吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (12): 3496-3504.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230094
不完全信息下高铁晚点与乘客选择行为博弈模型
- 1.南京理工大学 自动化学院,南京 210094
2.中国铁路上海铁路局集团有限公司,上海 200040
Game model of high⁃speed railway delay and passenger choice behavior under incomplete information
Ai-guo LEI1( ),Qi-zhou HU1(
),Qi-zhou HU1( ),Xiao-yu WU1,Si-yuan QU2
),Xiao-yu WU1,Si-yuan QU2
- 1.Nanjing University of Science and Technology,School of Automation,Nanjing 210094,China
2.China Railway Shanghai Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Shanghai 200040,China
摘要:
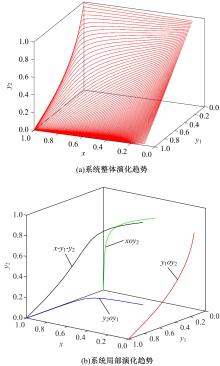
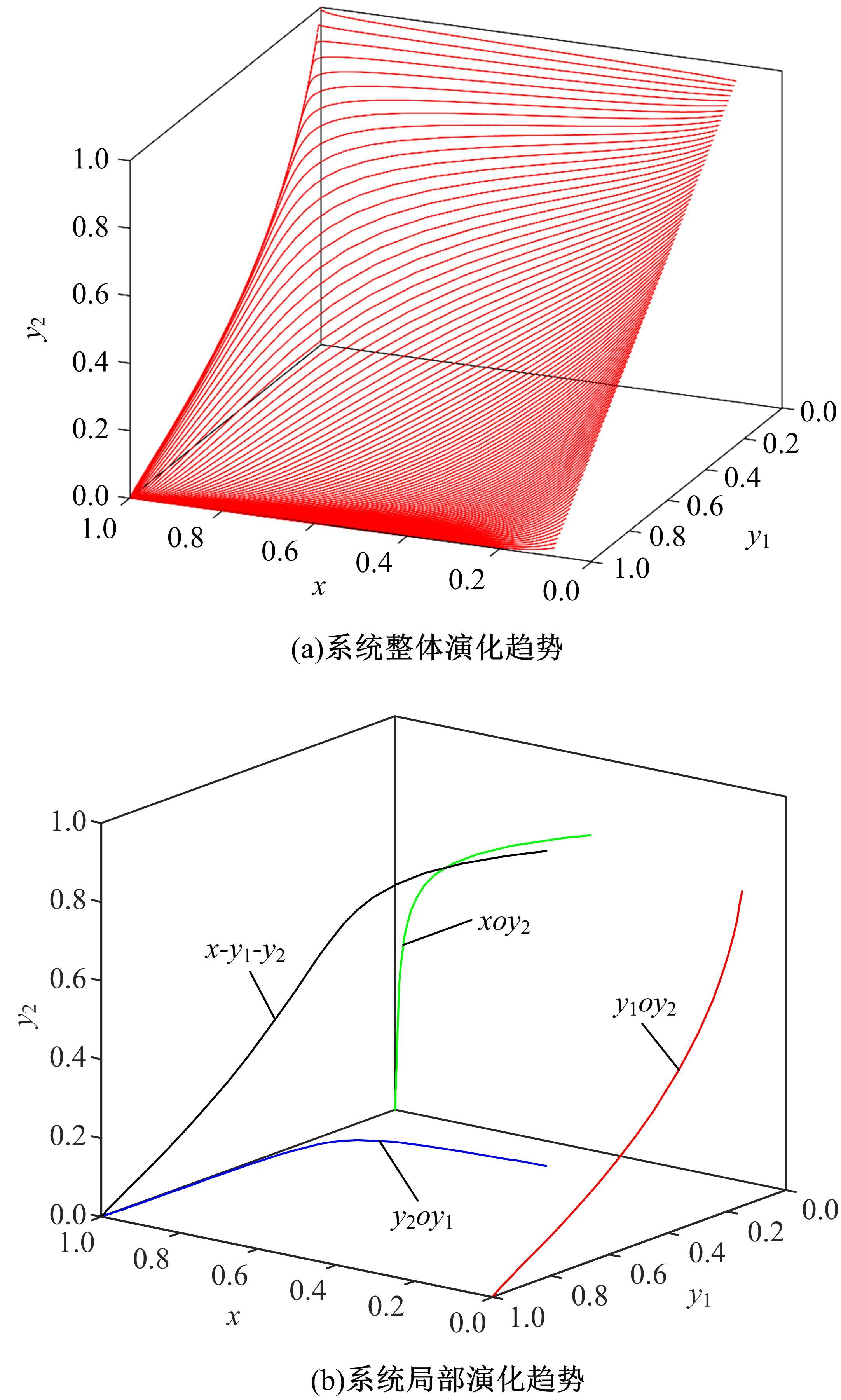
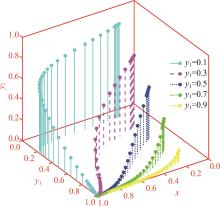
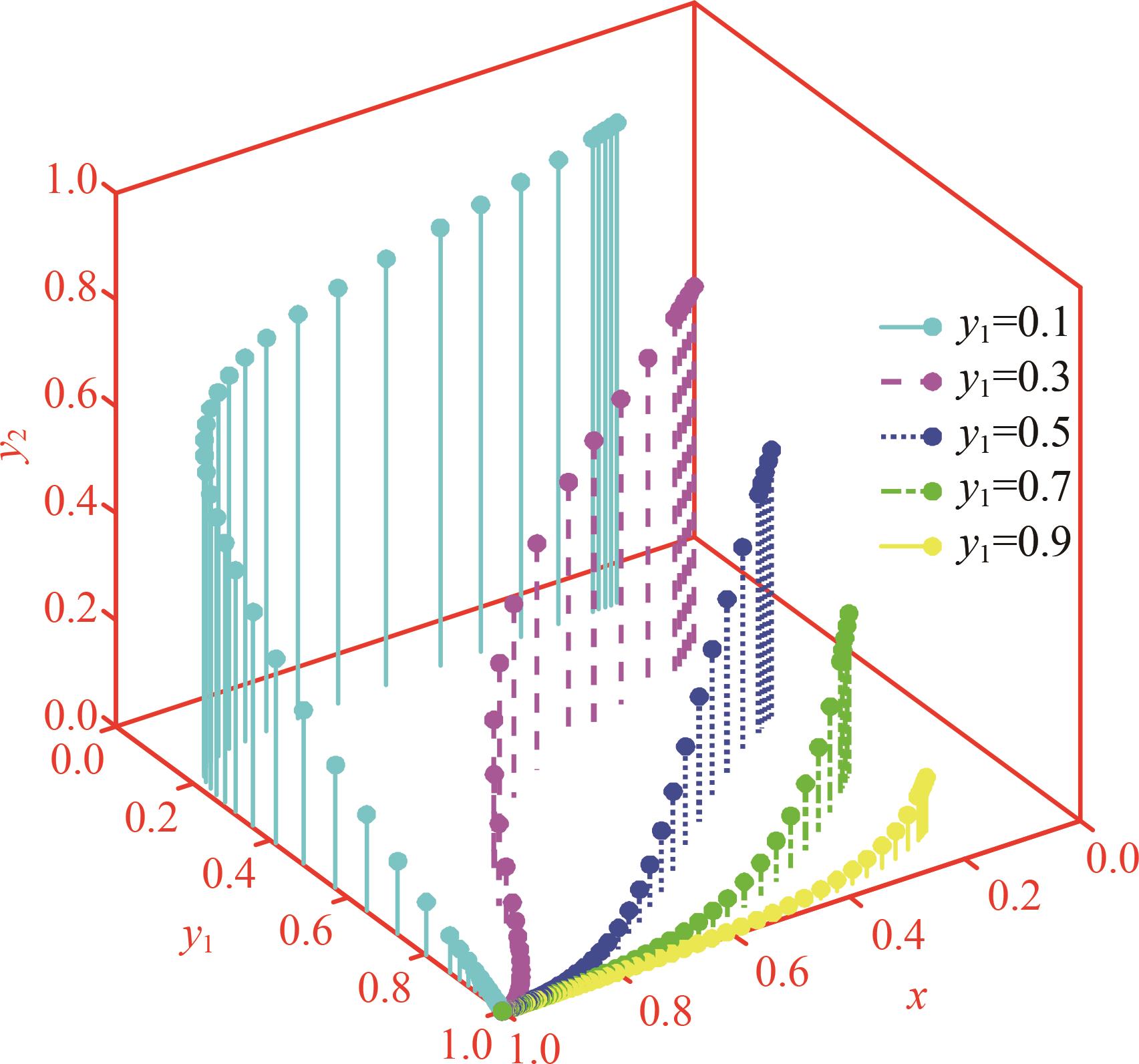
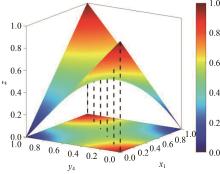
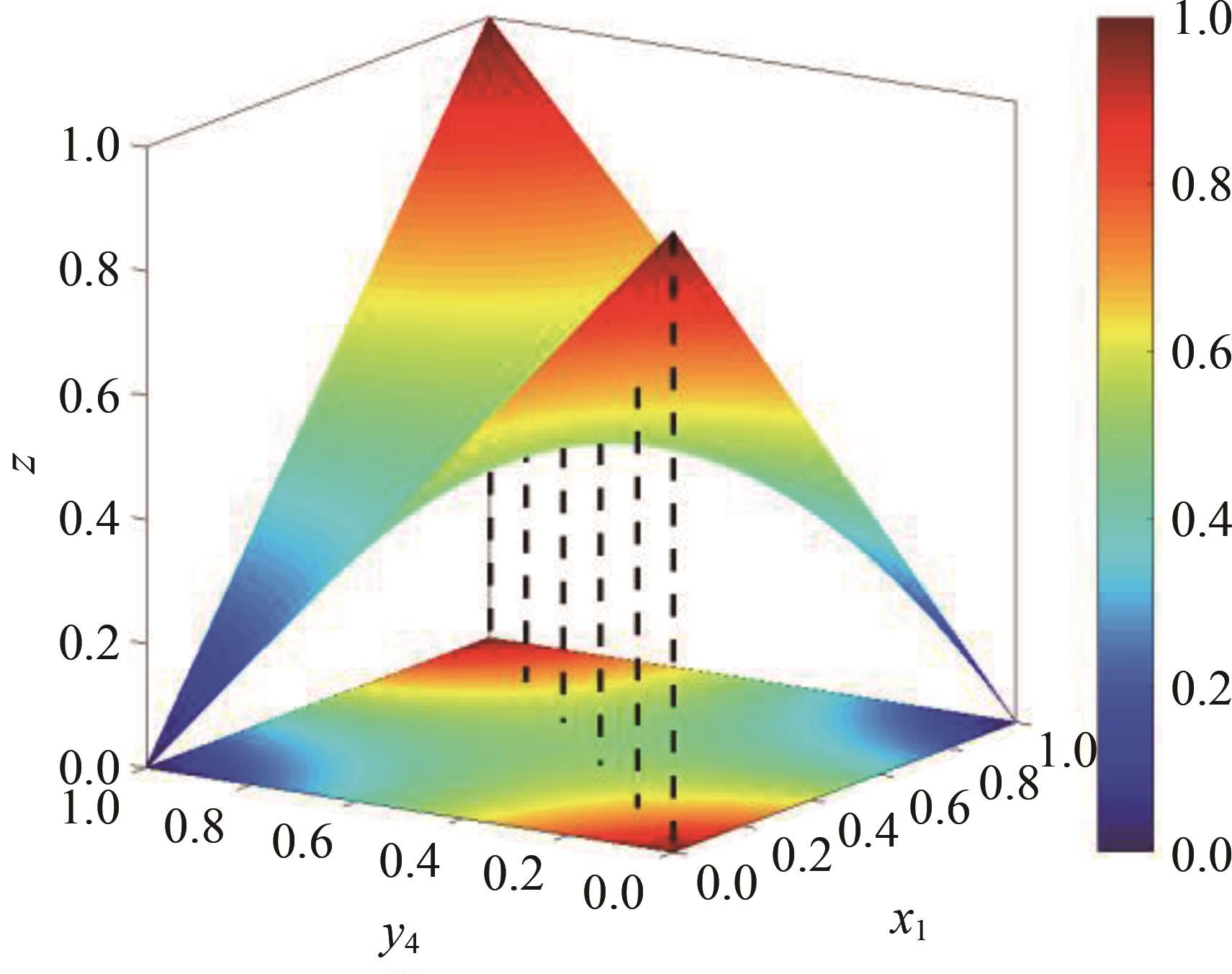
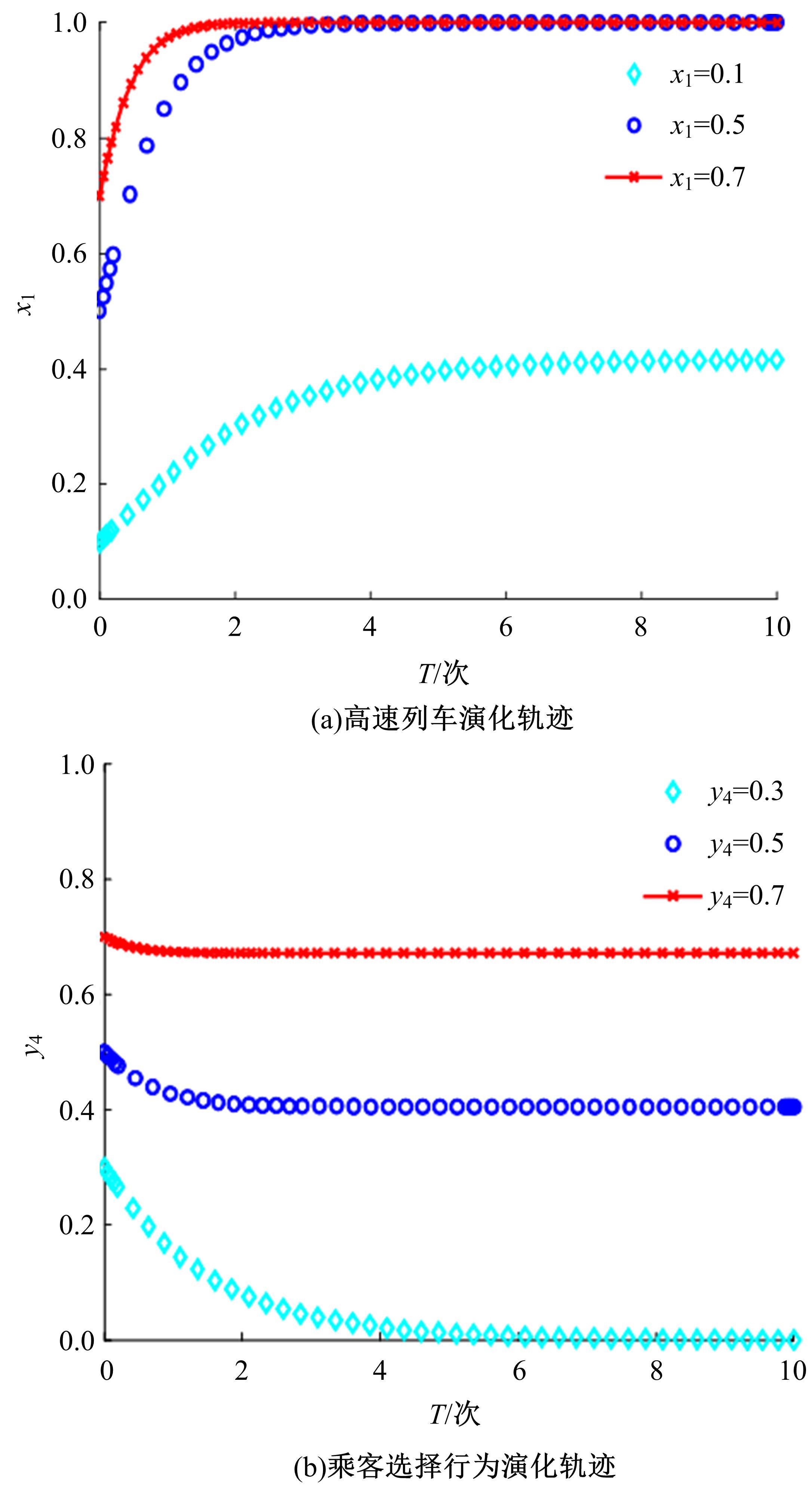
