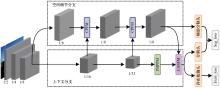
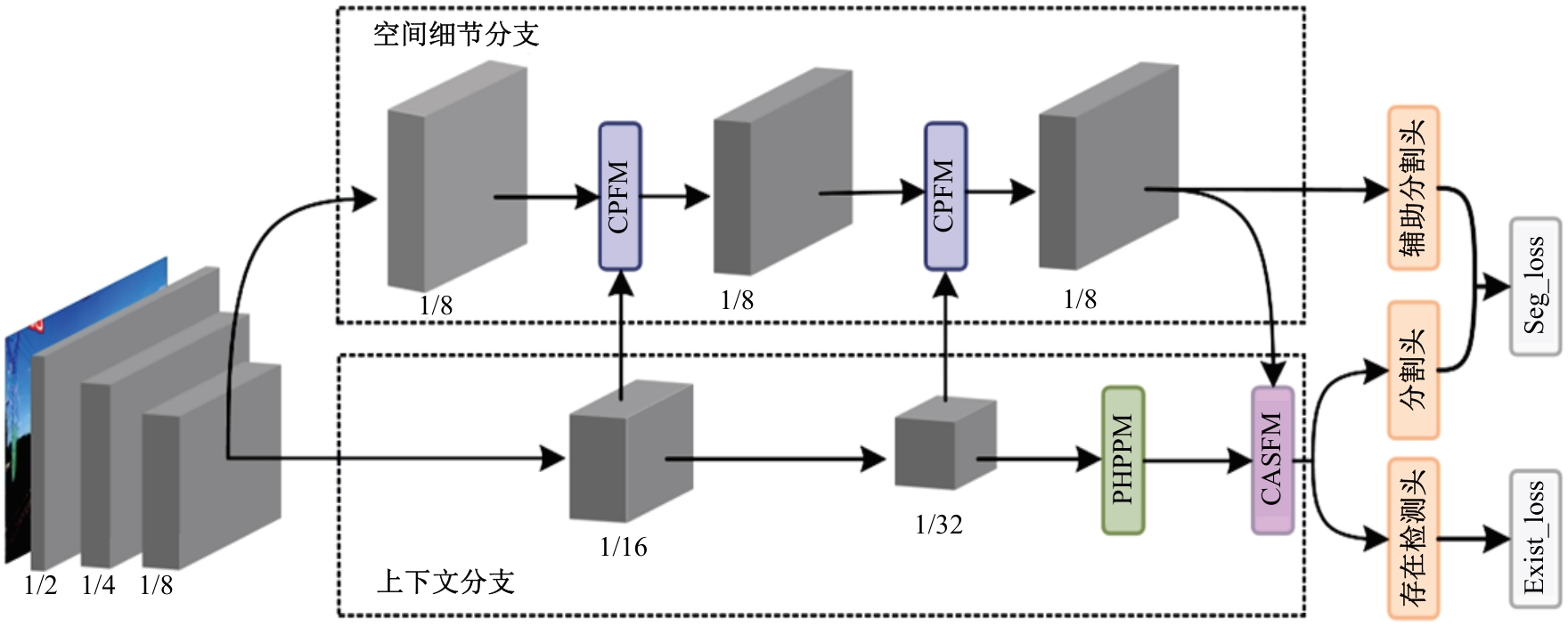
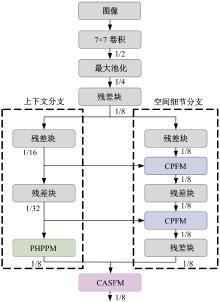
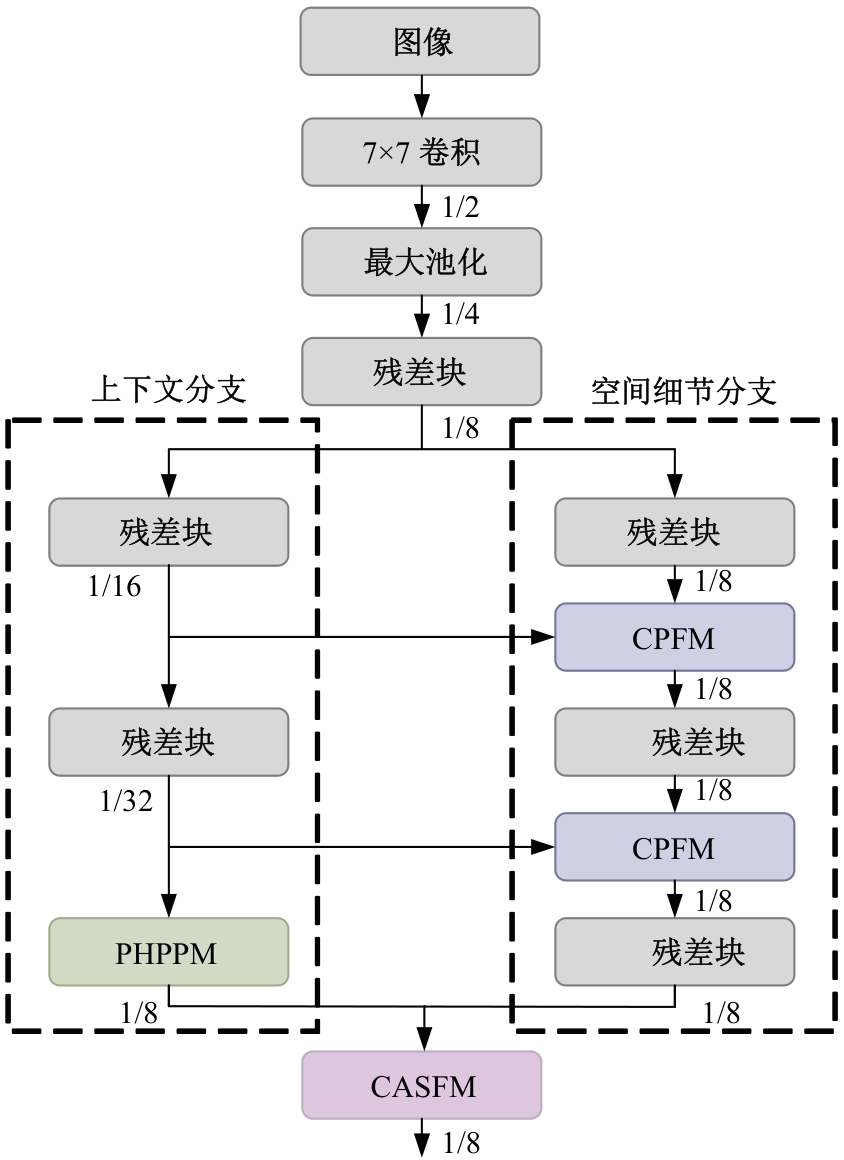
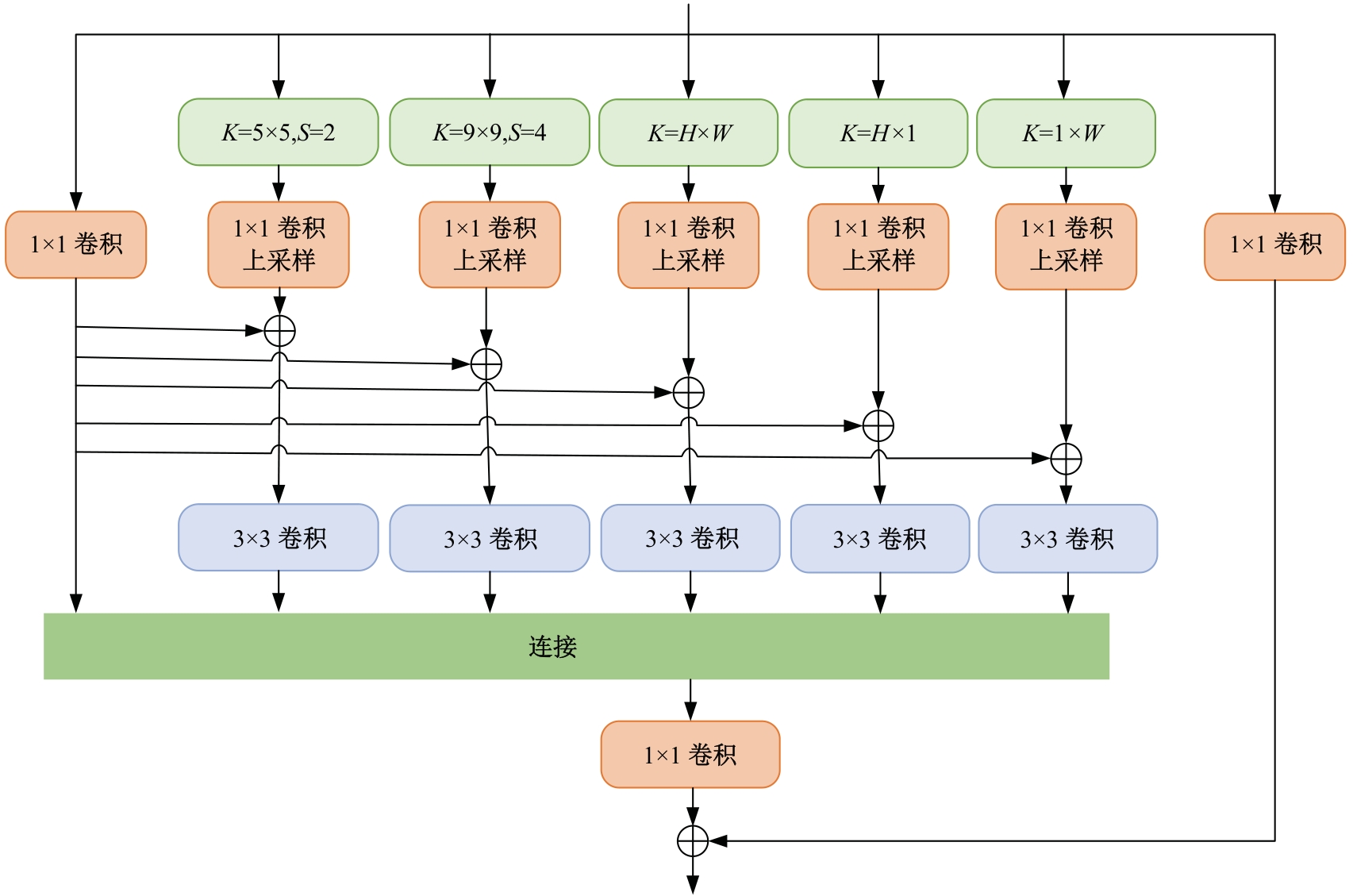
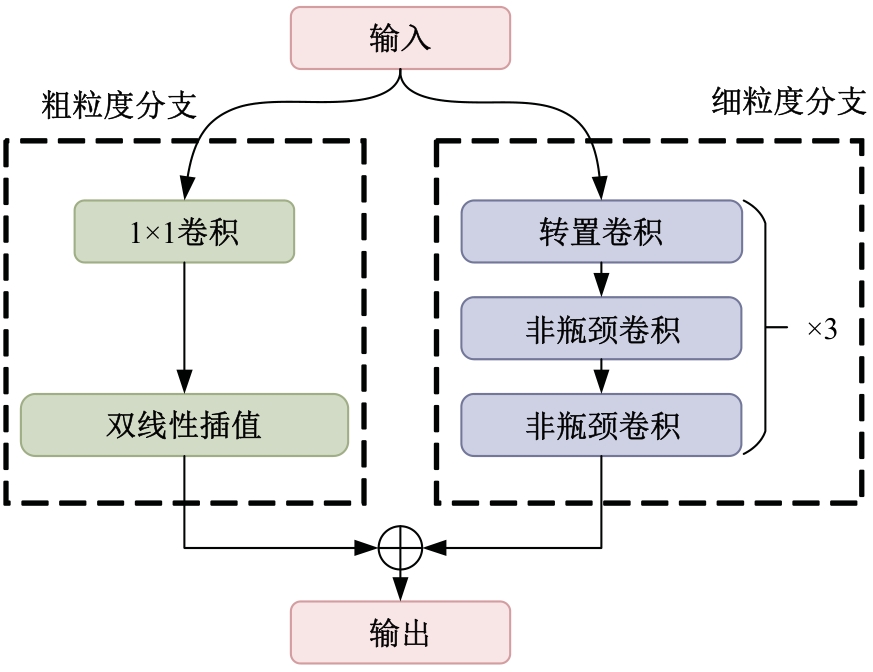
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (12): 3840-3851.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240397
Method of lane detection based on adaptive fusion of double branch features
Tian-min DENG( ),Peng-fei XIE,Yang YU,Yue-tian CHEN
),Peng-fei XIE,Yang YU,Yue-tian CHEN
- School of Traffic and Transportation,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
CLC Number:
- TP391.4
| [1] | Sun T Y, Tsai S J, Chan V, et al. HSI color model based lane-marking detection[C]∥IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference,Toronto, Canada, 2006: 1168-1172. |
| [2] | 赵颖, 王书茂, 陈兵旗. 基于改进Hough变换的公路车道线快速检测算法[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2006(3): 104-108. |
| Zhao Ying, Wang Shu-mao, Chen Bing-qi. Fast lane detection algorithm based on improved Hough transform[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2006(3):104-108. | |
| [3] | 蔡创新, 邹宇, 潘志庚, 等. 基于多特征融合和窗口搜索的新型车道线检测算法[J]. 江苏大学学报: 自然科学版, 2023, 44(4): 386-391. |
| Cai Chuang-xin, Zou Yu, Pan Zhi-geng, et al. Novel lane detection algorithm based on multi-feature fusion and windows searching[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 44(4): 386-391. | |
| [4] | 杨金鑫, 范英, 谢纯禄. 基于行距离及粒子滤波的车道线识别算法[J]. 江苏大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 41(2): 138-142, 198. |
| Yang Jin-xin, Fan Ying, Xie Chun-lu. Lane detection algorithm based on row distance and particle filter[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 41(2): 138-142, 198. | |
| [5] | Tabelini L, Berriel R, Paixao T M, et al. Polylanenet: lane estimation via deep polynomial regression[C]∥25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR),Milan, Italy, 2021: 6150-6156. |
