吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (7): 1876-1886.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230414
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
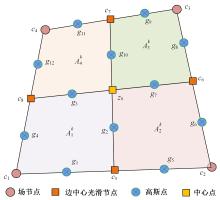
基于渐近均匀化的力-电-湿耦合光滑有限元法
- 1.西安建筑科技大学 机电工程学院,西安 710055
2.陕西省纳米材料与技术重点实验室,西安 710055
3.吉林大学 机械与航空航天工程学院,长春 130022
4.上海宝冶集团有限公司,上海 201999
Moisture-electro-mechanical coupling smoothed finite element method based on asymptotic homogenization
Jian-xiao ZHENG1,2( ),Wen-bo WANG1,Jin-song LIU1(
),Wen-bo WANG1,Jin-song LIU1( ),Li-ming ZHOU3,Yu LI4
),Li-ming ZHOU3,Yu LI4
- 1.School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology,Xi′an 710055,China
2.Shaanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Technology,Xi′an 710055,China
3.School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
4.Shanghai Baoye Group Corp. ,Ltd. ,Shanghai 201999,China
摘要:
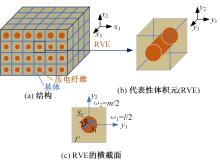
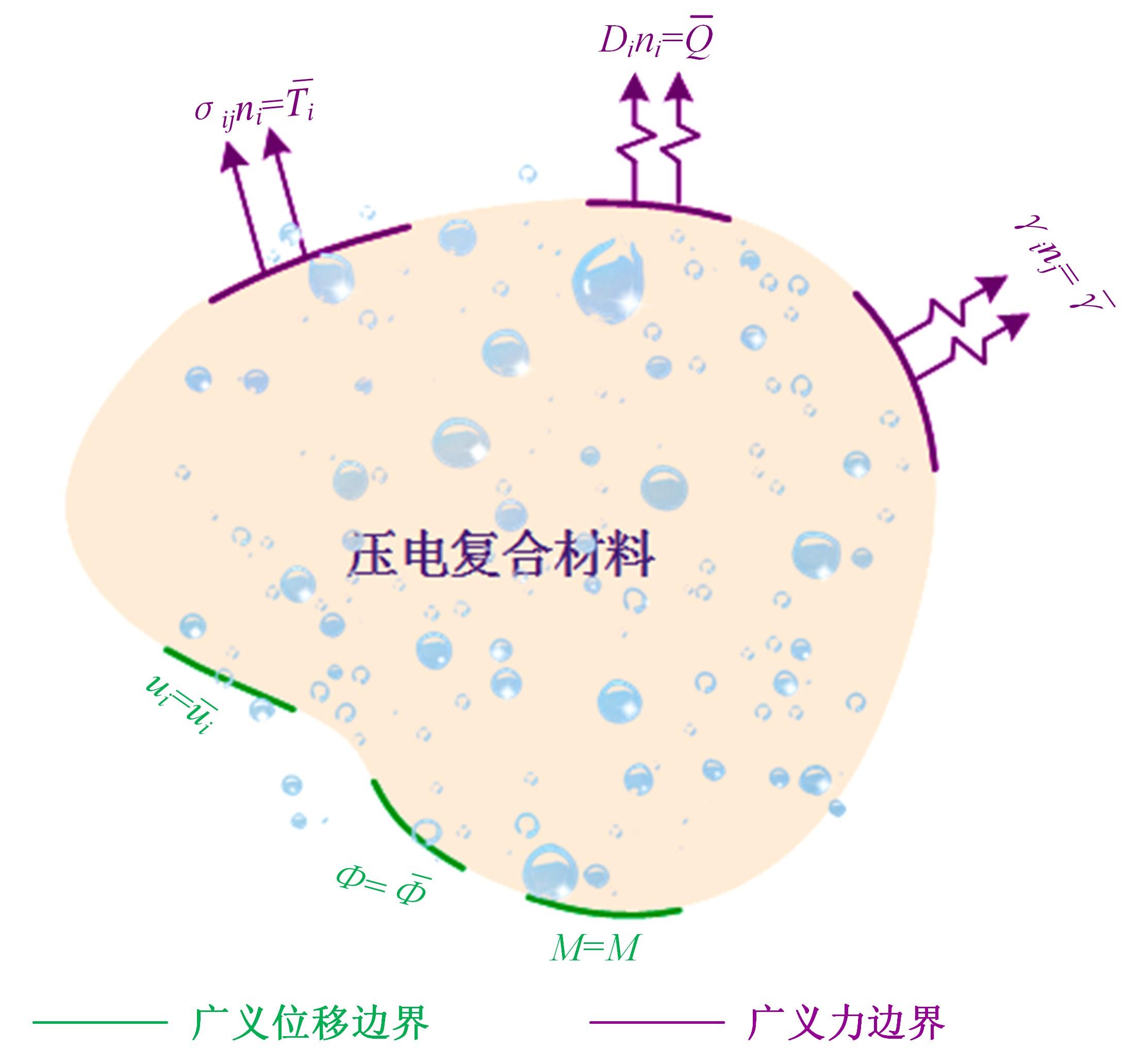
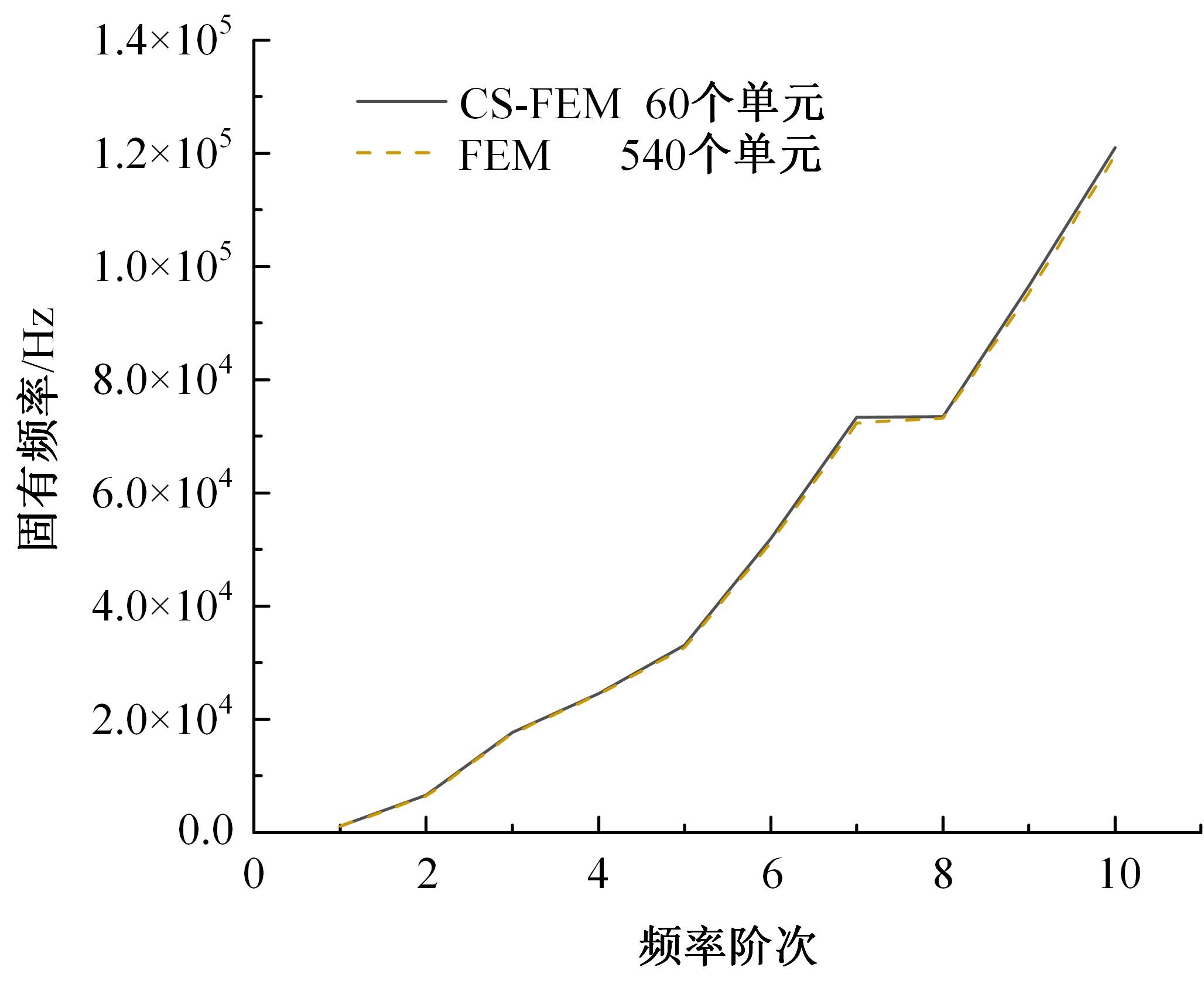
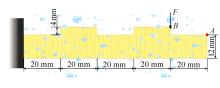
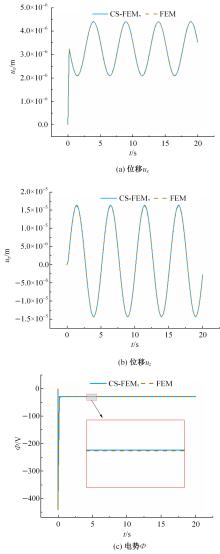
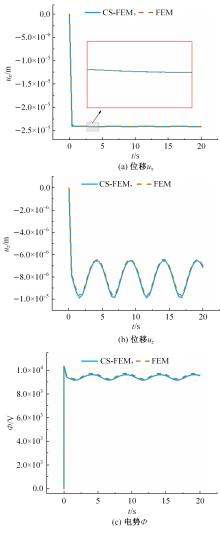
针对基于微观结构的力-电-湿多物理场耦合压电复合材料的力学特性分析问题,基于压电复合材料的基本方程、力-电-湿多物理场耦合效应,结合渐近均匀化方法预测的压电复合材料有效性能参数,提出基于渐近均匀化的力-电-湿耦合光滑有限元法。推导了力-电-湿耦合光滑有限元的动力学控制方程,并运用Wilson-θ法求解压电复合材料结构动力学问题,研究了湿度变化对结构固有频率和动力学响应的影响,并与有限元法的计算结果进行比较,验证了该方法的正确性和有效性。可见,该方法对分析压电复合材料元器件的多物理场耦合力学特性具有广阔的应用前景。
中图分类号:
- TB115
| 1 | Dagdeviren C, Joe P, Tuzman O L, et al. Recent progress in flexible and stretchable piezoelectric devices for mechanical energy harvesting, sensing and actuation[J]. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2016, 9:269-281. |
| 2 | Sappati K K, Bhadra S. Piezoelectric polymer and paper substrates: a review[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18:No.3605. |
