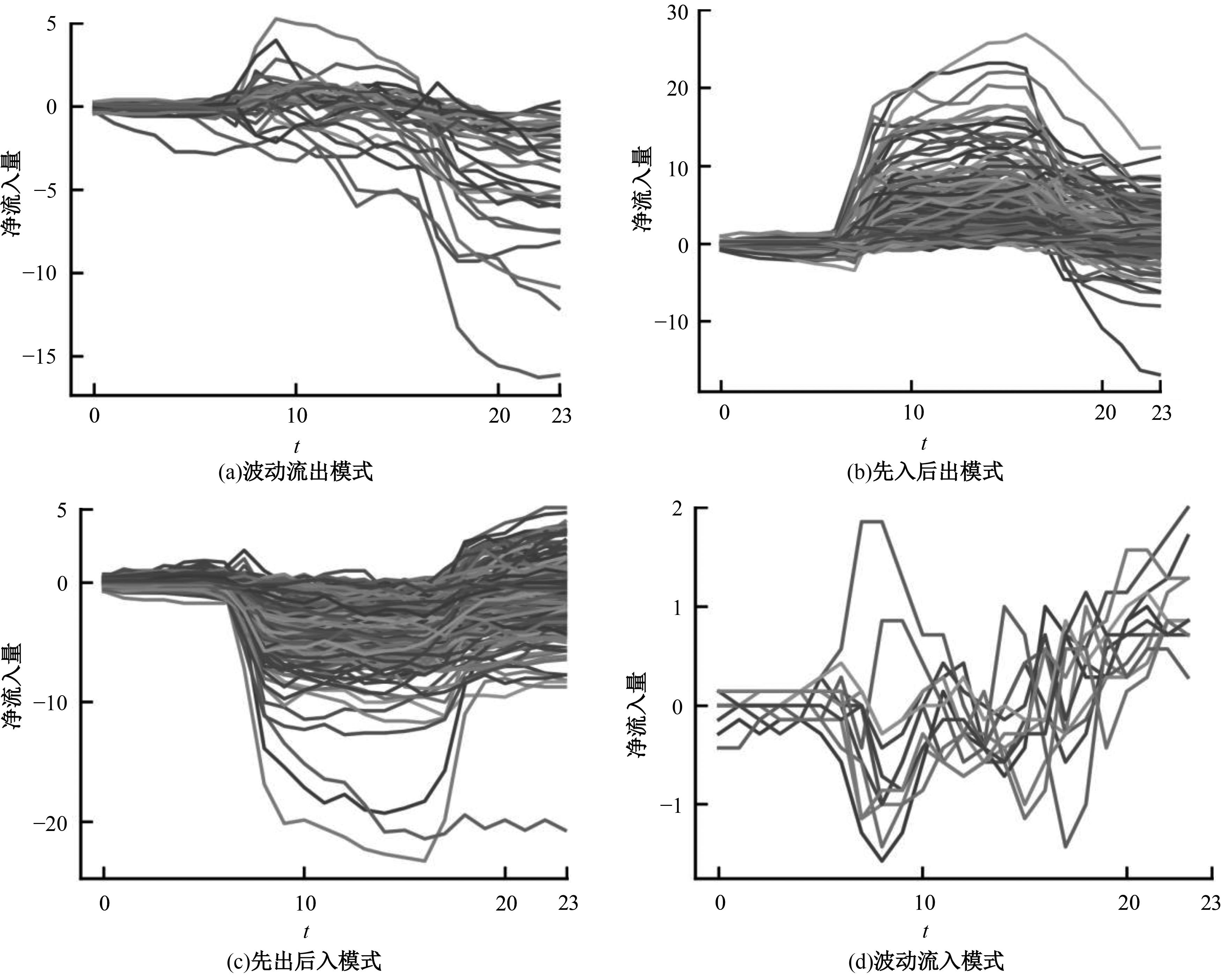
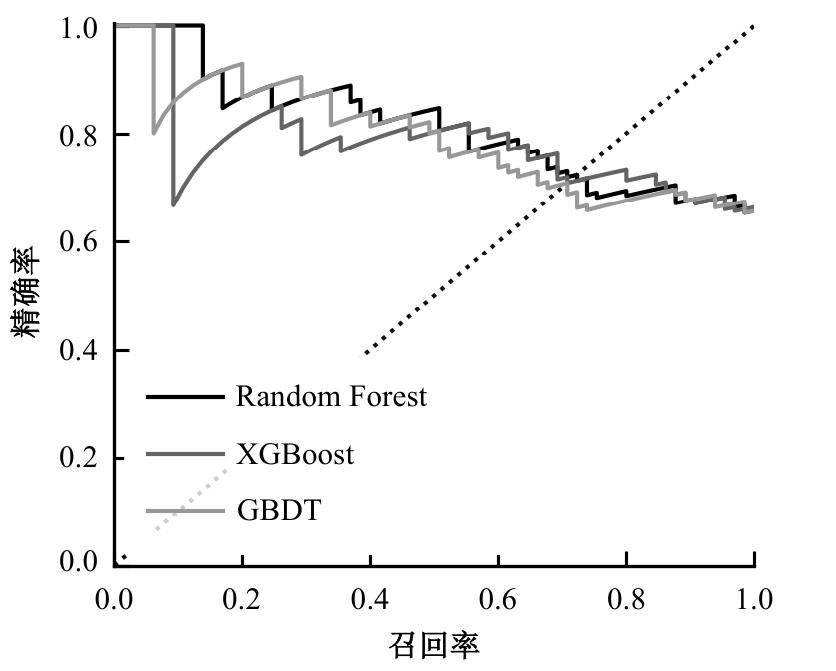
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (7): 2233-2242.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20231050
Nonlinear influence of built environment on temporal aggregation modes of shared bicycles
Xiao-feng JI( ),Ruo-fan DENG,Xin QIAO,Hao-tian GUAN
),Ruo-fan DENG,Xin QIAO,Hao-tian GUAN
- College of Transportation Engineering,Kunming University of Science and Technology,Kunming 650500,China
CLC Number:
- U491.225
| [1] | Shaheen S, Guzman S. Worldwide bikesharing[J]. ACCESS Magazine, 2011, 39(1): 22-27. |
| [2] | 邝嘉恒, 邬群勇. 接驳地铁站的共享单车时空均衡性分析与吸引区域优化[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2022, 24(7): 1337-1348. |
| Kuang Jia-heng, Wu Qun-yong. Spatial-temporal equilibrium analysis and attraction area optimization of dockless sharing bicycles connected to subway stations[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2022, 24(7):1337-1348. | |
| [3] | Faghih Imani A, Eluru N, El-Geneidy A M, et al. How land-use and urban form impact bicycle flows: Evidence from the bicycle-sharing system(BIXI) in montreal[J]. Journal of Transport Geography, 2014, 41: 306-314. |
| [4] | 黄颙昊, 杨新苗, 岳锦涛. 基于多尺度地理加权回归模型的城市道路骑行流量分析[J]. 清华大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 62(7): 1132-1141. |
| Huang Yong-hao, Yang Xin-miao, Yue Jin-tao. Urban street bicycle flow analysis based on multi-scale geographically weighted regression model[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2022, 62(7): 1132-1141. | |
| [5] | 马新卫, 季彦婕, 金雨川,等. 基于时空地理加权回归的共享单车需求影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(4): 1344-1354. |
| Ma Xin-wei, Ji Yan-jie, Jin Yu-chuan, et al. Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-temporal variation in dockless bikeshare usage demand[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(4):1344-1354. | |
| [6] | Ji Y, Ma X, Yang M, et al. Exploring spatially varying influences on metro-bikeshare transfer: A geographically weighted poisson regression approach[J]. Sustainability, 2018, 10(5): No.1526. |
| [7] | Wang K, Chen Y J. Joint Analysis of the impacts of built environment on bikeshare station capacity and trip attractions[J]. Journal of Transport Geography, 2020, 82: No.102603. |
| [8] | Shen Y, Zhang X, Zhao J. Understanding the usage of dockless bike sharing in Singapore[J]. International Journal of Sustainable Transportation, 2018, 12(9): 686-700. |
| [9] | Ding C, Chen P, Jiao J. Non-linear effects of the built environment on automobile-involved pedestrian crash frequency: a machine learning approach[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2018, 112: 116-126. |