| [6] | Liu R, Yuan Z, Liu T, et al. End-to-end lane shape prediction with transformers[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision,Waikoloa, USA, 2021: 3693-3701. |
| [7] | Feng Z, Guo S, Tan X, et al. Rethinking efficient lane detection via c ourve modeling[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conferencen Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,New Orleans,USA,2022: 17041-17049. |
| [8] | Qin Z, Wang H, Li X. Ultra fast structure-aware deep lane detection[C]∥Computer Vision-ECCV : 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 276-291. |
| [9] | 张云佐, 郑宇鑫, 武存宇, 等. 基于双特征提取网络的复杂环境车道线精准检测[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2024, 54(7): 1894-1902 . |
| Zhang Yun-zuo, Zheng Yu-xin, Wu Cun-yu, et al. Accurate detection of lane lines in complex environment based on dual feature extraction network [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024,54 (7): 1894-1902 . | |
| [10] | 时小虎, 吴佳琦, 吴春国, 等. 基于残差网络的弯道增强车道线检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(2): 584-592. |
| Shi Xiao-hu, Wu Jia-qi, Wu Chun-guo, et al. Detection method of enhanced lane lines in curves based on residual network [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023,53(2):584-592. | |
| [11] | Liu L, Chen X, Zhu S, et al. CondLaneNet: a top-to-down lane detection framework based on conditional convolution[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision,Montreal, Canada, 2021:3753-3762. |
| [12] | Pan X, Shi J, Luo P, et al. Spatial as deep: spatial CNN for traffic scene understanding[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence,New Orleans, USA,2018:7276-7283. |
| [13] | Su J, Chen C, Zhang K, et al. Structure guided lane detection[J/OL].[2024-04-05]. |
| [14] | Zheng T, Fang H, Zhang Y, et al. RESA: recurrent feature-shift aggregator for lane detection[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 35(4): 3547-3554. |
