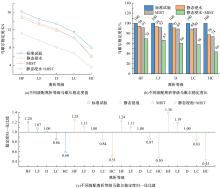
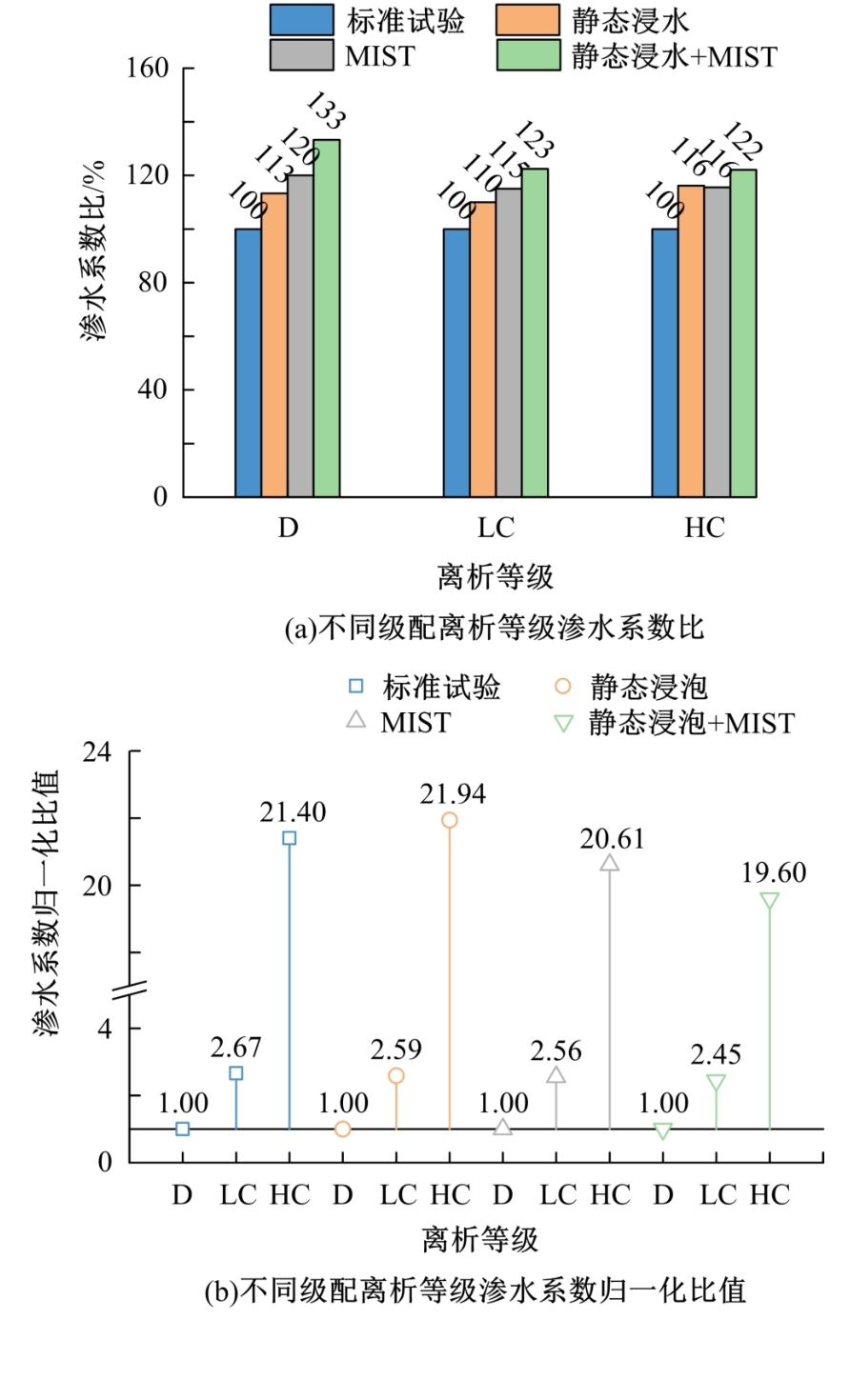
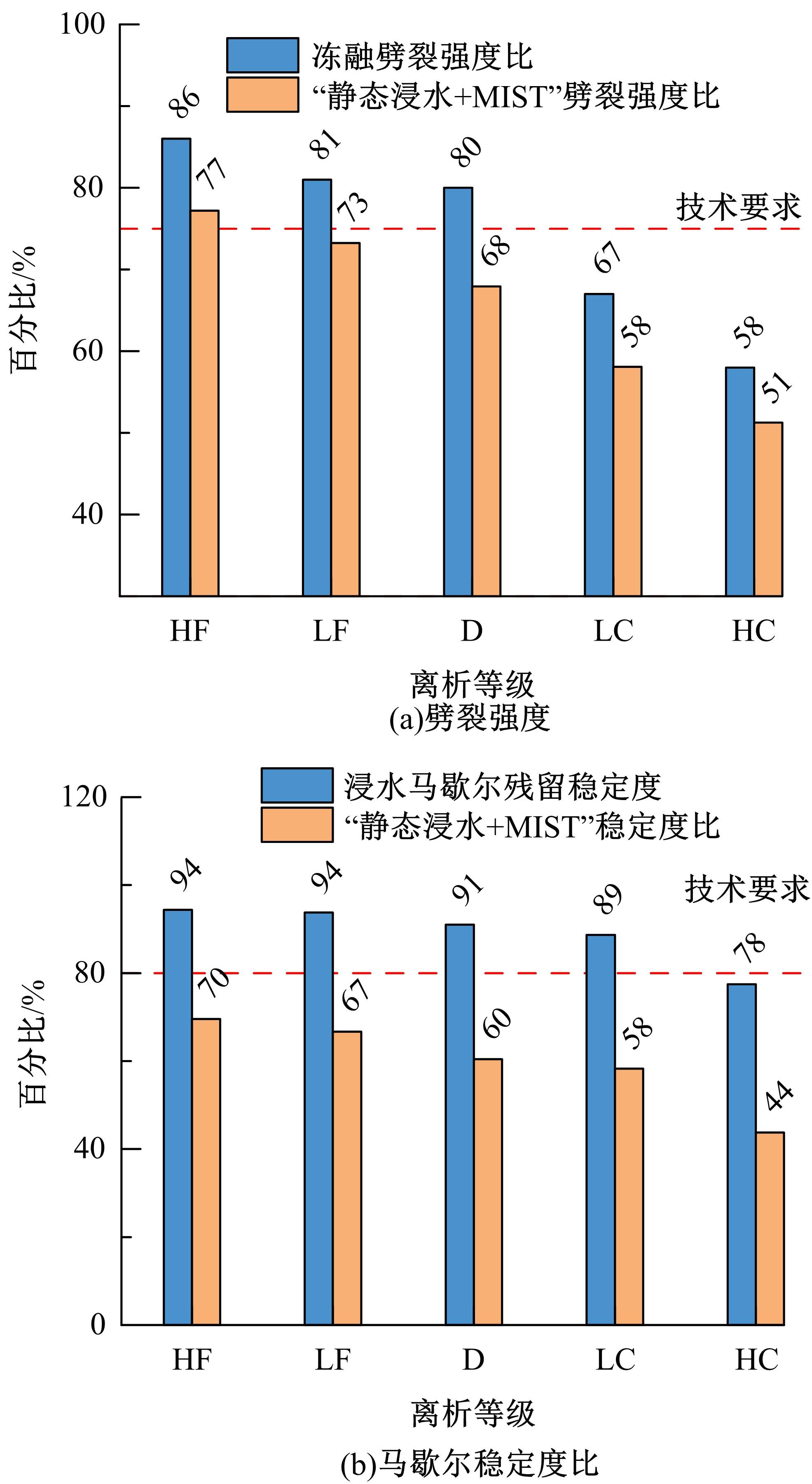
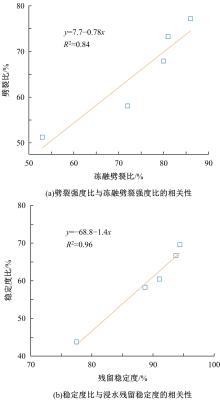
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 210-219.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210516
Evaluation of influence of gradation segregation on pavement moisture damage under action of dynamic and static water environment
Xu CHEN1,2( ),Chao-fei CAO1,2,Jing SHANG1,2,Ming-xing HUANG1,3,Chang-fa AI1,2,Dong-ya Ren1,2(
),Chao-fei CAO1,2,Jing SHANG1,2,Ming-xing HUANG1,3,Chang-fa AI1,2,Dong-ya Ren1,2( )
)
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Southwest Jiaotong University,Chengdu 610031,China
2.Highway Engineering Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province,Chengdu 610031,China
3.Sichuan Suiguangsuixi Expressway Co. ,Ltd. ,Suining 629000,China
CLC Number:
- U414
| 1 | 沙庆林. 高速公路沥青路面早期破坏现象及预防[M]. 北京:人民交通出版社 2001. |
| 2 | 沈金安. 沥青及沥青混合料路用性能[M]. 北京:人民交通出版社 2011. |
| 3 | Htet Y Z M. An assessment of moisture induced damage in asphalt pavements[D]. Worcester: Worcester Polytechnic Institute, 2015. |
| 4 | 沈金安,李福普,陈景. 高速公路沥青路面早期损坏分析与防治对策[M]. 北京:人民交通出版社 2004. |
| 5 | 姜旺恒. 沥青路面水损坏机理及动水压力试验应用研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学交通学院, 2008. |
| Jiang Wang-heng. Research on water damage mechanism of asphalt pavement and application of hydrodynamic pressure test[D]. Guangzhou: College of Transportation, South China University of Technology, 2008. | |
| 6 | Byzyka J, Rahman M, Chamberlain D A. Thermal segregation of asphalt material in road repair[J]. Journal of Traffic & Transportation Engineering, 2017,4(4):360-371. |
| 7 | 王文涛. 多因素耦合动态孔隙水压力对沥青路面破坏的影响研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学材料科学与工程学院, 2020. |
| Wang Wen-tao. Study on the influence of multi-factor coupling dynamic pore water pressure on the failure of asphalt pavement[D]. Beijing: College of Materials Sciences and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2020. | |
| 8 | Wang W, Wang L, Xiong H, et al. A review and perspective for research on moisture damage in asphalt pavement induced by dynamic pore water pressure[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 204: 631-642. |
