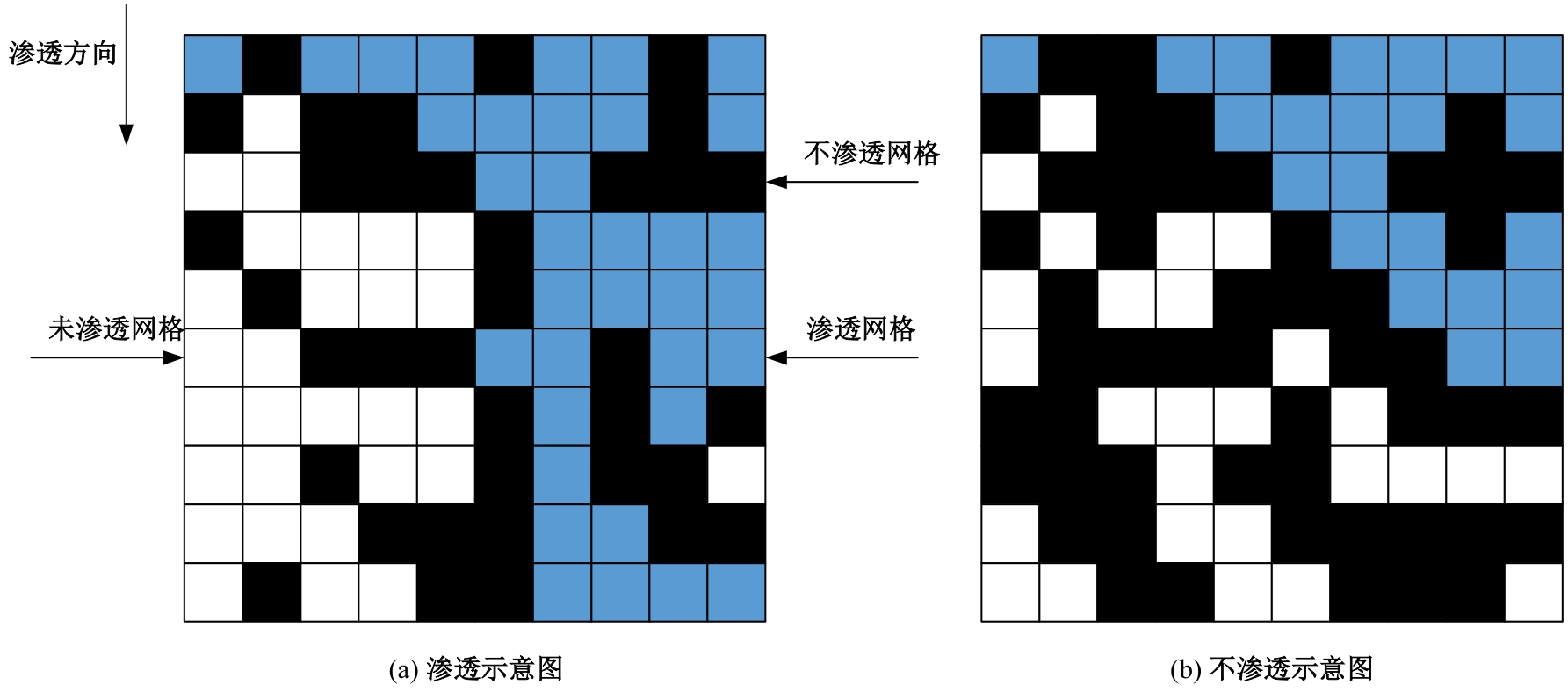
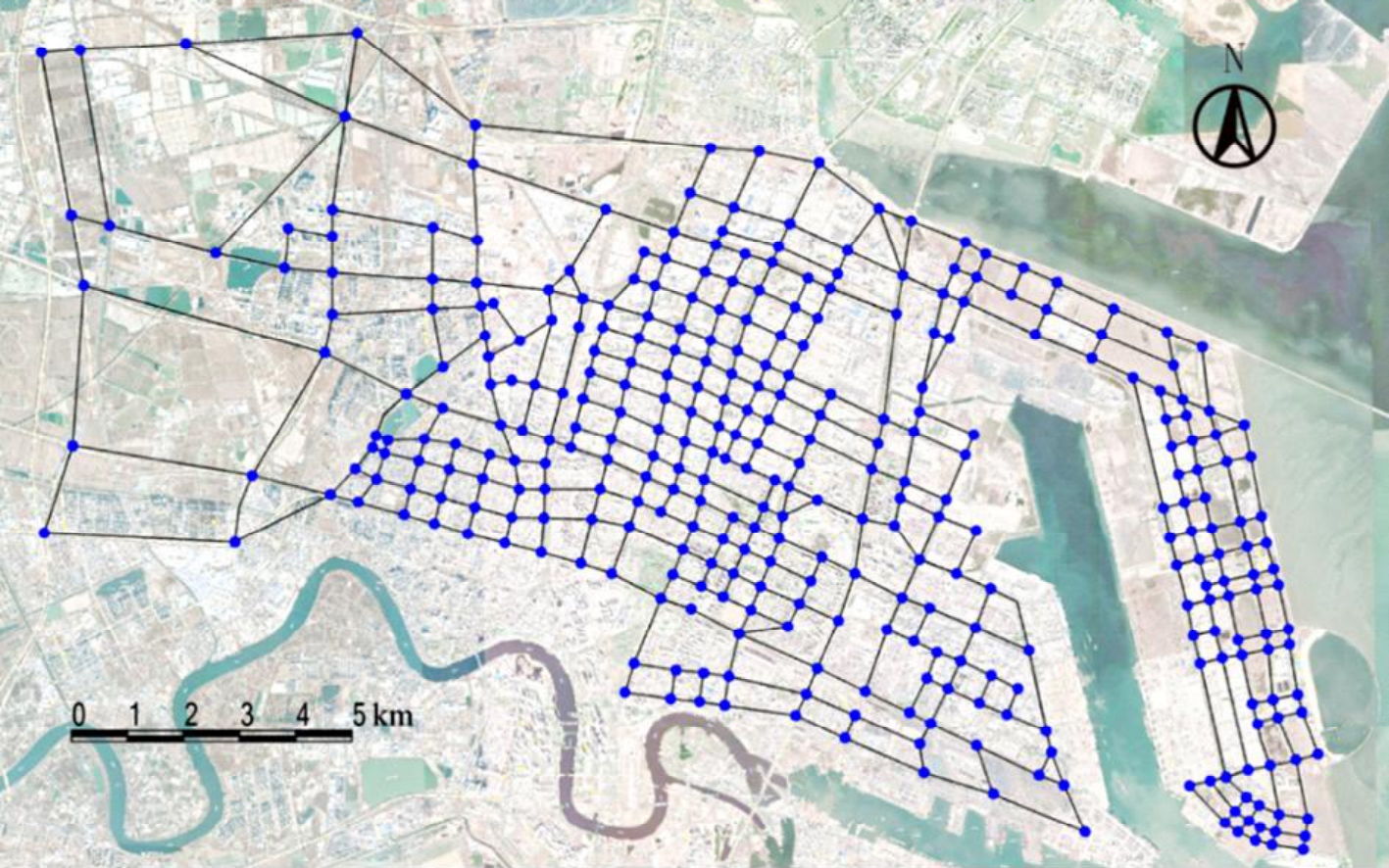
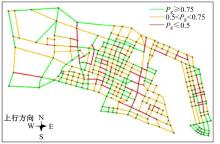
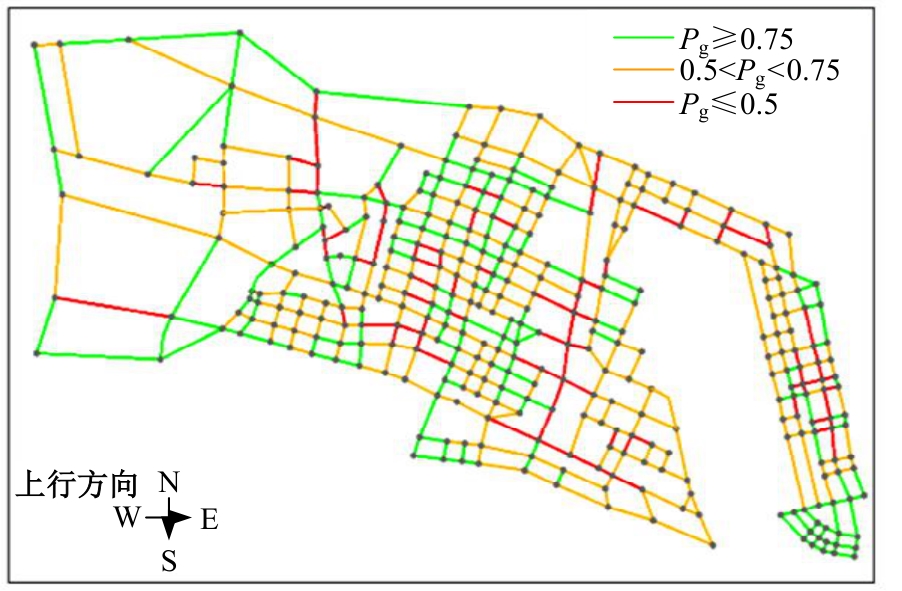
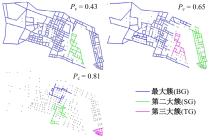
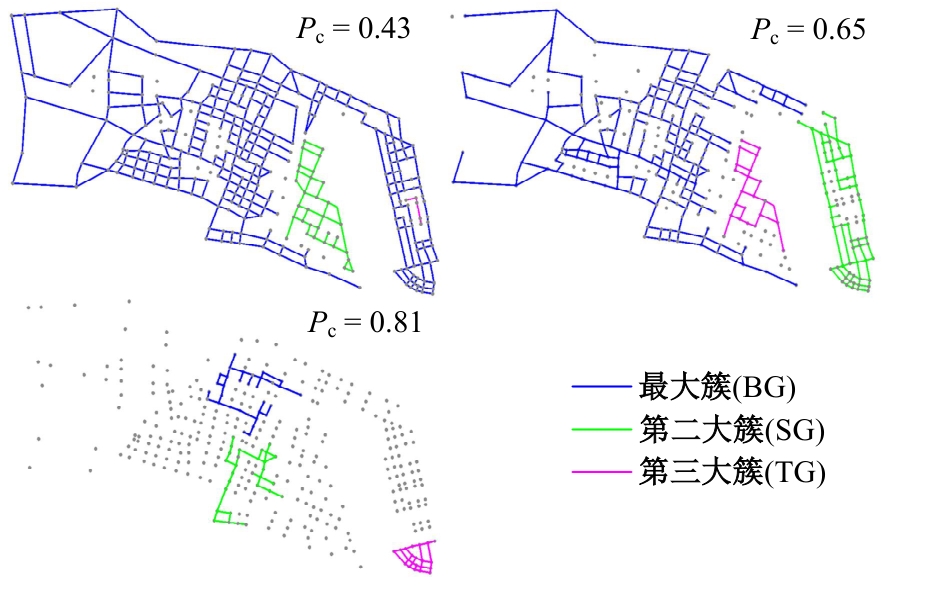
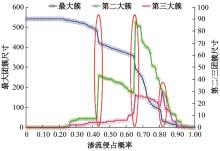
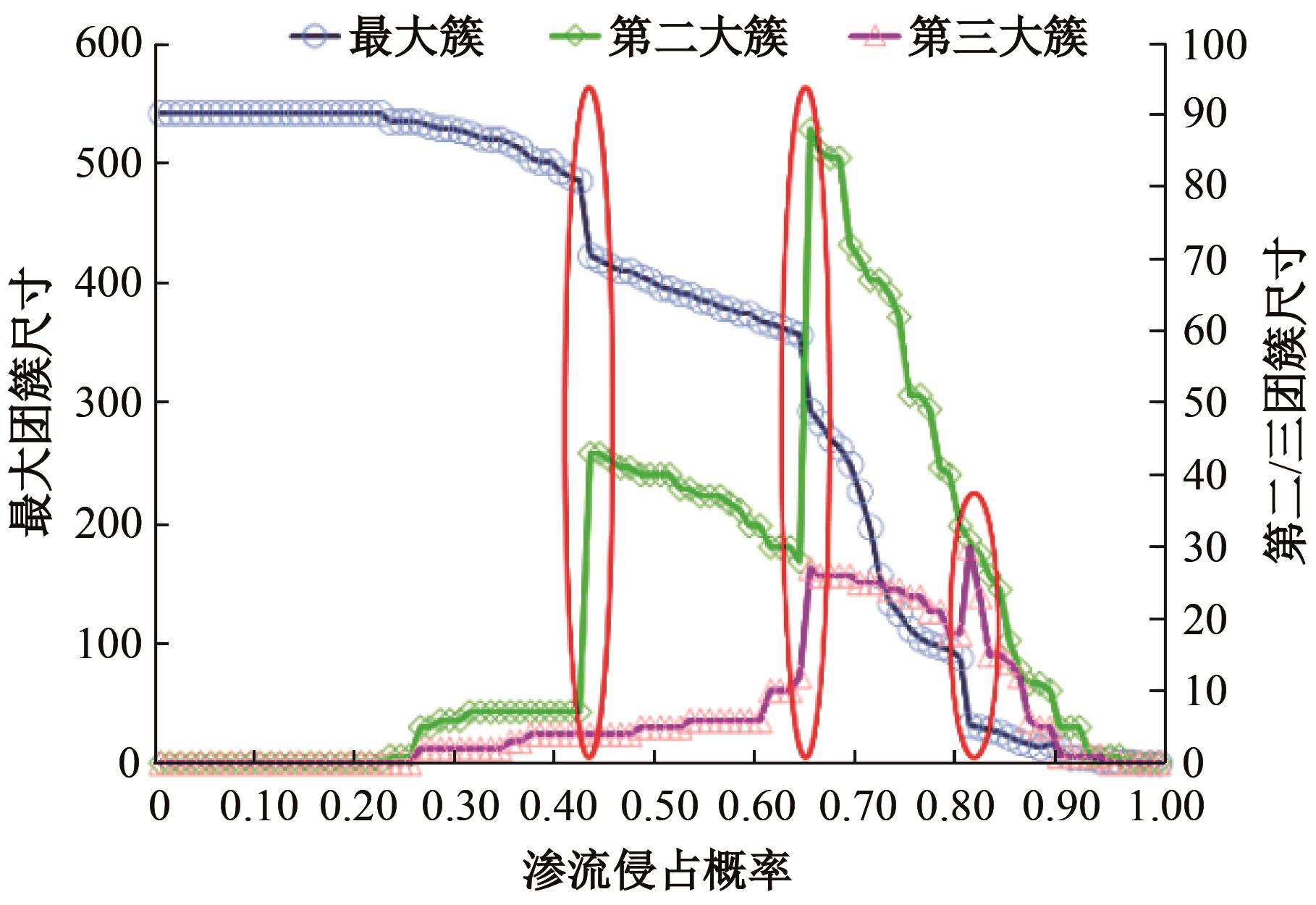
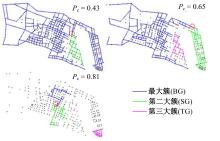
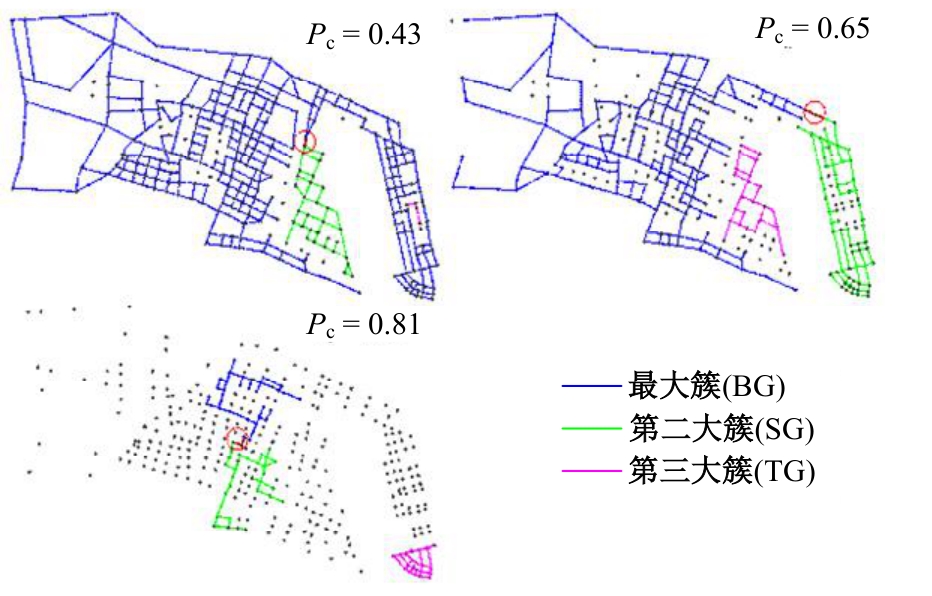
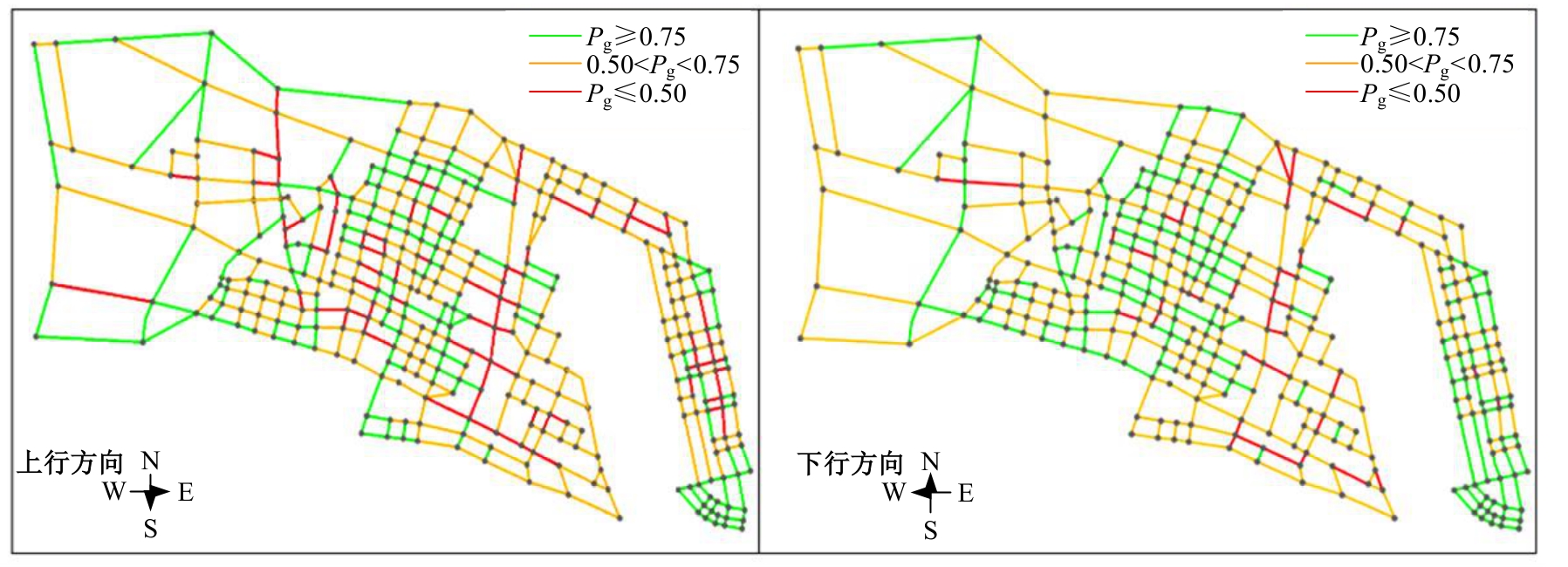
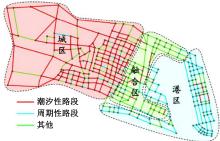
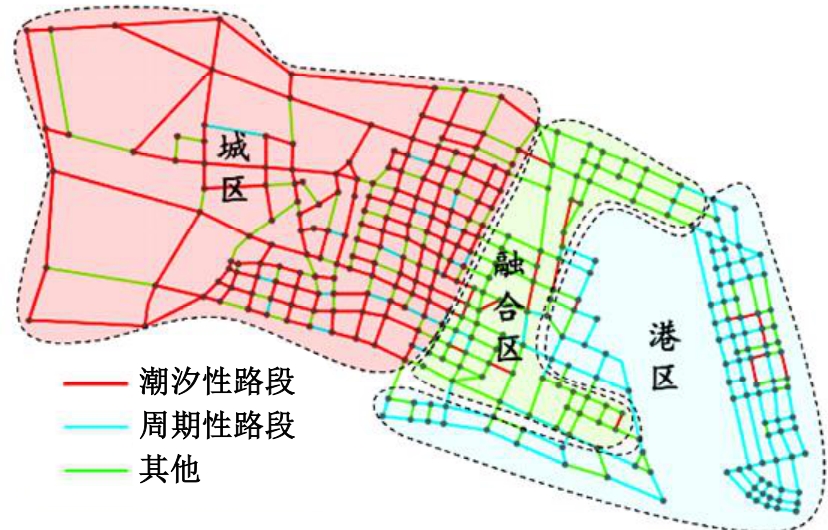
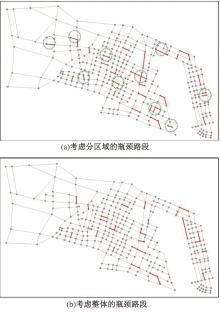
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2026, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 199-208.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240712
Previous Articles Next Articles
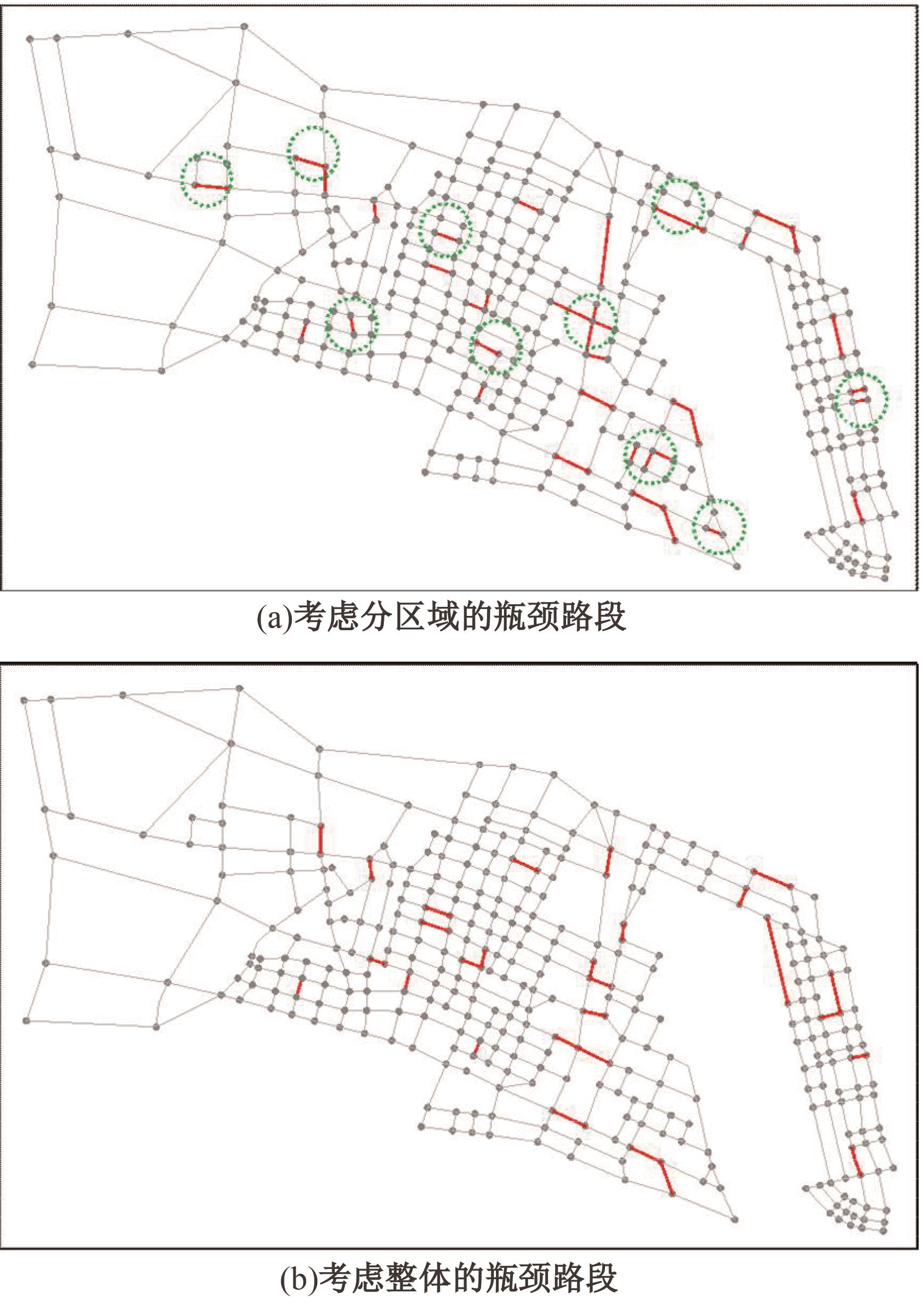
Characteristics analysis of port and city transportation network based on percolation theory
Yao SUN1,2( ),Dong-xuan BAI1,Bao-zhen YAO1(
),Dong-xuan BAI1,Bao-zhen YAO1( ),Zi-jian BAI2
),Zi-jian BAI2
- 1.School of Mechanical Engineering,Dalian University of Technology,Dalian 116024,China
2.Tianjin Municipal Engineering Design & Research Institute Co. ,Ltd. ,Tianjin 300051,China
CLC Number:
- U491.1
| [1] | 李勋高,李乃强,刘淑永,等. 青岛董家口港城公共交通安全规划探索与实践[J]. 城市公共交通, 2021(8): 46-50. |