| [15] | Hou Y, Ma Z, Liu C, et al. Learning lightweight lane detection CNNs by self attention distillation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision,Seoul, Korea (South),2019: 1013-1021. |
| [16] | Xu H, Wang S, Cai X, et al. Curvelane-nas: unifying lane-sensitive architecture search and adaptive point blending[C]∥Computer Vision-ECCV : 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 689-704. |
| [17] | Pan H, Hong Y, Sun W, et al. Deep dual-resolution networks for realtime and accurate semantic segmentation of traffic scenes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 24(3): 3448-3460. |
| [18] | Bae W, Yoo J, Chul Ye J. Beyond deep residual learning for image restoration: persistent homology-guided manifold simplification[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, USA, 2017:1141-1149. |
| [19] | Cheng M, Su J, Li L, et al. A-DFPN: adversarial learning and deformation feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]∥IEEE 5th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC),Beijing, China, 2020: 11-18. |
| [20] | Liu S, Qi L, Qin H, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8759-8768. |
| [21] | Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]∥NIPS'17: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems,Long Beach, USA,2017: 6000-6010. |
| [22] | Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6230-6239. |
| [23] | TuSimple. TuSimple lane detection benchmark[DB/OL]. [2024-04-06]. |
| [24] | Ghafoorian M, Nugteren C, Baka N, et al. EL-GAN: embedding loss driven generative adversarial networks for lane detection[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops,Munich, Germany, 2018: 256-272. |
| [25] | Yoo S, Lee H S, Myeong H, et al. End-to-end lane marker detection via row-wise classification[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, USA, 2020:4335-4343. |
