吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (5): 1187-1193.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210515
人脐带间充质干细胞对宫颈癌HeLa细胞增殖和凋亡的影响及其作用机制
- 河南大学淮河医院妇科, 河南 开封 475000
Effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer HeLa cells and its mechanism
Chen WANG( ),Jun TIAN,Hailing CHENG
),Jun TIAN,Hailing CHENG
- Department of Gynecology,Huaihe Hospital,Henan University,Kaifeng 475000,China
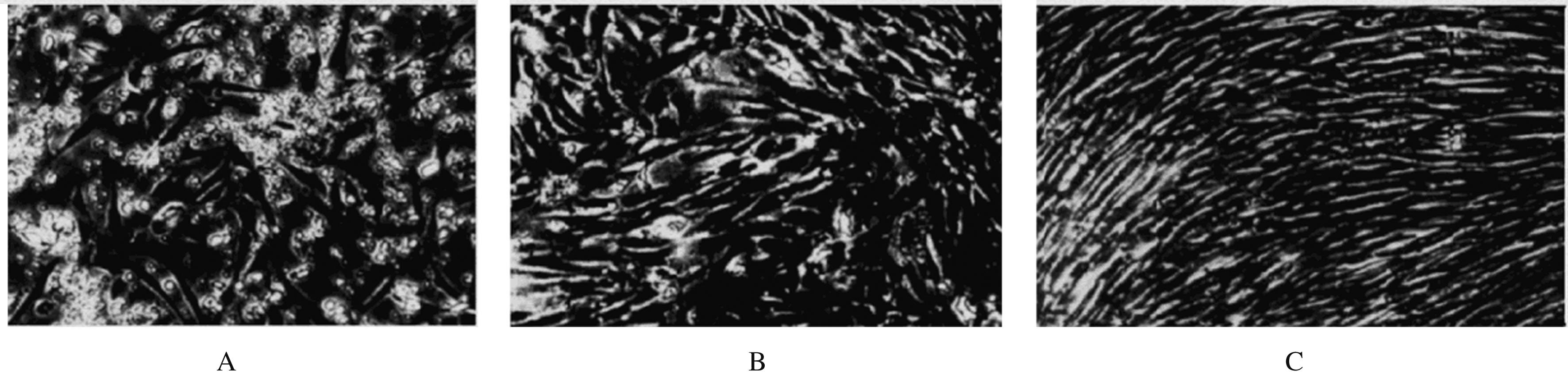
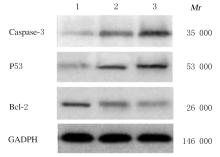
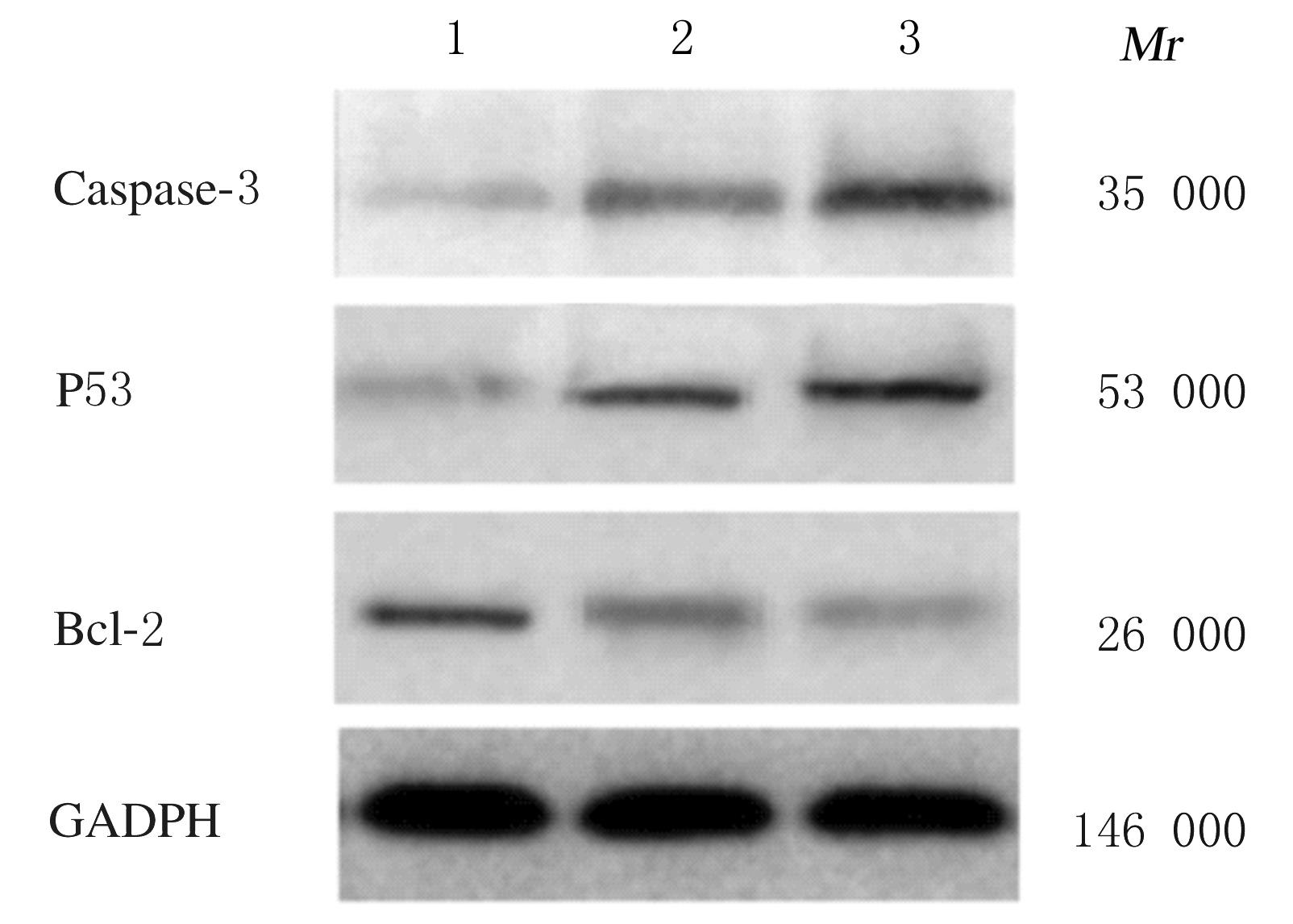