| Li Xun-gao, Li Nai-qiang, Liu Shu-yong, et al. Exploration and practice of public transport safety planning in Dongjiakou port city of Qingdao[J]. Urban Public Transport, 2021(8): 46-50. | |
| [2] | 郑长江, 陶童统, 陈志超. 基于流量可调重分配的级联失效模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2024, 54(9): 2441-2450. |
| Zheng Chang-jiang, Tao Tong-tong, Chen Zhi-chao. Cascading failure model based on adjustable redistribution of traffic flow[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2441-2450. | |
| [3] | 温晓岳, 钱国敏, 孔桦桦, 等. TrafficPro:一种针对城市信控路网的路段速度预测框架[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2024, 54(8): 2214-2222. |
| Wen Xiao-yue, Qian Guo-min, Kong Hua-hua, et al. TrafficPro: a framework to predict link speeds on signalized urban traffic network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2214-2222. | |
| [4] | 袁韵, 徐戈, 贾建民. 网约车流动行为的时空特征及网络分析[J]. 系统管理学报, 2021, 30(1): 28-39. |
| Yuan Yun, Xu Ge, Jia Jian-min. Spatiotemporal characteristics and network analysis of car-hailing mobility behavior[J]. Journal of Systems & Management, 2021, 30(1): 28-39. | |
| [5] | 丁祥颖, 胡尧, 刘智权. 基于交通数据分解和时空特征提取的车辆平均车速预测模型[J]. 运筹与模糊学, 2023, 13(2): 415-430. |
| Ding Xiang-ying, Hu Yao, Liu Zhi-quan. Vehicle average speed prediction model based on traffic data decomposition and spatio-temporal feature extraction[J]. Operations Research and Fuzziology, 2023, 13(2): 415-430. | |
