吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 1015-1027.
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于自适应大核注意力的轻量级图像超分辨率网络
- 1.中国矿业大学 信息与控制工程学院,江苏 徐州 221116
2.成都大学 模式识别与智能信息处理四川省高校重点实验室,成都 610106
3.中国矿业大学 计算机科学与技术学院,江苏 徐州 221116
Lightweight image super⁃resolution network based on adaptive large kernel attention fusion
De-qiang CHENG1( ),Gui LIU1,Qi-qi KOU3,Jian-ying ZHANG1,He JIANG1,2(
),Gui LIU1,Qi-qi KOU3,Jian-ying ZHANG1,He JIANG1,2( )
)
- 1.School of Information and Control Engineering,China University of Mining and Technology,Xuzhou 221116,China
2.Key Laboratory of Pattern Recognition and Intelligent Information Processing,Institutions of Higher Education of Sichuan Province,Chengdu 610106,China
3.School of Computer Science and Technology,China University of Mining and Technology,Xuzhou 221116,China
摘要:
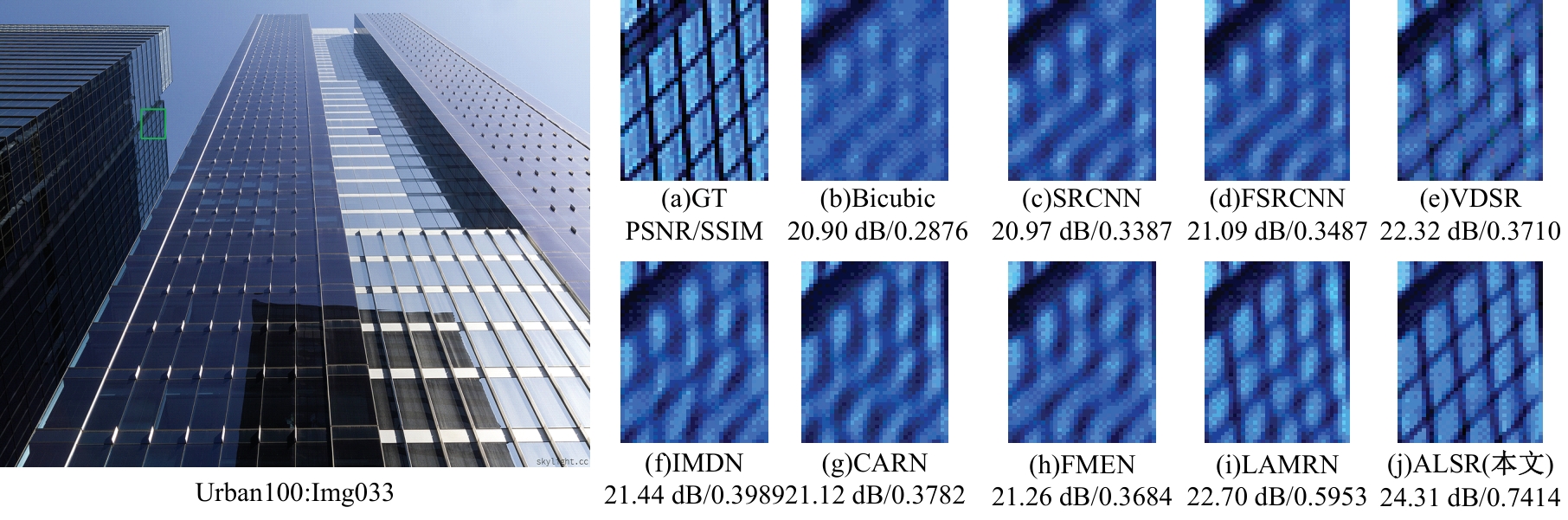
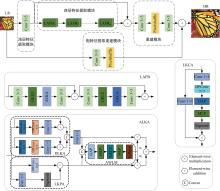
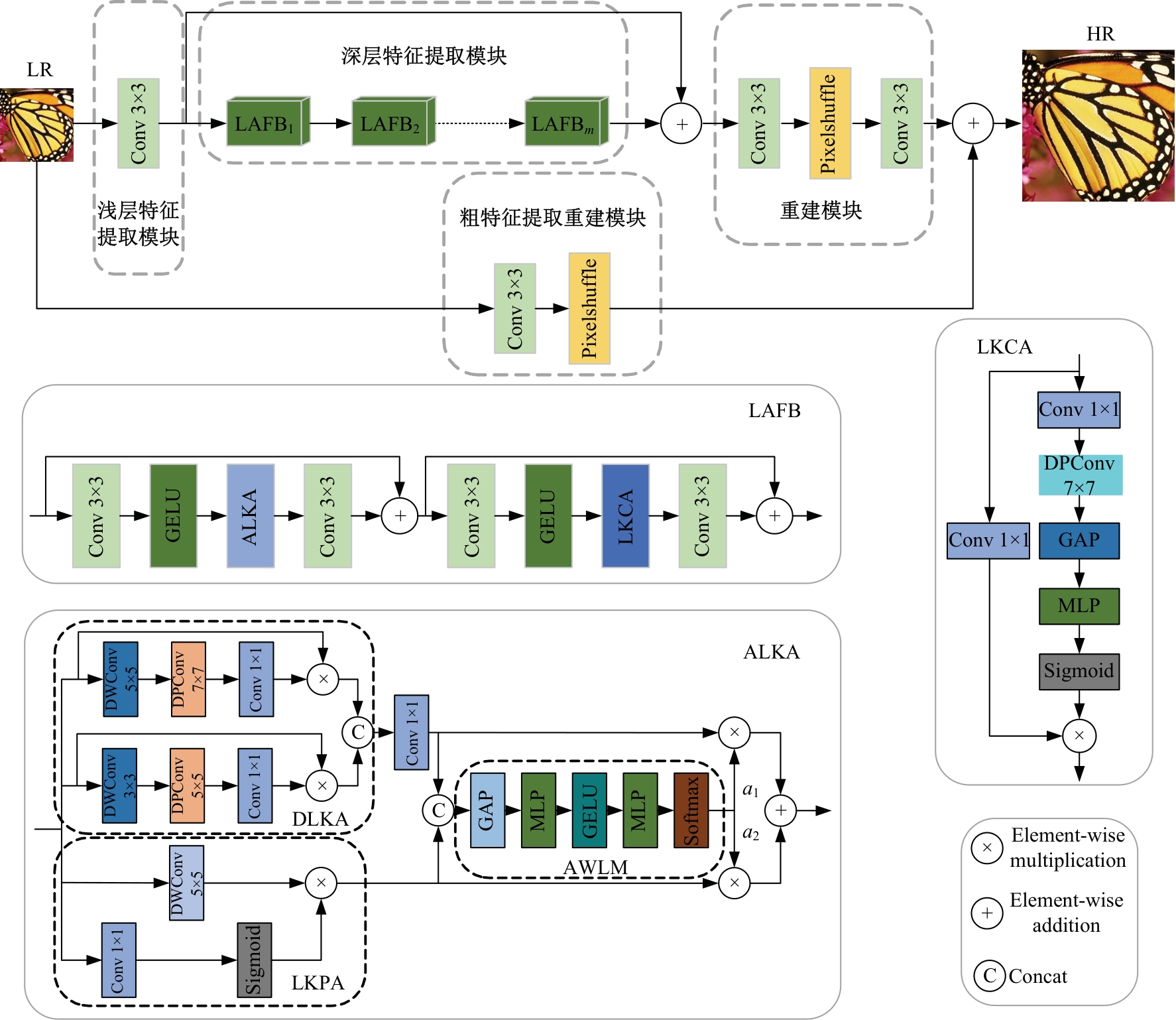
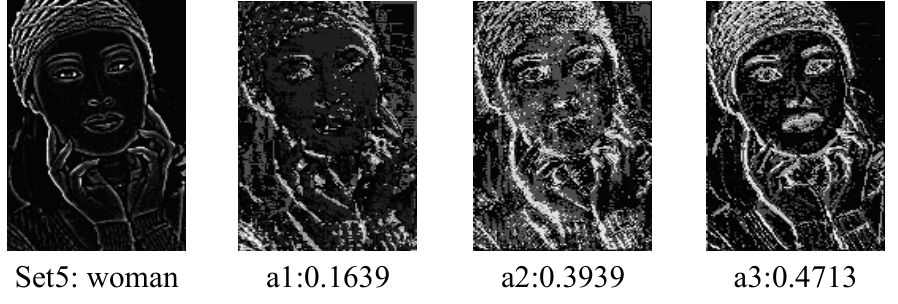
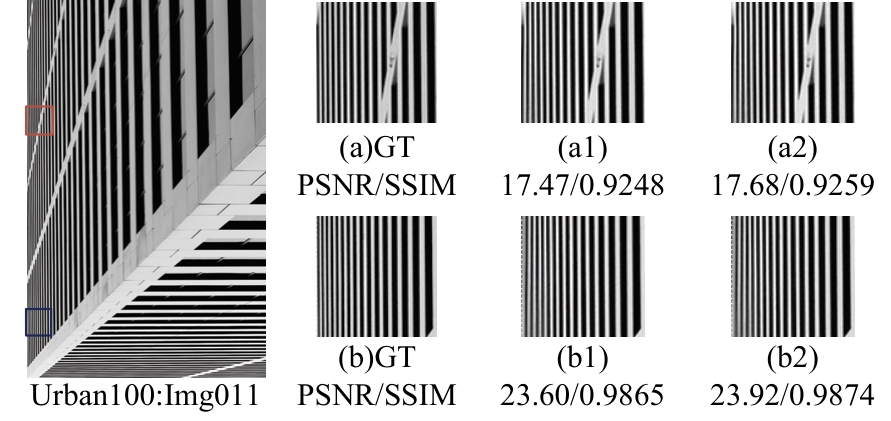
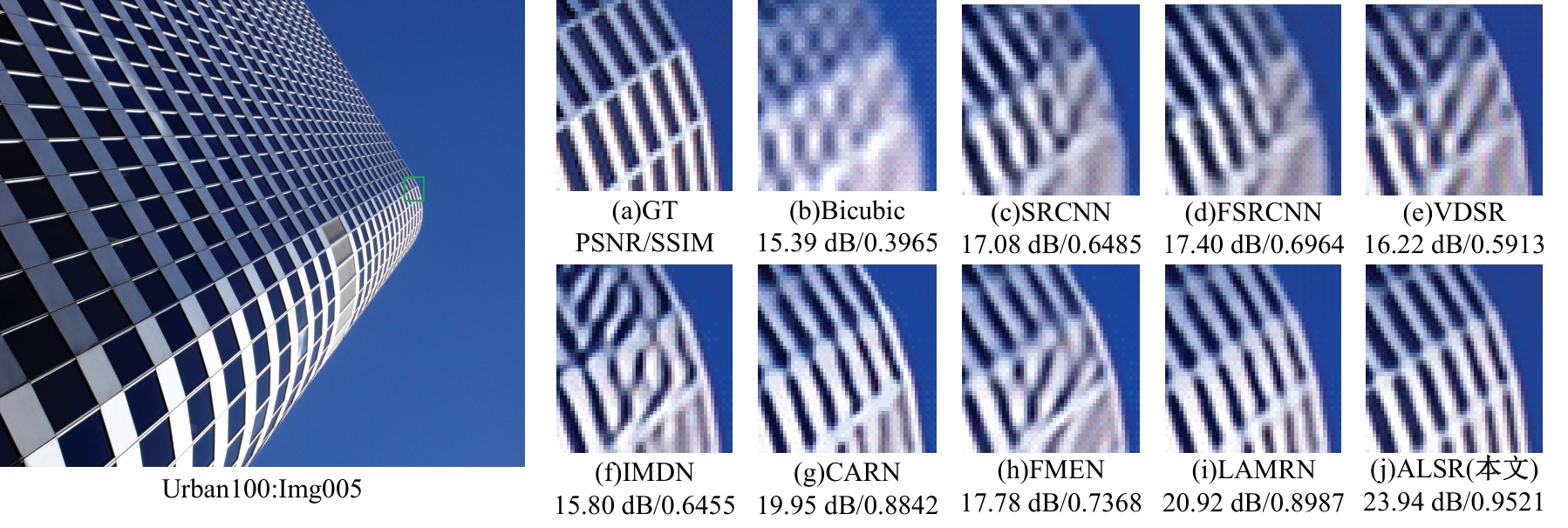
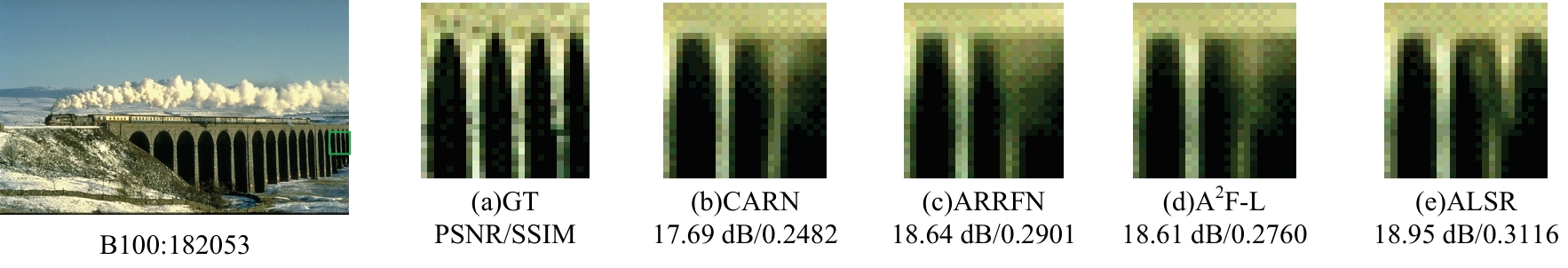
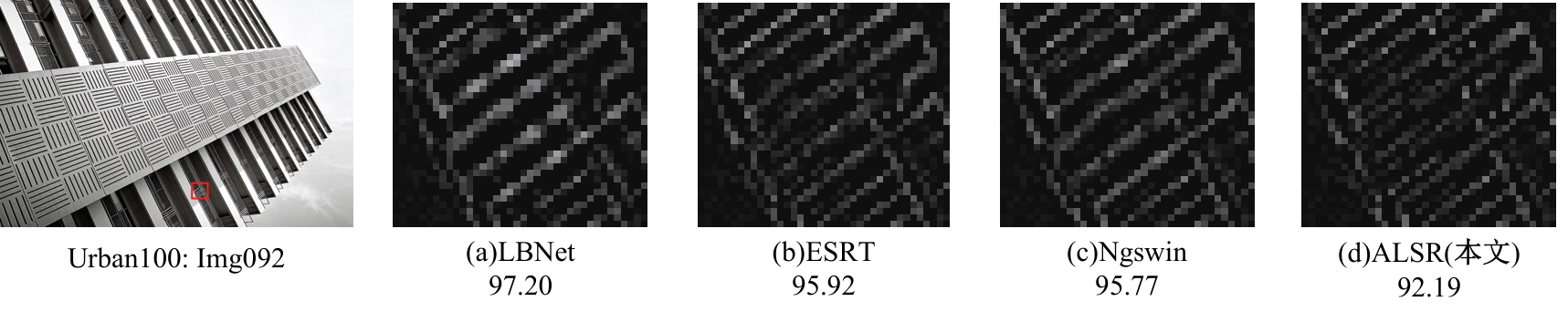
针对高性能图像超分辨网络通常参数量庞大的问题,提出了一种轻量级模型。首先,集成了3种大核注意力,即双路大核注意力、大核像素注意力和大核通道注意力,旨在扩大模型感受野,建立像素的长程依赖性。其次,引入了自适应注意力融合机制,增强了特征的表征能力,提升了模型性能。实验证明:本文模型在视觉感知和量化测试上表现优异。在Urban100数据集上,与目前流行的ARRFN算法相比,4倍重建结果的峰值信噪比均值提高了0.25 dB。重建图像视觉效果更逼真、纹理更为清晰和自然,充分证明了该算法的有效性。
中图分类号:
- TP391.41
| 1 | Cheng D Q, Chen L L, Lv C, et al. Light-guided and cross-fusion U-Net for anti-illumination image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transaction on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(12): 8436-8449. |