摘要: 探讨人脐带间充质干细胞(MSCs)对宫颈癌HeLa细胞增殖和凋亡的影响,阐明其可能的作用机制。 分离培养人脐带MSCs,采用光学显微镜观察细胞形态表现,并采用流式细胞仪分析鉴定其表面抗原标记物CD90、CD105、CD34和CD45的表达,以未加一抗仅加二抗的MSCs为平行对照组。将20%和60%浓度的MSCs条件培养基和宫颈癌HeLa细胞共培养72 h,集落形成实验观察MSCs条件培养基作用下HeLa细胞集落的形成能力;CCK-8实验检测HeLa细胞增殖抑制率;流式细胞术检测HeLa细胞凋亡率;蛋白质印迹法检测MSCs条件培养基作用下HeLa细胞增殖和凋亡相关基因蛋白表达水平。 脐带分离细胞接种72 h后有少量细胞贴壁,1周后逐渐变成扁平单层细胞,呈簇状和旋涡状生长,伴随细胞密度增加,细胞体随之变细长,形态与成纤维细胞类似。MSCs细胞表面抗原标记物CD90和CD105呈阳性表达,CD34和CD45呈阴性表达,符合干细胞表型。集落形成实验,加入20%和60%的MSCs条件培养基,宫颈癌HeLa细胞集落形成的抑制率分别为18.56%和37.64%。与对照组比较,MSCs处理48 h后宫颈癌HeLa细胞早期凋亡率升高(P<0.05)。MSCs处理0、24和48 h后HeLa细胞中半胱天冬氨酸蛋白酶3(caspase-3)和P53蛋白表达水平持续升高(P<0.05),B细胞淋巴瘤2(Bcl-2)蛋白相对表达水平持续降低(P<0.05)。 MSCs体外可抑制宫颈癌HeLa细胞增殖,并诱导HeLa细胞凋亡,其机制可能与上调促凋亡分子caspase-3与P53表达、下调抗凋亡因子Bcl-2表达有关。
中图分类号:
- R285.5