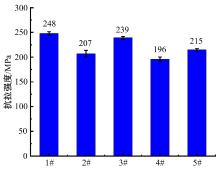
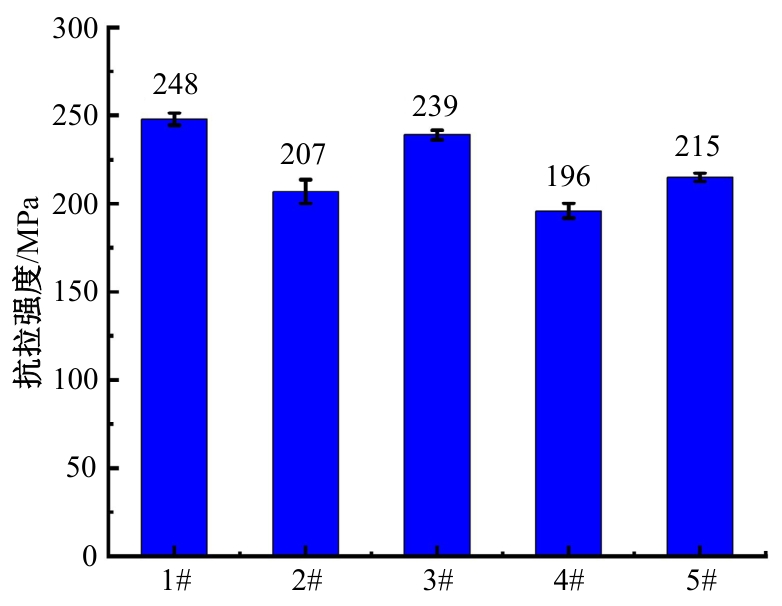
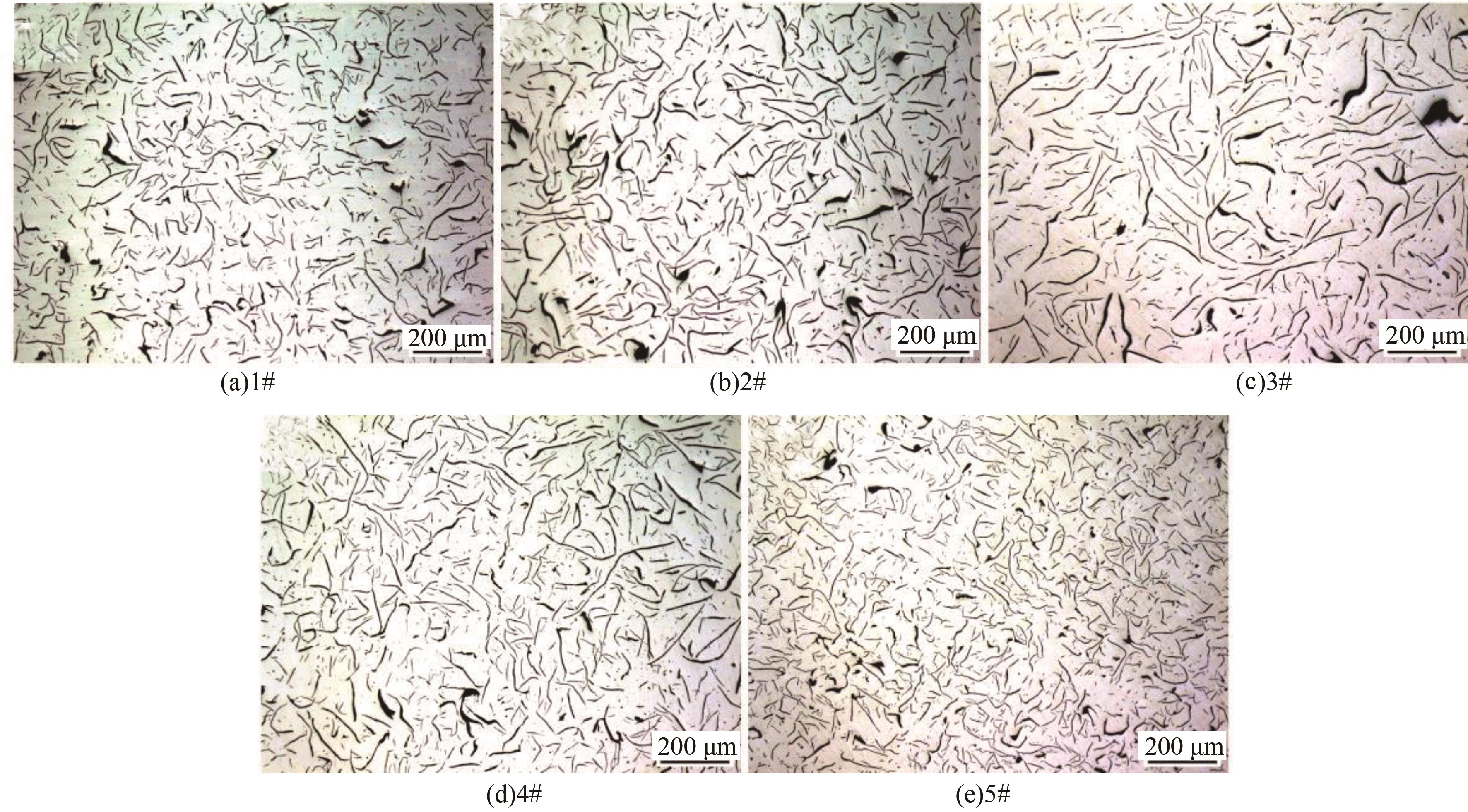
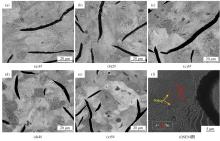
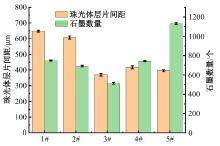
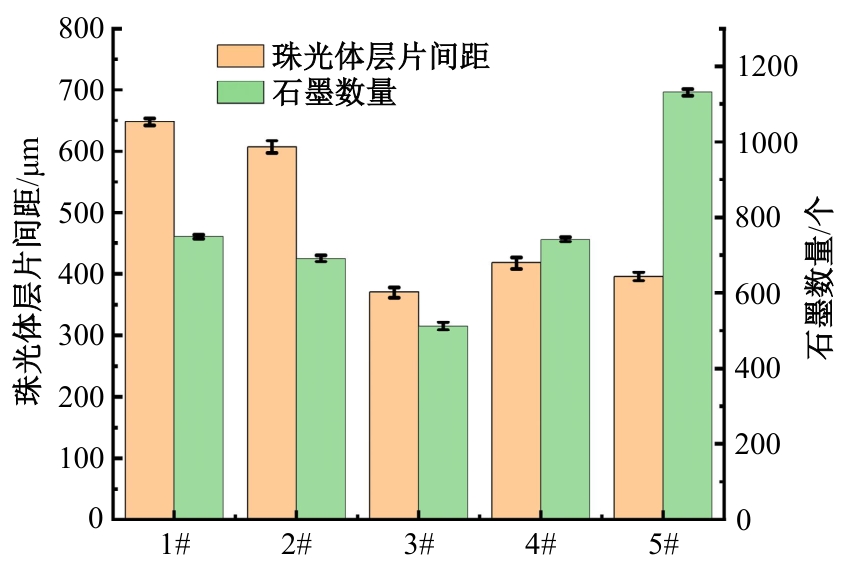
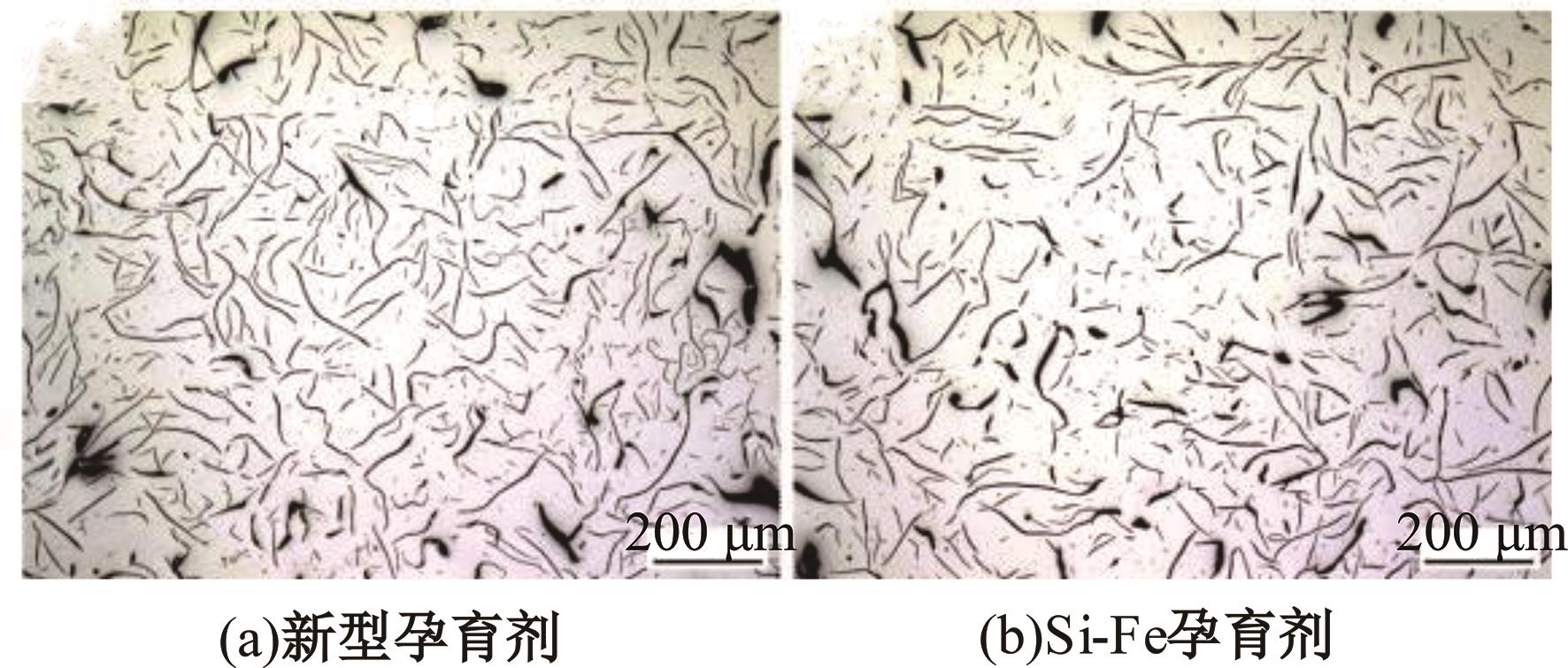
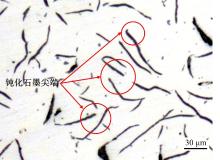
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 1940-1947.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230915
Previous Articles Next Articles
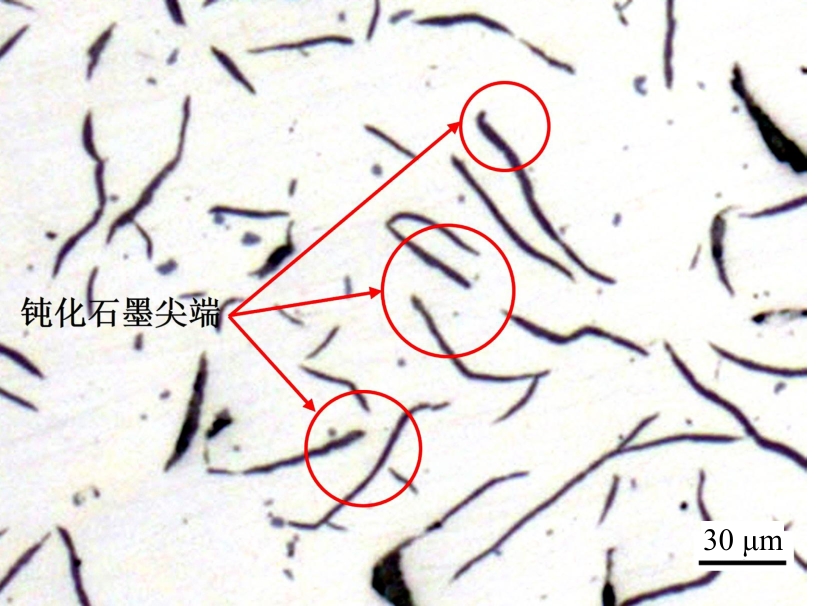
Effect of inoculation treatment on thermal conductivity and tensile strength of high carbongray cast iron
Jin-guo WANG1( ),Cheng-gang WANG2,Tian-shi LU1,Jian-dong WANG2,Feng LI2,Tie-fang CHENG1,Rui-fang YAN1
),Cheng-gang WANG2,Tian-shi LU1,Jian-dong WANG2,Feng LI2,Tie-fang CHENG1,Rui-fang YAN1
- 1.College of Materials Science and Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.FAW Casting Co. ,Ltd. ,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- TG143.5
| [1] | Wang G Q, Liu Z L, Li Y X, et al. Different thermal fatigue behaviors between gray cast iron and vermicular graphite cast iron[J]. China Foundry, 2022, 19(3): 245-252. |
| [2] | Wang G H, Li Y X. Thermal conductivity of cast iron:a review[J]. China Foundry, 2020, 17(2): 85-95. |
| [3] | Holmgren D. Review of thermal conductivity of cast iron[J]. International Journal of Cast Metals Research, 2005, 18(6): 331-345. |