| 2 | Jebkins W K, Mather B C, Jr D C M. Nearest neighbor and generalized inverse distance interpolation for fourier domain image reconstruction[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Tampa, USA, 1985:1069-1072. |
| 3 | Blu T, Thevenaz P, Unser M. Linear interpolation revitalized[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2004, 13(5): 710-719. |
| 4 | Lin C, Shen M, Chang H, et al. The efficient VLSI design of BICUBIC convolution interpolation for digital image processing[C]∥Proceedings of the International Symposium on Circuitsand Systems (ISCAS), Seattle, USA, 2008:480-483. |
| 5 | Dai S, Han M, Xu W,et al. Soft-cuts: a soft edge smoothness prior for color image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2009, 18(5): 969-981. |
| 6 | Sun J, Xu Z, Shun H Y. Image super-resolution using gradient profile prior[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Reco Anchorage, Anchorage, AK, USA, 2008: 1-8. |
| 7 | Yan Q, Xu Y, Yang X, et al. Single image super resolution based on gradient profile sharpness[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015,24(10):3187-3202 . |
| 8 | iang H J, Mujtaba A S A D, Liu J J, et al. Single image detail enhancement via metropolis theorem[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications,2024, 83: 36329-36353. |
| 9 | 程德强, 郭昕, 陈亮亮, 等. 多通道递归残差网络的图像超分辨率重建[J].中国图象图形学报, 2021, 26(3): 605-618. |
| Cheng De-qiang, Guo Xin, Chen Liang-liang, et al. Image super resolution reconstruction by multi-channel recursive residual networks[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2021, 26(3): 605-618. | |
