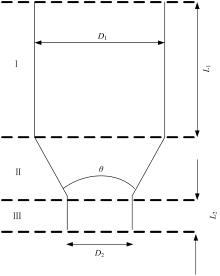
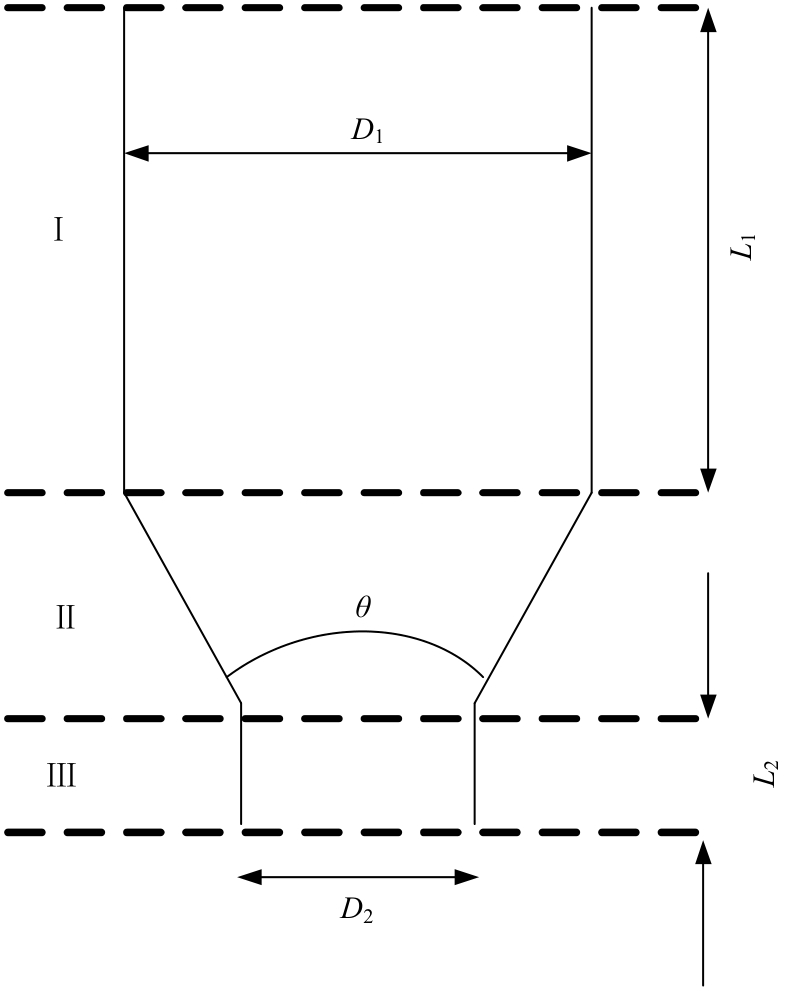
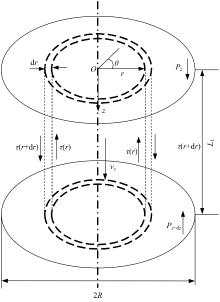
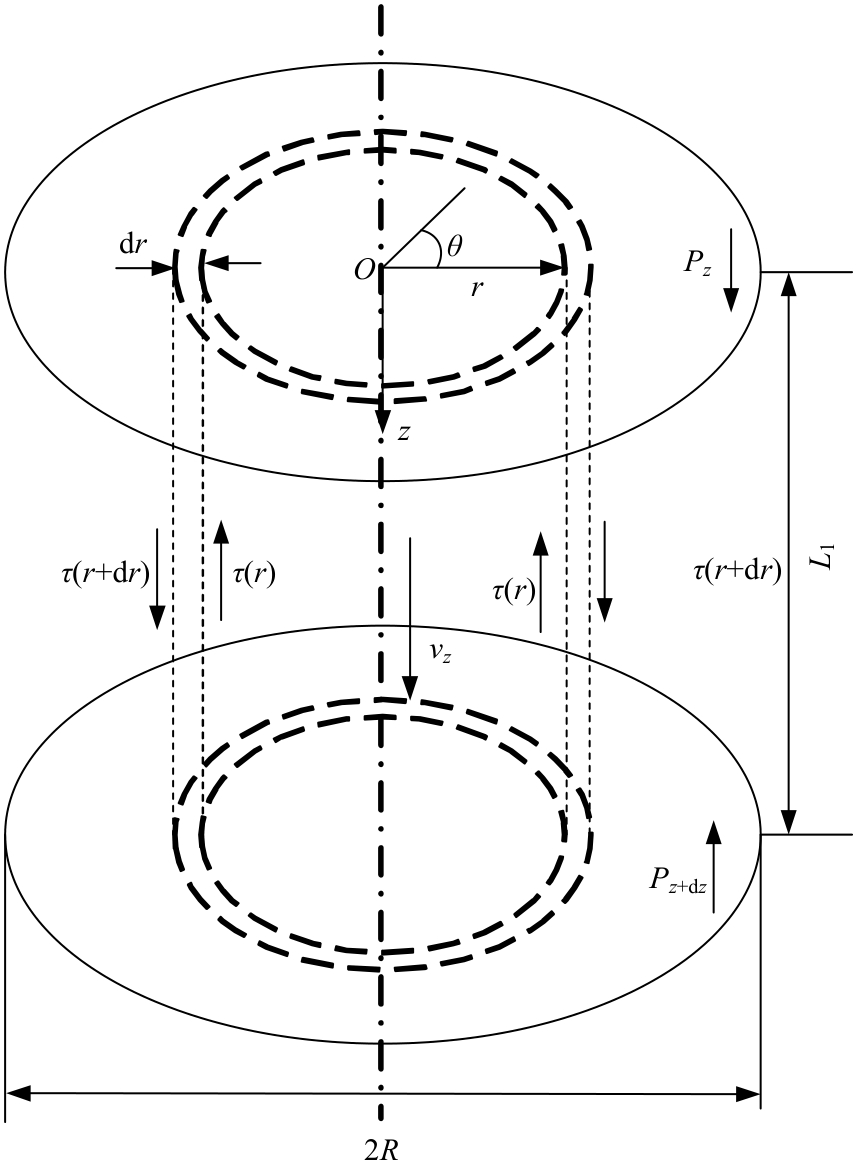
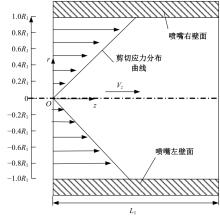
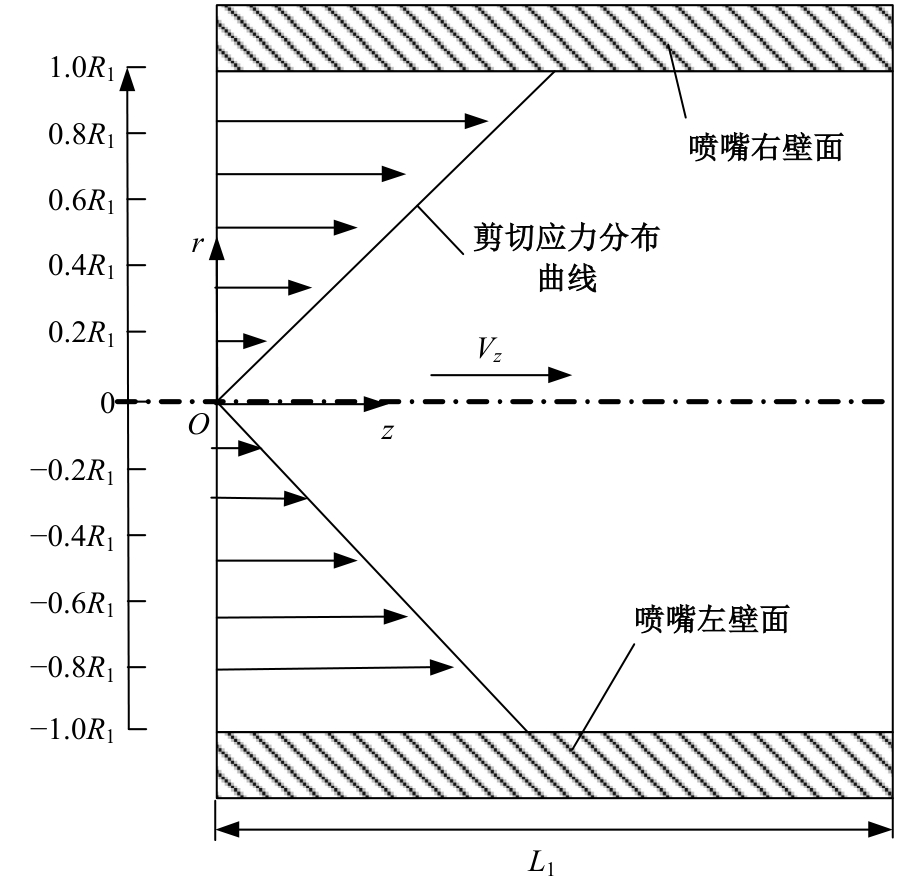
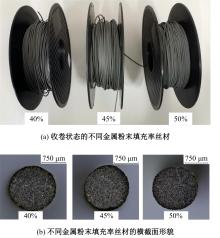
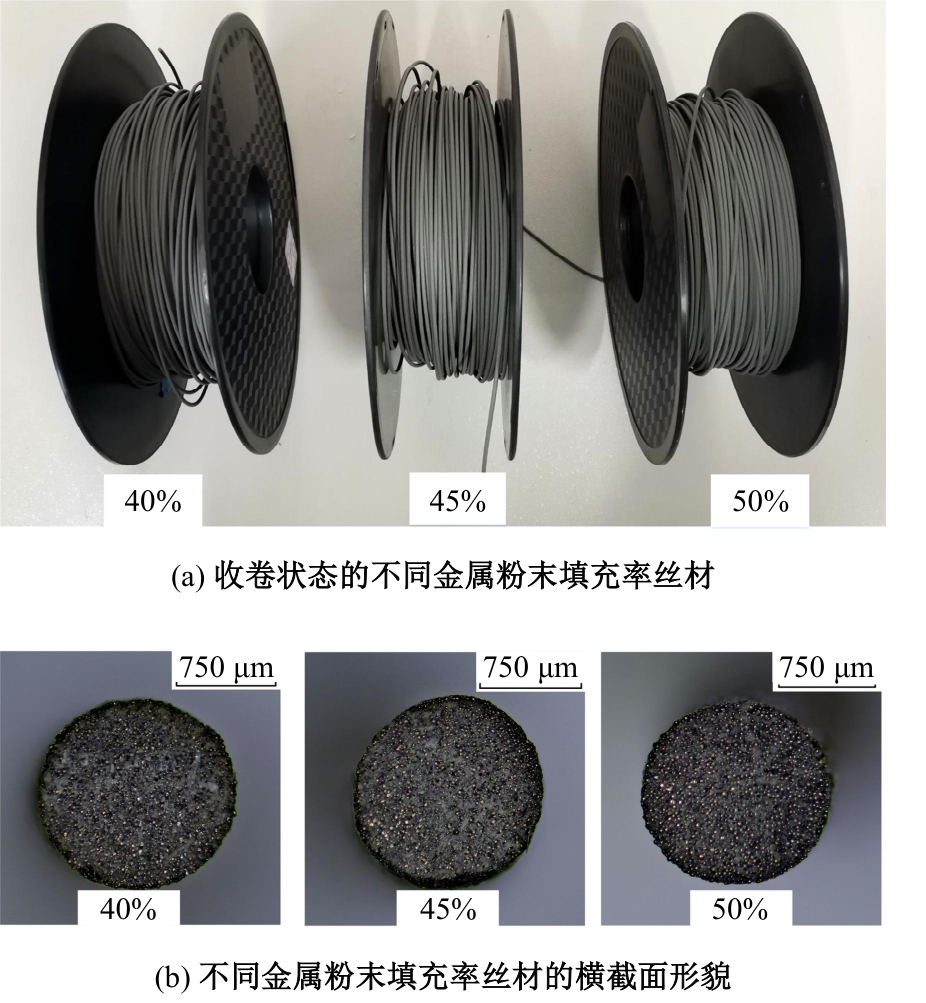
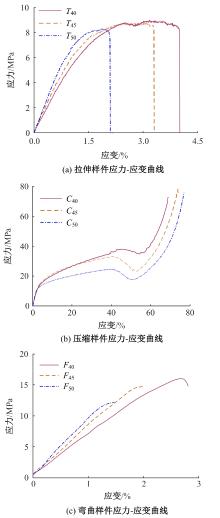
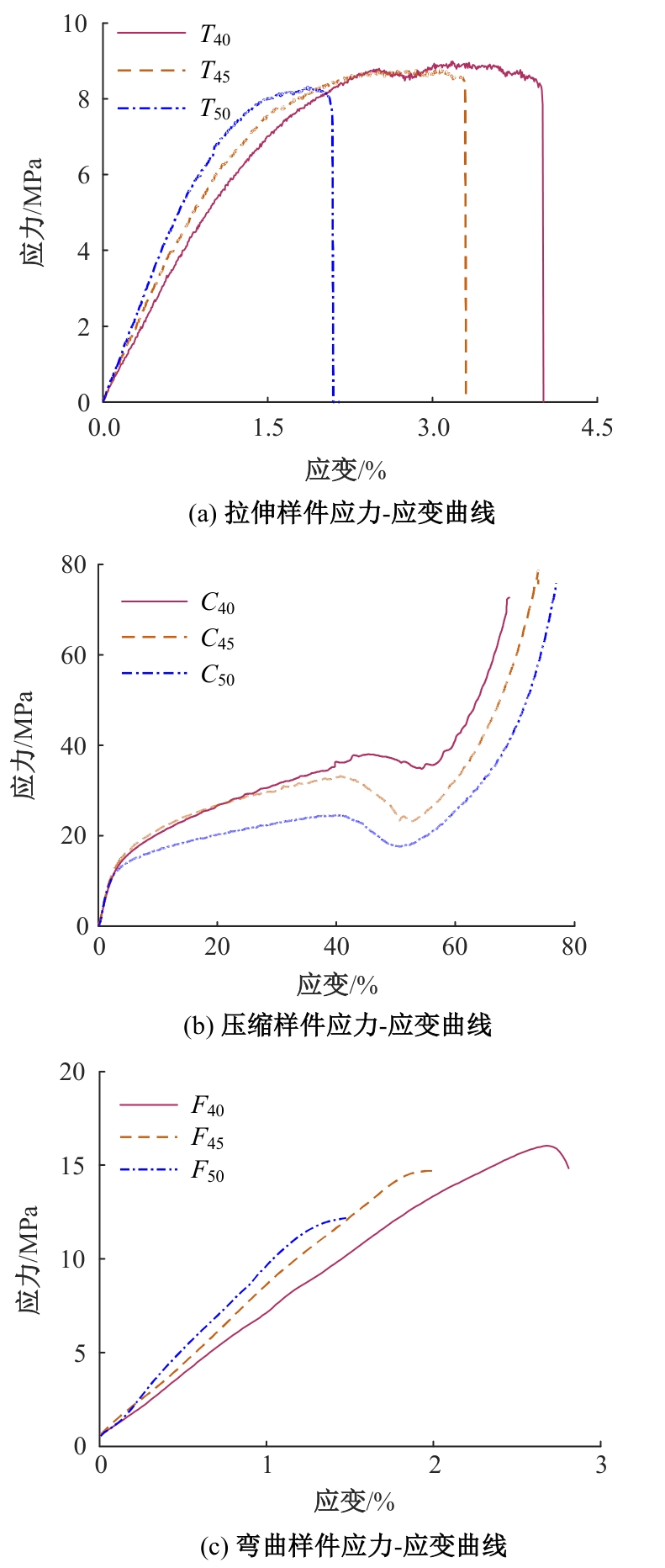
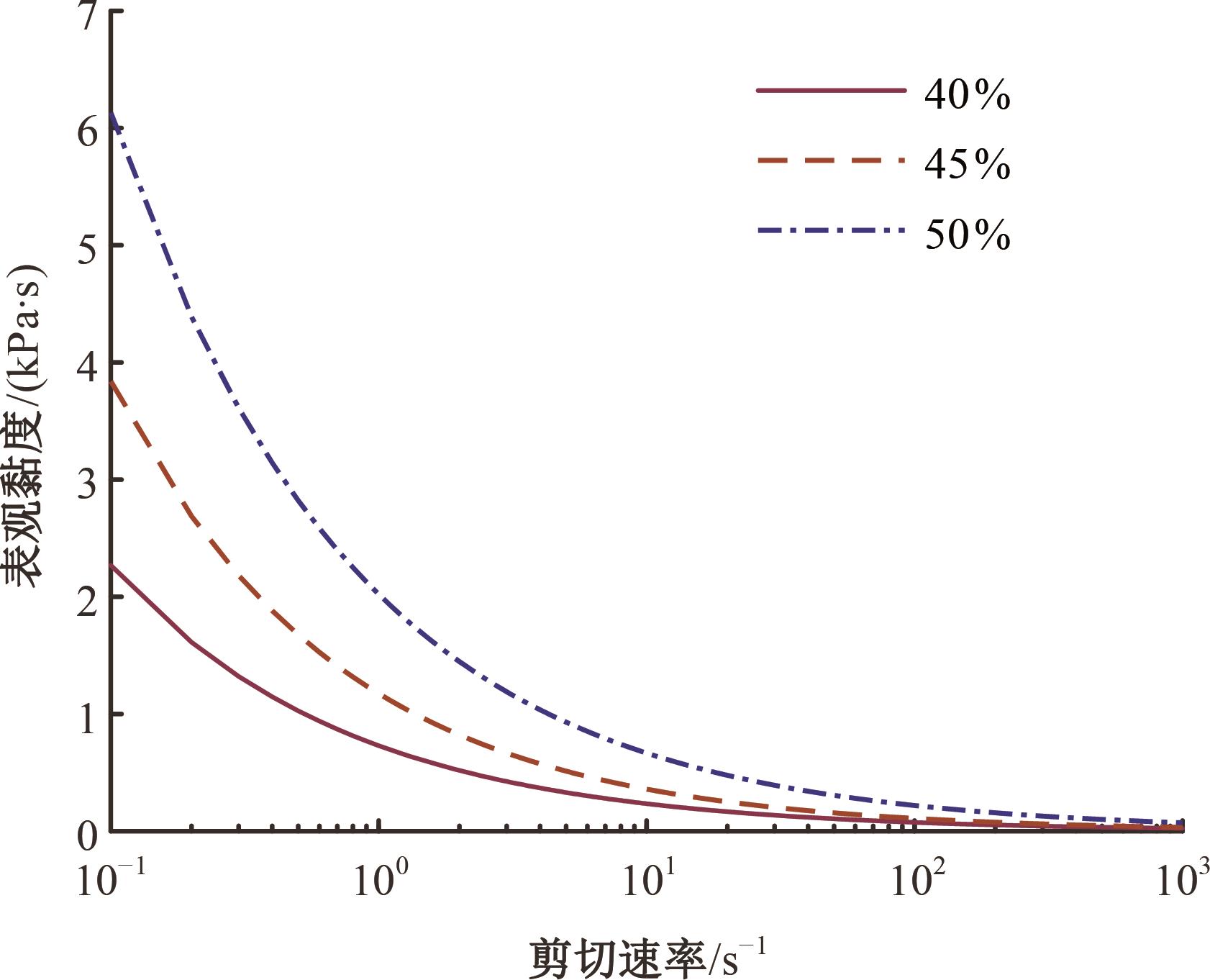
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (7): 2180-2192.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20231144
Rheological property of composite filament in metal fused filament fabrication process
Shi-jie JIANG1,2( ),Shu-guang LI1,Zi-zhao XU1,Fei WANG1
),Shu-guang LI1,Zi-zhao XU1,Fei WANG1
- 1.School of Mechanical Engineering & Automation,Northeastern University,Shenyang 110819,China
2.Key Laboratory of Dynamics Reliability of Mechanical Equipment of Liaoning Province,Northeastern University,Shenyang 110819,China
CLC Number:
- TH145.9