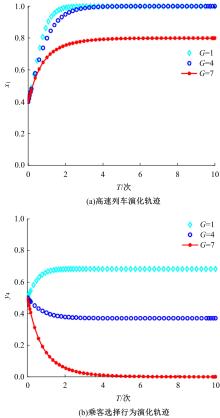
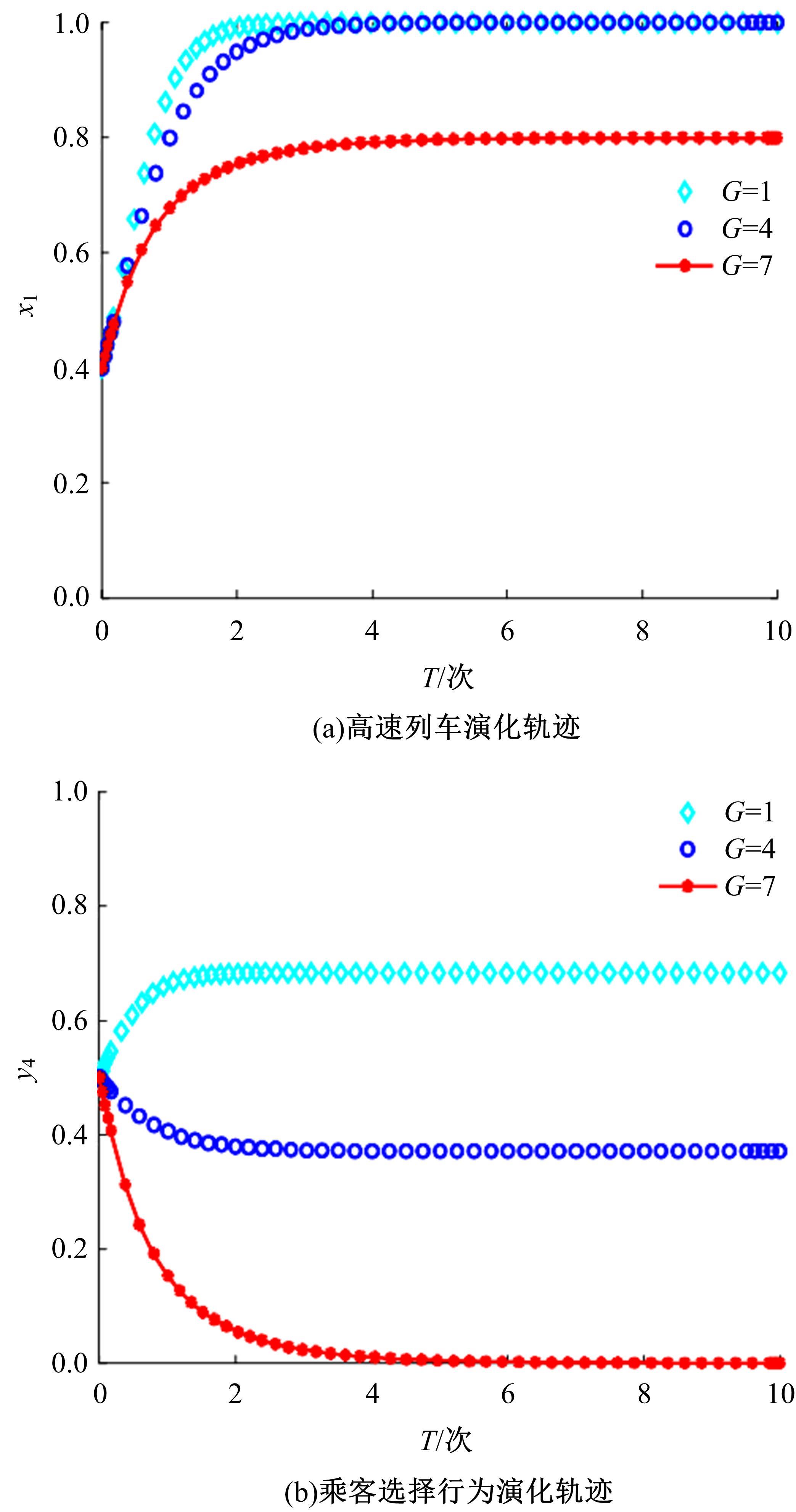
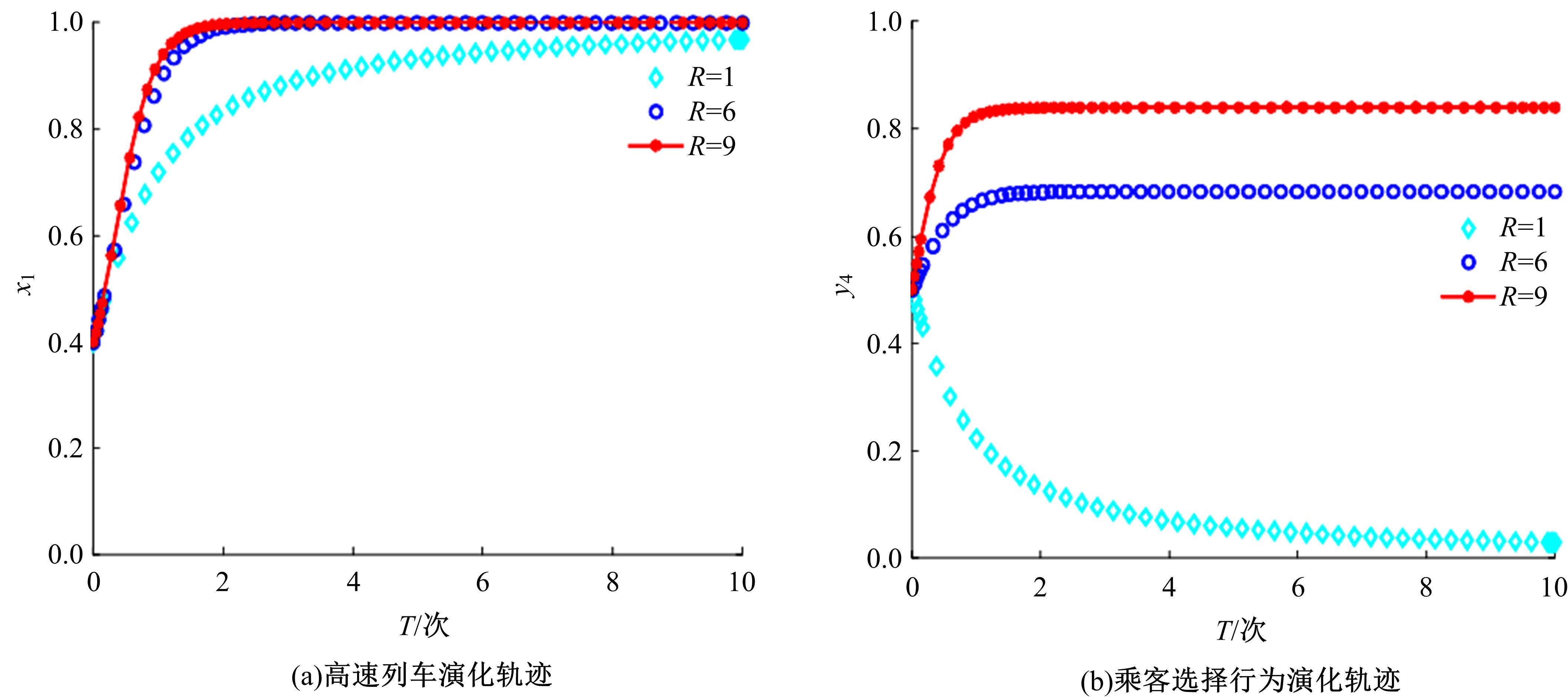
研究了高速铁路列车的到达状态对铁路乘客选择行为的具体影响因素。首先,构建高速列车到达状态与铁路乘客选择行为演化博弈模型。其次,分析博弈双方的演化行为,获得复制动态系统的演化均衡策略。最后,进行仿真验证,结果表明:演化博弈行为最终有两个演化稳定状态,当高速列车晚点时间在30 min以内,高速列车趋于准时到达策略,乘客趋于选择乘车策略;当晚点时间大于30 min,列车趋于准时到达策略,乘客趋于选择退票策略。改变博弈参数的值可以定向调整博弈双方的演化方向,能有效提高高速列车晚点时的铁路乘客乘车比例。
中图分类号:
- U293
| 1 | Hu Q Z, Bian L S, Tan M J. A data perception model for the safe operation of high-speed rail in rainstorms[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2020, 83: No.102326. |
| 2 | 廉志斌,帅斌,许旻昊.列车晚点下高速铁路车站到发线运用计划调整方法[J].铁道运输与经济, 2022, 44(2): 1-7. |
| Lian Zhi-bin, Bin Shuai, Xu Min-hao. Operation plan adjustment of arrival and departure tracks at high speed railway station in condition of train delay[J]. Railway Transport and Economy, 2022, 44(2): 1-7. | |