| 10 | Dong C, Loy C C, He K M, et al. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 295-307. |
| 11 | Shi W, Caballero J, Huszár F,et al. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016:1874-1883. |
| 12 | Lim B, Son S, Kim H,et al. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu,USA, 2016:1132-1140. |
| 13 | 郭继昌, 吴洁, 郭春乐, 等. 基于残差连接卷积神经网络的图像超分辨率重构[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版,2019, 49(5): 1726-1734. |
| Guo Ji-chang, Wu Jie, Guo Chun-le, et al.Image super-resolution reconstruction based on residual-connected convolutional neural networks[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition,2019, 49(5): 1726-1734. | |
| 14 | Zhang Y, Li K. Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich Germany, 2018: 286-301. |
| 15 | Niu B, Wen W L, Ren W Q,et al. Single image super-resolution via a holistic attention network[C]∥ 2020 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, USA, 2020:191-207. |
| 16 | Vaswan A, Shazeer N, Parmar, et al. Attention is all you need[J/OL].[2023-09-15]. |
| 17 | Liang J Y, Cao J Z, Sun G L,et al. Image restoration using swin transformer[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 1833-1844. |
| 18 | Lu Z S, Li J C, Liu H, et al. Transformer for single image super-resolution[C]∥Proc IEEE/CVF Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit Workshops, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 456-465. |
| 19 | Kou Q Q, Cheng D Q, Zhang H et al. Single Image super resolution via multi-attention fusion recurrent network[J]. IEEE Access,2023(11): 98653-98665. |
