,高菲. L3级自动驾驶接管过程驾驶员情景意识研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 410-418. |
| [13] | 吴骁,史文库,郭年程,赵燕燕,陈志勇,李鑫鹏,孙卓,刘健. 基于Ease off的准双曲面齿轮多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 76-85. |
| [14] | 王铁,李旭东,田程,赵宏伟. 基于多轴载荷投影构建轮辋双轴疲劳损伤模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 99-104. |
| [15] | 李旭东,王新宇,田程,张新峰,牛治慧,赵志强. 基于用户关联的车辆耐久性载荷谱编制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 66-75. |
|
||