| 3 | Khwanpruk S, Utapao C, Khwanpruk K, et al. Optimization-based train timetables generation with demand forecasting for thailand high speed rail system[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2021, 25(9): 3502-3510. |
| 4 | Zhang D L, Peng Y J, Zhang Y M, et al. Train time delay prediction for high-speed train dispatching based on spatio-temporal graph convolutional network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(3): 2434-2444. |
| 5 | Li Z, Huang P, Wen C, et al. Predictive models for influence of primary delays using high-speed train operation records[J]. Journal of Forecasting, 2020, 39(8): 1198-1212. |
| 6 | Briggs K, Beck C. Modelling train delays with qexponential functions[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2007, 378(2): 498-504. |
| 7 | Arshad M, Ahmed M. Train delay estimation in Indian railways by including weather factors through machine learning techniques[J]. Recent Advances in Computer Science and Communications, 2021, 14(4): 1300-1307. |
| 8 | Sara L, Houda J, Mohamed A. Predict France trains delays using visualization and machine learning techniques[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2020, 175: 700-705. |
| 9 | Hauck F, Kliewer N. Data analytics in railway operations: using machine learning to predict train delays[M].Berlin: Springer, 2020. |
| 10 | 刘岩,郭竞文,罗常津,等.列车运行实绩大数据分析及应用前景展望[J]. 中国铁路, 2015, 636(6): 70-73. |
| Liu Yan, Guo Jing-wen, Luo Chang-jin, et al. Big data analysis and application prospects for the performance of train operation [J]. Chinese Railways, 2015, 636(6): 70-73. | |
| 11 | Xu P J, Corman F, Peng Q Y. Analyzing railway disruptions and their impact on delayed traffic in Chinese high-speed railway[J]. IFAC-Papers On Line, 2016, 49(3): 84-89. |
