吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (6): 1137-1142.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20200605
M1型巨噬细胞对慢性牙周炎模型小鼠免疫状态的影响
- 1.锦州医科大学附属第二医院牙周黏膜科,辽宁 锦州 121000
2.锦州医科大学附属第一医院脑与脊髓损伤 重点实验室,辽宁 锦州 121000
Effect of M1 macrophages on immune status in chronic periodontitis model mice
Chen JI1,Wenjuan ZHANG1,Ning GUAN2,Xiuqiu GAO1,Linyuan WANG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Periodontics and Mucosa,Second Affiliated Hospital,Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121000,China
2.Key Laboratory of Brain and Spinal Cord Injury,First Affiliated Hospital,Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121000,China
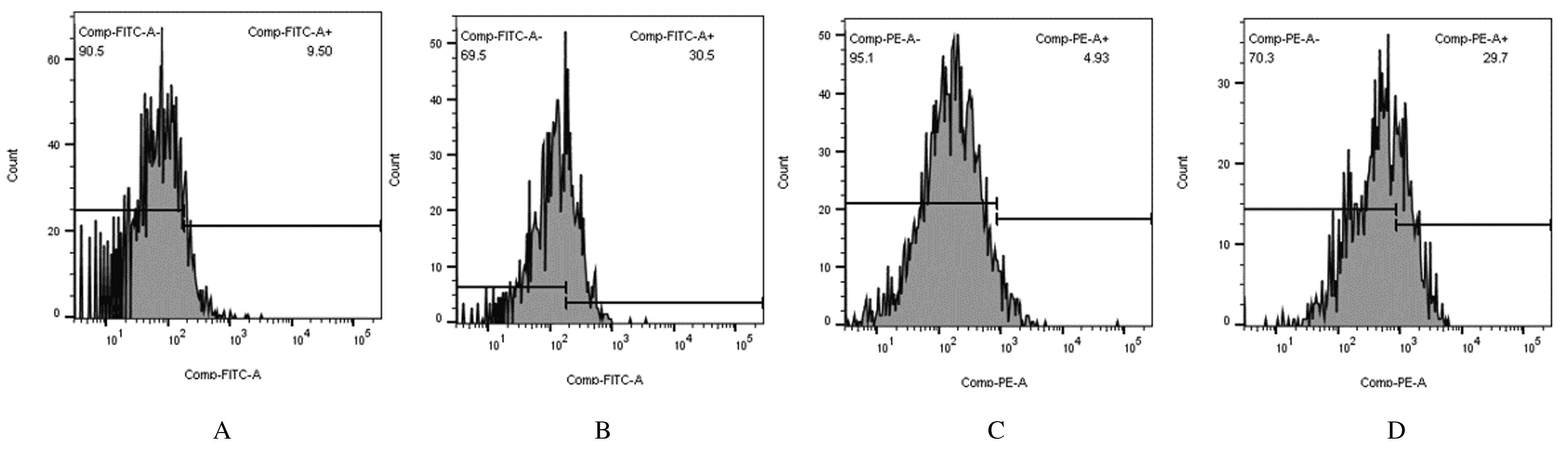
摘要: 探讨M1型巨噬细胞对牙龈卟啉单胞菌诱导的慢性牙周炎模型小鼠免疫状态的影响,阐明M1型巨噬细胞在慢性牙周炎中的作用。 10只7周龄C57BL/6雌性小鼠随机分为对照组(n=5)和慢性牙周炎组(n=5)。以牙龈卟啉单胞菌涂抹小鼠口腔建立慢性牙周炎模型。测量2组小鼠从釉牙骨质界(CEJ)到牙槽嵴顶(ABC)的距离,评价牙槽骨吸收情况;HE染色法观察2组小鼠牙周组织中炎性细胞浸润、结缔组织附着丧失和牙槽骨吸收情况;流式细胞术检测2组小鼠牙龈组织中F4/80+iNOS+ M1型巨噬细胞百分率和细胞数;实时定量PCR法检测2组小鼠牙龈组织中M1型巨噬细胞相关因子iNOS mRNA表达水平。 与对照组比较,慢性牙周炎组小鼠CEJ至ABC的距离明显增加(P<0.01);与对照组比较,慢性牙周炎组小鼠牙龈结合上皮附着位于CEJ的根方,ABC吸收变平,可见破骨细胞和骨吸陷窝形成;慢性牙周炎小鼠牙龈组织中M1型巨噬细胞百分率和细胞数明显高于对照组(P<0.01);慢性牙周炎小鼠牙龈组织中iNOS mRNA表达水平高于对照组(P<0.01)。 在慢性牙周炎小鼠模型中,M1型巨噬细胞介导的免疫应答增强,M1型巨噬细胞参与慢性牙周炎的炎症反应和组织损伤。
中图分类号:
- R781.42