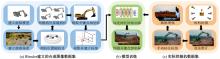
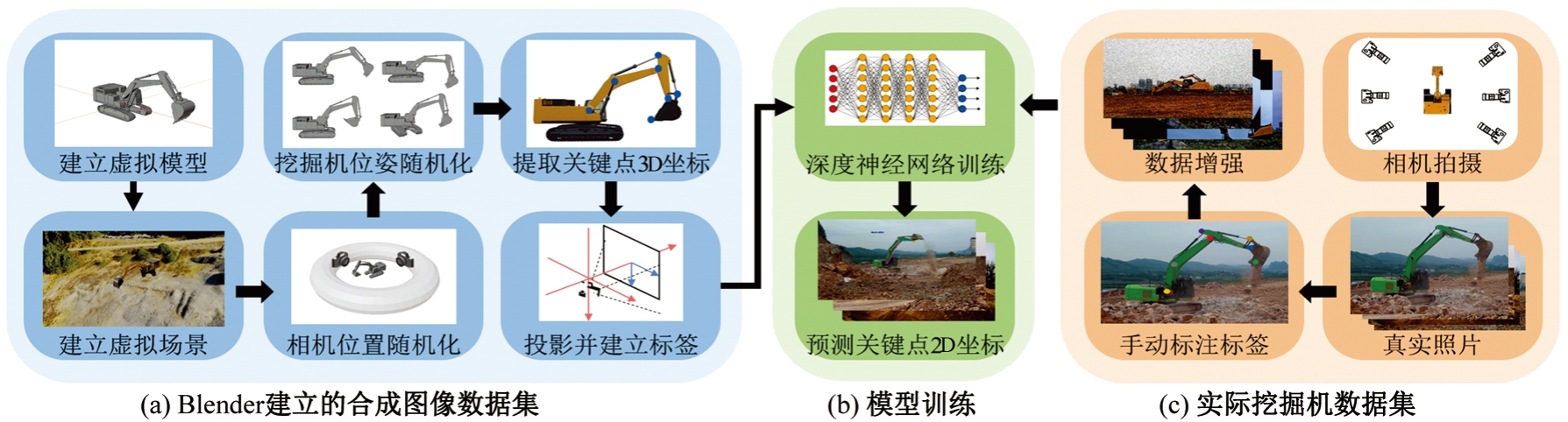
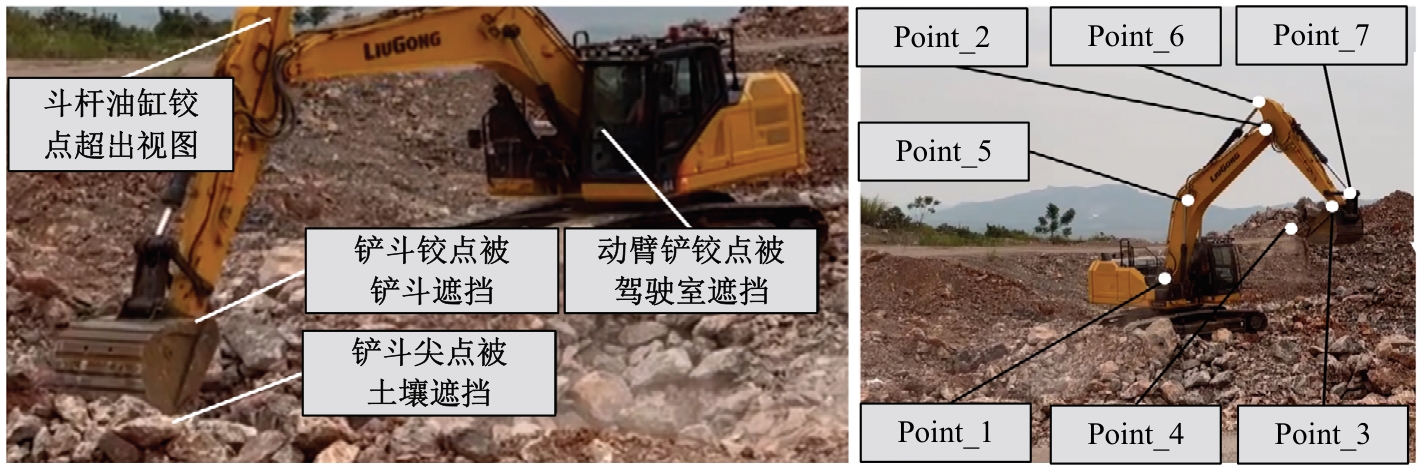
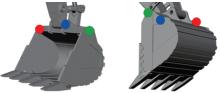
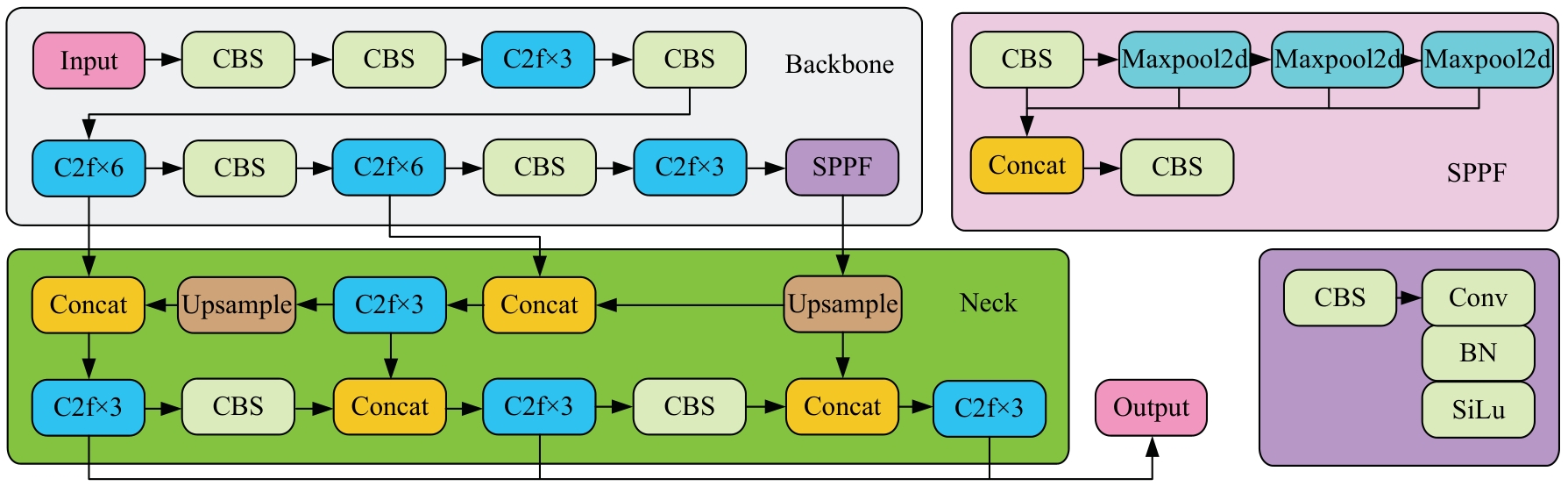
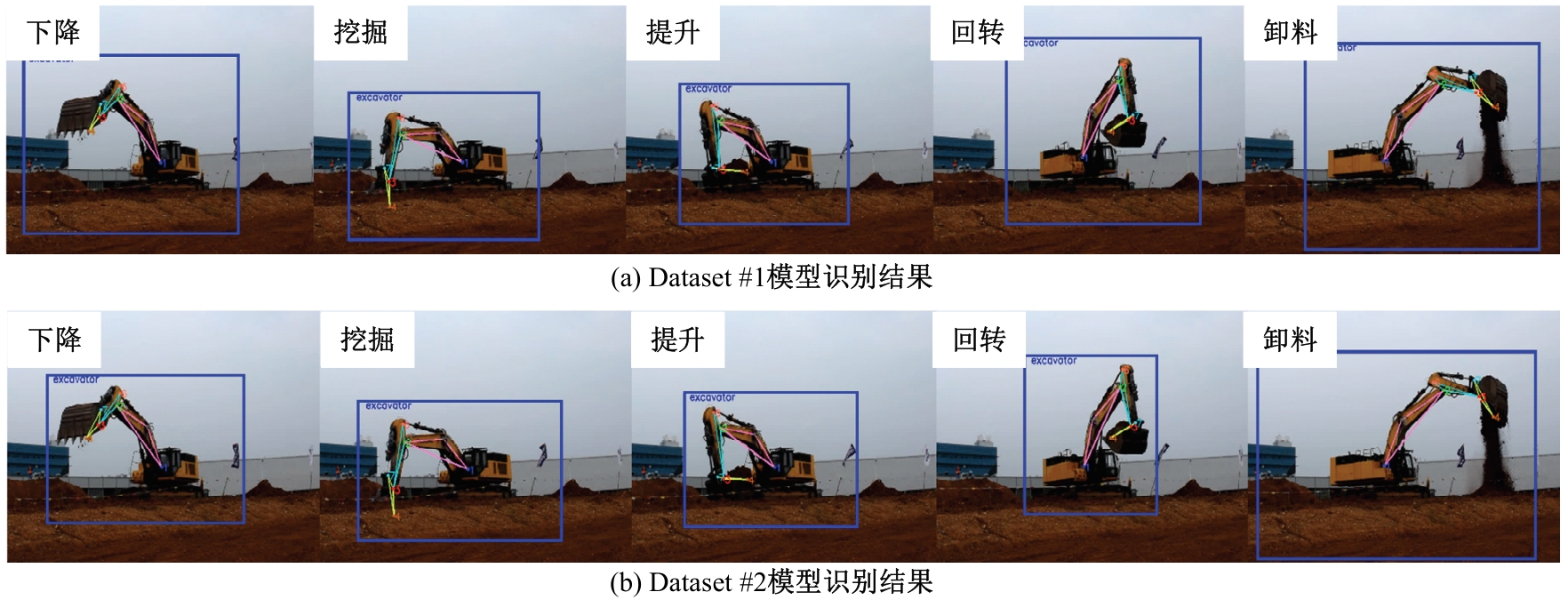
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2026, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 76-85.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240677
Previous Articles Next Articles
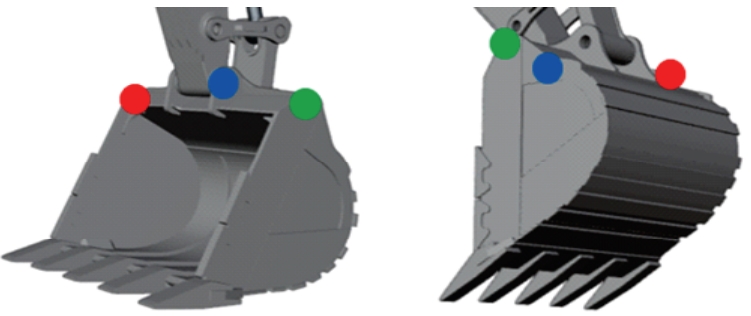
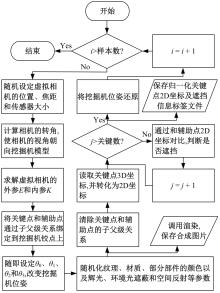
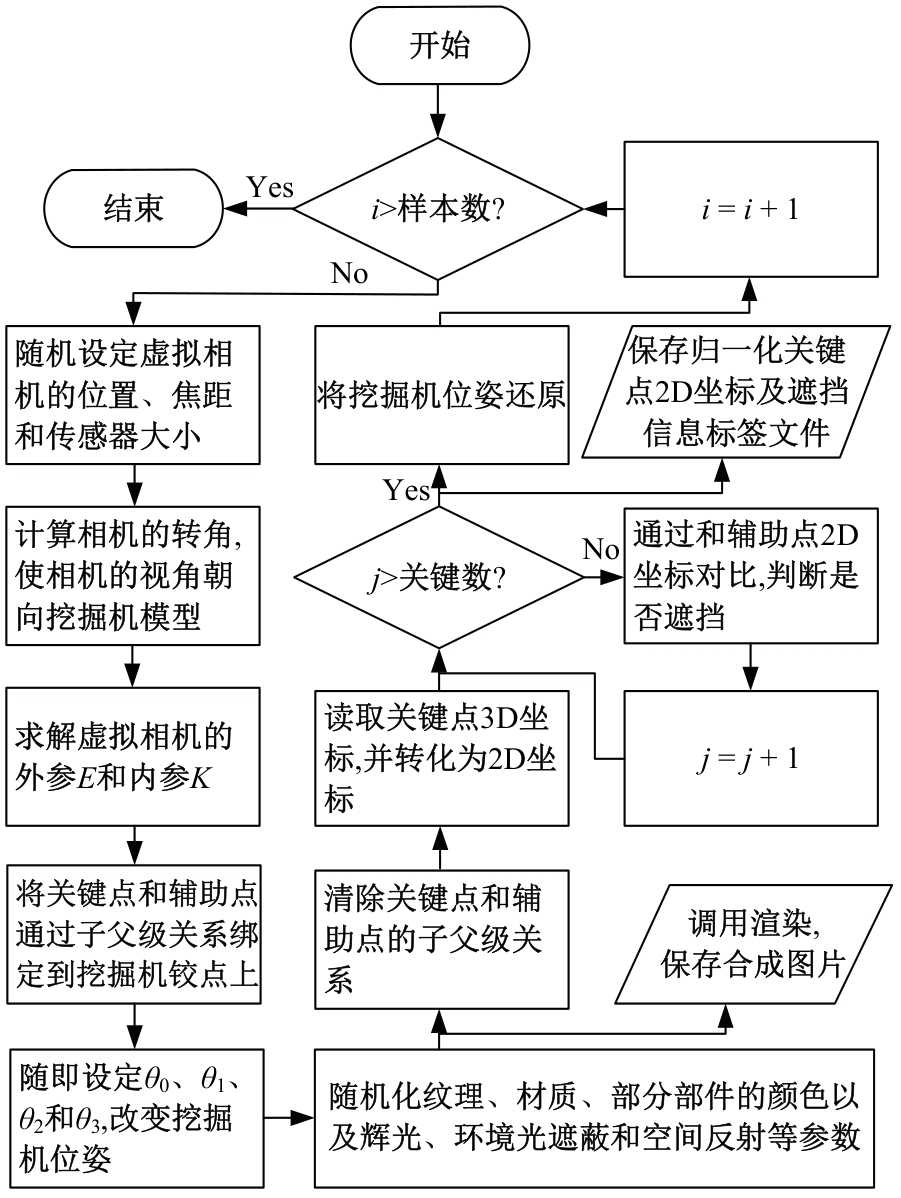
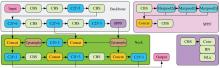
Visual recognition of excavator keypoints based on synthetic image datasets
Zong-wei YAO1( ),Chen CHEN1,Zhen-yun GAO2,Hong-peng JIN1,Hao RONG2,Xue-fei LI1,Hong-pu HUANG2(
),Chen CHEN1,Zhen-yun GAO2,Hong-peng JIN1,Hao RONG2,Xue-fei LI1,Hong-pu HUANG2( ),Qiu-shi BI1
),Qiu-shi BI1
- 1.School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.Liuzhou Liugong Excavator Co. ,Ltd. ,Liuzhou 545007,China
CLC Number:
- TP18
| [1] | 于向军, 槐元辉, 姚宗伟, 等. 工程车辆无人驾驶关键技术[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2021, 51(4): 1153-1168. |
| Yu Xiang-jun, Huai Yuan-hui, Yao Zong-wei, et al. Key technologies in autonomous vehicle for engineering[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1153-1168. | |
| [2] | 方成, 于盛鑫, 李永刚, 等. 基于深度学习的土木工程计算机视觉健康监测[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2024, 52(2): 213-222. |
| Fang Cheng, Yu Sheng-xin, Li Yong-gang, et al. Deep learning-based computer vision for health monitoring in civil engineering[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2024, 52(2): 213-222. | |