| 3 | Akdogan E K, Allahverdi M, Safari A. Piezoelectric composites for sensor and actuator applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 2005, 52(5): 746-775. |
| 4 | Bie Y H, Cui X Y, Li Z C. A coupling approach of state-based peridynamics with node-based smoothed finite element method[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 331: 675-700. |
| 5 | Zeng Y, Jiang L, Sun Y,et al. 3D-printing piezoelectric composite with honeycomb structure for ultrasonic devices[J]. Micromachines, 2020, 11(8):No.E713. |
| 6 | Zhou L, Ren S, Meng G,et al. A multi-physics node-based smoothed radial point interpolation method for transient responses of magneto-electro-elastic structures[J]. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Element, 2019, 101: 371-384. |
| 7 | 郑建校, 段志善, 周立明. 基于渐近均匀化的力-电-热耦合光滑有限元法研究[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2023, 54(4): 1325-1335. |
| Zheng Jian-xiao, Duan Zhi-shan, Zhou Li-ming. Research on thermo-electro-mechanical coupling smoothed finite element method based on asymptotic homogenization[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2023, 54(4):1325-1335. | |
| 8 | Chan H L W, Unsworth J. Simple model for piezoelectric ceramic/polymer 1-3 composites used in ultrasonic transducer applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 1989, 36(4): 434-441. |
| 9 | Hagood N, Bent A. Development of piezoelectric fiber composites for structural actuation[C]//The 34th Conference on Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials of AIAA, La Jolla, USA, 1993: No.1717. |
| 10 | Safari A, Janas V, Panda R K. Fabrication of fine-scale 1-3 Pb(Zr x,Ti1- x )O3/ceramic/polymer composites using a modified lost mold method[J]. Int Soc Opt Eng, 1996, 2721: 251-262. |