| [10] | 高楹, 宋辞, 郭思慧, 等. 接驳地铁站的共享单车源汇时空特征及其影响因素[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2021, 23(1): 155-170. |
| Gao Ying, Song Ci, Guo Si-hui, et al. Spatial-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of source and sink of dockless sharing bicycles connected to subway stations[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2021, 23(1): 155-170. | |
| [11] | Cao M, Cai B, Ma S, et al. Analysis of the cycling flow between origin and destination for dockless shared bicycles based on singular value decomposition[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2019, 8(12): 573. |
| [12] | 李武, 戢晓峰, 陈方, 等.建成环境对常规公交空间公平性的非线性影响[J]. 公路交通科技, 2023, 40(8): 207-213. |
| Li Wu, JI Xiao-feng, Chen Fang, et al. Nonlinear influence of built environment on spatial fairness of conventional transit[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2023, 40(8): 207-213. | |
| [13] | Ewing R, Cervero R. Travel and the built environment: A synthesis[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2001, 1780(1): 87-114. |
| [14] | 王建军, 王赛, 宋明洋, 等.大数据背景下城市建成环境对出行行为影响研究综述[J].长安大学学报:自然科学版,2022,42(1):61-78. |
| Wang Jian-jun, Wang Sai, Song Ming-yang, et al. Review of research on impact of urban built environment on travel behavior in big data context[J]. Journal of Chang'an University(Natural Science Edition),2022, 42(1): 61-78. | |
| [15] | Rodionov I V, Sozontov A N. 2020. On confidence estimation based on quantitative similarity coefficients[J]. Automation and Remote Control, 81(2): 320-332. |
| [16] | 李冬梅, 杨宇, 孟湘皓, 等.多标签分类综述[J].计算机科学与探索,2023,17(11):2529-2542. |
| Li Dong-mei, Yang Yu, Meng Xiang-hao, et al. Review on multi-lable classification[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2023,17(11):2529-2542. | |
| [17] | Aas K, Jullum M, Loland A. Explaining individual predictions when features are dependent: More accurate approximations to Shapley values[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 298: No.103502. |
| [1] | Sheng-yu YAN,Ming-jie CHENG,Hong-ce TIAN,Hong-yu WANG,Yong-heng ZHOU,Bo-hao MA. Scheduling algorithm for battery electric vehicle in closed scenic area [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1984-1993. |
| [2] | Yi-yong PAN,Jia-cong XU,Yi-wen YOU,Yong-jun QUAN. Multi-scale spatial heterogeneity analysis of influencing factors of ride-hailing travel demand [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1567-1575. |