| [3] | Yao Z W, Zhao S C, Tan X D, et al. Real-time task-oriented continuous digging trajectory planning for excavator arms[J]. Automation in Construction, 2023, 152: No.104916. |
| [4] | Park J, Chen J D, Cho Y K. Self-corrective knowledge-based hybrid tracking system using bim and multimodal sensors[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2017, 32: 126-138. |
| [5] | Vahdatikhaki F, Hammad A, Siddiqui H. Optimization-based excavator pose estimation using real-time location systems[J]. Automation in Construction, 2015, 56: 76-92. |
| [6] | 王太海, 陈建宏, 金俊. 基于挖掘机GNSS精确定位的开采姿态监测系统[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2016, 24(4): 101-106. |
| Wang Tai-hai, Chen Jian-hong, Jin Jun. Mining attitude monitoring system based on GNSS precise positioning of excavator[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2016, 24(4): 101-106. | |
| [7] | Yang W J, Zhang X H, Ma H W, et al. Infrared leds-based pose estimation with underground camera model for boom-type roadheader in coal mining[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 33698-33712. |
| [8] | Assadzadeh A, Arashpour M, Brilakis I, et al. Vision-based excavator pose estimation using synthetically generated datasets with domain randomization[J]. Automation in Construction, 2022, 134: No.104089. |
| [9] | 魏振忠, 冯广堃, 周丹雅, 等. 位姿视觉测量方法及应用综述[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2023, 60(3): 135-167. |
| Wei Zhen-zhong, Feng Guang-kun, Zhou Dan-ya, et al. A review of position and orientation visual measurement methods and applications[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(3): 135-167. | |
| [10] | 马伟, 宫乐, 冯浩, 等. 基于视觉的挖掘机工作装置位姿测量[J]. 机械设计与研究, 2018,34(5): 173-176, 182. |