| [4] | Wang G Q, Chen X, Li Y X. Fuzzy neural network analysis on gray cast iron with high tensile strength and thermal conductivity[J]. China Foundry, 2019, 16(3): 190-197. |
| [5] | Velichko A, Wiegmann A, Mucklich F. Estimation of the effective conductivities of complex cast iron microstructures using FIB-tomographic analysis[J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57(17): 5023-5035. |
| [6] | Lian X T, Zhu J N, Dong H, et al. Effects of micro-alloying elements on microstructure, element distribution and mechanical properties in gray irons[J]. International Journal of Metalcasting, 2020, 14(4): 1025-1032. |
| [7] | Liu Y Z, Li Y F, Xing J D. Effect of graphite morphology on the tensile strength and thermal conductivity of cast iron[J]. Materials Characterization, 2018, 144: 155-165. |
| [8] | 王金国, 黄恺, 闫瑞芳, 等. 元胞自动机-有限元法模拟碳当量元素对亚共晶球墨铸铁流动性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(3): 855-865. |
| Wang Jin-guo, Huang Kai, Yan Rui-fang, et al. Effect of cellular automaton-finite element method on the fluidity of subeutectic ductile iron[J].Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 855-865. | |
| [9] | Ding X F, Huang H, Matthias W, et al. Development of high performance cast iron with combination of improved mechanical and thermal properties through Mo addition [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A—Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 2018, 49A(8): 3173-3177. |
