吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 355-363.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240208
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
非小细胞肺癌A549细胞基因组不稳定性和MYC基因突变在吉西他滨耐药中的作用
- 1.海南医学院第二附属医院药学部,海南 海口 570311
2.海南医学院第二附属医院呼吸科,海南 海口 570311
3.海南医学院第一附属医院药学部,海南 海口 570216
4.海口市第四人民医院体检科,海南 海口 571100
Effects of genomic instability and MYC gene mutation of non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells on resistance of gemcitabine
Zongjun CHEN1,Yahong CHEN2( ),Liyun HUANG3,Ziying LIANG4
),Liyun HUANG3,Ziying LIANG4
- 1.Department of Pharmacy,Second Affiliated Hospital,Hainan Medical College,Haikou 570311,China
2.Department of Respiratory,Second Affiliated Hospital,Hainan Medical College,Haikou 570311,China
3.Department of Pharmacy,First Affiliated Hospital,Hainan Medical College,Haikou 570216,China
4.Department of Physical Examination,Fourth People’s Hospital,Haikou City,Haikou 571100,China
摘要:
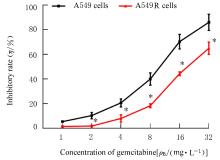
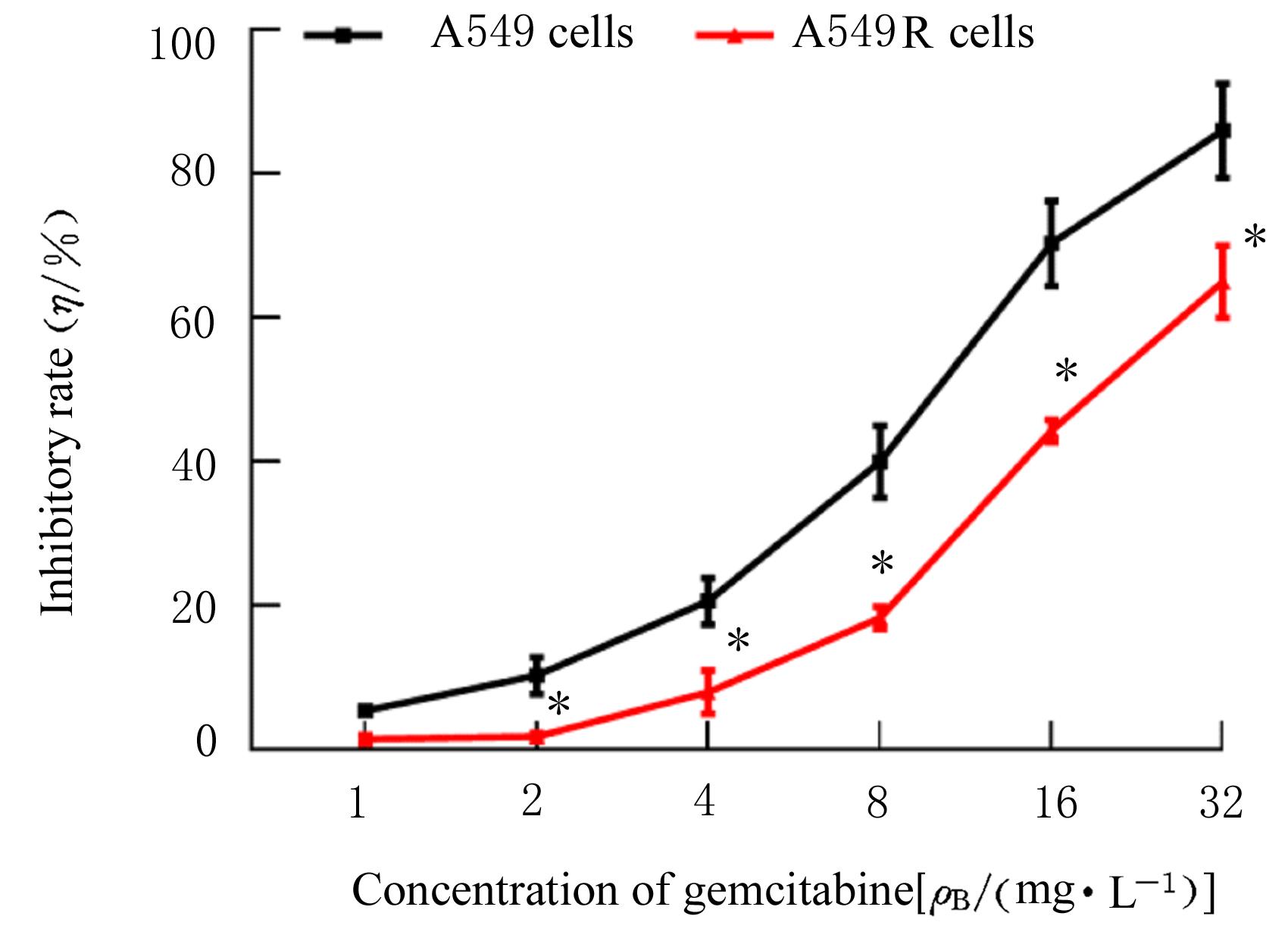
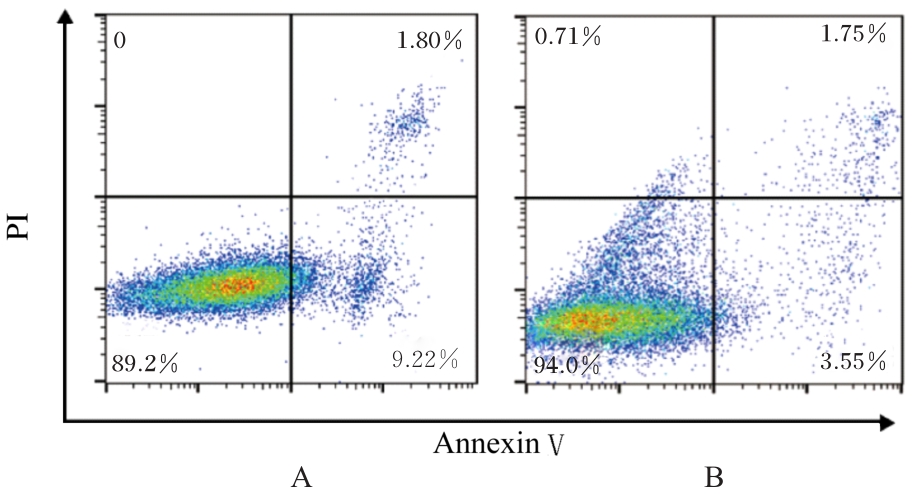
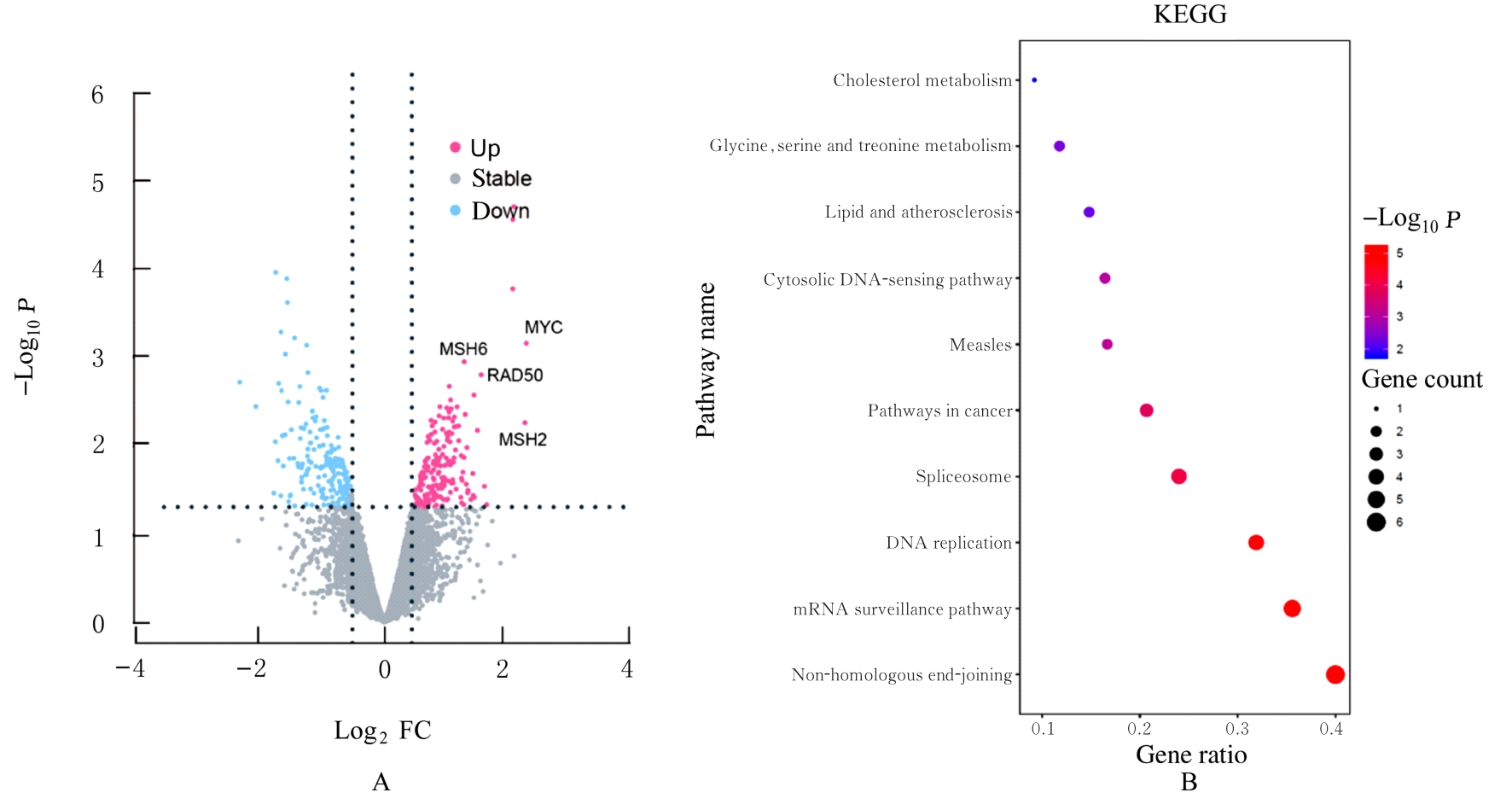
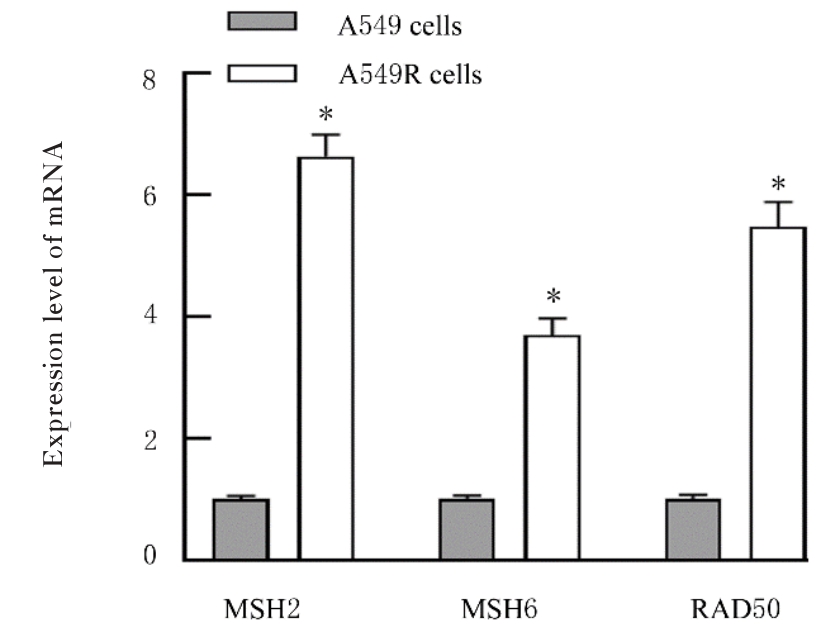