| Ma Wei, Gong Yue, Feng Hao, et al. Pose measurement of excavator device based on vision[J]. Machine Design and Research, 2018, 34(5): 173-176, 182. | |
| [11] | 王连明, 吴鑫. 基于姿态估计的物体3D运动参数测量方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2023, 53(7): 2099-2108. |
| Wang Lian-ming, Wu Xin. Method for 3D motion parameter measurement based on pose estimation[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2099-2108. | |
| [12] | 吴昊. 基于合成数据集的图像处理深度学习方法研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学信息科学与工程学院, 2021. |
| Wu Hao. Research on deep learning methods for image processing based on synthetic datasets[D]. Lanzhou: School of Information Science and Engineering, Lanzhou University, 2021. | |
| [13] | Kim J, Kim D, Lee S, et al. Hybrid DNN training using both synthetic and real construction images to overcome training data shortage[J]. Automation in Construction, 2023, 149: No.104771. |
| [14] | An X H, Zhou L, Liu Z G, et al. Dataset and benchmark for detecting moving objects in construction sites[J]. Automation in Construction, 2021, 122: No.103482. |
| [15] | Liang C J, Kamat V R, Menassa C M. Real-time construction site layout and equipment monitoring[C]∥Construction Research Congress, New Orleans,USA,2018: 64-74. |
| [16] | Zhang S B, Zhang L J. Construction site safety monitoring and excavator activity analysis system[J]. Construction Robotics, 2022, 6: 151-161. |
| [17] | 郭晓新, 李佳慧, 张宝亮. 基于高分辨率网络的视杯和视盘的联合分割[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2023, 53(8): 2350-2357. |
| Guo Xiao-xin, Li Jia-hui, Zhang Bao-liang. Joint segmentation of optic cup and disc based on high resolution network[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2350-2357. | |
