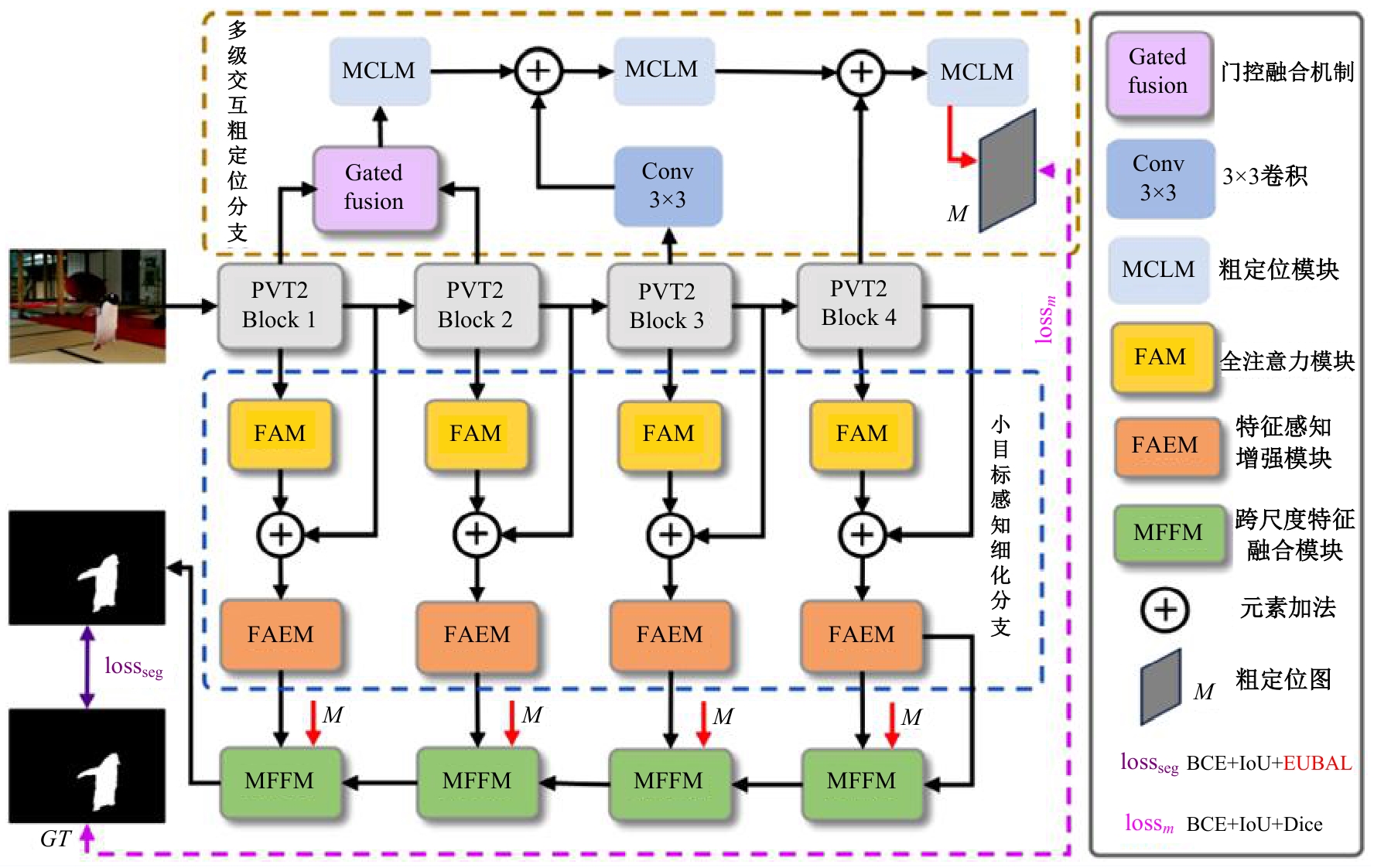
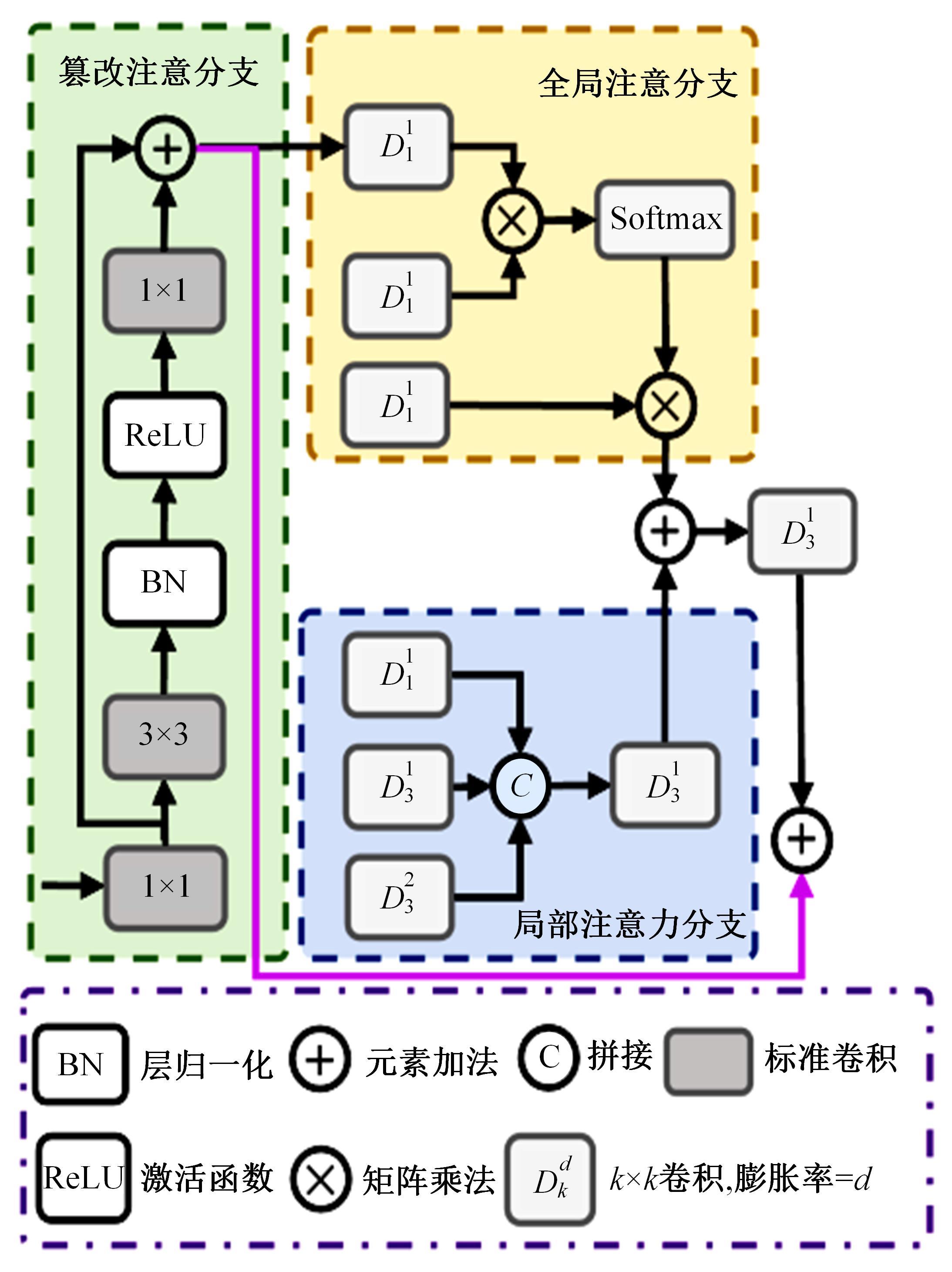
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (12): 4063-4071.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20250014
Image manipulation localization method based on boundary uncertainty learning
Hai-peng CHEN1,2( ),Hong-xin LIU1,2,Hui KANG1,2,Xue-jie LIU1(
),Hong-xin LIU1,2,Hui KANG1,2,Xue-jie LIU1( )
)
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
CLC Number:
- TP391
| [1] | 钟辉, 康恒, 吕颖达, 等. 基于注意力卷积神经网络的图像篡改定位算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(5): 1838-1844. |
| Zhong Hui, Kang Heng, Ying-da Lyu, et al. Image manipulation localization algorithm based on channel attention convolutional neural networks[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1838-1844. | |
| [2] | Shi Z, Chen H, Zhang D. Transformer-auxiliary neural networks for image manipulation localization by operator inductions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2023, 33(9): 4907-4920. |
| [3] | 石泽男, 陈海鹏, 张冬, 等. 预训练驱动的多模态边界感知视觉 Transformer[J]. 软件学报, 2023, 34(5): 2051-2067. |
| Shi Ze-nan, Chen Hai-peng, Zhang Dong, et al. Pretraining-driven multimodal boundary-aware vision transformer[J]. Journal of Software, 2023, 34(5): 2051-2067. | |
| [4] | Liu Y, Zhu X, Zhao X, et al. Adversarial learning for constrained image splicing detection and localization based on atrous convolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 14(10): 2551-2566. |
| [5] | Chen B, Tan W, Coatrieux G, et al. A serial image copy-move forgery localization scheme with source/target distinguishment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2020, 23: 3506-3517. |
| [6] | Zhang Y, Fu Z, Qi S, et al. Localization of inpainting forgery with feature enhancement network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Big Data, 2022, 9(3): 936-948. |
| [7] | Popescu A C, Farid H. Exposing digital forgeries in color filter array interpolated images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2005, 53(10): 3948-3959. |
| [8] | Bianchi T, Piva A. Image forgery localization via block-grained analysis of JPEG artifacts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2012, 7(3): 1003-1017. |