| [1] | Thompson Y, Gonzalez-Gutierrez J, Kukla C, et al. Fused filament fabrication, debinding and sintering as a low cost additive manufacturing method of 316L stainless steel[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2019, 30: No. 100861. |
| [2] | Ren L Q, Zhou X L, Song Z Y, et al. Process parameter optimization of extrusion-Based 3D metal printing utilizing PW-LDPE-SA binder system[J]. Materials, 2017, 10(3): 305-321. |
| [3] | Ismael M R, Clemens F, Graule T, et al. Effects of different thermoplastic binders on the processability of feedstocks for ceramic co-extrusion process[J]. Ceramics International, 2011, 37(8): 3173-3182. |
| [4] | Benz J, Bonten C. Influence of polymer-particle-interaction on the flow behavior of highly filled plastics[C]∥The 34th International Conference of the Polymer-Processing-Society(PPS), Taipei, China, 2019, 2065(1): No. 030045. |
| [5] | Hausnerova B, Mukund B N, Sanetrnik D. Rheological properties of gas and water atomized 17-4PH stainless steel MIM feedstocks: effect of powder shape and size[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 312: 152-158. |
| [6] | Kukla C, Gonzalez-Gutierrez J, Duretek I, et al. Effect of particle size on the properties of highly-filled polymers for fused filament fabrication[C]∥The 32nd International Conference of the Polymer-Processing-Society(PPS), Lyon, France, 2016, 1914(1): No. 190006. |
| [7] | Gonzalez-Gutierrez J, Duretek I, Holzer C, et al. Filler content and properties of highly filled filaments for fused filament fabrication of magnets[C]∥ Proceedings of the 75th Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition of the Society of Plastics Engineers, Anaheim, USA, 2017: 1-4. |
| [8] | Gloeckle C, Konkol T, Jacobs O, et al. Processing of highly filled polymer-metal feedstocks for fused Filament fabrication and the production of metallic implants[J]. Materials, 2020, 13(19): 4413-4429. |
| [9] | Dimitri C, Mohamed S, Thierry B, et al. Influence of particle-size distribution and temperature on the rheological properties of highly concentrated Inconel feedstock alloy 718[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 322: 273-289. |
| [10] | Singh P, Balla V K, Tofangchi A, et al. Printability studies of Ti-6Al-4V by metal fused filament fabrication(MF3)[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 2020, 91: No. 105249. |