| [18] | Tang J Y, Zhang X, Wong P K Y, et al. Method on pose estimation of excavators based on onboard depth camera[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2022, 1101:No. 072005. |
| [19] | Lin T Y, Maire M, Belongie S, et al. Microsoft coco: common objects in context[J]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, 2014, 8693: 740-755. |
| [20] | Ionescu C, Papava D, Olaru V, et al. Human3.6M: large scale datasets and predictive methods for 3d human sensing in natural environments[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2014, 36(7): 1325-1339. |
| [21] | Wen L Y, Kim D, Liu M Y, et al. 3D excavator pose estimation using projection-based pose optimization for contact-driven hazard monitoring [J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2023, 37: 1-15. |
| [22] | 郑义桀, 罗健欣, 陈卫卫, 等. 基于Unity3D三维多视角虚拟数据集构建[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2023, 33(5): 173-179. |
| Zheng Yi-jie, Luo Jian-xin, Chen Wei-wei, et al. 3D multi-view virtual dataset construction based on Unity3D[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2023, 33(5): 173-179. | |
| [23] | Luo H, Wang M Z, Wong P K Y, et al. Full body pose estimation of construction equipment using computer vision and deep learning techniques[J]. Automation in Construction, 2020, 110: No.103016. |
| [24] | Torres C, Roberts D, Golparvar F M. Synthesizing pose sequences from 3D assets for vision-based activity analysis[J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2021, 35: No.04020052. |
| [25] | Tian Z H, Yu Y, Xu F, et al. Dynamic hazardous proximity zone design for excavator based on 3D mechanical arm pose estimation via computer vision[J]. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 2023, 149: 1-17. |