| [26] | Tabelini L, Berriel R, Paixao T M, et al. Keep your eyes on the lane: real-time attention-guided lane detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 294-302. |
| [27] | Ko Y, Lee Y, Azam S, et al. Key points estimation and point instance segmentation approach for lane detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 23(7): 8949-8958. |
| [28] | Chen Z, Liu Q, Lian C.PointLaneNet: efficient end-to-end CNNs for accurate real-time lane detection[C]∥IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Paris, France, 2019: 2563-2568. |
| [29] | Qin Z Q, Zhang P Y, Li X, et al. Ultra fast deep lane detection with hybrid anchor driven ordinal classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 46(5): 2555-2568. |
| [1] | Zhen HUO,Li-sheng JIN,Qiang HUA, HEYang. Edge feature⁃guided semantic segmentation method for intelligent vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(9): 3032-3041. |
| [2] | Qing-lin AI,Yuan-xiao LIU,Jia-hao YANG. Small target swmantic segmentation method based MFF-STDC network in complex outdoor environments [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2681-2692. |
| [3] | Yu-fei ZHANG,Li-min WANG,Jian-ping ZHAO,Zhi-yao JIA,Ming-yang LI. Robot inverse kinematics solution based on center selection battle royale optimization algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2703-2710. |
| [4] | Yan PIAO,Ji-yuan KANG. RAUGAN:infrared image colorization method based on cycle generative adversarial networks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2722-2731. |
| [5] | Qiong-xin LIU,Tian-tian WANG,Ya-nan WANG. Non-dominated sorted particle swarm genetic algorithm to solve vehicle location routing problems [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2464-2474. |