| 12 | Luca O, Irene B, Alessandro L, et al. Dynamic, interpretable, and robust hybrid data analytics system for train movements in large-scale railway networks[J]. International Journal of Data Science and Analytics, 2020(9): 95-111. |
| 13 | 闫道锦,佟琼.引入客运专线列车晚点救济的必要性分析[J]. 北京交通大学学报:社会科学版, 2008(2): 72-75, 98. |
| Yan Dao-jin, Tong Qiong. Analysis on necessity of introducing delay remedy system into dedicated passenger lines[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University(Social Sciences Edition), 2008(2): 72-75, 98. | |
| 14 | 韩忻辰,俞胜平,袁志明,等.基于Q-learning的高速铁路列车动态调度方法[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2021, 38(10): 1511-1521. |
| Han Xin-chen, Yu Sheng-ping, Yuan Zhi-ming, et al. High-speed railway dynamic scheduling based on Q-learning method[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2021, 38(10): 1511-1521. | |
| 15 | 石晶,彭其渊,文超,等.铁路列车晚点时间预测方法研究[J]. 铁道运输与经济, 2020, 42(7): 33-39. |
| Shi Jing, Peng Qi-yuan, Wen Chao, et al. Prediction method of passenger train delay propagation[J]. Railway Transport and Economy, 2020, 42(7): 33-39. | |
| 16 | Zhang B Y, Shan P. Game theory and the evolution of cooperation[J]. Journal of the Operations Research Society of China, 2022, 10(2): 379-399. |
| 17 | 张维维,何家峰,高国旺,等.基于博弈论的无线Mesh网络路由与信道分配联合优化算法[J].吉林大学学报:工学版,2018,48(3):887-892. |
| Zhang Wei-wei, He Jia-feng, Gao Guo-wang, et al. Wireless Mesh network routing and channel allocation union optimization algorithm based on game theory[J]. Journal of Jilin University Engineering and Technology Edition, 2018,48(3): 887-892. | |
| 18 | Smith J M. Evolution and the theory of games[J]. American Scientist, 1976, 64(1): 41-45. |
| 19 | 程刚, 郭磊善. 基于GIS的公交换乘网络构建及可达性分析[J]. 江苏大学学报:自然科学版, 2024, 45(2): 191-197. |