| [26] | Lou H T, Duan X H, Guo J M, et al. DC-YOLOv8: small-size object detection algorithm based on camera sensor[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12: No.2323. |
| [27] | Mahmood B, Han S, Seo J. Implementation experiments on convolutional neural network training using synthetic images for 3D pose estimation of an excavator on real images[J]. Automation in Construction, 2022, 133: No.103996. |
| [1] | Lin-hong WANG,Yu-yang LIU,Zi-yu LIU,Ying-jia LU,Yu-heng ZHANG,Gui-shu HUANG. Defect recognition of lightweight bridges based on YOLOv5 [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(9): 2958-2968. |
| [2] | Zhi-feng LIU,Wei-ning LI,Bao-bao QI,Chuan-hai CHEN,Wei SHI,Zhao-jing ZHANG,Xiao-qing TAN,Chang-jun WU. Mechanism analysis and experimental of rolling⁃sliding motion in planetary roller screw [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(9): 2892-2901. |
| [3] | Yuan-ning LIU,Xing-zhe WANG,Zi-yu HUANG,Jia-chen ZHANG,Zhen LIU. Stomach cancer survival prediction model based on multimodal data fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2693-2702. |
| [4] | Jing LIAN,Ji-bao ZHANG,Ji-zhao LIU,Jia-jun ZHANG,Zi-long DONG. Text-based guided face image inpainting [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2732-2740. |
| [5] | Jing-shu YUAN,Wu LI,Xing-yu ZHAO,Man YUAN. Semantic matching model based on BERTGAT-Contrastive [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2383-2392. |
| [6] | Hui-zhi XU,Dong-sheng HAO,Xiao-ting XU,Shi-sen JIANG. Expressway small object detection algorithm based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2003-2014. |
| [7] | Ru-bo ZHANG,Shi-qi CHANG,Tian-yi ZHANG. Review on image information hiding methods based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1497-1515. |
