吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (11): 3103-3113.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230427
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
基于系统效率最优的双转子轮毂电机电动汽车驱动模式能量管理策略
- 1.江苏大学 汽车与交通工程学院,江苏 镇江 212003
2.安阳工学院 机械工程学院,河南 安阳 455000
Energy management strategy of drive mode for dual-rotor in-wheel motor driven electric vehicle based on optimal system efficiency
- 1.School of Automotive and Traffic Engineering,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang 212003,China
2.School of Mechanical Engineering,Anyang Institute of Technology,Anyang 455000,China
摘要:
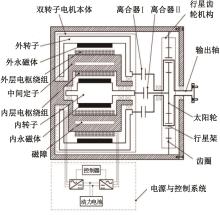
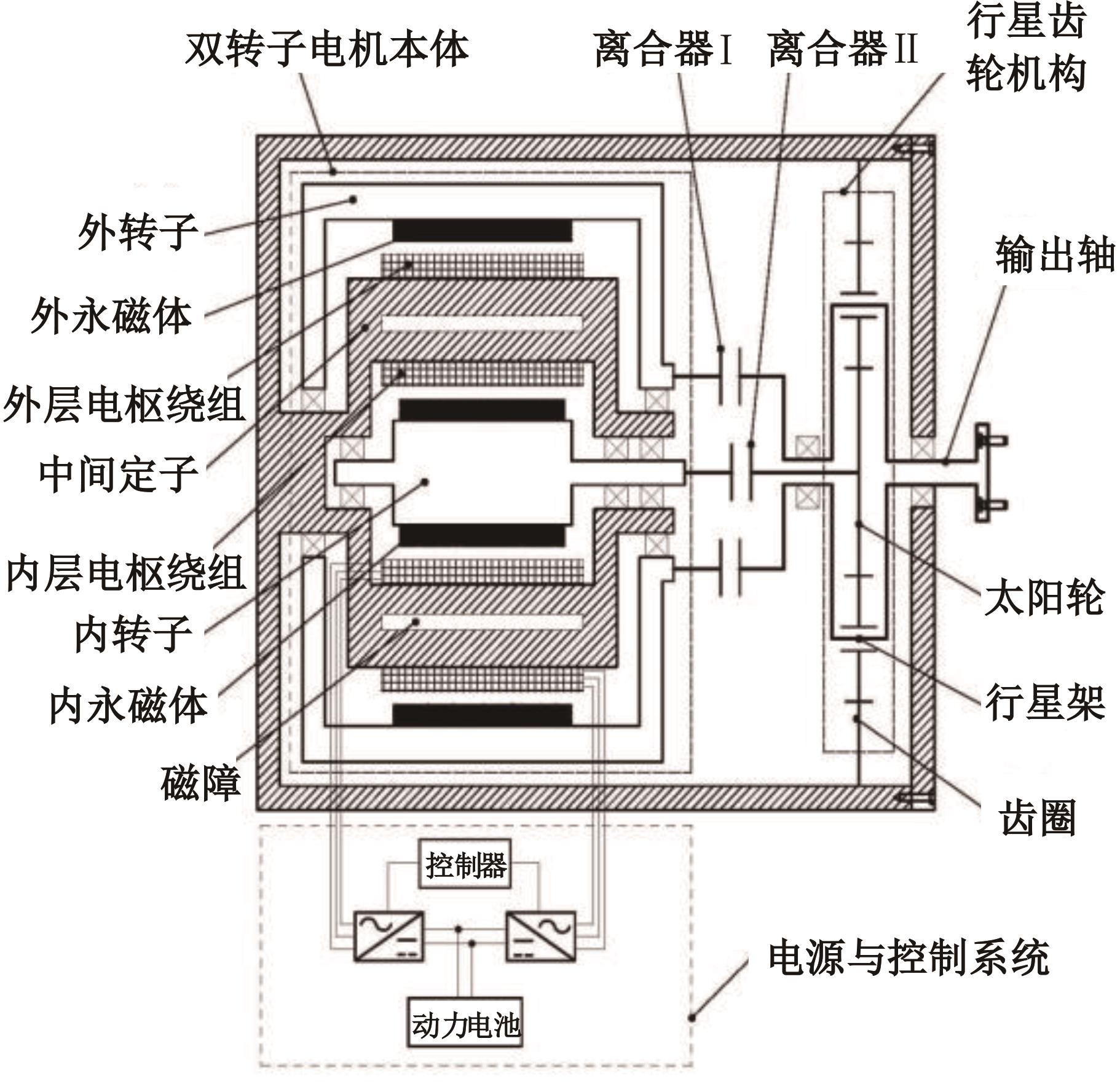
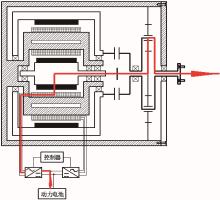
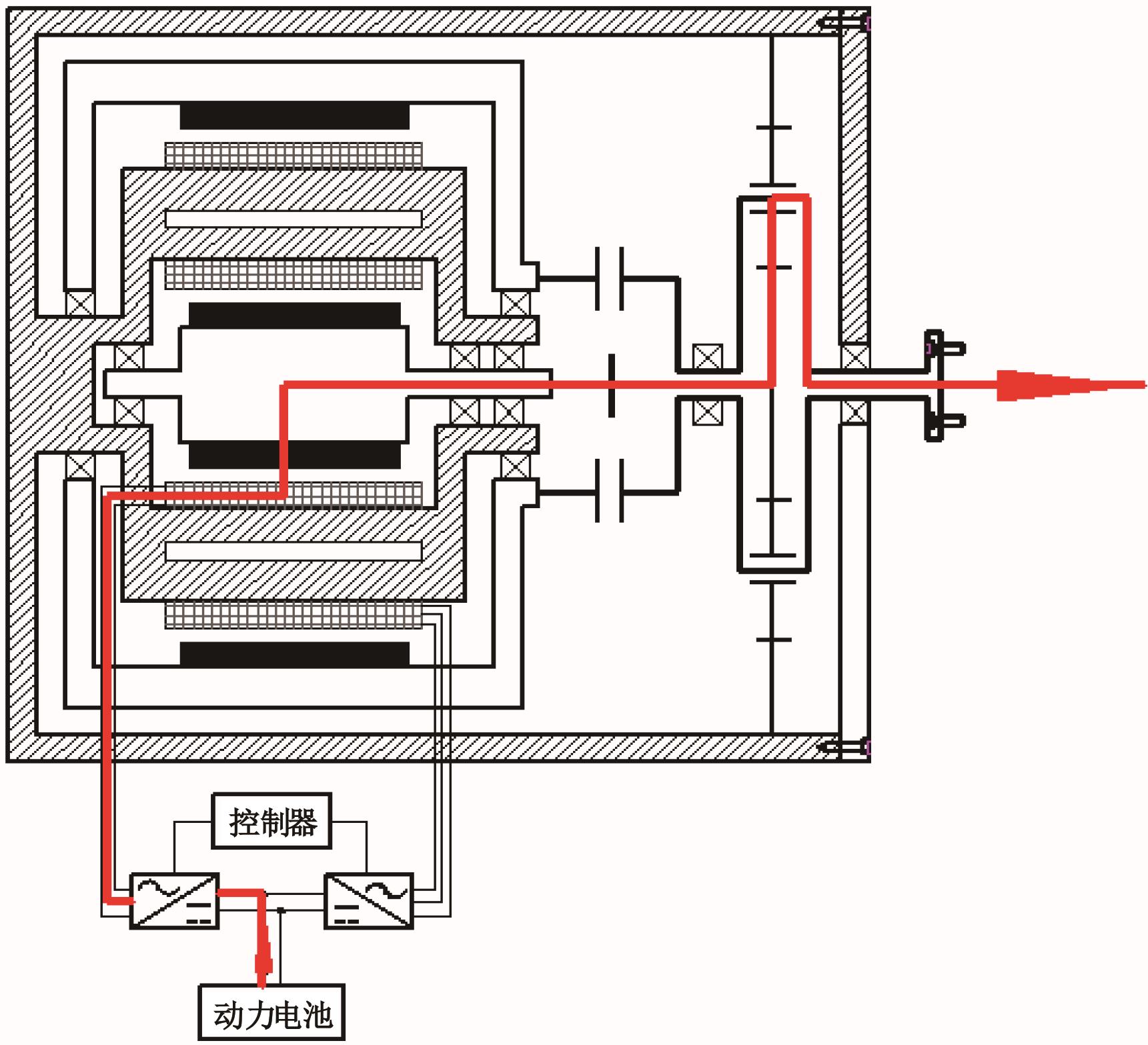
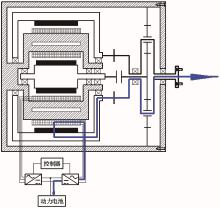
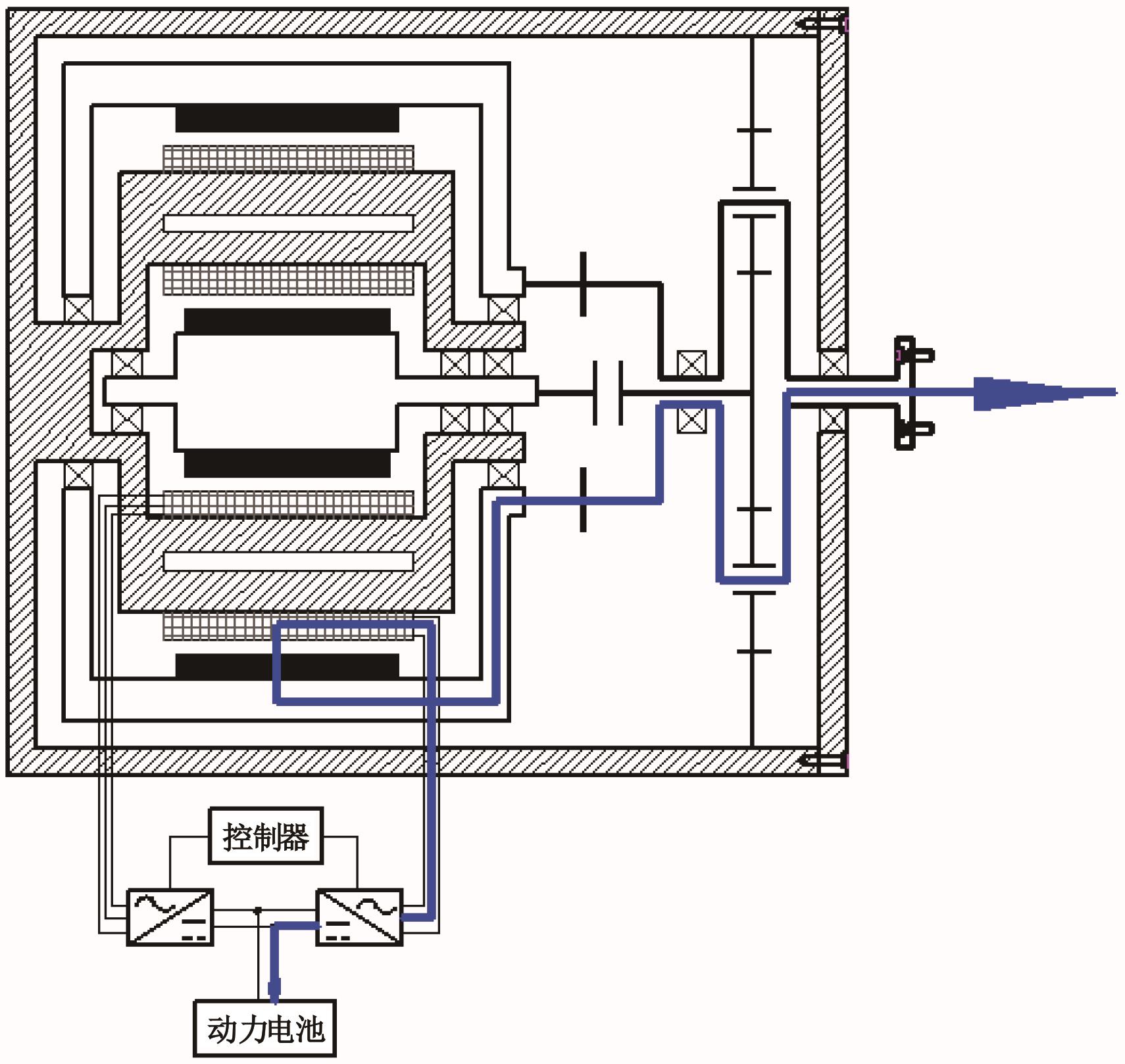
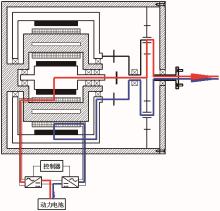
