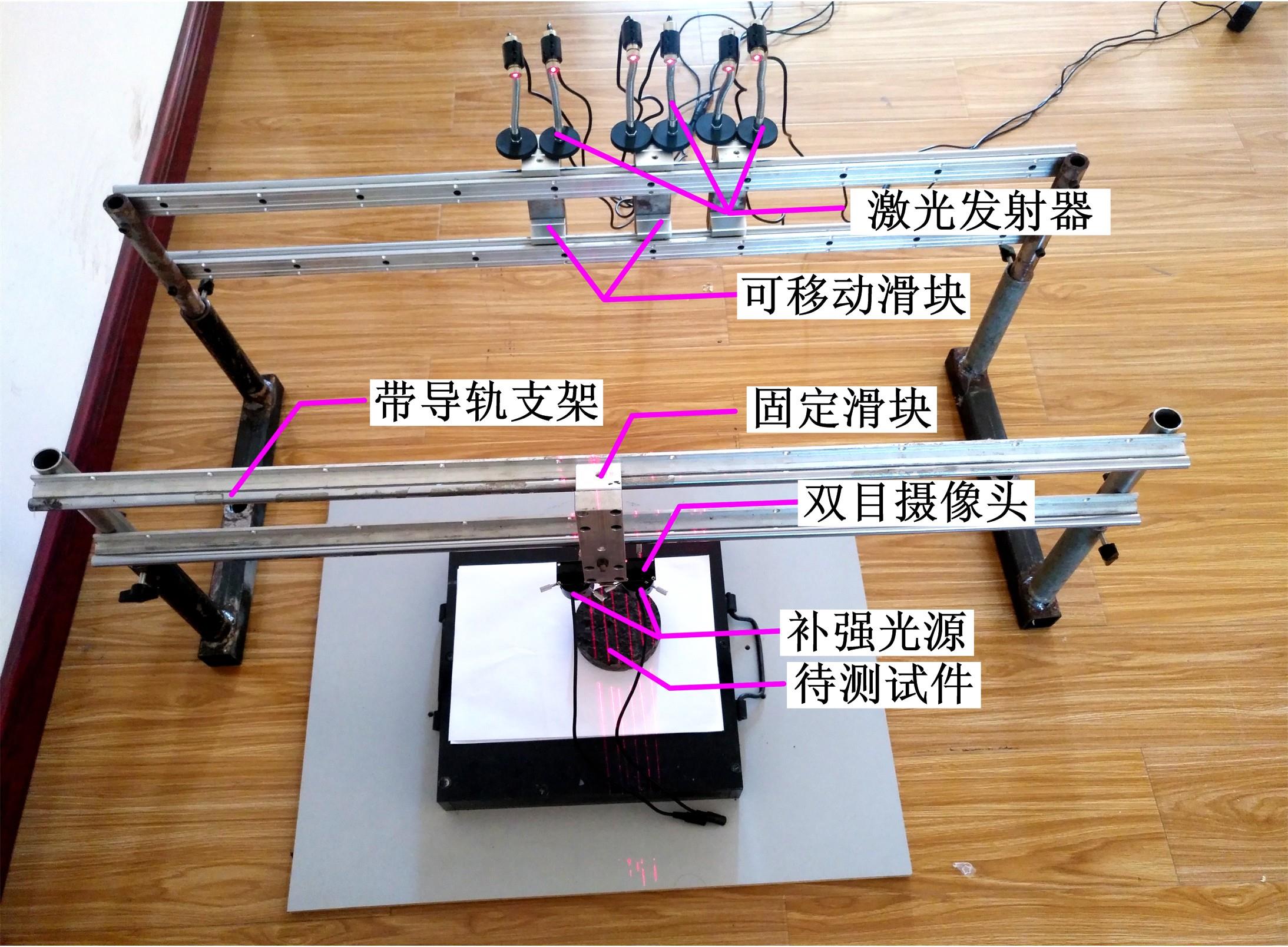
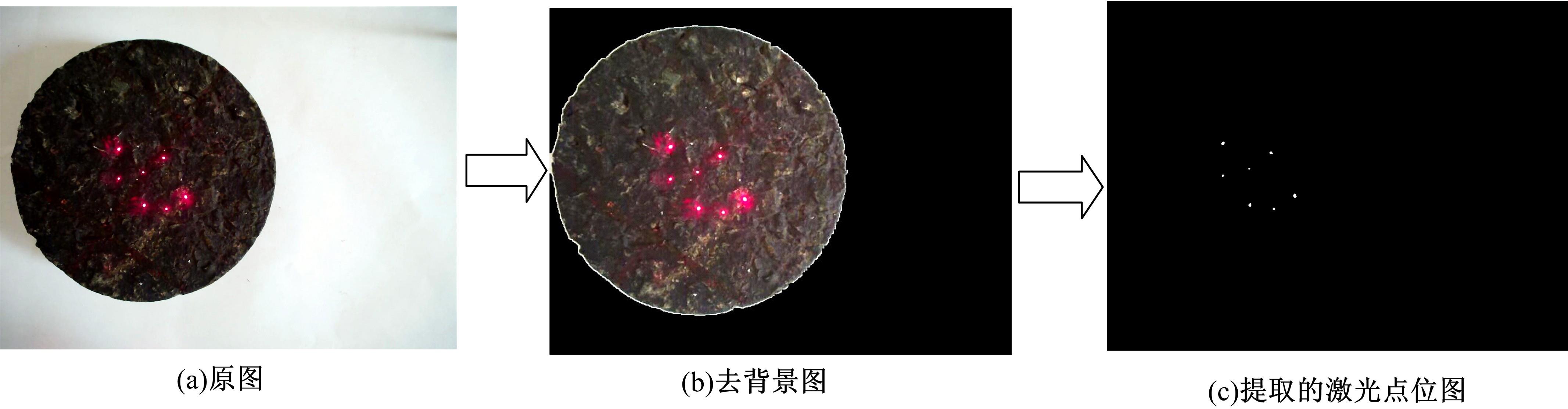
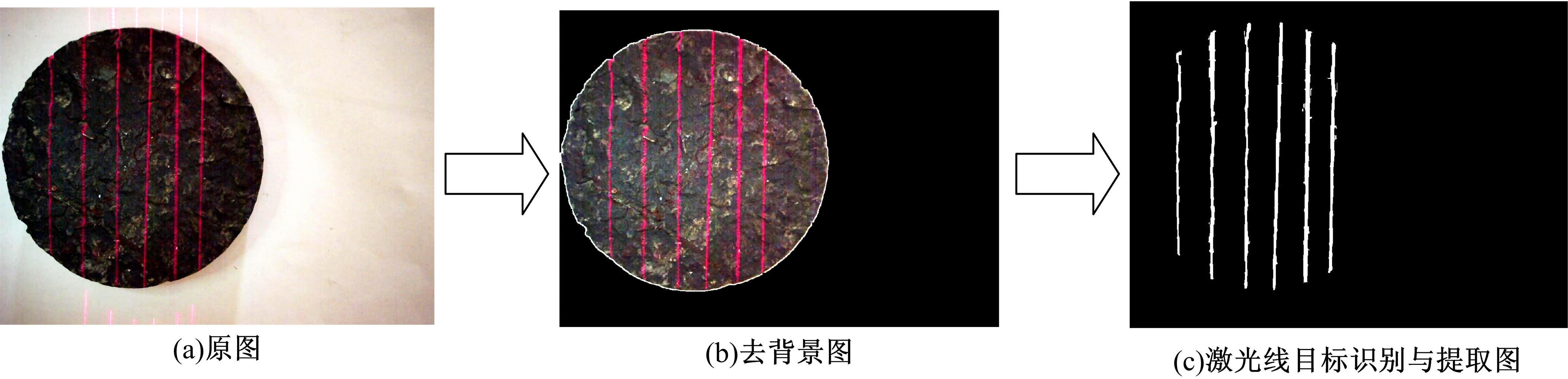
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 1342-1348.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200300
Constraint improvement of binocular reconstruction algorithm used to measure pavement three-dimensional texture
Yuan-yuan WANG1( ),Lu SUN2,Wei-dong LIU3,Jin-shun XUE1
),Lu SUN2,Wei-dong LIU3,Jin-shun XUE1
- 1.Hubei Key Laboratory of Power System Design and Test for Electrical Vehicle,Hubei University of Arts and Science,Xiangyang 441053,China
2.Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering,College Park,University of Maryland,MD 20742,USA
3.Guangxi Key Lab of Road Structure and Materials,Guangxi Transportation Science and Technology Group Co. Ltd. ,Nanning 530007,China
CLC Number:
- U416
| 1 | 中华人民共和国国家统计局.中国统计年鉴-2019 (第24章) [M].北京:中国统计出版社,2019. |
| 2 | 周兴林,肖神清,肖旺新,等. 粗集料表面纹理粗糙度的多重分形评价[J].华中科技大学学报:自然科学版,2017,45(2):29-33. |
| Zhou Xing-lin, Xiao Shen-qing, Xiao Wang-xin, et al. Multi fractal evaluation on roughness of coarse aggregate surface texture [J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2017,45(2):29-33. | |
| 3 | Wang Y, Lai X, Zhou F, et al. Evaluation of pavement skid resistance using surface three-dimensional texture data [J]. Coatings, 2020, 10(2):162. |
| 4 | Yang G, Li Q J, Zhan Y, et al. Convolutional neural network-based friction model using pavement texture data[J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2018, 32(6):04018052. |
| 5 | 曹平. 表面形貌与污染物对沥青路面抗滑性能影响的研究[D]. 武汉:武汉理工大学能源与动力工程学院, 2009. |
| Cao Ping. Study on effects of texture and contaminants to skid resistance of asphalt pavements[D]. Wuhan:School of Energy and Power Engineering, Wuhan University of Technology, 2009. | |
| 6 | Wang Y, Yang Z, Liu Y, et al. The characterisation of three-dimensional texture morphology of pavement for describing pavement sliding resistance[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2019, 20(5):1076-1095. |
