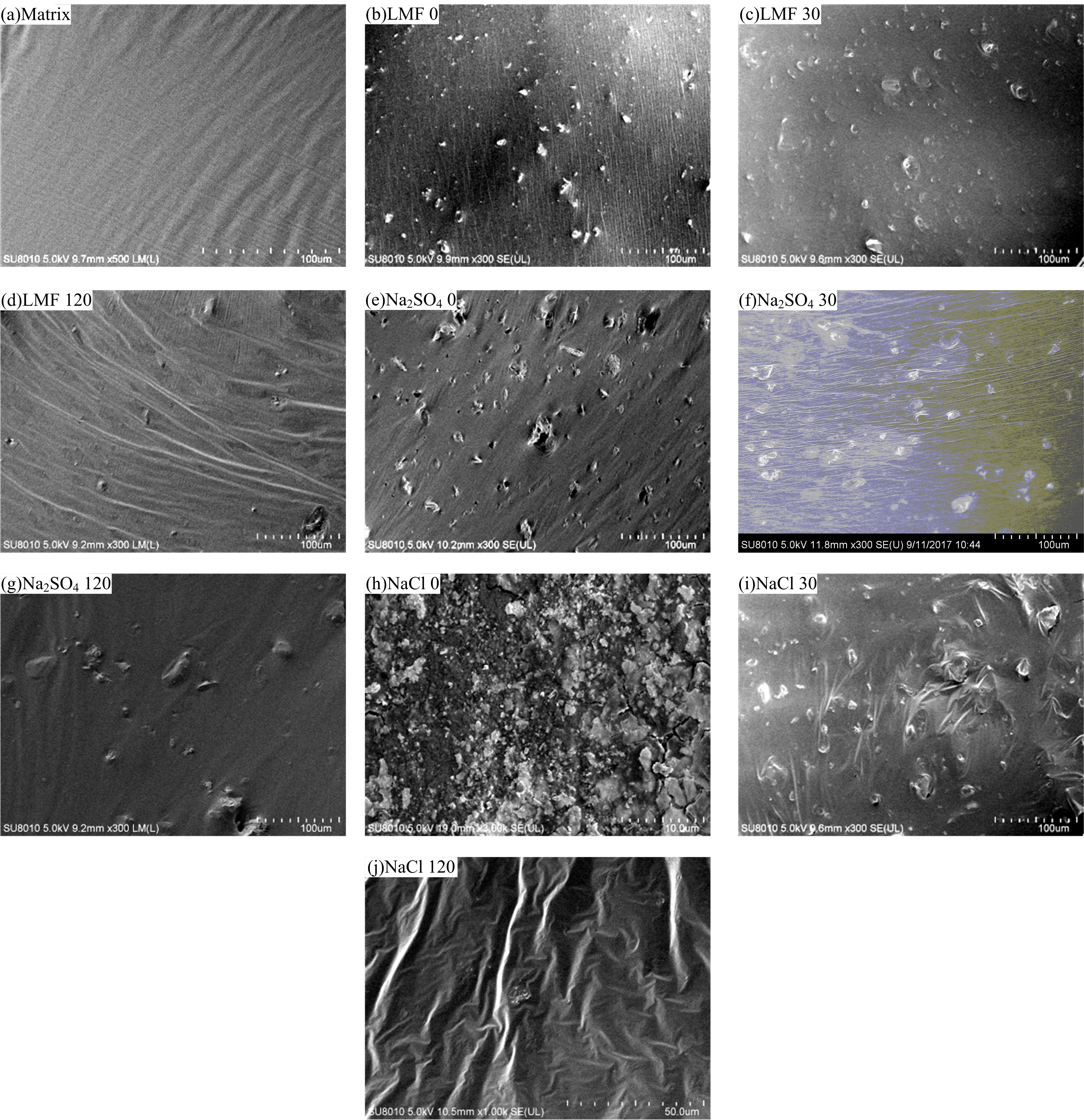
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 183-190.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180882
Investigation on low-temperature rheology and adhesion properties of salt-doped asphalt mortars
Rui XIONG1,2( ),Ning QIAO1,Ci CHU1,Fa YANG3,Bo-wen GUAN1,2,Yan-ping SHENG1,2,Dong-yu NIU1,2
),Ning QIAO1,Ci CHU1,Fa YANG3,Bo-wen GUAN1,2,Yan-ping SHENG1,2,Dong-yu NIU1,2
- 1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Chang′an University, Xi′an 710061, China
2. Engineering Research Center of Transportation Materials of Ministry of Education, Xi′an 710061, China
3. Yunnan Communications Investment and Construction Group Co. , Ltd. , Kunming 650228, China
CLC Number:
- U416.217
| 1 | Xiong R , Wang L , Guan B W , et al . Durability prediction of asphalt mixture exposed to sulfate and dry-wet circle erosion environment[J]. International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology, 2015, 8(1): 53-57. |
| 2 | 韩吉伟,崔亚楠,李嘉迪,等 . 盐冻循环条件下改性沥青的细观结构及低温流变性能[J]. 复合材料学报,2016,33(8):1718-1724. |
| Han Ji-wei , Cui Ya-nan , Li Jia-di , et al . Microstructure and rheological properties at lowtemperature of modified asphalt under salt freezing cycle[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2016, 33(8): 1718-1724. | |
| 3 | Feng D C , Yi J Y , Wang D S , et al . Impact of salt and freeze-thaw cycles on performance of asphalt mixtures in coastal frozen region of China[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2010, 62(1): 34-41. |
| 4 | Han J W , Cui Y N , Li Z , et al . Research on the microstructure and performance of asphalt after the salt Freezing cycle[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 575: 238-244. |
| 5 | 马慧莉 . 无机填料对沥青胶浆力学性能影响的细观力学分析[D]. 长春:吉林大学交通学院,2013. |
| Ma Hui-li . Research of inorganic filler on the properties of asphalt mastic by meso-mechanical method[D]. Changchun:College of Transportation, Jilin University, 2013. | |
| 6 | Guo Meng , Tan Yi-qiu , Hou Yue , et al . Improvement of evaluation indicator of interfacial interaction between asphalt binder and mineral fillers[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 151: 236-245. |
| 7 | 熊锐,关博文,盛燕萍 . 硫酸盐-干湿循环侵蚀环境下水镁石纤维沥青混合料抗疲劳性能[J]. 武汉理工大学学报,2014,36(10):45-51. |
| Xiong Rui , Guan Bo-wen , Sheng Yan-ping . Anti-fatigue property of brucite fiber reinforced asphalt mixture under sulfate and dry-wet circle corrosion environment[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2014, 36(10): 45-51. | |
