吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 855-865.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250401
• 基础研究 • 下一篇
右美托咪定对肠源性脓毒症大鼠小肠黏膜损伤的改善作用及其机制
- 1.昆明医科大学第一附属医院麻醉科,云南 昆明 650000
2.云南省文山州人民医院心血管外科,云南 文山 663000
Protective effect of dexmedetomidine on intestinal mucosal injury in rats with enterogenous sepsis and its mechanism
Kun YANG1,Qianyao FU1,Yongqiang SUN1,Kun YANG1,Jun MENG2( )
)
- 1.Department of Anesthesiology,First Affiliated Hospital,Kunming Medical University,Kunming 650000,China
2.Department of Cardiovascular Surgery,People’s Hospital,Wenshan Prefecture,Yunan Province,Wenshan 663000,China
摘要:
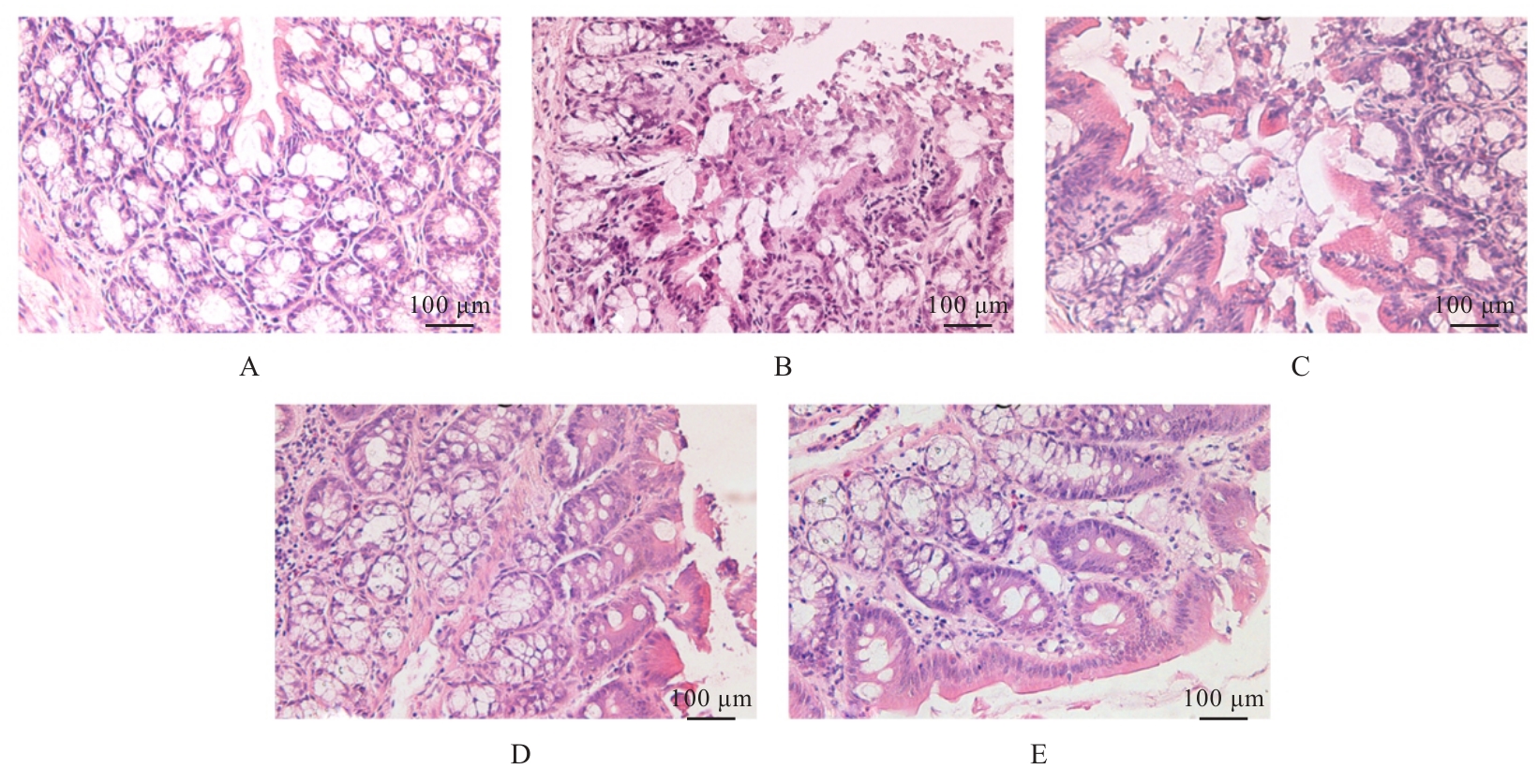
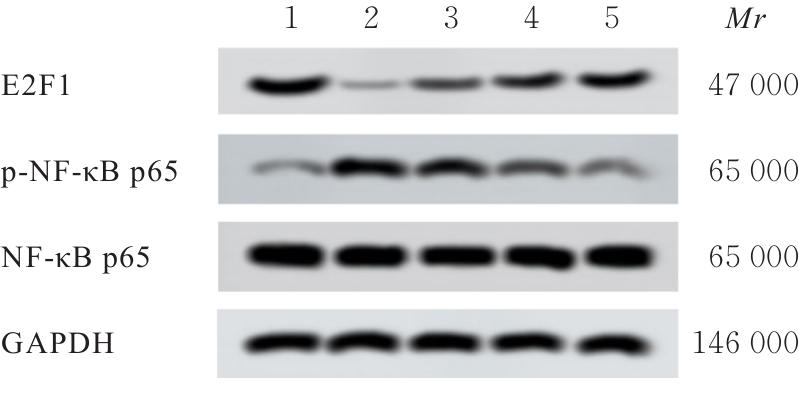
目的 探讨右美托咪定(DEX)对保护肠源性脓毒症大鼠肠道功能的影响,并基于E2F转录因子1(E2F1)/核因子κB(NF-κB)信号通路初步探讨其潜在作用机制。 方法 60只SD大鼠,其中50只大鼠以盲肠结扎穿孔法建立肠源性脓毒症大鼠模型,其余10只大鼠作为假手术组,假手术组大鼠仅分离盲肠远端,不结扎和穿孔。将40只造模成功的大鼠随机分为模型组、低剂量DEX组、中剂量DEX组和高剂量DEX组,每组10只。低、中和高剂量DEX组大鼠即刻腹腔注射20、40及60 μg·kg-1 DEX,假手术组和模型组大鼠腹腔注射等剂量生理盐水。给药24 h后检测各组大鼠肠道肌电活动情况,检测各组大鼠盲肠中大肠埃希菌、乳酸杆菌和双歧杆菌菌落数,HE染色检测各组大鼠小肠组织的病理形态表现,试剂盒检测各组大鼠小肠组织匀浆上清中分泌型免疫球蛋白A(sIgA)水平和血清中二胺氧化酶(DAO)及D-乳酸水平,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测各组大鼠小肠组织中巨噬细胞极化标志物mRNA表达水平,Western blotting法检测各组大鼠小肠组织中巨噬细胞极化标志物和E2F1、磷酸化NF-κB p65(p-NF-κB p65)及NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平。 结果 与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠肠道平滑肌慢波频率和振幅降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低剂量DEX组大鼠肠道平滑肌慢波振幅升高(P<0.05),中和高剂量DEX组大鼠肠道平滑肌慢波频率及振幅升高(P<0.05);与低剂量DEX组比较,中和高剂量DEX组大鼠肠道平滑肌慢波频率及振幅升高(P<0.05);与中剂量DEX组比较,高剂量DEX组大鼠肠道平滑肌慢波频率和振幅升高(P<0.05)。与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠肠道大肠埃希菌菌落数增加(P<0.05),双歧杆菌和乳酸杆菌菌落数减少(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低剂量DEX组大鼠肠道双歧杆菌菌落数增加(P<0.05),中和高剂量DEX组大鼠肠道大肠埃希菌菌落数减少(P<0.05),双歧杆菌和乳酸杆菌菌落数增加(P<0.05);与低剂量DEX组比较,中和高剂量DEX组大鼠肠道大肠埃希菌菌落数减少(P<0.05),双歧杆菌和乳酸杆菌菌落数增加(P<0.05);与中剂量DEX组比较,高剂量DEX组大鼠肠道大肠埃希菌菌落数减少(P<0.05),双歧杆菌和乳酸杆菌菌落数增加(P<0.05)。