Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 2082-2088.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230964
Previous Articles Next Articles
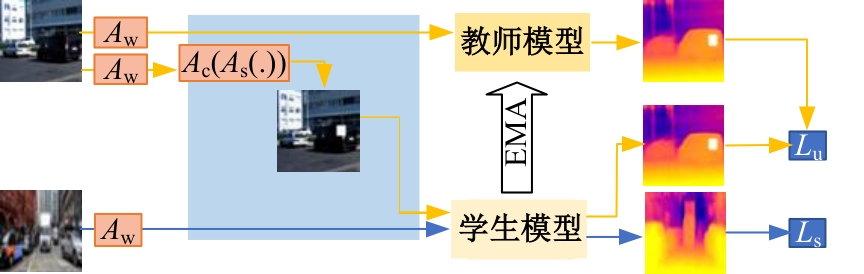
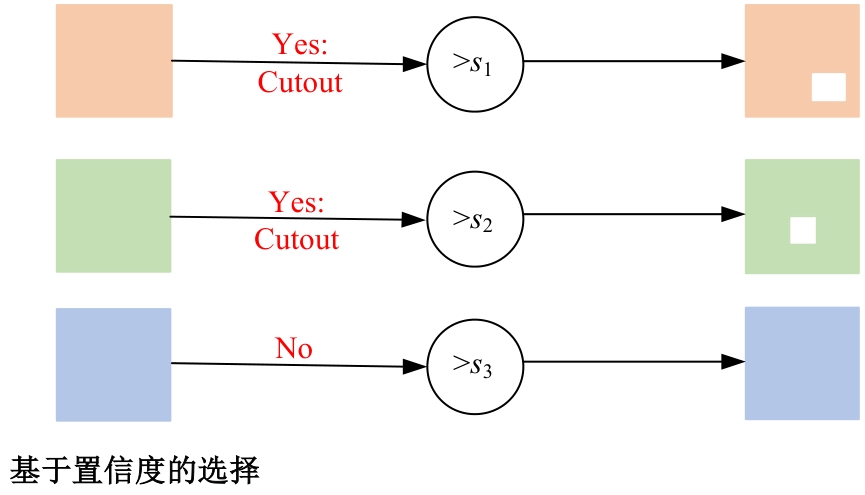
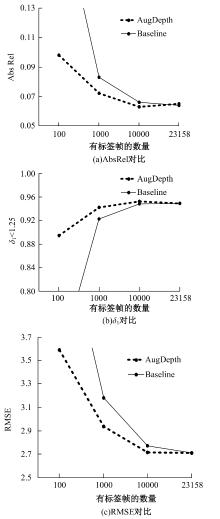
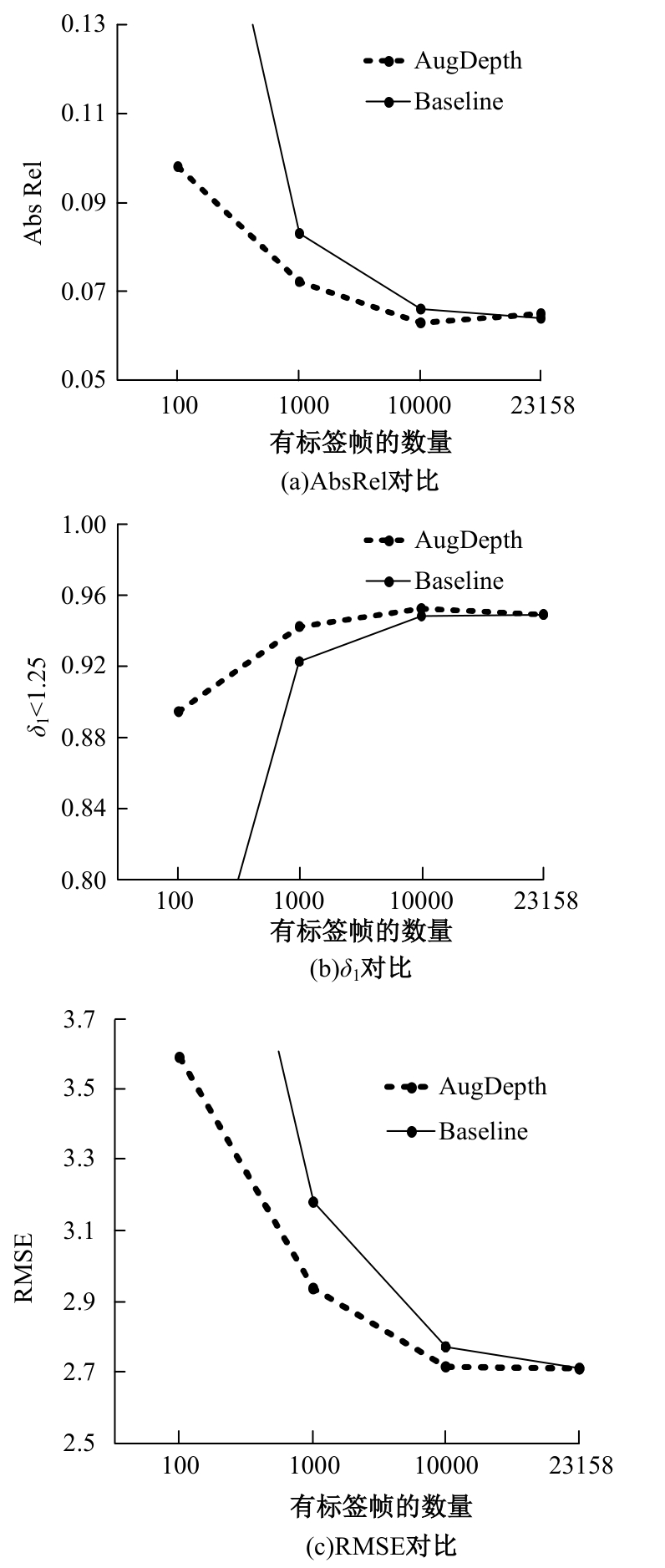
Semi⁃supervised monocular depth estimation framework based on data augmentation
- College of Software,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
CLC Number:
- TP391
| [1] | Eigen D, Puhrsch C, Fergus R. Depth map predictionfrom a single image using a multi-scale deep network[C]∥Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,Montreal, Canada, 2014: 2366-2374. |
| [2] | Song M, Lim S, Kim W. Monocular depth estimation using laplacian pyramid-based depth residuals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 31(11): 4381-4393. |
| [3] | Lee J H, Han M K, Ko D W, et al. From big to small: multi-scale local planar guidance for monocular depth estimation[J/OL].[2023-08-26]. |
| [4] | Ji R, Li K, Wang Y, et al. Semi-supervised adversarial monocular depth estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(10): 2410-2422. |
| [5] | Cho J, Min D, Kim Y, et al. A large RGB-D dataset for semi-supervised monocular depth estimation[J/OL]. [2023-08-27]. |
| [6] | Guo X, Li H, Yi S, et al. Learning monocular depth by distilling cross-domain stereo networks[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 506-523. |
| [7] | Cubuk E D, Zoph B, Shlens J, et al. Randaugment: practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops,Seattle, USA, 2020: 702-703. |
| [8] | Zhao Z, Yang L, Long S, et al. Augmentation matters: a simple-yet-effective approach to semi-supervisedsemantic segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Vancouver, Canada,2023: 11350-11359. |
| [9] | Zhao Z, Long S, Pi J, et al. Instance-specific and model-adaptive supervision for semi-supervised semantic segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada,2023: 23705-23714. |
| [10] | de Vries T, Taylor G W. Improved regularization of convolutional neural networks with cutout[J/OL].[2023-08-28]. |
| [11] | Tarvainen A, Valpola H. Mean teachers are better rolemodels: weight-averaged consistency targets improve semi-supervised deep learning results[C]∥Advances in Neural Information Processing System,Vancouver, Canada, 2017: 1195-1204. |
