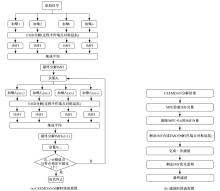
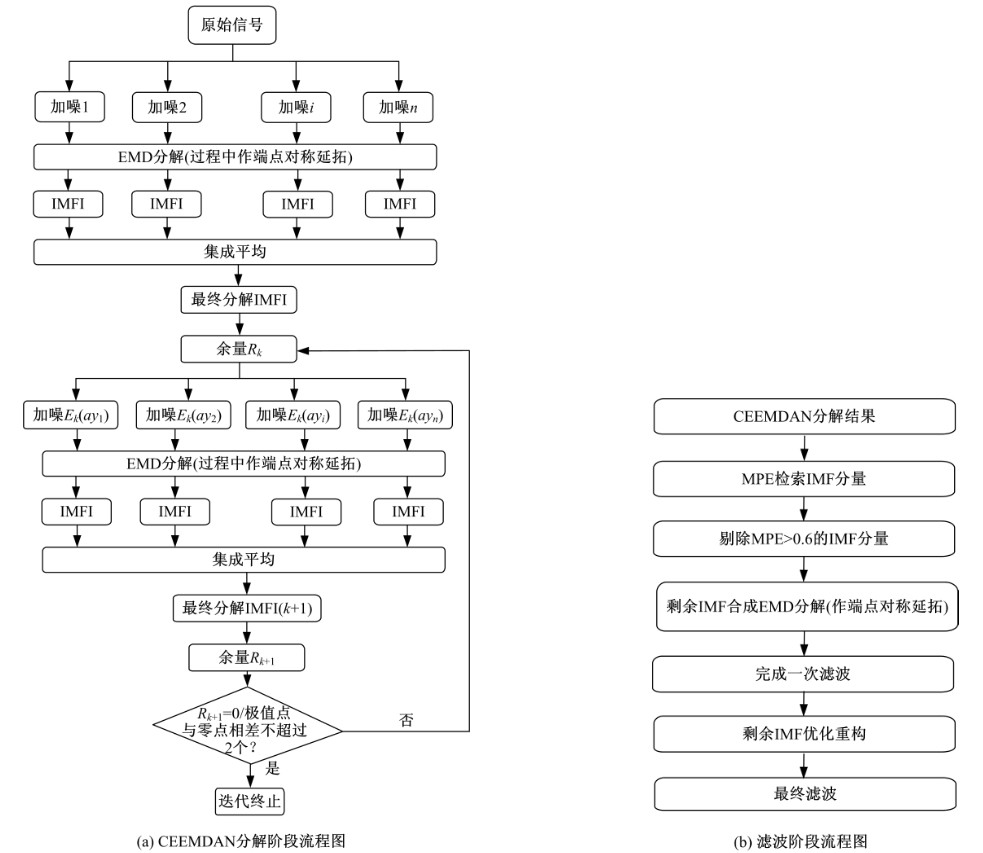
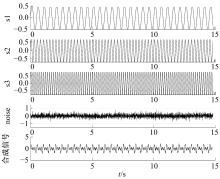
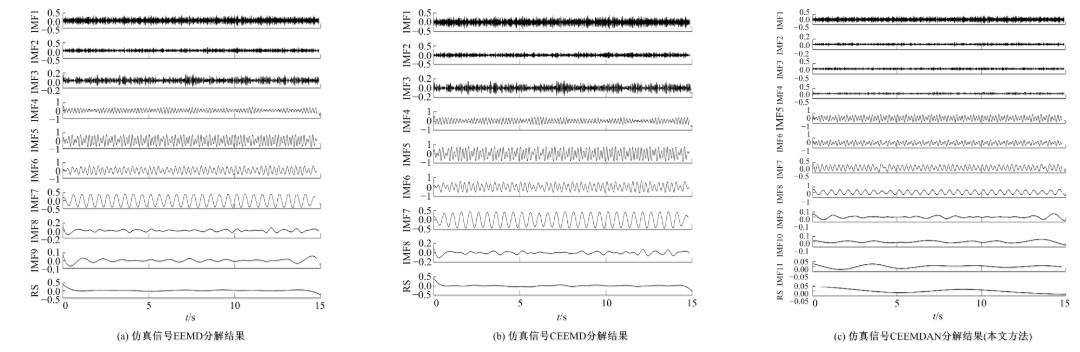
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 216-226.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190013
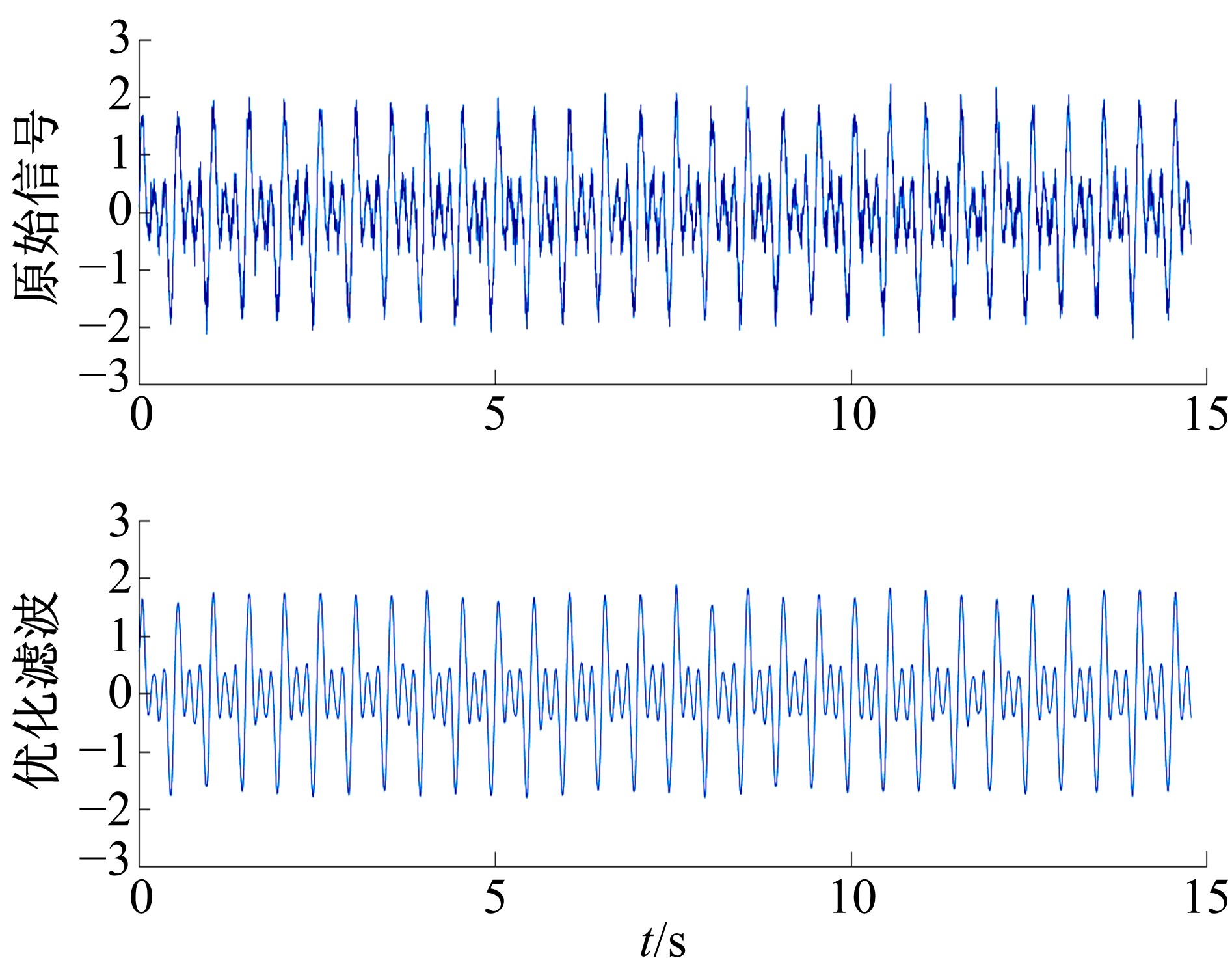
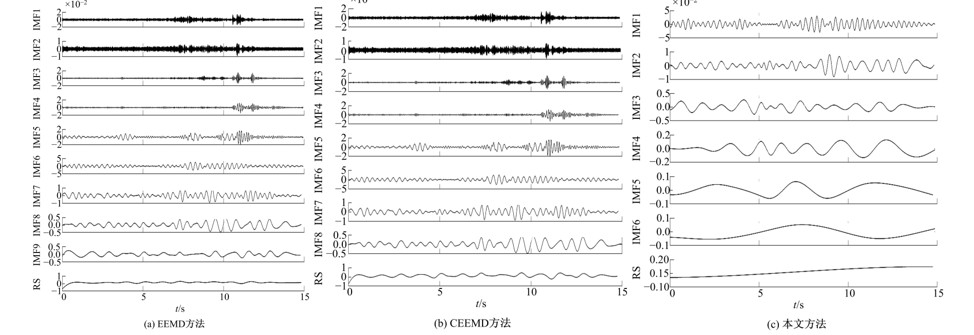
Bridge vibration signal optimization filtering method based on improved CEEMD⁃multi⁃scale permutation entropy analysis
Bo-xin WANG1( ),Hai-tao YANG1,Qing WANG1,Xin GAO1(
),Hai-tao YANG1,Qing WANG1,Xin GAO1( ),Xiao-xu CHEN2
),Xiao-xu CHEN2
- 1. College of Construction Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
2. Changchun Smart City Science and Technology Co. Ltd. , Changchun 130033, China
CLC Number:
- U448.27
| 1 | Huang N E , Shen Z , Long S R , et al . The empirical mode decomposition and the hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceeding of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903-995. |
| 2 | Gai G H . The processing of rotor startup signals based on empirical mode decomposition[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2006, 20(1): 222-235. |
| 3 | Huang N E , Shen Z , Long S R . A new view of non-linear water waves: the hilbert spectrum[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 1999, 31(1): 417-457. |
| 4 | Wu Z H , Huang N E , Chen X Y . The multi-dimensional ensemble empirical mode decomposition method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(3): 339-472. |
| 5 | Wu Z H , Huang N E . Ensemble empirical mode decomposition:a noise assisted data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(1): 1-41. |
| 6 | Yeh J R , Shieh J S , Huang N E . Complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a novel noise enhanced data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2010, 2(2): 135-156. |
| 7 | Huang N E , Wu M , Long S R , et al . A confidence limit for the empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert spectral analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A, 2003, 459: 2317-2345. |