| [10] | Maluf O, Angeloni M, Castro D B V, et al. Effect of alloying elements on thermal diffusivity of gray cast iron used in automotive brake disks[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2009, 18(7): 980-984. |
| [11] | Wang G Q, Chen X, Li Y X, et al. Effects of inoculation on the pearlitic gray cast iron with high thermal conductivity and tensile strength[J]. Materials, 2018, 11(10): No.1876. |
| [12] | 范洪远, 李伟, 唐正华, 等. 影响铸铁导热性的工艺因素[J]. 现代铸铁, 2001(2): 14-16. |
| Fan Hong-yuan, Li Wei, Tang Zheng-hua, et al. Process factors affecting the thermal conductivity of cast iron[J]. Modern Cast Iron, 2001(2): 14-16. | |
| [13] | Sun Y L. Effect of carbon content on microstructure and properties of gray cast iron[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 971-973: 44-48. |
| [1] | Chao YANG,Qing-yun YAO,Shuang-mei TANG,Qi-long CHEN,Feng QIN. Thermal conductivity and electrical insulation properties of fluorographene/polyimide composite films [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(3): 663-673. |
| [2] | Jia-cheng FENG,Wen-biao GONG,Chuan JU,Yu-peng LI,Yu-meng SUN,Rui ZHU. Thermal cycle and microstructures characteristic of bobbin tool friction stir welded 2024 aluminum alloy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(11): 3184-3191. |
| [3] | Di WU,Wen-hua GENG,Hong-mei LI,Da-qian SUN. Electron backscattered diffraction analysis on interface of aluminum/steel joints produced by plasma arc welding⁃brazing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1331-1337. |