| [12] | Yuan J, Liu Y, Shen C, et al. A simple baseline for semi-supervised semantic segmentation with strong data augmentation[C]∥IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, Canada, 2021: 8209-8218. |
| [13] | Poggi M, Aleotti F, Tosi F, et al. On the uncertainty of self-supervised monocular depth estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Seattle, USA, 2020: 3227-3237. |
| [14] | Baek J, Kim G, Park S, et al. MaskingDepth: masked consistency regularization for semi-supervised monocular depth estimation[J/OL]. [2023-08-29]. |
| [15] | Fu H, Gong M, Wang C, et al. Deep ordinal regression network for monocular depth estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Los Alamitos,USA, 2018: 2002-2011. |
| [16] | Godard C, Aodha O M, Firman M, et al. Digging into self-supervised monocular depth estimation[C]∥IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 2019: 3827-3837. |
| [17] | Shu C, Yu K, Duan Z, et al. Feature-metric loss for self-supervised learning of depth and egomotion[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision,Glasgow, UK, 2020: 572-588. |
| [18] | Amiri A J, Loo S Y, Zhang H. Semi-supervised monocular depth estimation with left-right consistency using deep neural network[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Dali,China,2019: 602-607. |
| [19] | Ranftl R, Bochkovskiy A, Koltun V. Vision transformers for dense prediction[C]∥IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, Canada, 2021: 12159-12168. |
| [1] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Yu-peng SUN. Graph node classification algorithm based on similarity random walk aggregation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2069-2075. |
| [2] | Ping-ping LIU,Wen-li SHANG,Xiao-yu XIE,Xiao-kang YANG. Unbalanced image classification algorithm based on fine⁃grained analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2122-2130. |
| [3] | Rui-shan DU,Zi-shan WANG. Multi perspective facial expression recognition algorithm based on spatiotemporal attention [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2097-2102. |
| [4] | Bin WEN,Shun PENG,Chao YANG,Yan-jun SHEN,Hui LI. Multi⁃depth adaptive fusion dehazing generation network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2103-2113. |
