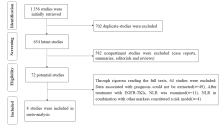
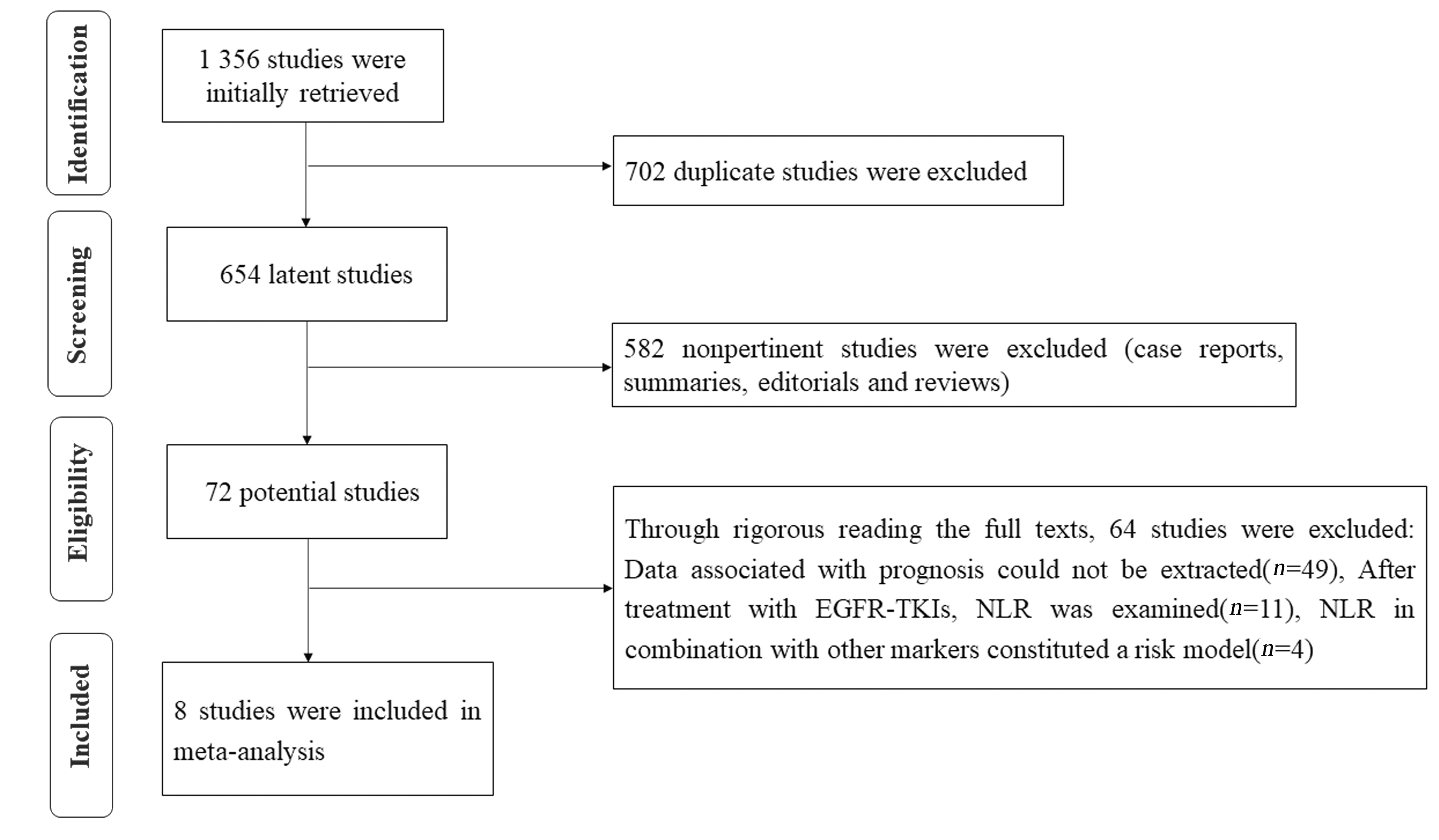
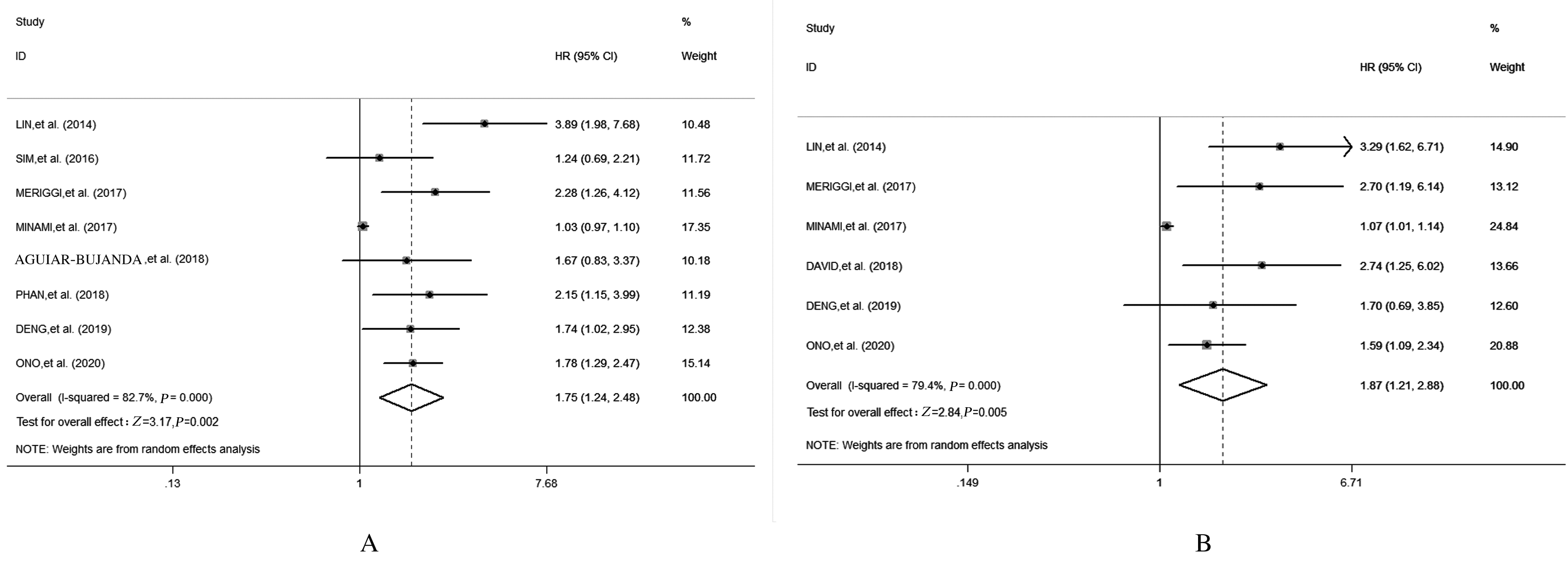
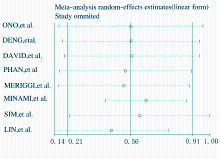
| 1 |
GLOBAL BURDEN OF DISEASE CANCER COLLABORATION, FITZMAURICE C, ALLEN C, et al. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2017, 3(4): 524-548.
|
| 2 |
SIEGEL R, DESANTIS C, VIRGO K, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2012, 62(4): 220-241.
|
| 3 |
孙洪帅, 朱 华, 高海燕, 等. 肿瘤标志物SCC-Ag、CEA、CYFRA21-1和D-二聚体联合检测对非小细胞肺癌的早期诊断价值[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2018, 44(5): 1020-1024.
|
| 4 |
周文盛, 张 伟, 韩宝惠. EGFR基因20外显子插入突变在非小细胞肺癌的研究及其进展[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2020, 23(2): 118-126.
|
| 5 |
ZHOU C C, WU Y L, CHEN G Y, et al. BEYOND: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, phase Ⅲ study of first-line carboplatin/paclitaxel plus bevacizumab or placebo in Chinese patients with advanced or recurrent nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2015, 33(19): 2197-2204.
|
| 6 |
NORMANDO S R, CRUZ F M, GIGLIO A D E L. Cumulative meta-analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors as first-line therapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Anticancer Drugs, 2015, 26(9): 995-1003.
|
| 7 |
徐小峰, 戴宏宇, 乔建兵, 等. 外周血NLR和PLR评估晚期非小细胞肺癌一线含铂双药化疗疗效和预后的价值[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2020, 28(15): 2627-2631.
|
| 8 |
LIU J X, LI A, ZHOU L Y, et al. Significance of combined preoperative serum Alb and dNLR for diagnosis of pancreatic cancer[J]. Future Oncol, 2018, 14(3): 229-239.
|
| 9 |
CHEN L, ZHANG F, SHENG X G, et al. Peripheral platelet/lymphocyte ratio predicts lymph node metastasis and Acts as a superior prognostic factor for cervical cancer when combined with neutrophil: Lymphocyte[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2016, 95(32): e4381.