| 9 | Mallick R B, Gould J S, Bhattacharjee S, et al. Development of a rational procedure for evaluation of moisture susceptibility of asphalt paving mixes[J]. Asphalt Paving Technology 2003,72:424-462. |
| 10 | 谭忆秋,李晓琳,胡斌. 动水作用对沥青混合料低温抗裂性的影响[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2010, 42(1): 119-122. |
| Tan Yi-qiu, Li Xiao-lin, Hu Bin. Effect of hydrodynamic action on crack resistance of asphalt mixture at low temperature[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010 42(1): 119-122. | |
| 11 | 潘宝峰. 动水压力作用下路面材料损伤的评价方法研究[D].大连:大连理工大学交通运输学院,2010. |
| Pan Bao-feng. Study on evaluation method of pavement material damage under hydrodynamic pressure[D]. Dalian: College of Traffic and Transportation, Dalian University of Technology, 2010. | |
| 12 | 2013―. Standard practice for moisture conditioning compacted asphalt mixture specimens by using hydrostatic pore pressure [S]. |
| 13 | Lacroix A, Regimand A, James L. Proposed approach for evaluation of cohesive and adhesive properties of asphalt mixtures for determination of moisture sensitivity[J]. Transportation Research Record Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2016, 2575: 61-69. |
| 14 | Varveri A, Avgerinopoulos S, Scarpas A. experimental evaluation of long- and short-term moisture damage characteristics of asphalt mixtures[J]. Road Materials & Pavement Design, 2016, 17(1): 168-186. |
| 15 | 李立寒,麻旭荣. 级配离析沥青混合料性能的试验研究[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2007, 35(12): 1622-1626. |
| Li Li-han, Ma Xu-rong. Experimental study on the performance of graded segregated asphalt mixture[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science Edition), 2007,35(12): 1622-1626. | |
| 16 | Chen X, Ai C, Du J, et al. Effect of gradation segregation on low-temperature crack resistance of asphalt pavement using 3D DEM[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 274(3):No.122060. |
| 17 | Li J, Liu G, Yang T, et al. Research on relationships among different distress types of asphalt pavements with semi-rigid bases in china using association rule mining: a statistical point of view[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2019, 2019: 1-15. |