| [5] | Hai-peng CHEN,Shi-bo ZHANG,Ying-da LYU. Multi⁃scale context⁃aware and boundary⁃guided image manipulation detection method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2114-2121. |
| [6] | Qing-liang JIN,Xin-sen ZHOU,Yi CHEN,Cheng-wen WU. Predictive model for identifying innovative university talents based on the swarm intelligence evolution enhanced kernel extreme learning machine [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1763-1771. |
| [7] | Yan-fei LI,Jia-ning WU. Human pose local feature recognition algorithm based on improved RBF neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1749-1755. |
| [8] | Yun-fei QIU,Hong-miao YU,Xiang WANG. 3D laser point cloud recognition based on point-to-point feature algorithm and SVD decomposition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1735-1741. |
| [9] | Hong XIAO,Xian-de LIU. A facial subtle feature recognition algorithm considering the correlation between learning interests and micro expressions [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1728-1734. |
| [10] | Ya-li XUE,Tong-an YU,Shan CUI,Li-zun ZHOU. Infrared small target detection based on cascaded nested U-Net [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1714-1721. |
| [11] | Bin WEN,Yi-fu DING,Chao YANG,Yan-jun SHEN,Hui LI. Self-selected architecture network for traffic sign classification [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1705-1713. |
| [12] | Yue HOU,Jin-song GUO,Wei LIN,Di ZHANG,Yue WU,Xin ZHANG. Multi-view video speed extraction method that can be segmented across lane demarcation lines [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1692-1704. |
| [13] | De-qiang CHENG,Wei-chen WANG,Cheng-gong HAN,Chen LYU,Qi-qi KOU. Self-supervised monocular depth estimation based on improved densenet and wavelet decomposition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1682-1691. |
| [14] | Hong-wei ZHAO,Ming-zhu ZHOU,Ping-ping LIU,Qiu-zhan ZHOU. Medical image segmentation based on confident learning and collaborative training [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1675-1681. |
| [15] | You-wei WANG,Ao LIU,Li-zhou FENG. New method for text sentiment classification based on knowledge distillation and comment time [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1664-1674. |
|