| 8 | 黄新颜,沙爱民,蒋玮,等 . 盐分侵蚀对沥青和沥青混合料性能影响及作用机理[J]. 长安大学学报:自然科学版,2017,37(3):33-38,46. |
| Huang Xin-yan , Sha Ai-min , Jiang Wei , et al . Effect and mechanism of salt erosion on performance of bitumen and asphalt mixtures[J]. Journal of Chang'an University(Natural Science Edition), 2017, 37(3): 33-38, 46. | |
| 9 | Liu Z Z , Sha A M , Xing M L , et al . Low temperature property and salt releasing characteristics of antifreeze asphalt concrete under static and dynamic conditions[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2015, 114: 9-14. |
| 10 | 陈拴发,刘状壮,邢明亮,等 . 融雪抑冰材料疏水性能影响因素研究[J]. 建筑材料学报,2013,16(6):1053-1057,1071. |
| Chen Shuan-fa , Liu Zhuang-zhuang , Xing Ming-liang , et al . Research on the factors influencing hydrophobic properties of anti-freezing material[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2013, 16(6): 1053-1057, 1071. | |
| 11 | 李海莲,李波,王起才,等 . 基于表面能理论的老化温拌SBS改性沥青结合料的粘附性[J].材料导报,2017,31(16):129-133,149. |
| Li Hai-lian , Li Bo , Wang Qi-cai , et al . Adhesion of aged SBS modified asphalt binder containing warm mix additive based on surface free energy[J]. Materials Review, 2017, 31(16): 129-133, 149. | |
| 12 | 张恺,罗蓉,张德润 . 基于表面自由能理论的彩色树脂类沥青材料润湿性分析[J]. 中国公路学报,2016,29(5):34-40. |
| Zhang Kai , Luo Rong , Zhang De-run . Wettability analysis on colored resin asphalt binder based on surface free energy theory[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2016, 29(5): 34-40. | |
| 13 | Liu S T , Cao W D , Shang S J , et al . Analysis and application of relationships between low-temperature rheological performance parameters of asphalt binders[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2010, 24(4): 471-478. |
| [1] | Ying WANG,Ping LI,Teng-fei NIAN,Ji-bin JIANG. Short-term water damage characteristics of asphalt mixture based on dynamic water scour effect [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 174-182. |
| [2] | Ping WAN,Chao-zhong WU,Xiao-feng MA. Discriminating threshold of driving anger intensity based on driving behavior features by ROC curve analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 121-131. |
| [3] | Chun-feng ZHU,Yong-chun CHENG,Chun-yu LIANG,Bo XIAO. Road performance experiment of diatomite⁃basalt fiber composite modified asphalt mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 165-173. |
| [4] | Sheng-tong DI,Chao JIA,Wei-guo QIAO,Kang LI,Kai TONG. Loading rate effect of meso⁃damage characteristics of crumb rubber concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1900-1910. |