| Cheng Gang, Guo Lei-shan. Bus transfer network construction and accessibility analysis based on GIS[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 45(2): 191-197. |
| [1] | 王宏志,宋明轩,程超,解东旋. 基于改进YOLOv5算法的道路目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2658-2667. |
| [2] | 张娜,陈峰,王剑坡,朱亚迪. 基于时空序列相似性的城轨乘客出行模式识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2588-2599. |
| [3] | 郑长江,陶童统,陈志超. 基于流量可调重分配的级联失效模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2441-2450. |
| [4] | 周锡浈,宫贺,李敦敦,季彦婕,严杰. 建成环境对路内停车泊位使用率的非线性影响模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2520-2530. |
| [5] | 严利鑫,曾涛,贺宜,郭军华,胡鑫辉. 共驾型智能车辆人机接管行为序列编码与解析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2547-2556. |
| [6] | 温晓岳,钱国敏,孔桦桦,缪月洁,王殿海. TrafficPro:一种针对城市信控路网的路段速度预测框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2214-2222. |
| [7] | 曲昭伟,李霖,陈永恒,吴场建. 长区间掉头车辆特性分析及其安全评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2206-2213. |
| [8] | 曲大义,刘浩敏,杨子奕,戴守晨. 基于车路协同的交通瓶颈路段车流动态分配机制及模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2187-2196. |
| [9] | 闫云娟,查伟雄,石俊刚,严丽平. 基于随机充电需求的充电桩优化双层模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2238-2244. |
| [10] | 程国柱,盛林,王浩宇,冯天军. 考虑右转车二次冲突的信号交叉口行人过街安全评价方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1903-1912. |
| [11] | 何永明,权聪,魏堃,冯佳,万亚楠,陈世升. 超高速公路车路协同路侧单元感知融合方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1923-1934. |
| [12] | 涂辉招,鹿畅,陆淼嘉,李浩. 基于避险脱离的自动驾驶路测安全影响因素[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1935-1943. |
| [13] | 胡钊政,孙勋培,张佳楠,黄戈,柳雨婷. 基于时空图模型的车-路-图协同定位方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1246-1257. |
| [14] | 戢晓峰,徐迎豪,普永明,郝京京,覃文文. 山区双车道公路货车移动遮断小客车跟驰风险预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1323-1331. |
| [15] | 秦雅琴,钱正富,谢济铭. 协同换道避障模型和轨迹数据驱动的车辆协同避障策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1311-1322. |
|