| [11] | Mostafa N, Masood S H, et al. A study of melt flow analysis of an ABS-Iron composite in fused deposition modelling process[J]. Tsinghua Science & Technology, 2009, 14: 29-37. |
| [12] | Hong X, Xiao X, Zhang Z, et al. Effects of ultrasonic vibration on the rheological behavior of high-density polyethylene composites filled with flash aluminum flake pigments[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2017, 134(23): 44906-44914. |
| [13] | Pandey A, Pradhan S K. Investigations into complete liquefier dynamics and optimization of process parameters for fused deposition modeling[C]∥International Conference on Materials Manufacturing and Modelling(ICMMM), Vellore, India, 2017: 12940-12955. |
| [14] | Turner B N, Strong R, Gold S A. A review of melt extrusion additive manufacturing processes: I. Process design and modeling[J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2014, 20(3): 192-204. |
| [1] | Ge-dong JIANG,Hao WANG,Ya-bin JING. Influence of contact thermal resistance on temperature rise characteristics of high⁃speed ball screw [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1915-1922. |
| [2] | Yong-gang WANG,He-jian LIU,Chuan-yang WANG,Lei WANG,Run-dong QIAN,Dong-ya LI,Yi-jun DONG. Hot corrosion behaviors of CrCoNi medium entropy alloy by laser melting deposition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1544-1551. |
| [3] | Chang-long ZHAO,Chen MA,Jun-bao YANG,Qin-xiang ZHAO,Xiao-yu JIA,Hong-nan MA. Influence of pre⁃set surface texture on laser cladding of 316L coatings [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 899-911. |
| [4] | Lei SHANG,Ping YANG,Xiang-guo YANG,Jian-xin PAN,Jun YANG,Meng-ru ZHANG. Temperature control of proton exchange membrane fuel cell thermal management system based on APSO-BP-PID control strategy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2401-2413. |
| [5] | Lin JIANG,Guo-long LI,Shi-long WANG,Kai XU,Zhe-yu LI. Thermal expansion error modeling of feed axis based on principal component regression [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2149-2155. |