| [5] | Yun-long ZHANG,Liu-guang ZHOU,Jing WANG,Chun-li WU,Xiang LYU. Effects of freeze-thaw cycles on mechanical properties of silty sand and subgrade slope stability [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1531-1538. |
| [6] | Yong PENG,Hua GAO,Lei WAN,Gui-ying LIU. Numerical simulation of influence factors of splitting strength of asphalt mixtures [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1521-1530. |
| [7] | Xiao⁃zhen LI,Jun⁃zhe LIU,Yan⁃hua DAI,Zhi⁃min HE,Ming⁃fang BA,Yu⁃shun LI. Effect of carbonation on nitrite ion distribution in cement paste [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1162-1168. |
| [8] | Tian⁃lai YU,Hai⁃sheng LI,Wei HUANG,Si⁃jia WANG. Shear strengthening of reinforced concrete beam with prestressed steel wire ropes [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1134-1143. |
| [9] | Xiao⁃ming HUANG,Qing⁃qing CAO,Xiu⁃yu LIU,Jia⁃ying CHEN,Xing⁃lin ZHOU. Simulation of vehicle braking performance on rainy daysbased on pavement surface fractal friction theory [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 757-765. |
| [10] | Jing WANG,Xiang LYU,Xiao⁃long QU,Chun⁃ling ZHONG,Yun⁃long ZHANG. Analysis of relationship between subgrade soil shear strength and chemical and minerals component [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 766-772. |
| [11] | LI Yi,LIU Li-ping,SUN Li-jun. Prediction model on rutting equivalent temperature for asphalt pavement at different depth [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1703-1711. |
| [12] | NIAN Teng-fei, LI Ping, LIN Mei. Micro-morphology and gray entropy analysis of asphalt characteristics functional groups and rheological parameters under freeze-thaw cycles [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1045-1054. |
| [13] | ZANG Guo-shuai, SUN Li-jun. Method based on inertial point for setting depth to rigid layer [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1037-1044. |
| [14] | GONG Ya-feng, SHEN Yang-fan, TAN Guo-jin, HAN Chun-peng, HE Yu-long. Unconfined compressive strength of fiber soil with different porosity [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 712-719. |
| [15] | CHENG Yong-chun, BI Hai-peng, MA Gui-rong, GONG Ya-feng, TIAN Zhen-hong, LYU Ze-hua, XU Zhi-shu. Pavement performance of nano materials-basalt fiber compound modified asphalt binder [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 460-465. |
|
||