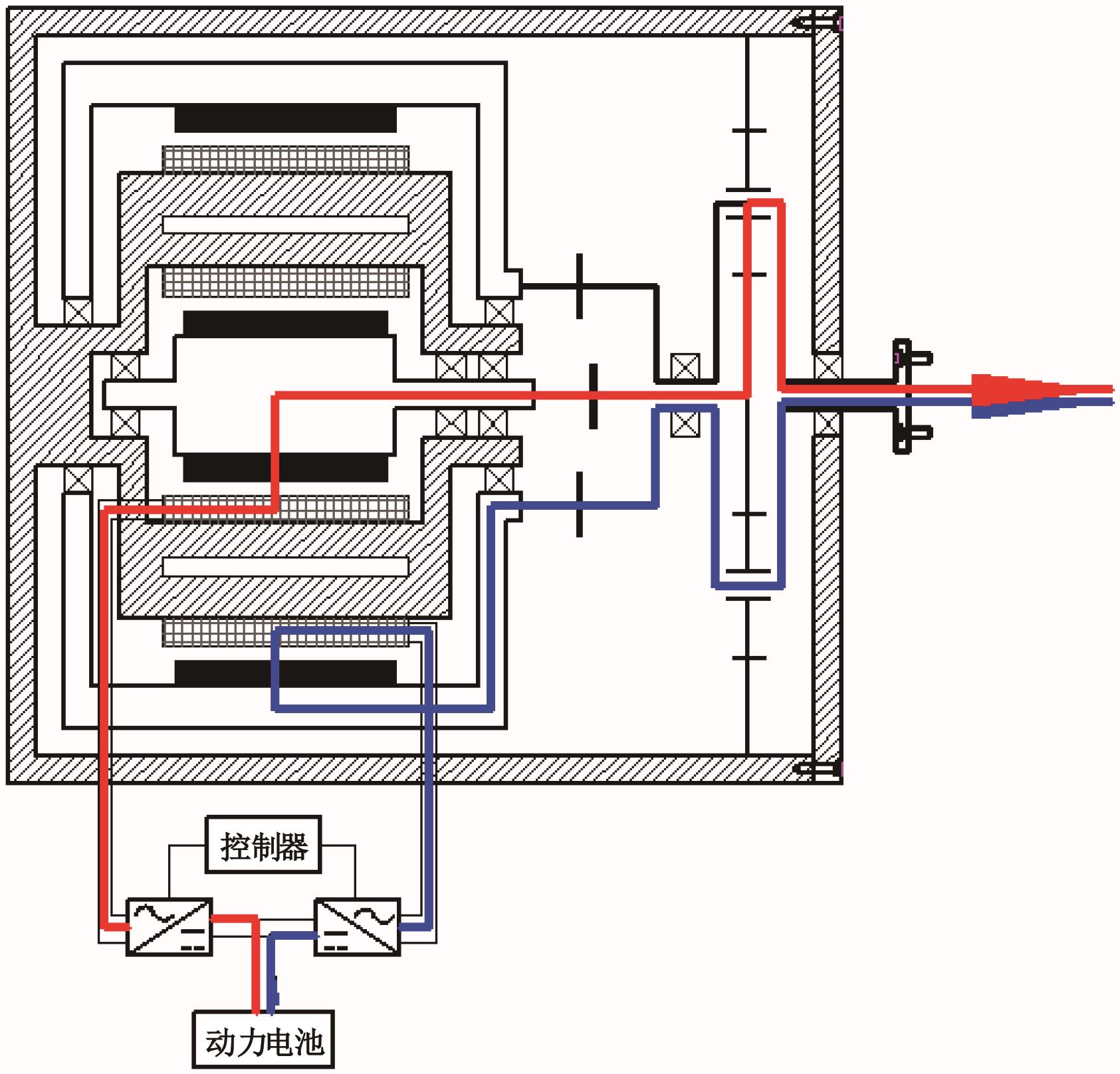
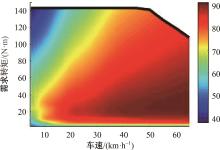
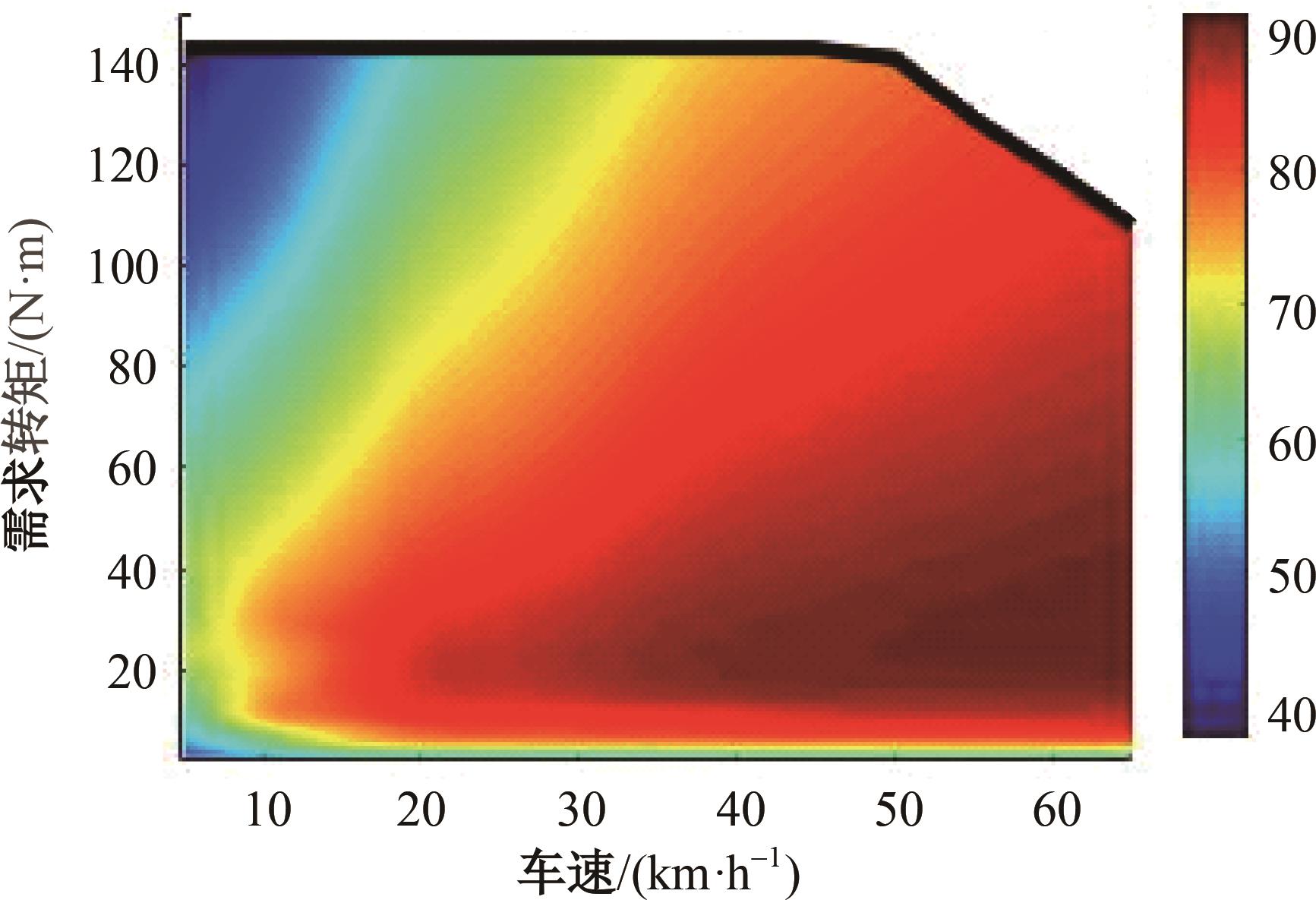
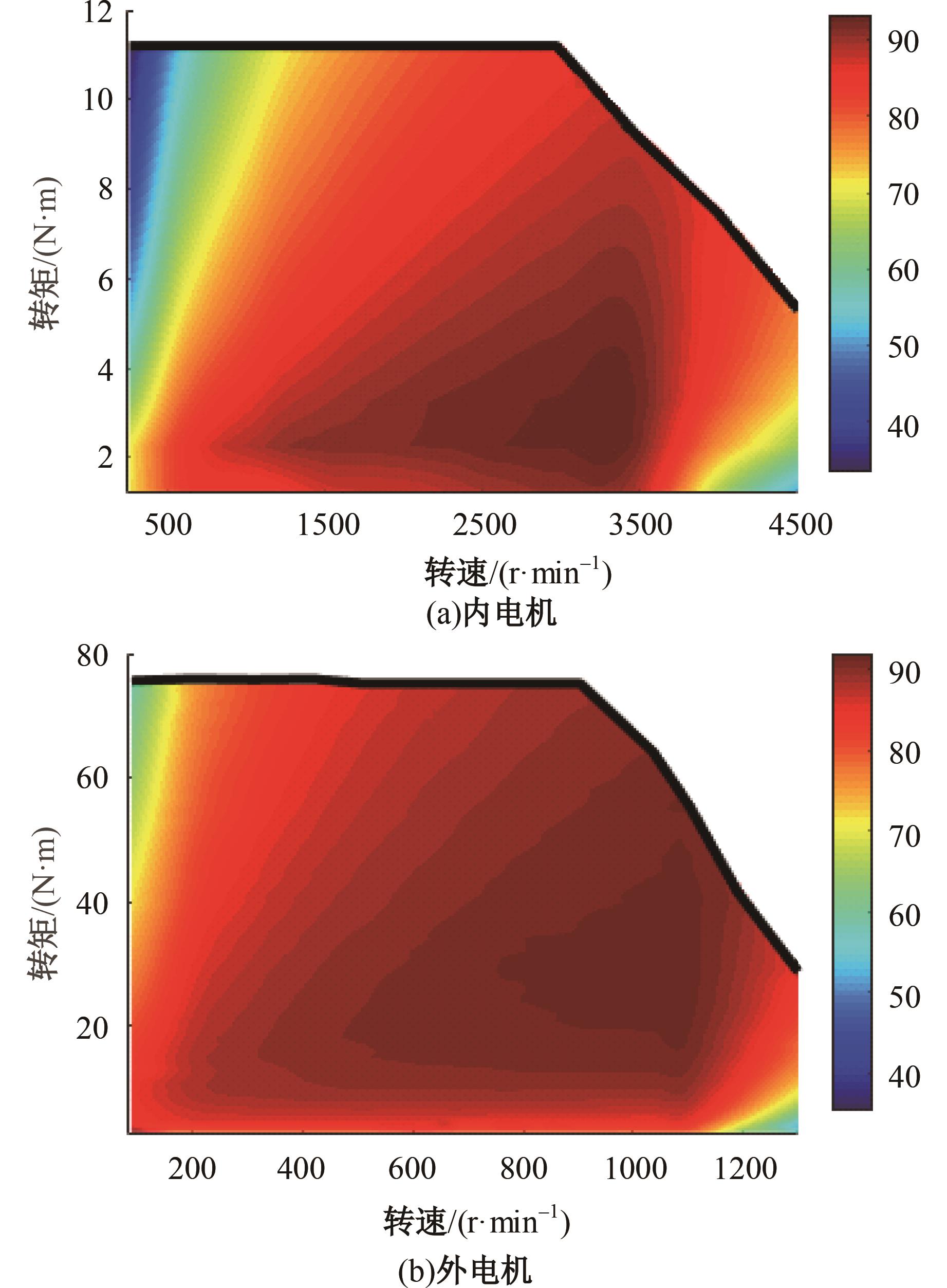
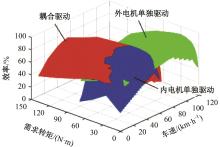
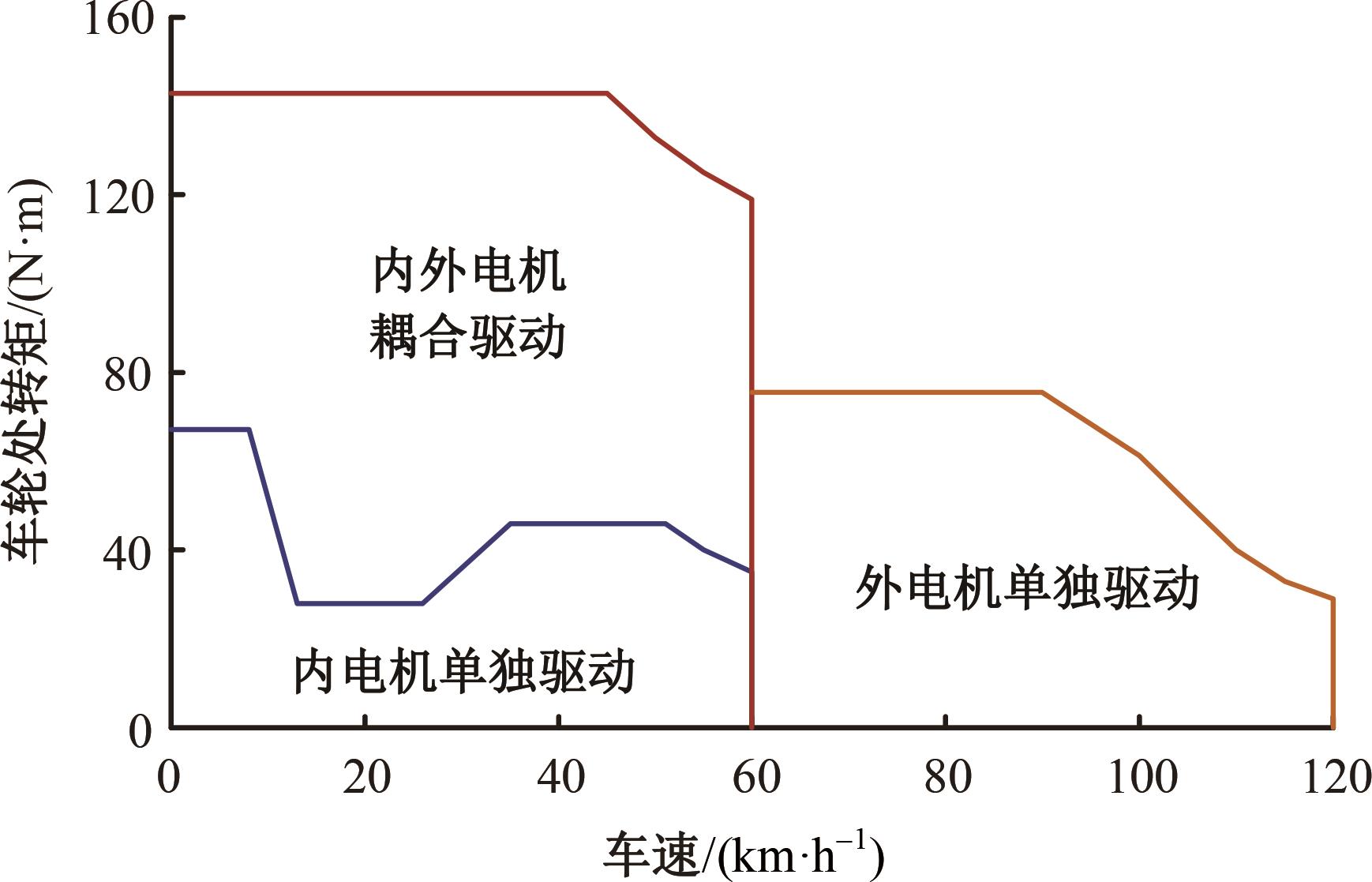
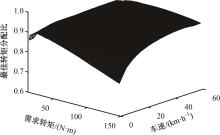
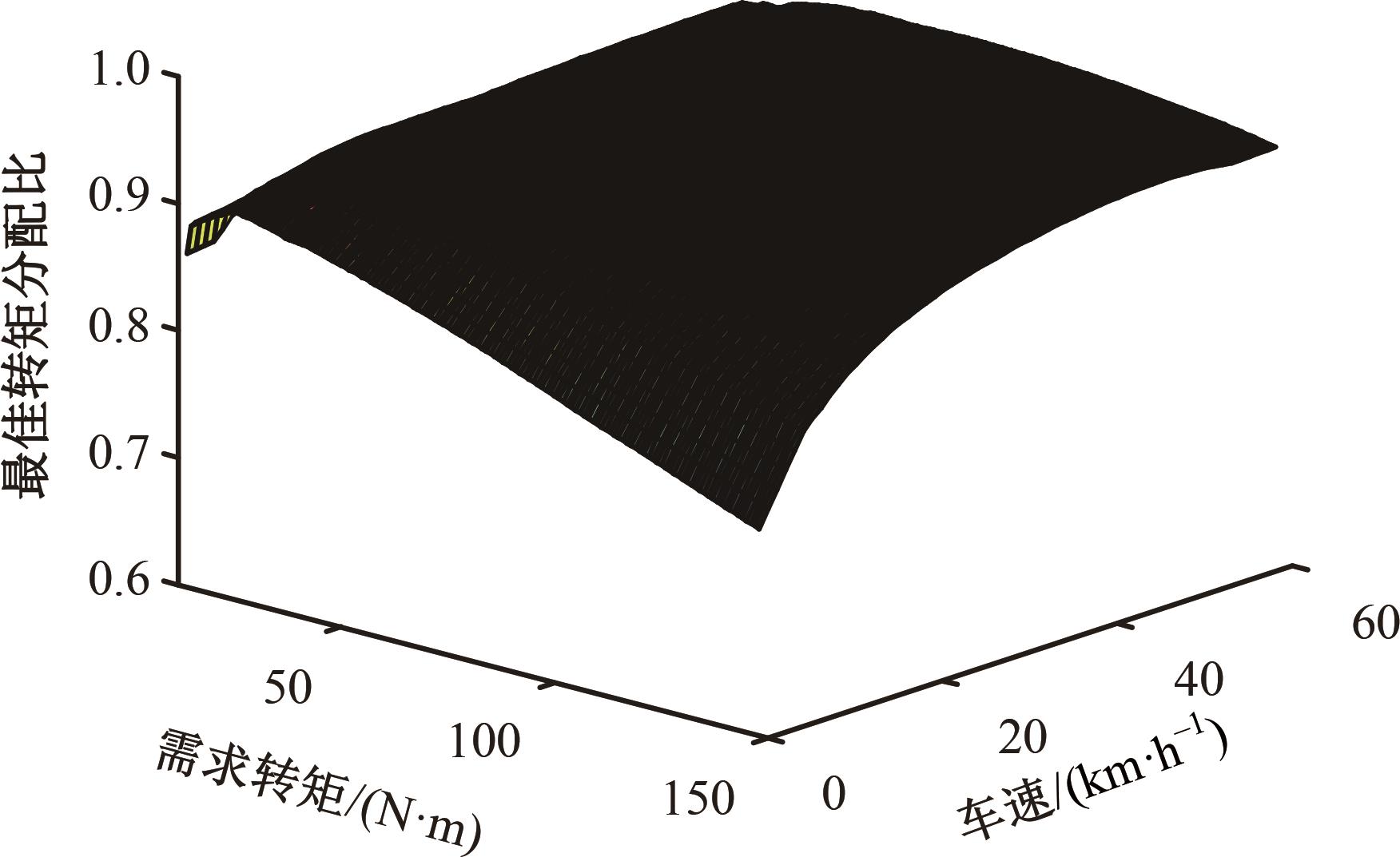
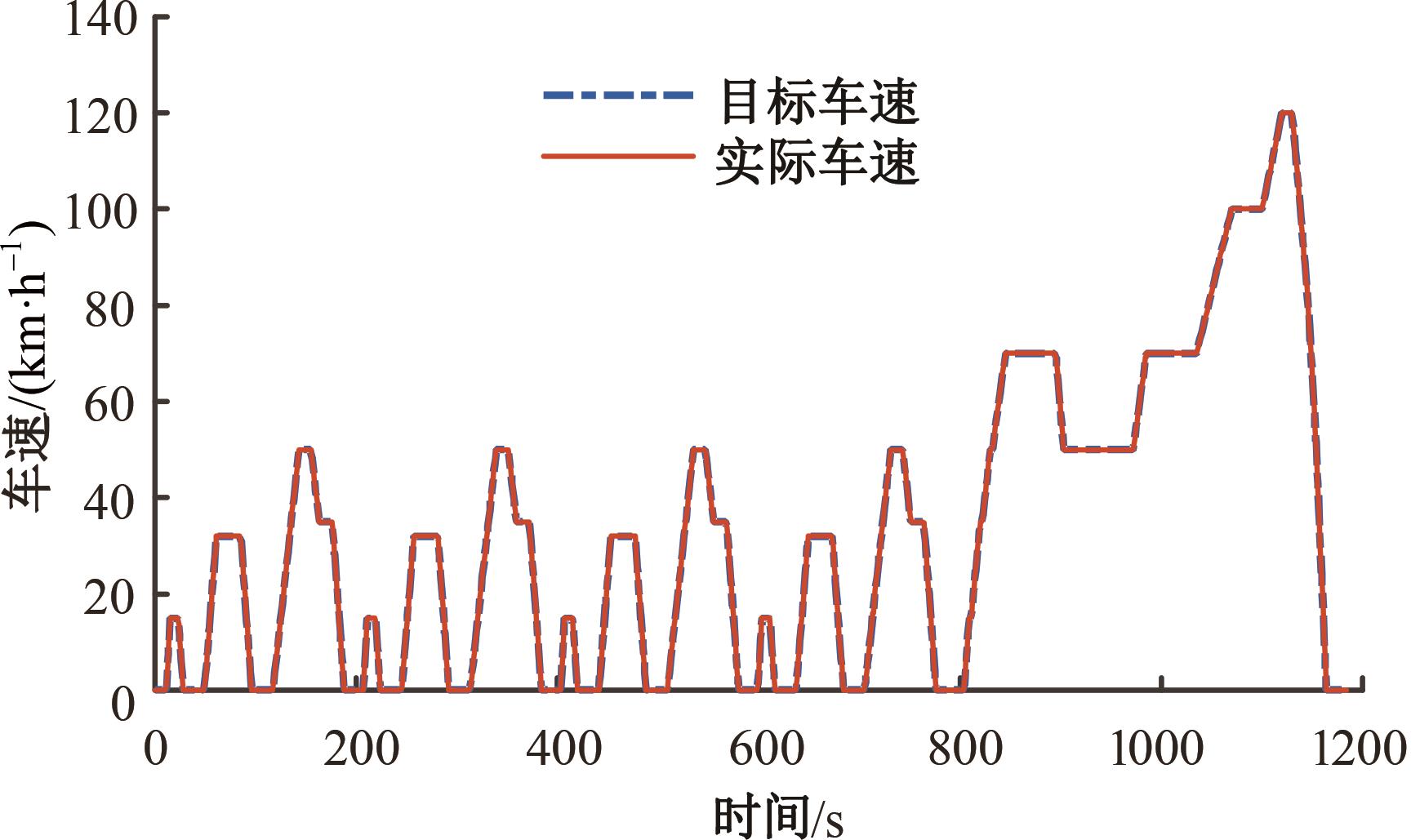
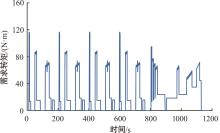
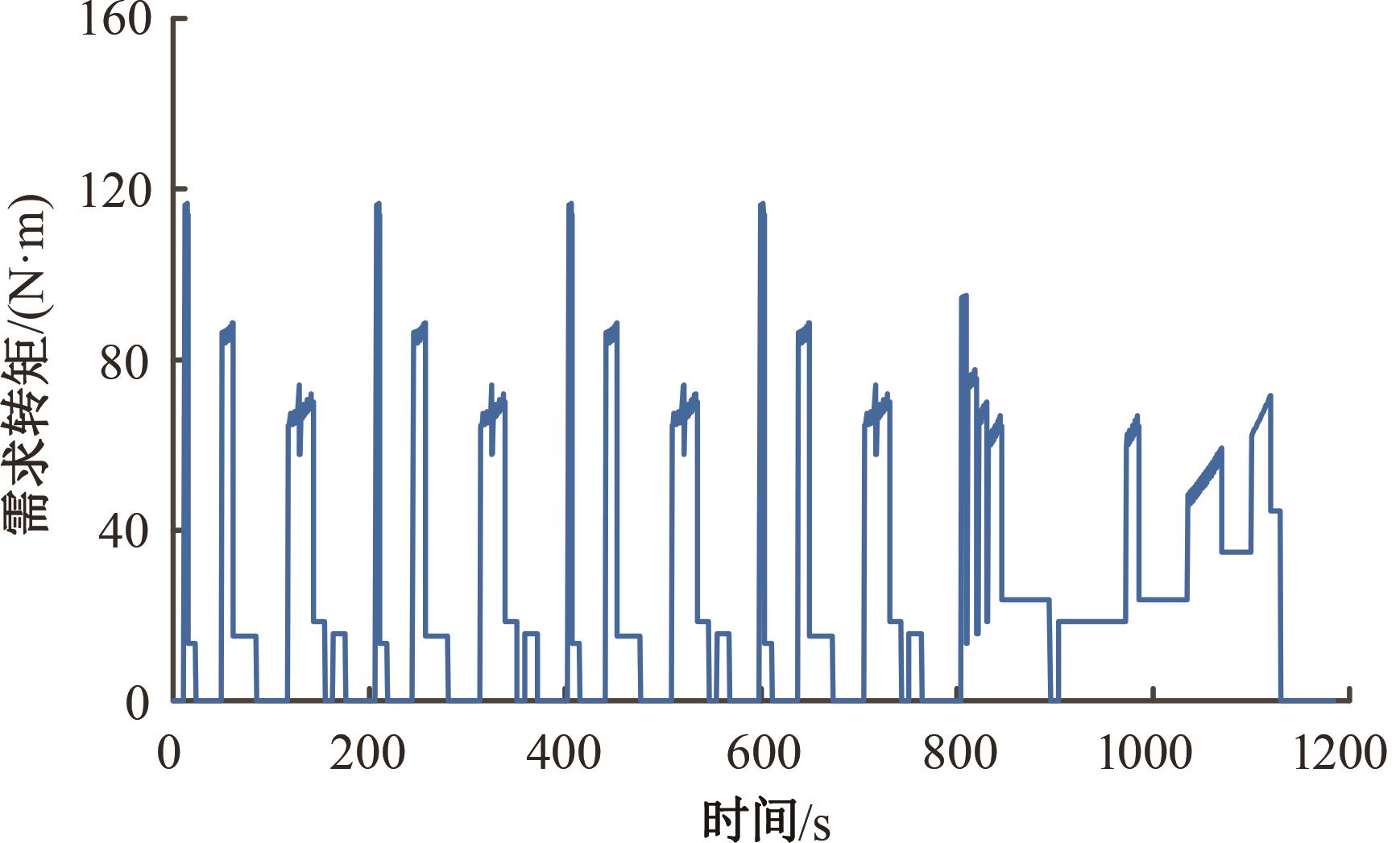
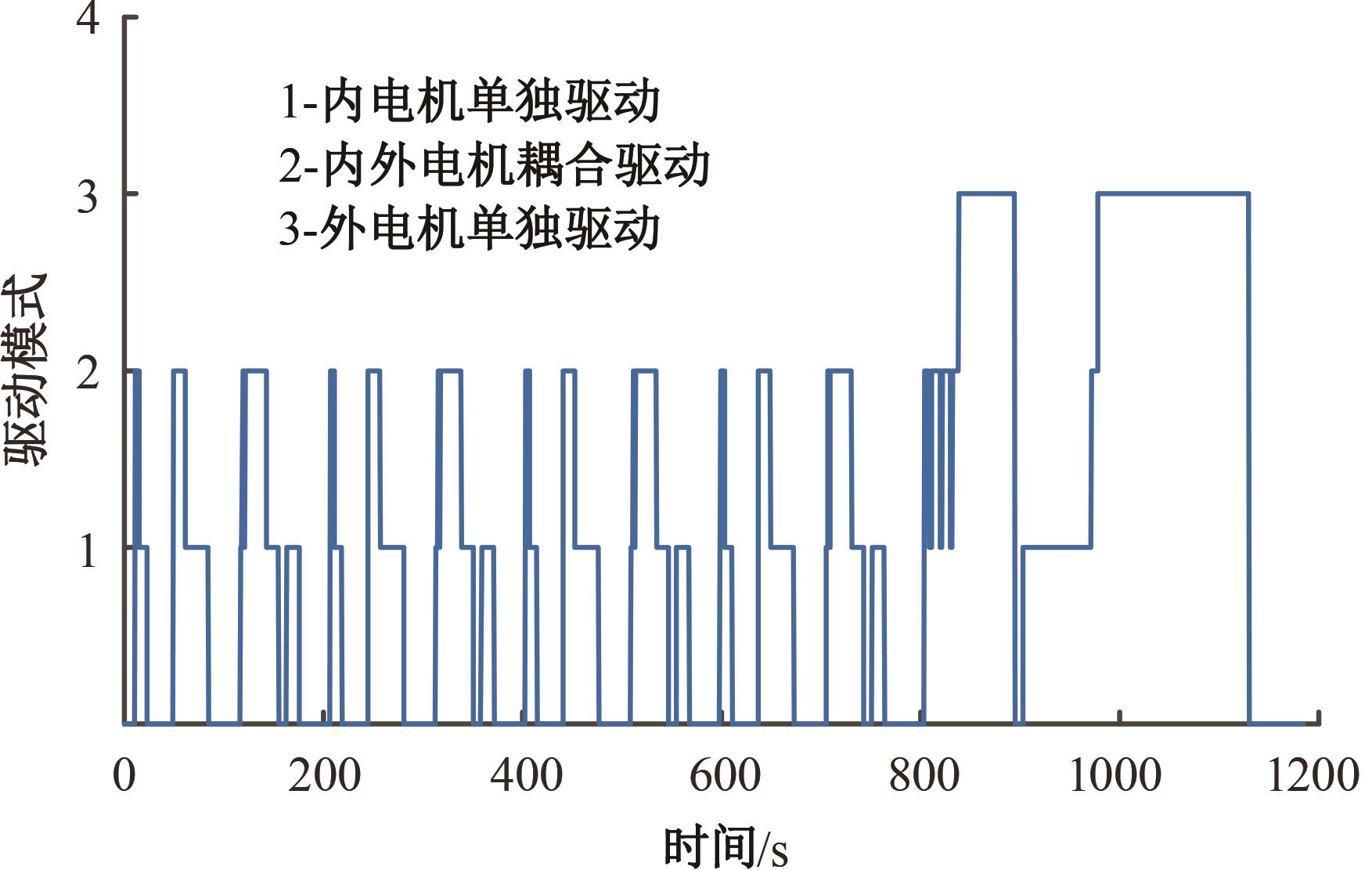
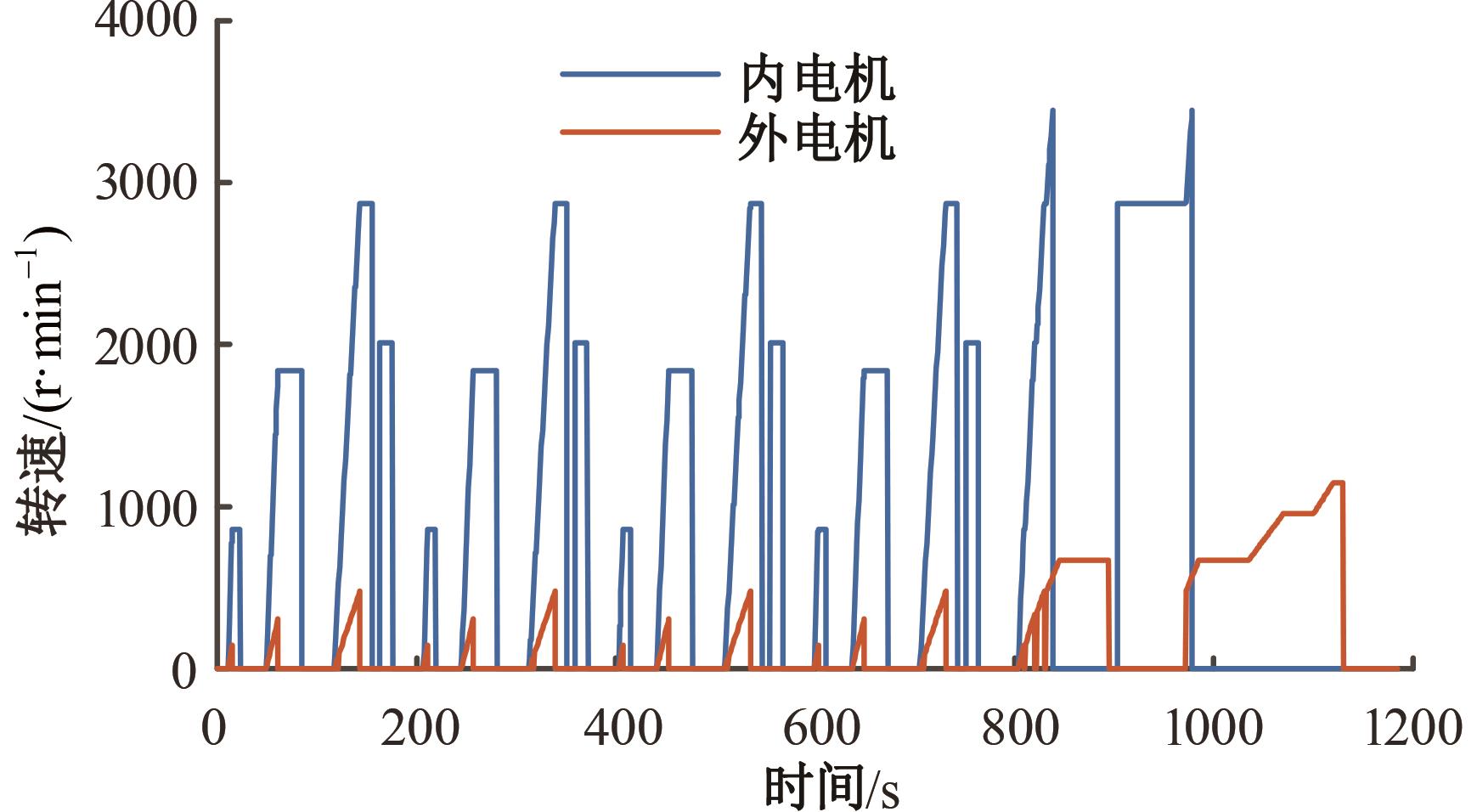
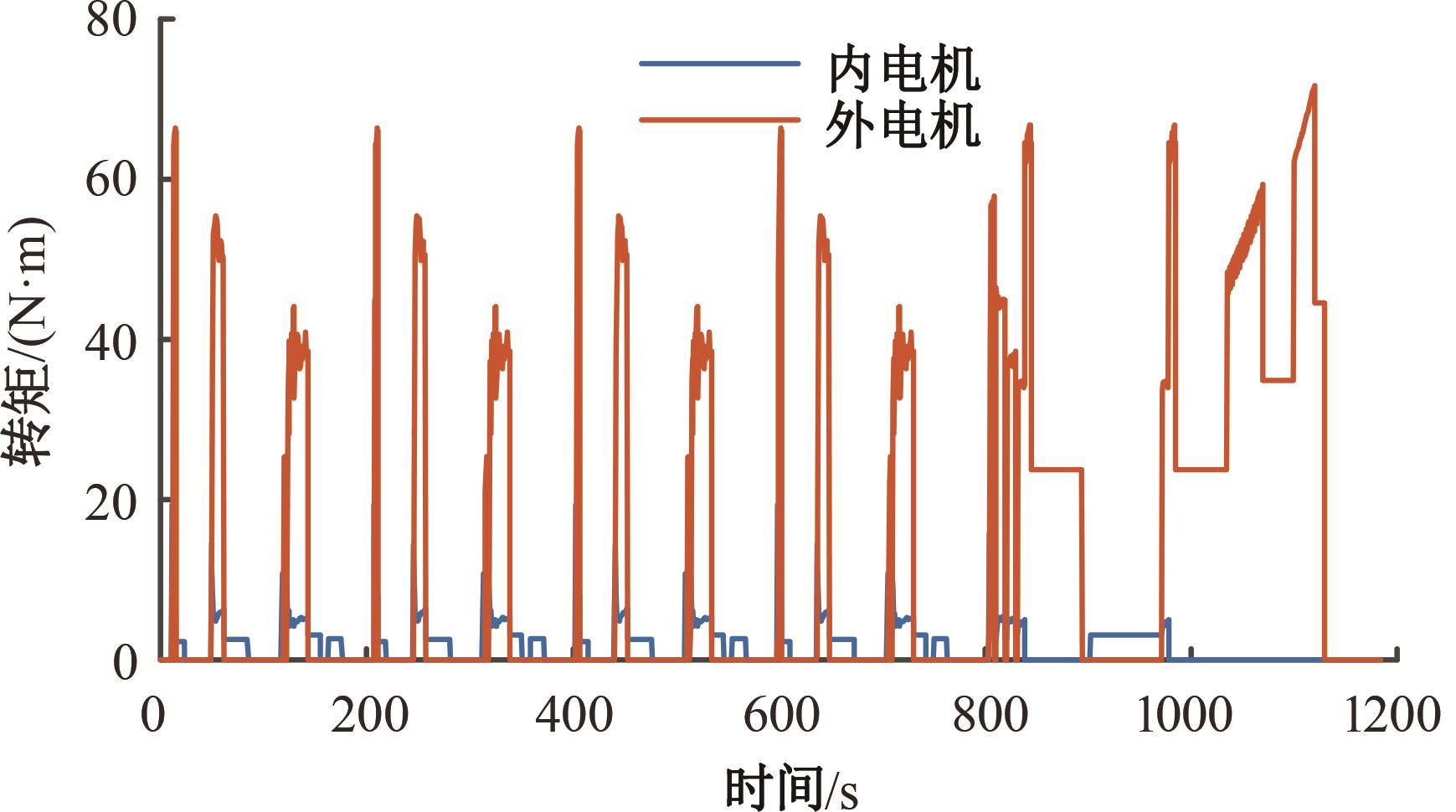
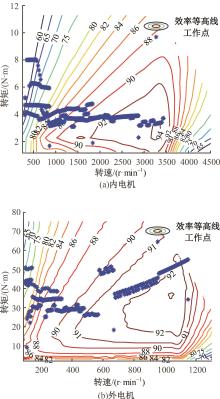
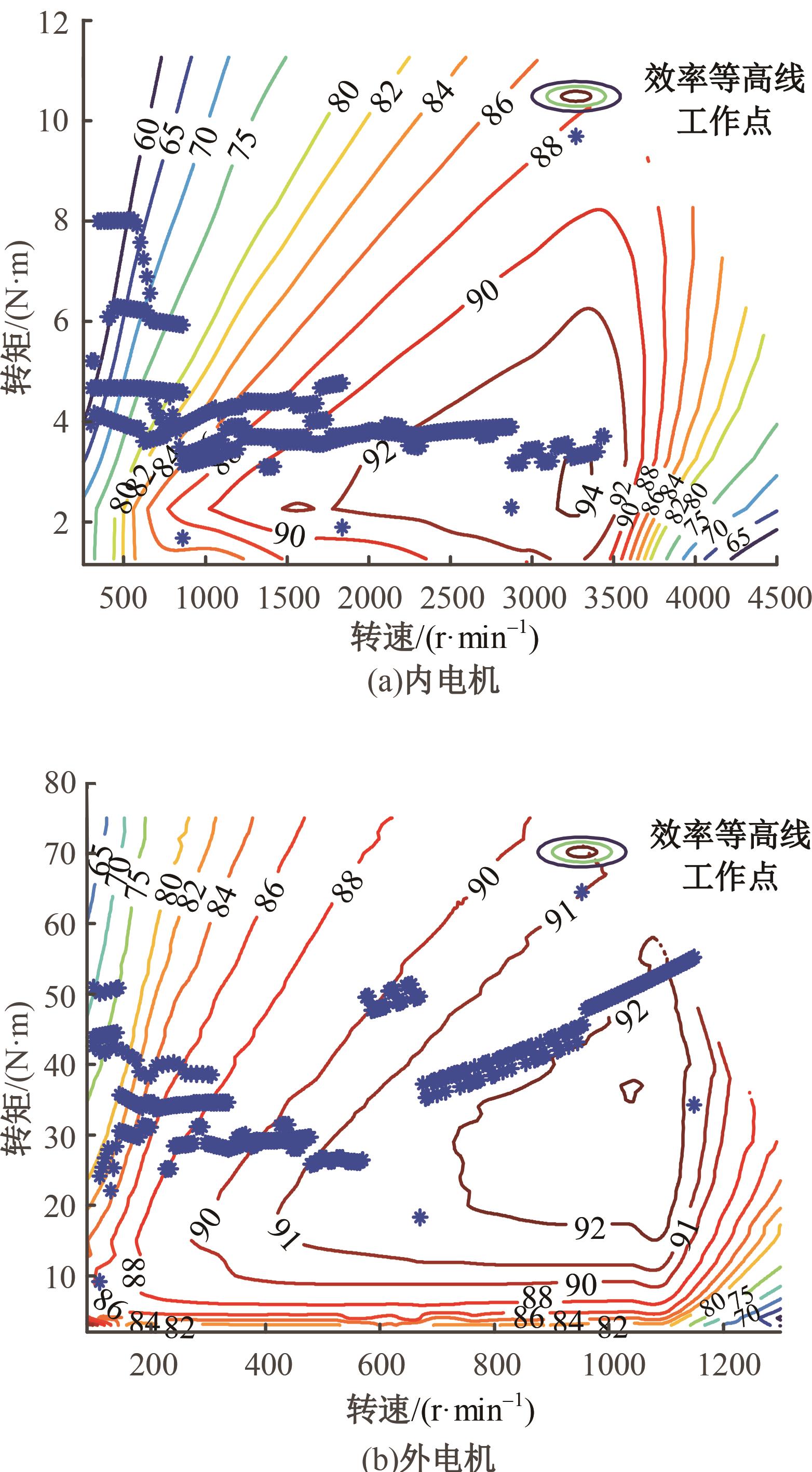
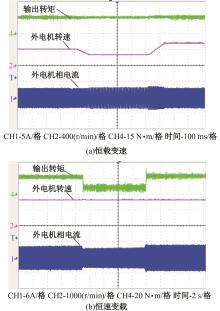
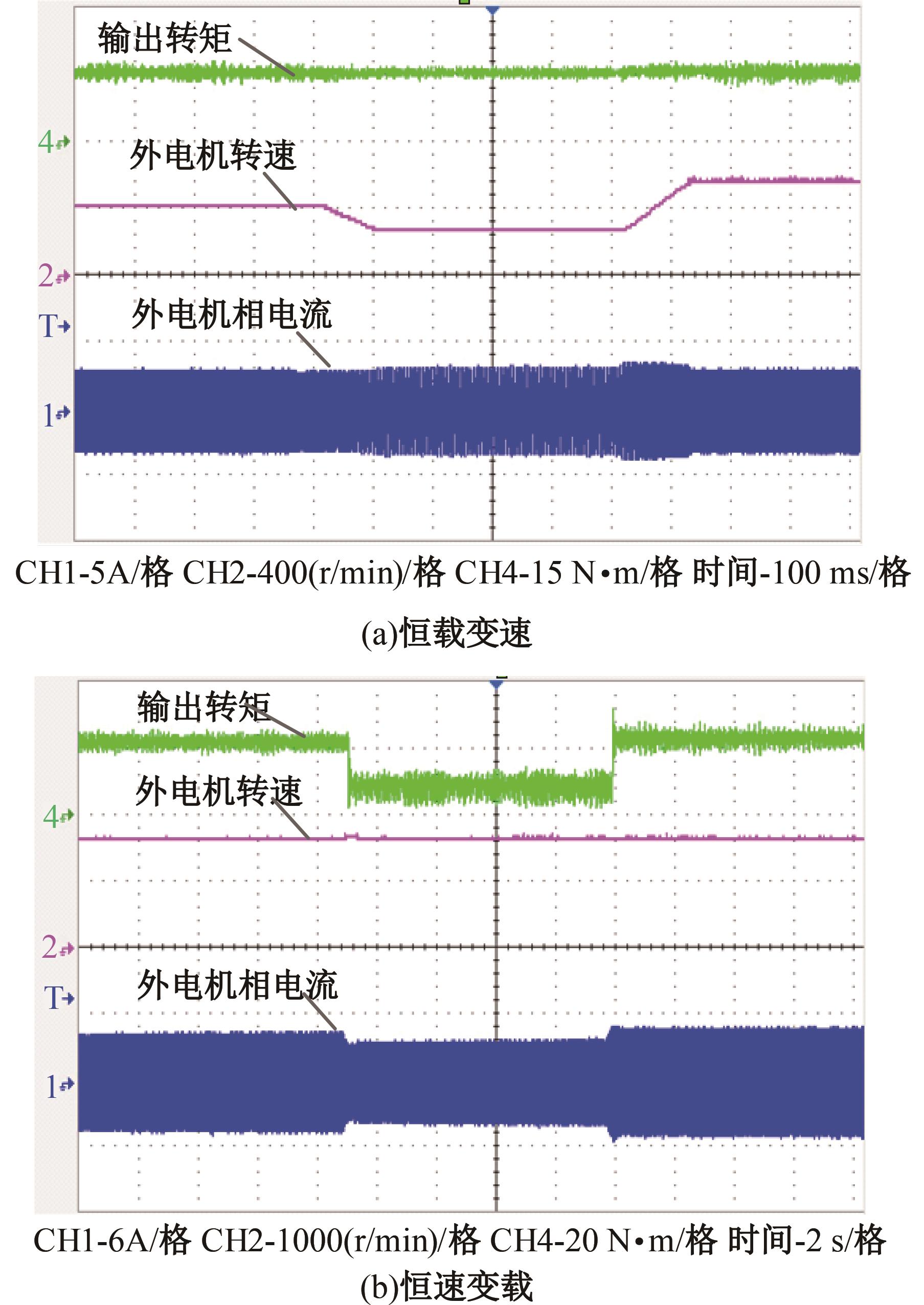
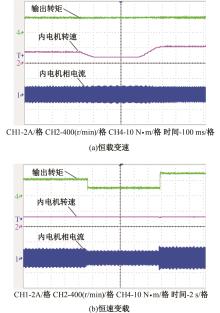
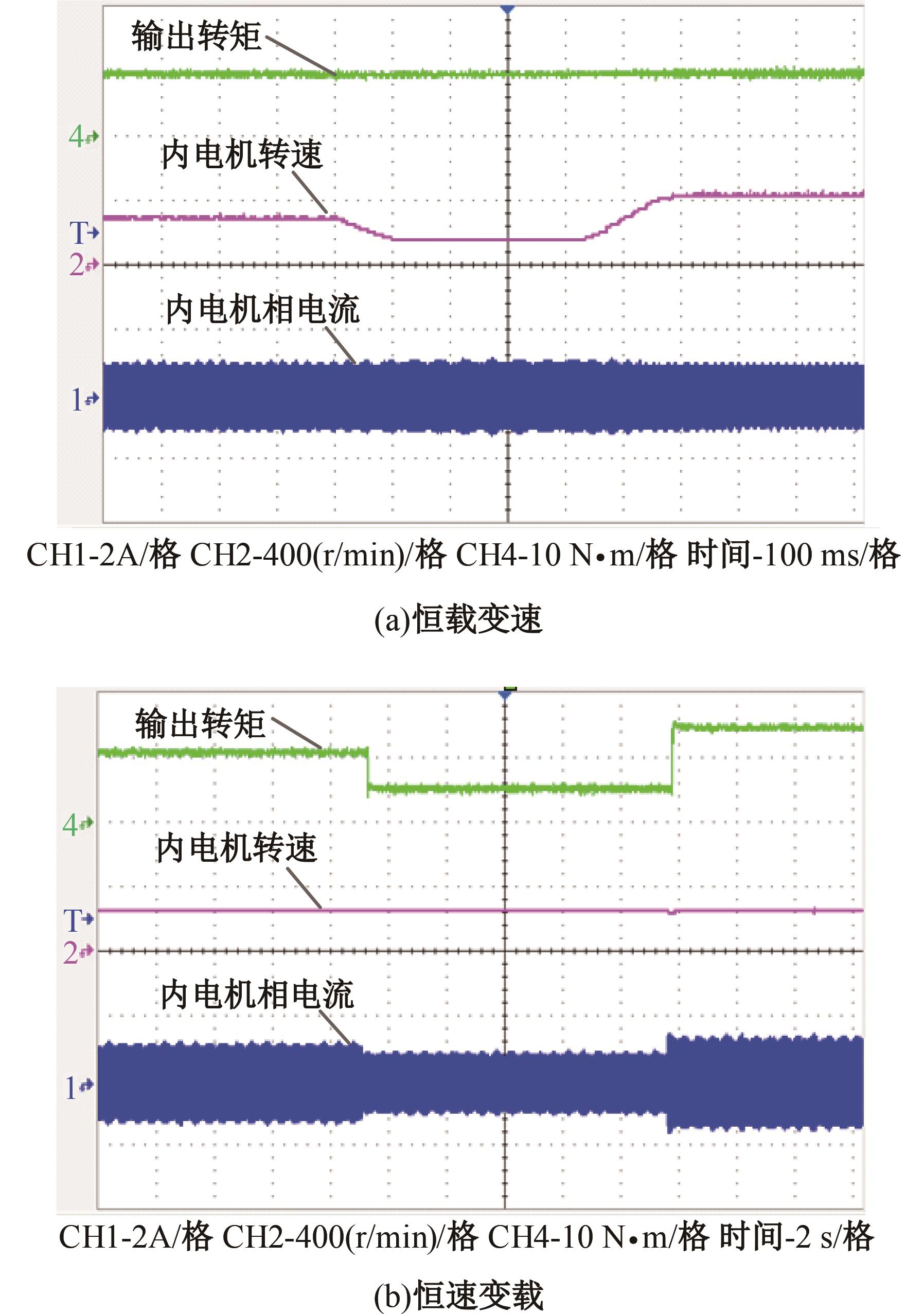
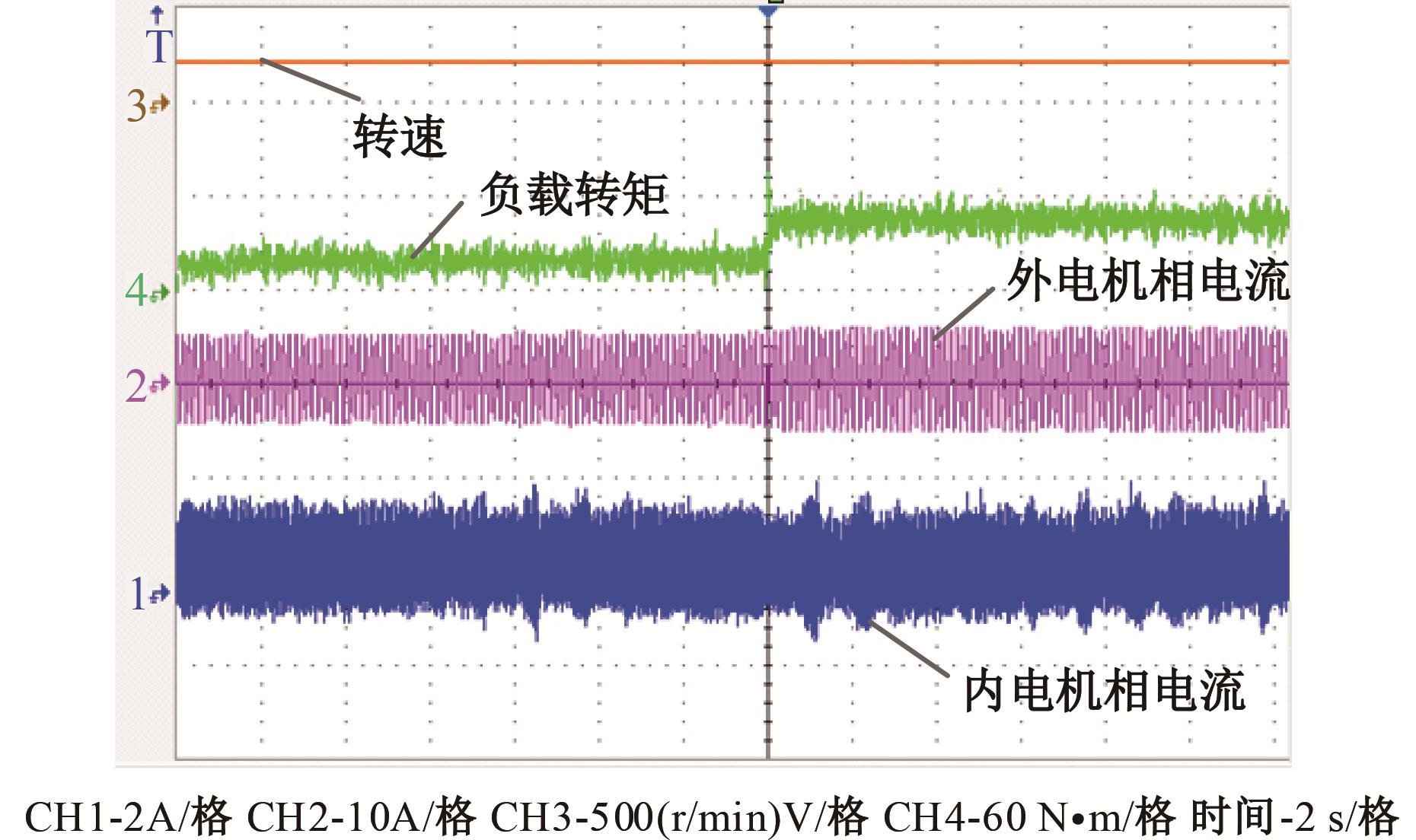