| [4] | Xiao-hong LU,Jin-hui QIAO,Yu ZHOU,Chong MA,Guo-chuan SUI,Zhuo SUN. Research progress of temperature field in friction stir welding [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(1): 1-17. |
| [5] | Jin-guo WANG,Zhi-qiang WANG,Shuai REN,Rui-fang YAN,Kai HUANG,Jin GUO. Effect of Ti addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of ductile iron [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1653-1662. |
| [6] | Yin-bao TIAN,Jun-qi SHEN,Sheng-sun HU,Jian GOU. Effect of EP/EN Balance on droplet transfer and weld formation of Al alloy by VP⁃CMT [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1663-1668. |
| [7] | Wen-biao GONG,Rui ZHU,Xin-zhe QIE,Heng CUI,Ming-yue GONG. Microstructure and properties of 6082 aluminum alloyultra⁃thick plate preparated by friction stir weld [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 512-519. |
| [8] | Jin-guo WANG,Shuai REN,Rui-fang YAN,Kai HUANG,Zhi-qiang WANG. Effect of TiC particles on microstructure and mechanical properties of as cast ductile iron [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 2010-2018. |
| [9] | Yu⁃peng LI,Da⁃qian SUN,Wen⁃biao GONG. Temperature fields in bobbin⁃tool friction stir welding for 6082⁃T6 aluminum alloy sheet [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 836-841. |