| [6] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Liang LI. Graph similarity measurement algorithm combining global and local fine-grained features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2365-2371. |
| [7] | Wen-hui LI,Chen YANG. Few-shot remote sensing image classification based on contrastive learning text perception [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2393-2401. |
| [8] | Shan-na ZHUANG,Jun-shuai WANG,Jing BAI,Jing-jin DU,Zheng-you WANG. Video-based person re-identification based on three-dimensional convolution and self-attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2409-2417. |
| [9] | Hai-peng CHEN,Shi-bo ZHANG,Ying-da LYU. Multi⁃scale context⁃aware and boundary⁃guided image manipulation detection method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2114-2121. |
| [10] | Jian WANG,Chen-wei JIA. Trajectory prediction model for intelligent connected vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1963-1972. |
| [11] | Feng-feng ZHOU,Zhe GUO,Yu-si FAN. Feature representation algorithm for imbalanced classification of multi⁃omics cancer data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2089-2096. |
| [12] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Yu-peng SUN. Graph node classification algorithm based on similarity random walk aggregation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2069-2075. |
| [13] | Ping-ping LIU,Wen-li SHANG,Xiao-yu XIE,Xiao-kang YANG. Unbalanced image classification algorithm based on fine⁃grained analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2122-2130. |
| [14] | You-wei WANG,Ao LIU,Li-zhou FENG. New method for text sentiment classification based on knowledge distillation and comment time [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1664-1674. |
| [15] | Hong-wei ZHAO,Ming-zhu ZHOU,Ping-ping LIU,Qiu-zhan ZHOU. Medical image segmentation based on confident learning and collaborative training [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1675-1681. |
|
||