| [6] | Zhang M Y, Huang T, Guo Z X, et al. Complex-network-based traffic network analysis and dynamics: A comprehensive review[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2022, 607: No.128063. |
| [7] | Latora V, Marchiori M. Is the Boston subway a small-world network?[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2002, 314(1-4):109-113. |
| [8] | Sen P, Dasgupta S, Chatterjee A, et al. Small-world properties of the Indian railway network[J]. Physical Review E, 2003, 67(3): No.036106. |
| [9] | 吴样平, 郭飞, 曾明华. 基于复杂网络的城市综合交通网络特征分析与优化研究[J]. 江西师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 39(3): 326-330. |
| Wu Yang-ping, Guo Fei, Zeng Ming-hua. The characteristic analyses and optimization of urban integrated transport network based on complex network[J]. Journal of Jiangxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 39(3): 326-330. | |
| [10] | 王国明. 城市群道路网络特性及演化研究[D]. 长沙:中南大学交通运输工程学院, 2012. |
| Wang Guo-ming. A study on property and evolution of road network of urban agglomeration[D]. Changsha: School of Traffic & Transportation Engineering, Central South University, 2012. | |
| [11] | Zou H, Yue Y, Li Q. Urban traffic state explained by road networks and spatial variance approach using floating car data[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2014(2467):40-48. |
| [12] | 胡垚, 吕斌. 城市地铁网络特征分析及类型划分[J]. 规划师, 2013, 29(5): 96-101. |
| Hu Yao, Lv Bin. Metro system character analysis and categorization[J]. Planners, 2013, 29(5): 96-101. | |