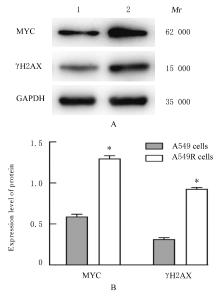
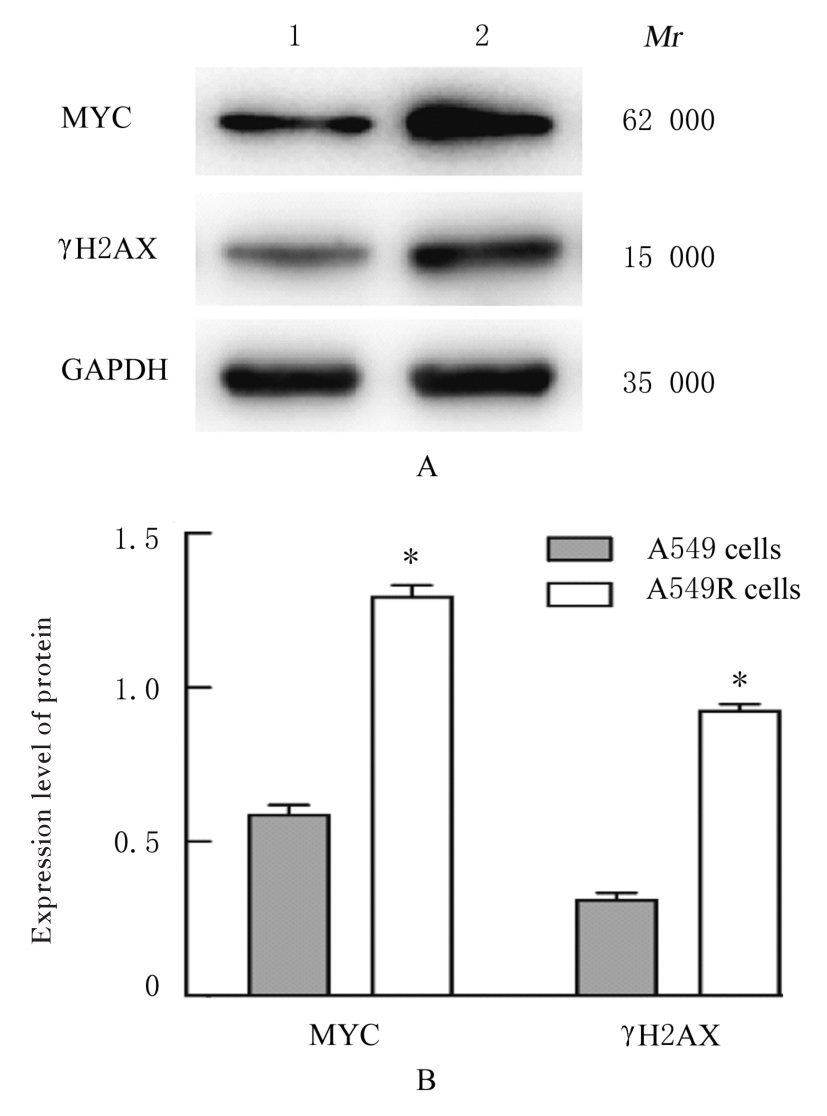
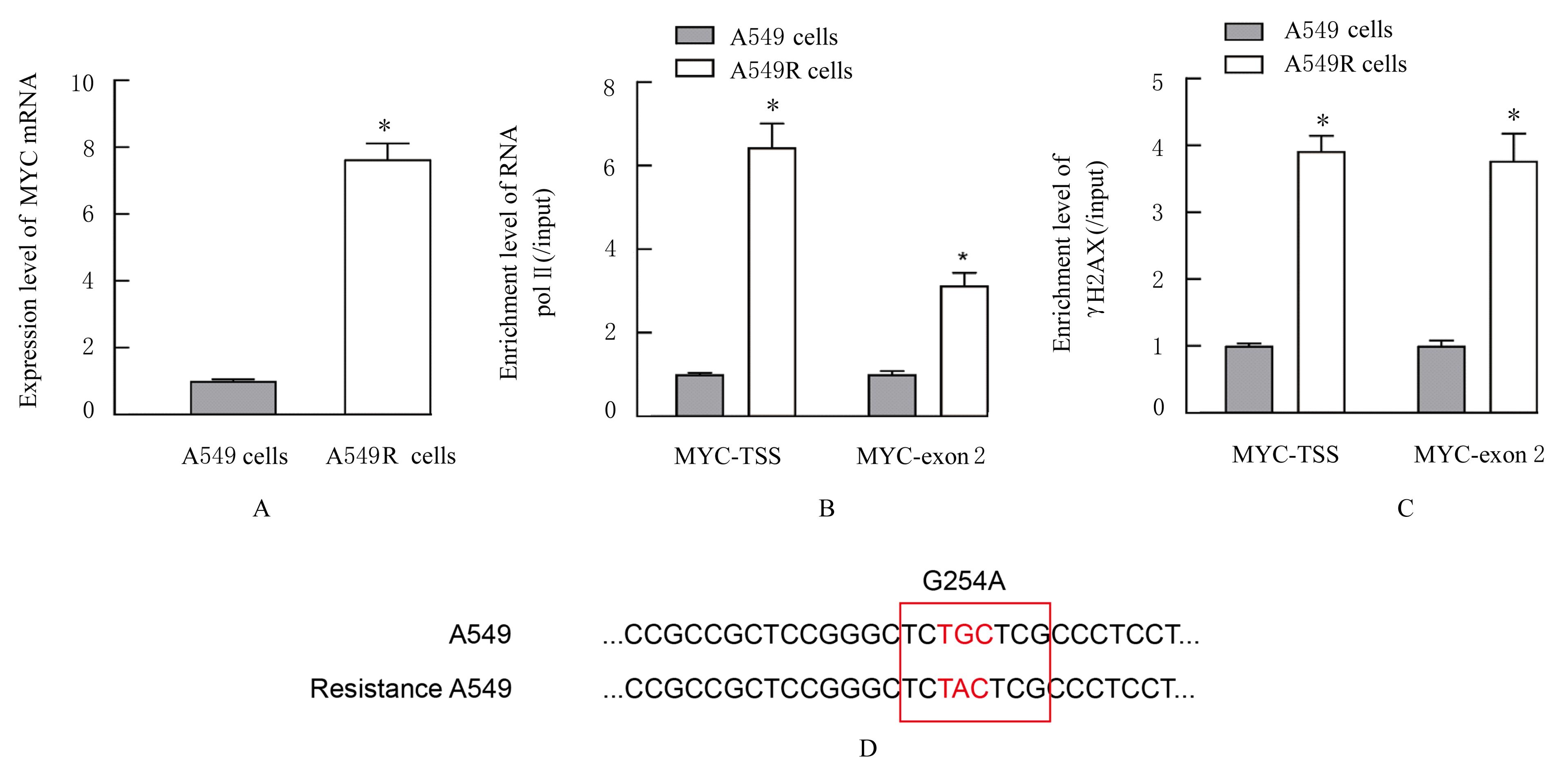
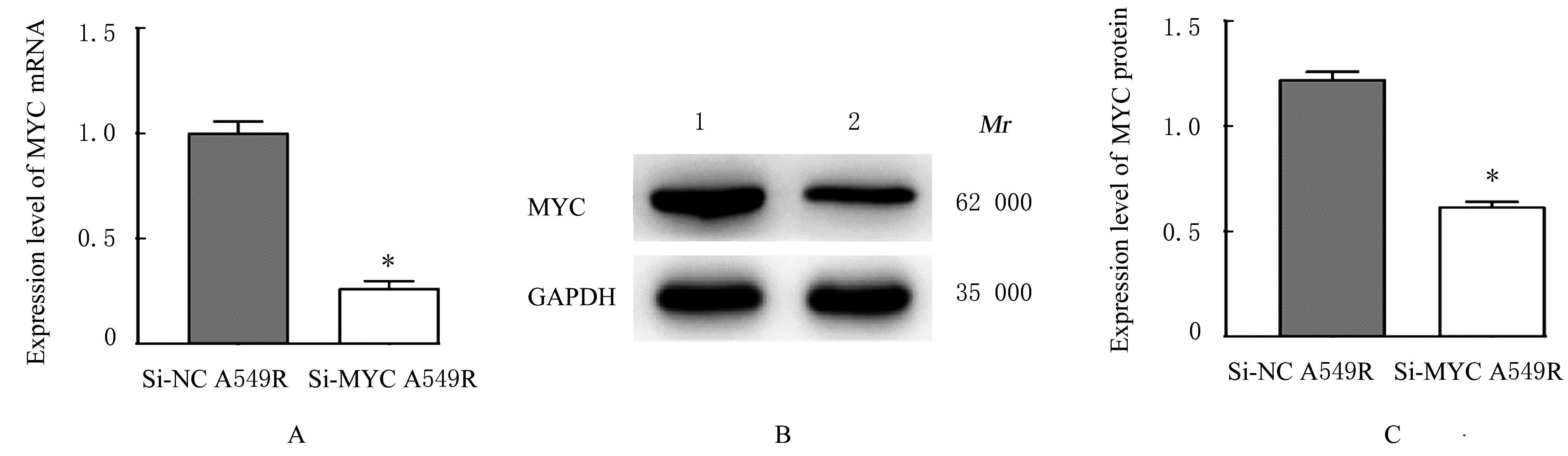
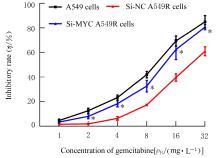
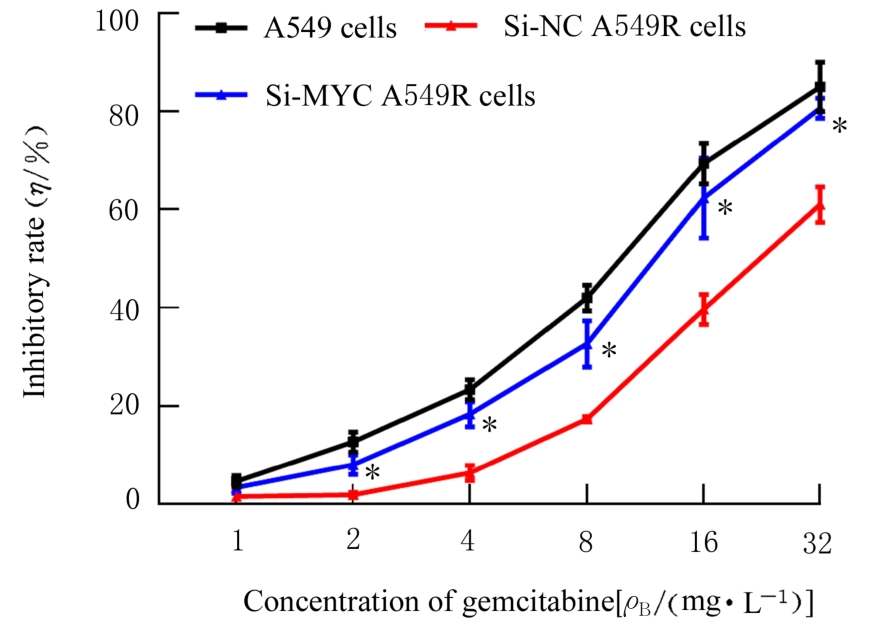
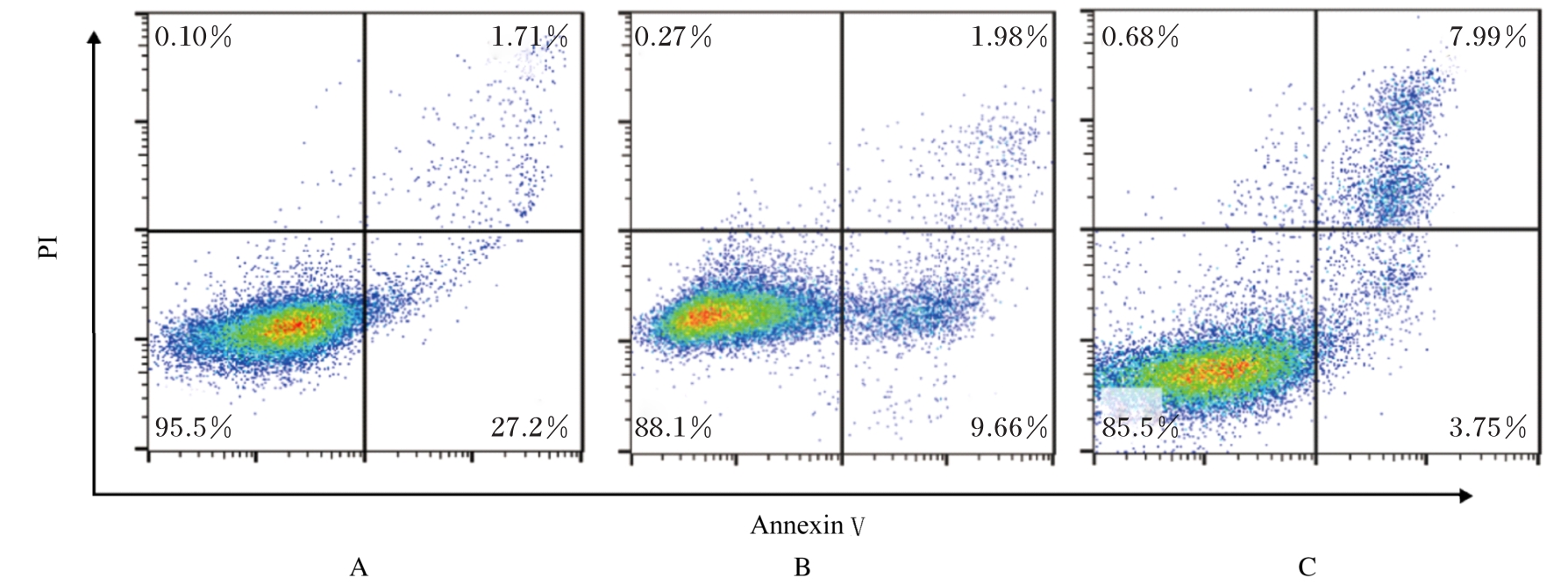
目的 探讨非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)A549细胞基因不稳定性和MYC基因突变在吉西他滨耐药中的作用,并阐明其作用机制。 