| 20 | Wang Z, Gao G, Li J,et al. Lightweight image super-resolution with multi-scale feature interaction network[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Shenzhen, China, 2021: No.9428136. |
| 21 | Lan R, Sun L, Liu Z,et al. MADNet:a fast and lightweight network for single-image super resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021,51(3):1443-1453. |
| 22 | Guo M H, Lu C Z, Liu Z N,et al. Visual attention network[J/OL].[2023-09-18]. |
| 23 | Jie H, Li S, Samuel A, et al. Squeeze-and-excita⁃tion networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni⁃tion, Wellington, New Zealand, 2018: 7132-7141. |
| 24 | Bevilacqua M, Roumy A, Guillemot C, et al. Low-complexity single image super-resolution based on nonnegative neighbour embedding[C]∥British Machine Vision Conference, Oxford,UK, 2012:1-10. |
| 25 | Zeyde R, Elad M, Protter M. On single image scale-up using sparse-representations[C]∥International Conference on Curves and Surfaces,Avignon, France, 2010: 711-730. |
| 26 | Kim J, Lee J K, Lee K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks[C]∥2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016:1646-1654. |
| 27 | Huang J B, Singh A, Ahuja N. Single image super-resolution from transformed self-exemplars[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Boston, USA, 2015:5197-5206. |
| 28 | Dong C, Loy C C, Tang X. Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision,Amsterdam, Holland, 2016:391-407. |
| 29 | Kim J, Lee J K, Lee K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1646-1654. |
| 30 | Kim J, Lee J K, Lee K M. Deeply-recursive convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA,2016:1637-1645. |