| 7 | Liu Q, Shalaby A. Relating concrete pavement noise and friction to three-dimensional texture parameters[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2015, 18(5): 450-458. |
| 8 | Kanafi M M, Kuosmanen A, Pellinen T K, et al. Macro-and micro-texture evolution of road pavements and correlation with friction[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2015, 16(2):168-179. |
| 9 | El Gendy A, Shalaby A, Saleh M, et al. Stereo-vision applications to reconstruct the 3D texture of pavement surface[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2011, 12(3):263-273. |
| 10 | Sun L, Wang Y Y. Three-dimensional reconstruction of macrotexture and microtexture morphology of pavement surface using six light sources—based photometric stereo with low-rank approximation[J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2017,31(2): 04016054. |
| 11 | 马双涛, 韩九强, 张新曼. 复杂光照条件下非凸表面形状恢复[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2009, 30(3):559-563. |
| Ma Shuang-tao, Han Jiu-qiang, Zhang Xin-man. Shape recovery of non-convex surface under complex illum ination[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2009, 30(3):559-563. | |
| 12 | 王昊,刘雍翡.基于双目视觉计算的车辆跟驰状态实时感知系统[J].中国公路学报,2019,32(12):88-97, 105. |
| Wang Hao, Liu Yong-fei. Car-following state real-time estimation system based on binocular vision[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019,32(12):88-97, 105. | |
| 13 | 张辉, 张丽艳. 面向三维点云测量的双目立体匹配算法[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2009, 41(5):588-594. |
| Zhang Hui, Zhang Li-Yan. Binocular stereo matching algorithm for 3D point cloud acquisition[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics&Astronautics, 2009,41(5):588-594. | |
| 14 | Cochran S D, Medioni G. 3-D surface description from binocular stereo[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 1992, 14(10):981-994. |