方法 采用2 mg·L-1吉西他滨持续作用A549细胞(A549组),构建耐药细胞株A549R(A549R组),并将si-NC和si-MYC转染至A549R细胞,作为si-NC A549R组和si-MYC A549R组。采用CCK-8法检测不同浓度(0、1、2、4、8、16和32 mg·L-1)吉西他滨对各组细胞的抑制率,流式细胞术检测各组细胞凋亡率。转录组测序技术(RNA-seq)和京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)信号通路富集分析A549组及A549R组细胞中的差异表达基因,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测A549组和A549R组细胞中基因组不稳定性相关基因错配修复基因2(MSH2)、错配修复基因6(MSH6)和DNA修复蛋白RAD50(RAD50)的表达水平,Western blotting法检测基因组不稳定性相关蛋白MYC原癌基因(MYC)和磷酸化组蛋白(γH2AX)的表达水平,染色质免疫共沉淀(ChIP)法检测RNA polⅡ和γH2AX在MYC基因上的富集程度,PCR法扩增并检测A549R细胞MYC基因突变情况。 结果 与A549组比较,2、4、8、16和32 mg·L-1吉西他滨作用后A549R组细胞抑制率降低(P<0.05),8 mg·L-1吉西他滨作用后细胞凋亡率降低(P<0.05)。与A549组比较,A549R组细胞中有234个mRNAs表达水平升高,205个mRNAs表达水平降低,其中错配修复相关基因(MSH2和MSH6)、RAD50和MYC表达水平明显升高(P<0.05)。KEGG信号通路富集分析,表达水平升高基因主要参与非同源末端连接、mRNA监测途径和DNA复制等信号通路。与A549组比较,A549R组细胞中MYC和γH2AX蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05)。ChIP法检测,RNA pol Ⅱ和γH2AX在MYC转录起始位点及exon 2上富集程度增加,MYC exon 2上存在G254A基因突变。与si-NC A549R组比较,si-MYC A549R组细胞中MYC mRNA和蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05),2、4、8、16和32 mg·L-1吉西他滨作用后si-MYC A549R组细胞抑制率升高(P<0.05),细胞凋亡率增加(P<0.05)。 结论 对吉西他滨耐药的NSCLC细胞中A549R基因组不稳定性增加,MYC基因发生突变和扩增,而敲减MYC可以恢复A549R细胞对吉西他滨的敏感性。
中图分类号:
- R734.2