| [13] | 张李盈, 任景莉. 渗流理论、方法、进展及存在问题[J]. 自然杂志, 2019, 41(2): 119-131. |
| Zhang Li-ying, Ren Jing-li. Percolation theory, method, progress, and existing problems[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2019, 41(2): 119-131. | |
| [14] | Flory P J. Molecular size distribution in three dimensional polymers. I. gelation[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1941, 63(11): 3083-3090. |
| [15] | Broadbent S R, Hammersley J M. Percolation processes[J]. Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 1957, 53(3): 629-641. |
| [16] | Werner W, Schramm O, Lawler G F.Conformal invariance of planar loop-erased random walks and uniform spanning trees[J]. The Annals of Probability, 2004, 32(1B): 939-995. |
| [17] | 于少波, 吴玲达, 张喜涛, 等. 面向空间信息网络的多特征可视化方法综述[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2018, 13(2): 201-208. |
| Yu Shao-bo, Wu Ling-da, Zhang Xi-tao, et al. Survey of multi-feature visualization for space information network[J]. Journal of China Academy of Electronics and Information Technology, 2018, 13(2): 201-208. | |
| [18] | Sander L M, Warren C P, Sokolov I M, et al. Percolation on heterogeneous networks as a model for epidemics[J]. Mathematical Biosciences, 2002, 180(1/2): 293-305. |
| [19] | Guo C, Zhao Y D, David J H, et al. Attack structural vulnerability of power grids: a hybrid approach based on complex networks[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2010, 389(3): 595-603. |