| 15 | Chu L, Tang B, Fwa T F. Evaluation of functional characteristics of laboratory mix design of porous pavement materials[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018,191:281-289. |
| 16 | Liu Y, Wang Y, Cai X, et al. The detection effect of pavement 3D texture morphology using improved binocular reconstruction algorithm with laser line constraint[J]. Measurement, 2020,157: No. 107638. |
| 17 | 刘江江. 围棋矩阵模拟信号远程数字传输控制系统的研究[D].天津: 天津大学自动化学院,2007. |
| Liu Jiang-jiang. Research on remote digital transmission control system for go-matrix analog signal[D]. Tianjing: School of Automation,Tianjing University, 2007. |
| [1] | Yong PENG,Han-duo YANG,Xue-yuan LU,Yan-wei LI. Effect of void characteristics on virtual shear fatigue life of asphalt mixtures using discrete element method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 956-964. |
| [2] | Wei-gang ZHU,Chao ZHU,Ya-qiu ZHANG,Hai-bin WEI. Construction and quality evaluation of digital elevation model based on convolution grid surface fitting algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1073-1080. |
| [3] | Yong-chun CHENG,He LI,Li-ding LI,Hai-tao WANG,Yun-shuo BAI,Chao CHAI. Analysis of mechanical properties of asphalt mixture affected by aggregate based on grey relational degree [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 925-935. |
| [4] | Ya-feng GONG,Yun-ze PANG,Bo WANG,Guo-jin TAN,Hai-peng BI. Mechanical properties of new prefabricated box culvert structure based on road conditions in Jilin Province [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 917-924. |
| [5] | En-hui YANG,Jia-qiu XU,You-zhi TANG,Ao LI,Yan-jun QIU. Effect of warm mixing agents on fracture and aging properties of asphalt [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 604-610. |
| [6] | Wen-ting DAI,Ze-hua SI,Zhen WANG,Qi WANG. Test on road performance of soils stabilized by sisal fiber and ionic soil stabilizer with cement [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 589-593. |