| [8] | Jian LI,Huan LIU,Yan-qiu LI,Hai-rui WANG,Lu GUAN,Chang-yi LIAO. Image recognition research on optimizing ResNet-18 model based on THGS algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1629-1637. |
| [9] | Bin WEN,Yi-fu DING,Chao YANG,Yan-jun SHEN,Hui LI. Self-selected architecture network for traffic sign classification [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1705-1713. |
| [10] | Zhen-jiang LI,Li WAN,Shi-rui ZHOU,Chu-qing TAO,Wei WEI. Dynamic estimation of operational risk of tunnel traffic flow based on spatial-temporal Transformer network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1336-1345. |
| [11] | Xue-zhong FU,Hou-bing HE,Xu-dong LIU,Jing-zhen LI. Tooth width design of helical face gear with non-orthogonal offset modification integration [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1207-1214. |
| [12] | Meng-xue ZHAO,Xiang-jiu CHE,Huan XU,Quan-le LIU. A method for generating proposals of medical image based on prior knowledge optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 722-730. |
| [13] | Hu JIN,Yu-sheng SHEN,Yong FANG,Li YU,Jia-mei ZHOU. Identification of small cracks in highway tunnel lining based on deep learning SSD algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(11): 3653-3659. |
| [14] | Yi-xin CHEN,Zai-xu CHEN,Yong-sheng LIU,Shuai YANG,Hao-jie GUO,Jin-san JIA. Structural optimization design of excavator bucket based on improved depth surrogate model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(11): 3485-3497. |
| [15] | Lai-wei JIANG,Ce WANG,Hong-yu YANG. Review of multi-object tracking based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(11): 3429-3445. |
|
||