| 18 | Mannan U A, Ahmad M, Tarefder R A. Influence of moisture conditioning on healing of asphalt binders[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2017, 146(8): 360-369. |
| 19 | Stroup-Gardiner M, Brown E R. Segregation in hot-mix asphalt pavements[J]. Caring national association for home care magazine, 2000. |
| 20 | .公路沥青路面施工技术规范 [S]. |
| 21 | 孙立军. 沥青路面结构行为理论[M]. 北京:人民交通出版社 2005. |
| 22 | 沈金安.关于沥青混合料的均匀性和离析问题[J].公路交通科技,2001(6):20-24. |
| Shen Jin-an. On uniformity and segregation of asphalt mixture [J]. Highway traffic science and technology, 2001(6):20-24. | |
| 23 | Florida D. Florida method of test for measurement of water permeability of compacted asphalt paving mixtures[J]. FM5-565, Dept of Transportation, Tallahassee, 2004. |
| 24 | .公路工程沥青及沥青混合料试验规程 [S]. |
| 25 | .公路沥青路面设计规范 [S]. |
| [1] | Liu YANG,Chuang-ye WANG,Meng-yan WANG,Yang CHENG. Traffic flow characteristics of six⁃lane freeways with a dedicated lane for automatic cars [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2043-2052. |
| [2] | Zheng-feng ZHOU,Xiao-tao YU,Ya-le TAO,Mao ZHENG,Chuan-qi YAN. High-temperature performance evaluation of resin and elastomer high viscosity asphalt based on grey correlation analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2078-2088. |
| [3] | Tao MA,Yuan MA,Xiao-ming HUANG. Optimal combination of key parameters of intelligent compaction based on multiple nonlinear regression [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2067-2077. |
| [4] | Hai-bin WEI,Shuan-ye HAN,Hai-peng BI,Qiong-hui LIU,Zi-peng MA. Intelligent sensing road active ice and snow removal system and experimental technology [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1411-1417. |
| [5] | Sui-ning ZHENG,Rui HE,Tian-yu LU,Zi-yi XU,Hua-xin CHEN. Preparation and evaluation of RET/rubber composite modified asphalt and asphalt mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1381-1389. |