| [20] | Glauche I, Krause W, Sollacher R, et al. Continuum percolation of wireless ad hoc communication networks[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2003, 325(3/4): 577-600. |
| [21] | Ferraro G D, Moreno A, Min B, et al. Finding influential nodes for integration in brain networks using optimal percolation theory[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1):No. 2274. |
| [22] | Li D Q, Fu B W, Wang Y P,et al. Percolation transition in dynamical traffic network with evolving critical bottlenecks[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2015, 112(3):669-672. |
| [23] | Zeng G W, Li D Q, Guo S M, et al. Switch between critical percolation modes in city traffic dynamics[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116: 23-28. |
| [24] | Chen Z, Yang C, Qian J H, et al. Recursive traffic percolation on urban transportation systems[J]. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2023, 33(3): No.033132. |
| [25] | 傅裕寿. 交通流理论[J]. 力学与实践, 1989(4): 5-16, 25. |
| Fu Yu-shou. Traffic flow theory[J]. Mechanics in Engineering, 1989(4): 5-16, 25. | |
| [26] | 林豪, 江竹, 李树彬. 基于机器学习的城市快速路速度-密度关系模型[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2020, 40(6): 1109-1116. |
| Lin Hao, Jiang Zhu, Li Shu-bin. Speed-density relationship model of urban expressway based on machine learning[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2020, 40(6): 1109-1116. | |
| [27] | Chen B Y, Lam W H K, Sumalee A, et al. Reliable shortest path finding in stochastic networks with spatial correlated link travel times[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2012, 26(2): 365-386. |
| [28] | 张平, 王聪, 谢长青, 等. 关于非饱和渗透理论中的几项基本问题的剖析[J]. 沈阳大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 26(5): 386-390. |
| Zhang Ping, Wang Cong, Xie Chang-qing, et al. Basic issues in unsaturated hydraulic theory[J]. Journal of Shenyang University(Natural Science), 2014, 26(5): 386-390. | |
| [29] | 彬楠, 樊贵盛. 土壤水分特征曲线Van-Genuchten 模型参数的土壤传输函数比选[J]. 农村水利水电, 2018(5): 33-36. |
| nan Bin, Fan Gui-sheng. Van-Genuchten model parameters of soil water characteristics curve are compared with the soil transfer[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2018(5): 33-36. | |
| [30] | 城市道路工程设计规范 .[S]. |
| [1] | Yi ZHANG,Sha-wen CHEN,Yan CHEN,Xiang-yu FAN,Si-qi WANG,Huan WU,Peng-fei JIAO. Dynamic operation and maintenance evaluation and predictive maintenance of mechanical and electrical equipment on highways [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2026, 56(1): 170-182. |
| [2] | Dong WANG,Yu-xuan LI,Huan WU,Fang ZONG. Rating algorithm for open test road of intelligent connected vehicle based on random forest [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(9): 2998-3006. |