| 8 | 刘薇娜, 周小龙, 姜振海, 等 . 基于最优特征的改进经验模态分解方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2017, 47(6): 1957-1963. |
| Liu Wei-na , Zhou Xiao-long , Jiang Zhen-hai , et al . Improved empirical mode decomposition method based on optimal features[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(6): 1957-1963. | |
| 9 | 吴琛, 项洪, 杜喜朋 . 基于数据/极值联合对称延拓的端点效应处理及其应用[J]. 振动与冲击, 2017, 36(22): 178-184. |
| Wu Chen , Xiang Hong , Du Xi-peng . A process method for end effects of HHT based on data/extrema symmetrical extension and its application[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(22): 178-184. | |
| 10 | 刘慧婷, 张旻, 程家兴 . 基于多项式拟合算法的EMD端点问题的处理[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2004, 40(16): 84-86, 100. |
| Liu Hui-ting , Zhang Min , Cheng Jia-xing . Dealing with the end issue of EMD based on polynomial fitting algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2004, 40(16): 84-86, 100. | |
| 11 | 徐健, 周志祥, 赵丽娜 . 基于AEEMD和改进DATA-SSI算法桥梁结构模态参数自动化识别[J]. 土木工程学报, 2017, 50(7): 87-98. |
| Xu Jian , Zhou Zhi-xiang , Zhao Li-na . Automatic identification of modal parameter for bridges based on AEEMD and improved DATA-SSI[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2017, 50(7): 87-98. | |
| 12 | 陈永高, 钟振宇 . 基于CEEMD分解和DATA-SSI算法的斜拉桥模态参数识别[J]. 振动与冲击, 2016, 35(8): 166-172, 200. |
| Chen Yong-gao , Zhong Zhen-yu . Modal parameter identification of a cable-stayed bridge based on CEEMD and DATA-SSI algorithm[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2016, 35(8): 166-172, 200. | |
| 13 | 单德山, 李乔, 黄珍 . 桥梁动力测试信号的自适应分解与重构[J]. 振动与冲击, 2015, 34(3): 1-6, 13. |
| Shan De-shan , Li Qiao , Huang Zhen . Adaptive decomposition and reconstruction for bridge dynamic testing signals[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(3): 1-6, 13. | |
| 14 | 郑近德, 程军圣, 杨宇 . 改进的EEMD算法及其应用研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2013, 32(21): 21-26, 46. |
| Zheng Jin-de , Cheng Jun-sheng , Yang Yu . Modified EEMD algorithm and its applications[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(21): 21-26, 46. | |