| 31 | Ahh N, Kang B, Sohn K A. Fast, accurate, and lightweight super-resolution with cascading residual network[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 256-272. |
| 32 | Hui Z, Gao X, Yang Y, et al. Lightweight image super-resolution with information multi-distillation network[C]∥Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Xi'an, China, 2019: 2024-2032. |
| 33 | Wang X H, Wang Q, Zhao Y Z, et al. Lightweight single-image super-resolution network with attentive auxiliary feature learning[C]∥Asian Conference on Computer Vision(ACCV),Kyoto, Japan, 2020: 3023-3041. |
| 34 | Du Z C, Liu D, Liu J, et al. Fast and memory-efficient network towards efficient image super-resolution[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,New Orleans, USA, 2022 :853-862. |
| 35 | Yan Y, Xu X, Chen W, et al. Lightweight attended multi-scale residual network for single image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 52202-52212. |
| 36 | Qin J, Zhang R. Lightweight single image super-resolution with attentive residual refinement network[J].Neurocomputing, 2022, 500: 846-855. |
| 37 | Gao G W, Wang Z X, Li J C, et al. Lightweight bimodal network for single-image super-resolution via symmetric CNN and recursive transformer[C]∥International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence,Shenzhen, China, 2022: 913-919. |
| 38 | Choi H, Lee J, Yang J. N-Gram in swin transformers for efficient lightweight image super-resolution[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canadian, 2023: 2071-2081. |
| 39 | Jie H, Li S, Samuel A, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Wellington, New Zealand, 2018: 7132-7141. |