| [9] | Mahdian B, Saic S. Using noise inconsistencies for blind image forensics[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2009, 27(10): 1497-1503. |
| [10] | Chen X, Dong C, Ji J, et al. Image manipulation detection by multi-view multi-scale supervision[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF. International Conference on Computer Vision. Montreal, QC, Canada, 2021: 14165-14173. |
| [11] | Shi C, Wang C, Zhou X, et al. DAE-net: Dual attention mechanism and edge supervision network for image manipulation detection and localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024(73): No.5028112. |
| [12] | Wang W, Xie E, Li X, et al. Pvt v2: Improved baselines with pyramid vision transformer[J]. Computational Visual Media, 2022, 8(3): 415-424. |
| [13] | Park T, Liu M Y, Wang T C, et al. Semantic image synthesis with spatially-adaptive normalization[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, CA: USA, 2019: 2337-2346. |
| [14] | Pang Y, Zhao X, Xiang T Z, et al. Zoom in and out: A mixed-scale triplet network for camouflaged object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New Orleans, LA: USA, 2022: 2160-2170. |
| [15] | Dong J, Wang W, Tan T. Casia image tampering detection evaluation database[C]∥2013 IEEE. China Summit and International Conference on Signal and Information Processing.Beijing: China, 2013: 422-426. |
| [16] | Guan H, Kozak M, Robertson E, et al. MFC datasets: Large-scale benchmark datasets for media for ensic challenge evaluation[C]∥2019 IEEE.Winter Applications of Computer Vision Workshops (WACVW). Waikoloa, HI: USA, 2019: 63-72. |
| [17] | Wen B, Zhu Y, Subramanian R, et al. COVERAGE—a novel database for copy-move forgery detection[C]∥2016 IEEE. International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP).Phoenix, AZ: USA, 2016: 161-165. |
| [18] | Hsu Y F, Chang S F. Detecting image splicing usinggeometry invariants and camera characteristics consistency[C]∥2006 IEEE. International Conference on Multimedia and Expo. Toronto, ON: Canada, 2006: 549-552. |