为了克服传统轮毂电机在电动汽车实际应用中存在的缺点,提出了一种双转子轮毂电机结构,可实现内、外电机单独驱动和双电机耦合驱动多种模式。如何选择最适合当前行驶工况的驱动模式和动态分配内外电机的功率是解决整车能耗问题的关键。在分析电机驱动特性的基础上,基于系统效率最优设计了双转子轮毂电机电动汽车驱动模式的切换规则,并确定了3种驱动模式的具体工作范围;在耦合驱动模式下,根据内、外电机的效率特性,提出了基于系统能耗最小的转矩分配策略。仿真结果表明:车辆在爬坡度分别为5%、10%和15%的坡道上行驶时,与未采用优化策略相比,采用本文的转矩分配策略时系统功率消耗分别降低了4.1%、2.7%和1.6%。在NEDC循环工况中,双转子轮毂电机的3种驱动模式能够随着车速和需求转矩的变化自由切换;内、外电机的大部分工作点均分布在较高的效率范围内,说明两个电机在承担最佳需求转矩的同时,均能以最优效率工作,减小整车能量消耗。双转子轮毂电机动态特性实验结果表明:内、外电机具有较快的响应速度和较强的定速巡航能力,验证了电机结构方案的合理性。
中图分类号:
- U469.72
| 1 | Lu D B, Ouyang M G, Lu L G, et al. Theoretical performance of a new kind of range extended electric vehicle[J]. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 2011, 4(1): 655-661. |
| 2 | He R, Wang J C. Vertical vibration control of an in-wheel motor-driven electric vehicle using an in-wheel active vibration system[J]. Asian Journal of Control, 2020, 22(2): 879-896. |