| [6] | Ze-qiang ZHANG,Can WANG,Jun-qi LIU,Dan JI,Si-lu LIU. Parallel row ordering problem based on improved sparrow search algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1851-1861. |
| [7] | Cai-xia SHU,Jia YANG,Qing-xi LIAO,Xing-yu WAN,Jia-cheng YUAN. Design and experiment of diversion type double-cylinder cyclone separation system for rapeseed combine harvester [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1807-1820. |
| [8] | Li HUI,Lei JIN,Wan-wan SONG,Song ZHOU,Jin-lan AN. Crack growth rate of SMA490BW steel in different welding areas for bogie [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(3): 650-656. |
| [9] | Zhi-jun YANG,Chi ZHANG,Guan-xin HUANG. Mechanical model of rigid⁃flexible coupling positioning stage based on floating coordinate method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 385-393. |
| [10] | Yun-tong LI,Xing-yu WAN,Qing-xi LIAO,Yin-lei LIU,Qing-song ZHANG,Yi-tao LIAO. Design and experiment of wide folding rape windrower based on crawler type power chassis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3740-3754. |
| [11] | Wei-jun WU,Jiang-bo WU,Jia-le ZHANG,Qiang ZHOU,Qiao-hong YANG,Xun-peng QIN. Stability analysis and scale synthesis of new multifunctional aerial work platform [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3450-3459. |
| [12] | Lei WANG,Xiao-peng LIU,Song ZHOU,Jin-lan AN,Hong-jie ZHANG,Jia-hui CONG. Effect of ultrasonic rolling on fatigue crack propagation behavior of 2024 aluminum alloy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3486-3495. |
| [13] | Huan-lin ZHOU,Xin GUO,Xuan WANG,Li-xue FANG,Kai LONG. Topology optimization design of multiphase porous structures considering geometric nonlinearity [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 2754-2763. |
| [14] | Lin-rong SHI,Wu-yun ZHAO. Design and test of rolling spoon type flaxes precision hole sower for caraway in northwest cold and arid agricultural region [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2706-2717. |
| [15] | Bo-sen CHAI,Guang-yi WANG,Dong YAN,Guo-ren ZHU,Jin ZHANG,Heng-sheng LYU. Numerical simulation of cavitation in torque converter and analysis of its influence on performance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2236-2244. |
|
||