| [19] | Novozamsky A, Mahdian B, Saic S. IMD2020 a largescale annotated dataset tailored for detecting manipulated images[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF. Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision Workshops. Snowmass Village, CO: USA, 2020: 71-80. |
| [20] | Wu Y, AbdAlmageed W, Natarajan P. Mantra-net manipulation tracing network for detection and localization of image forgeries with anomalous features[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF. Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, CA: USA, 2019: 9543-9552. |
| [21] | Hu X, Zhang Z, Jiang Z, et al. SPAN spatial pyramid attention network for image manipulation localization[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Glasgow: UK, 2020: 312-328. |
| [22] | Zhuang P, Li H, Tan S, et al. Image tampering localization using a dense fully convolutional network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2021, 16: 2986-2999. |
| [23] | Zhuo L, Tan S, Li B, et al. Self-adversarial training incorporating forgery attention for image forgery localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2022, 17: 819-834. |
| [24] | Xia X, Su L C, Wang S P, et al. DMFF-net: Double-stream multilevel feature fusion network for image forgery localization[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2024, 127: No.107200. |
| [1] | Qing-lin AI,Yuan-xiao LIU,Jia-hao YANG. Small target swmantic segmentation method based MFF-STDC network in complex outdoor environments [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2681-2692. |
| [2] | Yu-fei ZHANG,Li-min WANG,Jian-ping ZHAO,Zhi-yao JIA,Ming-yang LI. Robot inverse kinematics solution based on center selection battle royale optimization algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2703-2710. |
| [3] | Yan PIAO,Ji-yuan KANG. RAUGAN:infrared image colorization method based on cycle generative adversarial networks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2722-2731. |
| [4] | Qiong-xin LIU,Tian-tian WANG,Ya-nan WANG. Non-dominated sorted particle swarm genetic algorithm to solve vehicle location routing problems [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2464-2474. |