| 11 | Bisegna P, Luciano R. Variational bounds for the overall properties of piezoelectric composites[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1996, 44(4): 583-602. |
| 12 | Meng G, Wang L, Zhang Q,et al. Coupled thermal-electrical-mechanical inhomogeneous cell-based smoothed finite element method for transient responses of functionally graded piezoelectric structures to dynamic loadings[J]. International Journal of Computational Methods, 2020, 17(6): No.1950012. |
| 13 | Zheng J, Duan Z, Zhou L. A coupling electromechanical cell-based smoothed finite element method based on micromechanics for dynamic characteristics of piezoelectric composite materials[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2019, No.4913784. |
| 14 | Yang H, Cui X Y, Li S, et al. A stable node-based smoothed finite element method for metal forming analysis[J]. Computational Mechanics, 2019, 63:1147-1164. |
| 15 | Aliqué M, Simão C D, Murillo G, et al. Fully-printed piezoelectric devices for flexible electronics applications[J]. Advances Materials Technologies, 2021, 6(3): No. 2001020. |
| 16 | Pettermann H E, Suresh S. A comprehensive unit cell model: a study of coupled effects in piezoelectric 1-3 composites[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2000, 37(39): 5447-5464. |
| 17 | Berger H, Kari S, Gabbert U, et al. An analytical and numerical approach for calculating effective material coefficients of piezoelectric fiber composites[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2005, 42(21/22): 5692-5714. |
| 18 | Poizat C, Sester M. Effective properties of composites with embedded piezoelectric fibres[J]. Computational Materials Science, 1999, 16(1/4): 89-97. |
| 19 | Zhang F, Feng P, Wang T,et al. Mechanical-electric response characteristics of 1—3 cement based piezoelectric composite under impact loading[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 228: No.116781. |