| [10] | ZHAO Yu-guang, YANG Xue-hui, XU Xiao-feng, ZHANG Yang-yang, NING Yu-heng. Effects of Al-10Sr modifiers with different states, modification temperature and holding time on microstructure of ZL114A alloy [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 212-220. |
| [11] | TANG Hua-guo, MA Xian-feng, ZHAO Wei, LIU Jian-wei, ZHAO Zhen-ye. Synthesis microstructure and thermal properties of high performance bulk Al [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1542-1547. |
| [12] | LIU Xiao-bo, ZHOU De-kun, ZHAO Yu-guang. Microstructure and mechanical property of Mg2Si/Al composites fabricated by semi-solid extrusion under different isothermal heat treatments [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1577-1582. |
| [13] | CUI Jin-sheng, HOU Xu-yan, DENG Zong-quan, PAN Wan-jing, JIANG Sheng-yuan. Measurement system and experiment study of the effective thermal conductivity of granular system in a vacuum [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 457-464. |
| [14] | LI Chun-ling, FAN Ding, WANG Bin, YU Shu-rong. 5A06 aluminum alloy and galvanized steel butt welding-brazing by laser with preset filler powder [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 516-521. |
| [15] | ZHANG Jia-tao, ZHAO Yu-guang, TAN Juan. Effect of starting microstructure on refining potency of electro-pulsing on reverse austenite grain [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 193-198. |
|