| [1] | 董华松,连远锋. 海量数字媒体视频无损转码重压缩的轻量化检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 741-747. |
| [2] | 才华,郑延阳,付强,王晟宇,王伟刚,马智勇. 基于多尺度候选融合与优化的三维目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 709-721. |
| [3] | 张曦,库少平. 基于生成对抗网络的人脸超分辨率重建方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 333-338. |
| [4] | 朱圣杰,王宣,徐芳,彭佳琦,王远超. 机载广域遥感图像的尺度归一化目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2329-2337. |
| [5] | 才华,寇婷婷,杨依宁,马智勇,王伟刚,孙俊喜. 基于轨迹优化的三维车辆多目标跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2338-2347. |
| [6] | 郭昕刚,何颖晨,程超. 抗噪声的分步式图像超分辨率重构算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 2063-2071. |
| [7] | 孙铭会,薛浩,金玉波,曲卫东,秦贵和. 联合时空注意力的视频显著性预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [8] | 王殿伟,张池,房杰,许志杰. 基于高分辨率孪生网络的无人机目标跟踪算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1426-1434. |
| [9] | 王宇,赵凯. 基于亚像素定位的人体姿态热图后处理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1385-1392. |
| [10] | 张自超,陈建. 基于双目仿鹰眼视觉与超分辨的果园三维点云重建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1469-1481. |
| [11] | 高云龙,任明,吴川,高文. 基于注意力机制改进的无锚框舰船检测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1407-1416. |
| [12] | 毛琳,苏宏阳,杨大伟. 时间显著注意力孪生跟踪网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(11): 3327-3337. |
| [13] | 孙文财,胡旭歌,杨志发,孟繁雨,孙微. 融合GPNet与图像多尺度特性的红外-可见光道路目标检测优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(10): 2799-2806. |
| [14] | 李本怀,刘艳文,王璐,陈雪乾,左文杰. 吸能与压溃位移约束下的轨道车辆前端结构抗撞性优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 982-988. |
| [15] | 刘晶红,邓安平,陈琪琪,彭佳琦,左羽佳. 基于多重注意力机制的无锚框目标跟踪算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3518-3528. |
|
||