| 15 | 胡显能, 蔡改贫, 罗小燕, 等 . 基于CEEMDAN和多尺度排列熵的球磨机负荷识别方法[J]. 噪声与振动控制, 2018, 38(3): 146-151. |
| Hu Xian-neng , Cai Gai-pin , Luo Xiao-yan , et al . Load identification method for ball mills based on CEEMDAN and multi-scale permutation entropy[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2018, 38(3): 146-151. | |
| 16 | Bandt C , Pompe B . Permutation entropy: a natural complexity measure for time series[J]. Physical Review Letters, The American Physiological Society, 2002, 88(17): 174102. |
| 17 | 姚文坡, 刘铁兵, 戴加飞, 等 . 脑电信号的多尺度排列熵分析[J]. 物理学报, 2014, 63(7): 078704. |
| Yao Wen-po , Liu Tie-bing , Dai Jia-fei , et al . Multiscale permutation entropy analysis of electro encephalogram[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63(7): 078704. |
| [1] | Miao ZHANG,Yong-jiu QIAN,Fang ZHANG,Shou-qin ZHU. Experimental analysis of spatial force performance of concrete-reinforced stone arch bridge based on enlarged section method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 210-215. |
| [2] | Yi JIA,Ren-da ZHAO,Yong-bao WANG,Fu-hai LI. Sensitivity analysis of viscous damper parameters for multi⁃span and long⁃unit continuous girder bridges [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1871-1883. |
| [3] | En-ze LIU,Wen-fu WU. Monochrome fruit growth detection internet architecture based oncomprehensive indicator quality evaluation algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 2019-2026. |
| [4] | Chun-ling ZHONG,Dong LIANG,Yun-long ZHANG,Jing WANG. Calculation of natural vibration frequency of simply supported beam strengthened by external prestressing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1884-1890. |
| [5] | Lun-hua BAI,Rui-li SHEN,Xing-biao ZHANG,Lu WANG. In-plane stability of self-anchored suspension bridge [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1500-1508. |
| [6] | Jin⁃gang ZHAO,Ming ZHANG,Yu⁃lin ZHAN,Ming⁃zhi XIE. Damage criterion of reinforced concrete pier based on plastic strain energy density [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1124-1133. |