| 3 | 王震坡, 孙逢春. 电动汽车能耗分配及影响因素分析[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2004(4): 306-310. |
| Wang Zhen-po, Sun Feng-chun. Analysis of energy consumption distribution and factors of influence in electric vehicles[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2004(4): 306-310. | |
| 4 | Hoeijmakers M J, Rondel M. The electrical variable transmission in a city bus[C]∥ 35th IEEE Power Electronics Specialist Conference, Aachen, Germany, 2004: 2273-2278. |
| 5 | Eriksson S, Sadarangani C. A four-quadrant HEV drive system[C]∥ 56th Vehicular Technology Conference, Vancouver, Canada, 2002: 1510-1514. |
| 6 | Xu L, Zhang Y, Wen X. Multioperational modes and control strategies of dual-mechanical-port machine for hybrid electrical vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2009, 45(2): 747-755. |
| 7 | 庄兴明, 宋强, 温旭辉, 等. 辐型磁钢双机械端口电机的解耦控制[J].中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34(33): 5925-5933. |
| Zhuang Xing-ming, Song Qiang, Wen Xu-hui, et al. Decoupling control of dual mechanical ports machine with spoke type permanent-magnet arrangement[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34(33): 5925-5933. | |
| 8 | 陈云云, 全力, 朱孝勇, 等. 新型定子永磁式双转子电机运行模式分析与实验研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34(33): 5895-5901. |
| Chen Yun-yun, Quan Li, Zhu Xiao-yong, et al. Analysis and experimental study on operational modes of a novel stator permanent magnet double rotor motor[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34(33): 5895-5901. | |
| 9 | 莫丽红, 全力, 朱孝勇, 等. 定子永磁式双转子电机设计与实验研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2014, 29(9): 74-82. |
| Mo Li-hong, Quan Li, Zhu Xiao-yong, et al. Optimal design and experiment of a novel double-rotor machine with PMs in stator[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2014, 29(9): 74-82. | |