| [7] | Yu FANG,Li-jun SUN. Urban bridge performance decay model based on survival analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 557-564. |
| [8] | Ying WANG,Ping LI,Teng-fei NIAN,Ji-bin JIANG. Short-term water damage characteristics of asphalt mixture based on dynamic water scour effect [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 174-182. |
| [9] | Ping WAN,Chao-zhong WU,Xiao-feng MA. Discriminating threshold of driving anger intensity based on driving behavior features by ROC curve analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 121-131. |
| [10] | Rui XIONG,Ning QIAO,Ci CHU,Fa YANG,Bo-wen GUAN,Yan-ping SHENG,Dong-yu NIU. Investigation on low-temperature rheology and adhesion properties of salt-doped asphalt mortars [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 183-190. |
| [11] | Chun-feng ZHU,Yong-chun CHENG,Chun-yu LIANG,Bo XIAO. Road performance experiment of diatomite⁃basalt fiber composite modified asphalt mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 165-173. |
| [12] | Sheng-tong DI,Chao JIA,Wei-guo QIAO,Kang LI,Kai TONG. Loading rate effect of meso⁃damage characteristics of crumb rubber concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1900-1910. |
| [13] | Yun-long ZHANG,Liu-guang ZHOU,Jing WANG,Chun-li WU,Xiang LYU. Effects of freeze-thaw cycles on mechanical properties of silty sand and subgrade slope stability [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1531-1538. |
| [14] | Yong PENG,Hua GAO,Lei WAN,Gui-ying LIU. Numerical simulation of influence factors of splitting strength of asphalt mixtures [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1521-1530. |
| [15] | Xiao⁃zhen LI,Jun⁃zhe LIU,Yan⁃hua DAI,Zhi⁃min HE,Ming⁃fang BA,Yu⁃shun LI. Effect of carbonation on nitrite ion distribution in cement paste [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1162-1168. |
|
||