| [7] | Shi⁃cheng WAN,Qiao HUANG,Jian GUAN,Zhao⁃yuan GUO. Strengthening of continuous steel⁃concrete composite beams in negative moment region using prestressed carbon fiber⁃reinforced polymer plates [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1114-1123. |
| [8] | Jing LI,Qiu⁃jun SHI,Peng LIU,Ya⁃wei HU. Neural network sliding mode control of commercial vehicle ABS based on longitudinal vehicle speed estimation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1017-1025. |
| [9] | Wan⁃heng LI,Lin SHEN,Shao⁃peng WANG,Shang⁃chuan ZHAO. Damage assessment of bridge construction based onmulti⁃stage subregion mobile test [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 773-780. |
| [10] | Tohtonur,Hai⁃long ZHANG,Jie WANG,Na WANG,Xin⁃chen YE,Wan⁃qiong WANG. High speed median filtering algorithm based on graphics processing unit [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 979-985. |
| [11] | HUI Ying-xin,MAO Ming-jie,LIU Hai-feng,ZHANG Shang-rong. Influence of structural seismic response of bridges crossing active fault [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1725-1734. |
| [12] | LIU Yuan-ning, LIU Shuai, ZHU Xiao-dong, CHEN Yi-hao, ZHENG Shao-ge, SHEN Chun-zhuang. LOG operator and adaptive optimization Gabor filtering for iris recognition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1606-1613. |
| [13] | LIU Shu, JIANG Qi-gang, ZHU Hang, LI Xiao-dong. Reconstruction of Landsat NDVI time series of Xianghai natural deserve based on a hybrid filtering algorithm Hyb-F [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 957-967. |
| [14] | ZHENG Yi-feng, ZHAO Qun, BAO Wei, LI Zhuang, YU Xiao-fei. Wind resistance performance of long-span continuous rigid-frame bridge in cantilever construction stage [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 466-472. |
| [15] | GONG Ya-feng, HE Yu-long, TAN Guo-jin, SHEN Yang-fan. Anti-overturning stability analysis for three-span continuous curved girder bridge with single column pier [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 133-140. |
|
||