| 10 | Xiang Z X, Zhu X Y, Quan L, et al. Multi-level design optimization and operation of a brushless double mechanical ports flux-switching permanent magnet motor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(10): 6042-6054. |
| 11 | 何仁, 胡东海. 基于双转子电机的电动轮及其控制方法[P]. 中国: ZL201410162607.X, 2016-03-02. |
| 12 | 何仁, 倪赟磊. 用于车辆轮毂驱动的双转子电机结构及其动力传递模式[P]. 中国: ZL201310659506.9, 2016-01-20. |
| 13 | 何仁, 杨祺. 四轮驱动电动汽车的双转子轮毂电机及其动力传递方法[P]. 中国: ZL201510453976.9, 2018-02-27. |
| 14 | 邢杰, 马士奔, 叶辉, 等. 用于电动汽车的双转子电机轮毂驱动系统[P]. 中国: CN106627101A, 2017-05-10. |
| 15 | 孟德建, 陈辛波, 张立军, 等. 一种双转子电机集成鼓式制动器的轮毂电机驱动系统[P]. 中国: CN109435676A, 2019-03-08. |
| 16 | 陈龙, 朱斌, 孙晓东, 等. 基于模型预测控制的多电机驱动系统能量最优分配策略[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(10): 403-409. |
| Chen Long, Zhu Bin, Sun Xiao-dong, et al. Optimal allocation strategy for multi-motor drive system based on model predictive control[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(10): 403-409. |
| [1] | 朱冰,范天昕,赵文博,李伟男,张培兴. 自动驾驶汽车连续测试场景复杂度评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 456-467. |
| [2] | 曲俊龙,史文库,玄圣夷,陈志勇. 面向汽车传动系统多挡共振的多级吸振器参数设计方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 444-455. |
| [3] | 陈鑫,张祥源,武子涛,于贵申,杨立飞. 工艺顺序对车用铝薄板胶-PFSSW接头拉剪性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 468-475. |
| [4] | 胡宏宇,张争光,曲优,蔡沐雨,高菲,高镇海. 基于双分支和可变形卷积网络的驾驶员行为识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 93-104. |
| [5] | 王军年,曹宇靖,罗智仁,李凯旋,赵文伯,孟盈邑. 基于双目视觉的道路水深在线检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 175-184. |
| [6] | 谭草,任浩鑫,葛文庆,宋亚东,陆佳瑜. 直驱阀控液压振动平台改进自抗扰控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 84-92. |
| [7] | 李寿涛,杨路,屈如意,孙鹏鹏,于丁力. 基于模型预测控制的滑移率控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2687-2696. |
| [8] | 吴量,顾义凡,邢彪,马芳武,倪利伟,贾微微. 基于线性二次型调节器的四轮转向与分布式集成控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2414-2422. |
| [9] | 王玉海,李晓之,李兴坤. 面向高速工况的混合动力卡车预见性节能算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2121-2129. |
| [10] | 常胜,刘宏飞,邹乃威. 汽车变曲率路径循迹H∞回路成形鲁棒控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2141-2148. |
| [11] | 刘建泽,柳江,李敏,章新杰. 基于最小二乘的车速解耦路面辨识方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1821-1830. |
| [12] | 谢宪毅,张明君,金立生,周彬,胡涛,白宇飞. 考虑舒适度的智能汽车人工蜂群轨迹规划方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1570-1581. |
| [13] | 刘从臻,陈高,刘洪柱,马强,徐成伟,孟辉,王国林. 湿滑路面轮胎接地力学特性模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1501-1511. |
| [14] | 黄玲,崔躜,游峰,洪佩鑫,钟浩川,曾译萱. 适用于多车交互场景的车辆轨迹预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1188-1195. |
| [15] | 郭洪艳,王连冰,赵旭,戴启坤. 考虑侧向运动的整车质量与道路坡度估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1175-1187. |
|
||