HE染色,假手术组大鼠小肠黏膜组织结构正常且完好;模型组大鼠小肠黏膜上皮细胞坏死,绒毛受损、塌陷、排列紊乱;与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量DEX组大鼠小肠组织的病理学明显改善。与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠小肠组织匀浆上清中sIgA水平降低(P<0.05),血清中DAO和D-乳酸蛋白水平升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低剂量DEX组大鼠血清中DAO水平降低(P<0.05),中和高剂量DEX组大鼠小肠组织匀浆上清中sIgA水平升高(P<0.05),血清中DAO和D-乳酸蛋白水平降低(P<0.05);与低剂量DEX组比较,中和高剂量DEX组大鼠小肠组织匀浆上清中sIgA水平升高(P<0.05),血清中DAO和D-乳酸蛋白水平降低(P<0.05);与中剂量DEX组比较,高剂量DEX组大鼠小肠组织匀浆上清中sIgA水平升高(P<0.05),血清中DAO和D-乳酸蛋白水平降低(P<0.05)。与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠小肠组织中CD86、单核细胞趋化蛋白1(MCP-1)和CD80 mRNA及蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05),CD206、白细胞介素(IL-4)和CD163 mRNA及蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低剂量DEX组大鼠小肠组织中CD80 mRNA、CD86蛋白和MCP-1蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05),IL-4 mRNA、CD163 mRNA、CD206蛋白和CD163蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05),中和高剂量DEX组大鼠小肠组织中CD86、MCP-1和CD80 mRNA及蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05),CD206、IL-4和CD163 mRNA及蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05);与低剂量DEX组比较,中和高剂量DEX组大鼠小肠组织中CD86、MCP-1和CD80 mRNA及蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05),CD206、IL-4和CD163 mRNA及蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05);与中剂量DEX组比较,高剂量DEX组大鼠小肠组织中CD86、MCP-1和CD80 mRNA及蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05),CD206、IL-4和CD163 mRNA及蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05)。与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠小肠组织中E2F1蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05),p-NF-κB p65/NF-κB p65比值升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量DEX组大鼠小肠组织中E2F1蛋白表达水平和p-NF-κB p65/NF-κB p65比值降低(P<0.05);与低剂量DEX组比较,中和高剂量DEX组大鼠小肠组织中E2F1蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05),p-NF-κB p65/NF-κB p65比值降低(P<0.05);与中剂量DEX组比较,高剂量DEX组大鼠小肠组织中E2F1蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05),p-NF-κB p65/NF-κB p65比值降低(P<0.05)。 结论 DEX对肠源性脓毒症大鼠小肠黏膜损伤具有改善作用,并促进小肠组织中巨噬细胞向M2型极化转变,其机制可能与DEX调控E2F1/NF-κB信号通路有关。
中图分类号:
- R614