| [1] | 石忠华,宋权威,康振航,谢强,章继峰. 机翼结构超声除冰系统数值模拟与实验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1561-1573. |
| [2] | 惠迎新,孙晓荣,王红雨,高晨. 预制T梁早期水化热温度效应及梁端开裂机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1734-1741. |
| [3] | 王金国,黄恺,闫瑞芳,任帅,王志强,郭劲. 元胞自动机-有限元法模拟碳当量元素对亚共晶球墨铸铁流动性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 855-865. |
| [4] | 刘纯国,于晓彤,岳韬,李东来,张明哲. 双曲率筋条壁板铣削回弹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 188-199. |
| [5] | 周晓勤,杨璐,张磊,陈立军. 具有负压缩性的铰接八面体结构的有限元分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 865-871. |
| [6] | 刘程, 史文库, 陈志勇, 何伟, 荣如松, 宋怀兰. 汽车驱动桥准双曲面齿轮齿根弯曲应力预测与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 344-352. |
| [7] | 闫光, 庄炜, 刘锋, 祝连庆. 具有增敏效果的光纤光栅应变传感器的预紧封装及传感特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1739-1745. |
| [8] | 胡玉明, 黄音, 古海东. 排桩支护结构内力与变形三维有限元数值分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 445-450. |
| [9] | 肖湘, 黄恩厚, 尼颖升. 预应力混凝土梁板体系有效翼缘的理论分析及试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 1784-1790. |
| [10] | 庄蔚敏, 解东旋, 余天明, 于皖东. 基于损伤-相变本构模型的高强钢热成形数值模拟分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1206-1212. |
| [11] | 孟广伟,李霄琳,李锋,周立明,王晖. 裂隙介质渗流的光滑多尺度有限元法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 481-486. |
| [12] | 马彪1, 赵家昕1, 李和言1, 宁克炎2, 何春平3. 离合器结构参数对其热弹性不稳定性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(4): 933-938. |
| [13] | 李晓军,梁路路,谢诚伟,杨硕. 沥青混凝土虚拟力学仿真模型自动生成及应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 655-660. |
| [14] | 庄蔚敏, 曹德闯, 叶辉. 基于连续介质损伤力学预测7075铝合金热冲压成形极限图[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(2): 409-414. |
| [15] | 彭勇, 孙立军. 集料水平向分布状态对沥青混合料劈裂试验影响数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(04): 891-896. |
|
||