| [6] | Bo-wen GUAN,Wen-jin DI,Fa-ping WANG,Jia-yu WU,Shuo-wen ZHANG,Zhi-xun JIA. Damage of concrete subjected to sulfate corrosion under dry⁃wet cycles and alternating loads [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1112-1121. |
| [7] | Fan YANG,Chen-chen LI,Sheng LI,Hai-lun LIU. Numerical simulation of continuously reinforced concrete pavement with double⁃layer reinforcement under effect of temperature shrinkage [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1122-1132. |
| [8] | Hai-bin WEI,Zi-peng MA,Hai-peng BI,Han-tao LIU,Shuan-ye HAN. Conductive rubber composite pavement paving technology based on mechanical response analysis method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 531-537. |
| [9] | Zhuang-zhuang LIU,You-wei ZHANG,Peng-yu JI,Abshir Ismail Yusuf,Lin LI,Ya-zhen HAO. Study on heat transfer characteristics of electric heating snow melting asphalt pavement [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 523-530. |
| [10] | Shuang SHI,Lan-qin LIN,Tao MA,Lin-hao GU,Yan-ning ZHANG. Molecular dynamics‒based stability of biomass prime coat oil [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(1): 197-209. |
| [11] | Yong PENG,Xiu-fang ZHANG,Ze-yu GUO,Xue-yuan LU,Yan-wei LI. Influence of aggregate contact characteristics on shear fatigue life of asphalt mixtures using discrete element method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(1): 178-187. |
| [12] | Ya-zhen SUN,Zhi ZHENG,Wei-ming HUANG,Jin-chang WANG. Structural analysis of cement pavement with cracks based on state⁃space method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(1): 188-196. |
| [13] | Cheng-lin SHI,Yong WANG,Chun-li WU,Wen-zhu SONG. Modification of calculation method for active earth pressure on embankment retaining wall [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1394-1403. |
| [14] | Qing-lin GUO,Qiang LIU,Chun-li WU,Li-li LI,Yi-ming LI,Fu-chun LIU. Local temperature field and healing level of crack in conductive asphalt and mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1386-1393. |
| [15] | Yu-quan YAO,Jian-gang YANG,Jie GAO,Liang SONG. Optimal design on recycled hot⁃mix asphalt mixture based on performance⁃cost model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 585-595. |
|
||