|
| 10 |
谢明明. 术前中性粒细胞/淋巴细胞比值在非转移性结肠癌预后中的价值[D]. 福州:福建医科大学,2019.
|
| 11 |
ONO T, IGAWA S, KURAHAYASHI S, et al. Impact of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors[J]. Invest New Drugs, 2020, 38(3): 885-893.
|
| 12 |
DENG C, ZHANG N, WANG Y P, et al. High systemic immune-inflammation index predicts poor prognosis in advanced lung adenocarcinoma patients treated with EGFR-TKIs[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2019, 98(33): e16875.
|
| 13 |
SIM S H, BEOM S H, AHN Y O, et al. Pretreatment neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio is not a significant prognostic factor in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2016, 7(2): 161-166.
|
| 14 |
LIN G N, PENG J W, LIU P P, et al. Elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts poor outcome in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer receiving first-line gefitinib or erlotinib treatment[J]. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol, 2017, 13(5): e189-e194.
|
| 15 |
AGUIAR-BUJANDA D, DUEÑAS-COMINO A, SAURA-GRAU S, et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in European patients with epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small cell lung cancer treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors[J]. Oncol Res Treat, 2018, 41(12): 755-761.
|
| 16 |
PHAN T T, HO T T, NGUYEN H T, et al. The prognostic impact of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with EGFR TKI[J]. Int J Gen Med, 2018, 11: 423-430.
|
| 17 |
MERIGGI F, CODIGNOLA C, BERETTA G D, et al. Significance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in Western advanced EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer receiving a targeted therapy[J]. Tumori J, 2017, 103(5): 443-448.
|
| 18 |
MINAMI S, OGATA Y, IHARA S, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts overall survival of advanced non-small cell lung cancer harboring mutant epidermal growth factor receptor[J]. World J Oncol, 2017, 8(6): 180-187.
|
| 19 |
凌丰宇, 李 明, 陈青娟, 等. 贝伐珠单抗联合第一代表皮生长因子受体-酪氨酸激酶抑制剂一线治疗EGFR基因突变阳性晚期非小细胞肺癌的Meta分析[J]. 肿瘤, 2020, 40(5): 339-347.
|
| 20 |
DENARDO D G, COUSSENS L M. Inflammation and breast cancer. Balancing immune response: crosstalk between adaptive and innate immune cells during breast cancer progression[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2007, 9(4): 212.
|
| 21 |
HANAHAN D, WEINBERG R A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation[J]. Cell, 2011, 144(5): 646-674.
|
| 22 |
YANG J J, HU Z G, SHI W X, et al. Prognostic significance of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21(9): 2807-2815.
|
| 23 |
DE LARCO J E, WUERTZ B R, FURCHT L T. The potential role of neutrophils in promoting the metastatic phenotype of tumors releasing interleukin-8[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2004, 10(15): 4895-4900.
|
| 24 |
TURAN N, EDWARDS M J, BATES S, et al. IL-6 pathway upregulation in subgroup of severe asthma is associated with neutrophilia and poor lung function[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2018, 48(4): 475-478.
|
| 25 |
ROTONDO R, BERTOLOTTO M, BARISIONE G, et al. Exocytosis of azurophil and arginase 1-containing granules by activated polymorphonuclear neutrophils is required to inhibit T lymphocyte proliferation[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2011, 89(5): 721-727.
|
| 26 |
BALERMPAS P, RÖDEL F, WEISS C, et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes favor the response to chemoradiotherapy of head and neck cancer[J]. Oncoimmunology, 2014, 3(1): e27403.
|
| 27 |
ZIKOS T A, DONNENBERG A D, LANDRENEAU R J, et al. Lung T-cell subset composition at the time of surgical resection is a prognostic indicator in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2011, 60(6): 819-827.
|
| 28 |
童晶涛, 张欢乐, 郑 璐, 等. 血小板和淋巴细胞的比值、中性粒细胞和淋巴细胞的比值与非小细胞肺癌的临床病理学关系及预后效果研究[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2019, 29(24): 3020-3023.
|
| 29 |
陈浩然, 薛 昊, 刘文静, 等. 血小板淋巴细胞比值作为非小细胞肺癌预后因素的meta分析[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2019, 22(5): 289-298.
|
| 30 |
于秀艳, 万广财, 孙洪帅, 等. 纤维蛋白原与乳腺癌患者预后关系的Meta分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2019, 45(5): 1092-1097.
|
 )
)