| [3] | Hong-fei JIA,Bo ZHUANG,Qing-yu LUO,Ling LIU,Qiu-yang HUANG. Decision optimization of urban road network performance restoration under waterlogged conditions [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(9): 2969-2977. |
| [4] | Hui-zhi XU,Dong-sheng HAO,Xiao-ting XU,Shi-sen JIANG. Expressway small object detection algorithm based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2003-2014. |
| [5] | Qing-ling HE,Yu-long PEI,Lin HOU,Jing LIU,Sheng PAN. Hybrid strategy improves WOA⁃BiLSTM speed prediction of expressway exit ramp [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2038-2049. |
| [6] | Xiang-hai MENG,Guo-rui WANG,Ming-yang ZHANG,Bi-jiang TIAN. Traffic accident prediction model of mountain highways based on selection integration [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1298-1306. |
| [7] | Hao YUE,Xiao CHANG,Jian-ye LIU,Qiu-shi QU. Customized bus route optimization with vehicle window [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1266-1274. |
| [8] | Wen-jing WU,Chun-chun DENG,Hong-fei JIA,Shu-hang SUN. Evaluation of road network unblocked reliability and identification of critical sections under influence of flooding [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1250-1257. |
| [9] | Yu-ran LI,Fei WANG,Cai-hua ZHU,Fei HAN,Yan LI. Chain-effect utility of factors influencing residents' commuting mode choice in polluted weather [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 577-590. |
| [10] | Tian-yang GAO,Da-wei HU,Rui-sen JIANG,Xue WU,Hui-tian LIU. Optimization study of zonal-based flexible feeder bus routes based on modular vehicle system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 537-545. |
| [11] | Shu-hong MA,Jun-jie ZHANG,Xi-fang CHEN,Guo-mei LIAO. Identifying urban functional structures using time-series taxi data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 603-613. |
| [12] | Da-yi QU,Shou-chen DAI,Yi-cheng CHEN,Shan-ning CUI,Yu-xiang YANG. Modeling of vehicle game cut-out and merging behavior based on trajectory data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(10): 3208-3220. |
| [13] | Hui-zhi XU,Shi-sen JIANG,Xiu-qing WANG,Shuang CHEN. Vehicle target detection and ranging in vehicle image based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 185-197. |
| [14] | Chang-jiang ZHENG,Tong-tong TAO,Zhi-chao CHEN. Cascading failure model based on adjustable redistribution of traffic flow [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2441-2450. |
| [15] | Yun-juan YAN,Wei-xiong ZHA,Jun-gang SHI,Li-ping YAN. Double layer optimization model of charging pile based on random charging demand [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2238-2244. |
|
||