| [3] | Yan-yan QIN,Teng-fei XIAO,Qin-zhong LUO,Bao-jie WANG. Car-following safety analysis and control strategy for foggy freeway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1241-1249. |
| [4] | Yi-yong PAN,Xiang-yu XU. Model for predicting severity of accidents based on MobileViT network considering imbalanced data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 947-953. |
| [5] | Jiao-rong WU,Xu-dong LIU. Analysis of influence of built environment of spatial units of different housing types on commuting mode choice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 554-565. |
| [6] | Guang-yue NIAN,Hai-xiao PAN,Jian SUN. Exploring relationship between urban built environment and road traffic performance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 141-149. |
| [7] | Xi-zhen ZHOU,He GONG,Dun-dun LI,Yan-jie JI,Jie YAN. Nonlinear model for impact of built environment on curb parking spaces occupancy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2520-2530. |
| [8] | Shu-hong MA,Guo-mei LIAO,Yan HUANG,Jun-jie ZHANG. Heterogeneity of built environment on commuter passenger flow of subway in traffic analysis zones [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1913-1922. |
| [9] | Ya-qin QIN,Zheng-fu QIAN,Ji-ming XIE. Vehicle cooperative obstacle avoidance strategy driven by CLAM model and trajectory data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1311-1322. |
| [10] | Shi-jun SONG,Min FAN. Design of big data anomaly detection model based on random forest algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2659-2665. |
| [11] | Hong-tao LI,Lin-hong WANG,Jun-da LI. Influence of lighting and speed limit on visual search ability at highway intersections [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2287-2297. |
| [12] | Chao-ying YIN,Ying LU,Chun-fu SHAO,Jian-xiao MA,De-jie XU. Impacts of built environment on commuting mode choice considering spatial autocorrelation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 1994-2000. |
| [13] | Wei-tiao WU,Kun ZENG,Wei ZHOU,Peng LI,Wen-zhou JIN. Deep learning method for bus passenger flow prediction based on multi-source data and surrogate-based optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| [14] | Zhen-liang LIU,Cun-bao ZHAO,Yun-peng WU,Mi-na MA,Long-shuang MA. Life⁃cycle seismic resilience assessment of highway bridge networks using data⁃driven method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1695-1701. |
| [15] | Hong-fei JIA,Ying-jun XU,Li-li YANG,Nan WANG. League member selection and benefit distribution of commercial vehicles multi⁃modal transportation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1060-1069. |
|
||