| [5] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Liang LI. Graph similarity measurement algorithm combining global and local fine-grained features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2365-2371. |
| [6] | Wen-hui LI,Chen YANG. Few-shot remote sensing image classification based on contrastive learning text perception [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2393-2401. |
| [7] | Shan-na ZHUANG,Jun-shuai WANG,Jing BAI,Jing-jin DU,Zheng-you WANG. Video-based person re-identification based on three-dimensional convolution and self-attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2409-2417. |
| [8] | Hai-peng CHEN,Shi-bo ZHANG,Ying-da LYU. Multi⁃scale context⁃aware and boundary⁃guided image manipulation detection method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2114-2121. |
| [9] | Jian WANG,Chen-wei JIA. Trajectory prediction model for intelligent connected vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1963-1972. |
| [10] | Feng-feng ZHOU,Zhe GUO,Yu-si FAN. Feature representation algorithm for imbalanced classification of multi⁃omics cancer data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2089-2096. |
| [11] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Yu-peng SUN. Graph node classification algorithm based on similarity random walk aggregation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2069-2075. |
| [12] | Ping-ping LIU,Wen-li SHANG,Xiao-yu XIE,Xiao-kang YANG. Unbalanced image classification algorithm based on fine⁃grained analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2122-2130. |
| [13] | You-wei WANG,Ao LIU,Li-zhou FENG. New method for text sentiment classification based on knowledge distillation and comment time [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1664-1674. |
| [14] | Hong-wei ZHAO,Ming-zhu ZHOU,Ping-ping LIU,Qiu-zhan ZHOU. Medical image segmentation based on confident learning and collaborative training [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1675-1681. |
| [15] | Zi-hao SHEN,Yong-sheng GAO,Hui WANG,Pei-qian LIU,Kun LIU. Deep deterministic policy gradient caching method for privacy protection in Internet of Vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1638-1647. |
|
||