吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 881-890.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240401
• 基础研究 • 下一篇
基于M2型巨噬细胞来源的Siglec15对食管鳞癌细胞恶性生物学行为影响的生物信息学分析及实验验证
任祎琳1,臧翌辰1,薛乐乐1,杨凯歌1,陈素芳1,王魏楠1,罗成华1,梁伟华1,王良海1,李锋1,胡建明1,2( )
)
- 1.石河子大学第一附属医院病理科,新疆 石河子 832002
2.石河子大学医学院病理学系,新疆 石河子 832002
Bioinformatics analysis based on effect of M2 macrophage-derived Siglec15 on malignant biological behaviour of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells and its experimental validation
Yilin REN1,Yichen ZANG1,Lele XUE1,Kaige YANG1,Sufang CHEN1,Weinan WANG1,Chenghua LUO1,Weihua LIANG1,Lianghai WANG1,Feng LI1,Jianming HU1,2( )
)
- 1.Department of Pathology, First Affiliated Hospital, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832002, China
2.Department of Patholegy, School of Medical Sciences, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832002, China
摘要:
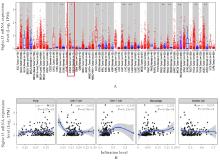
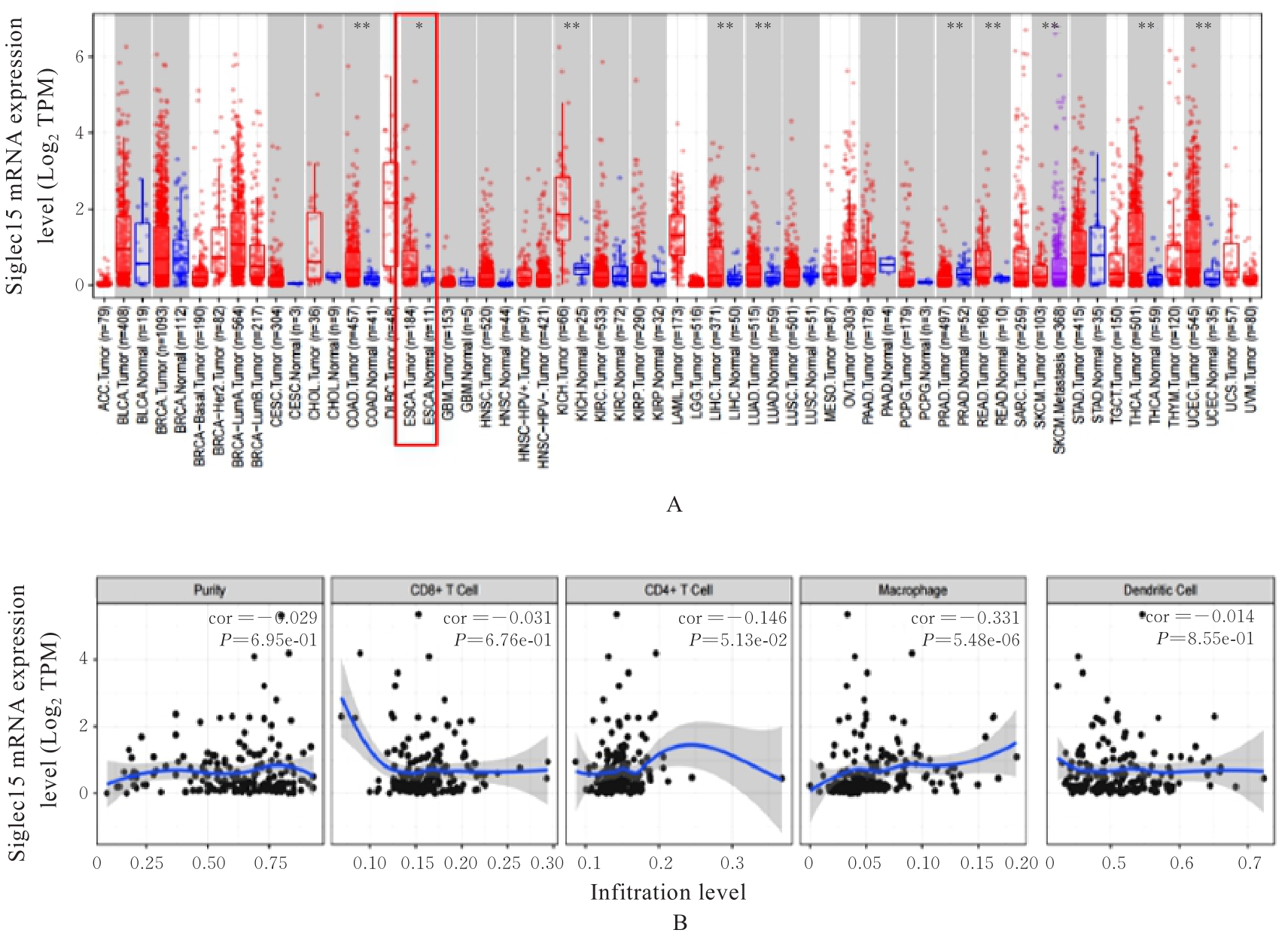
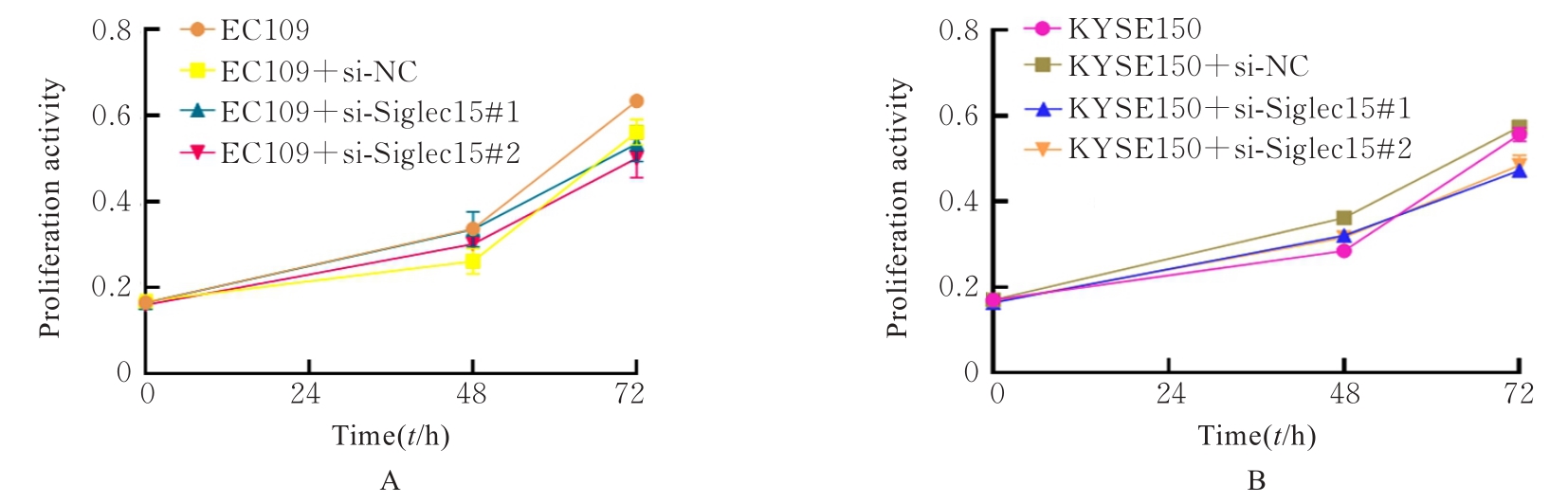
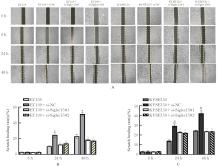
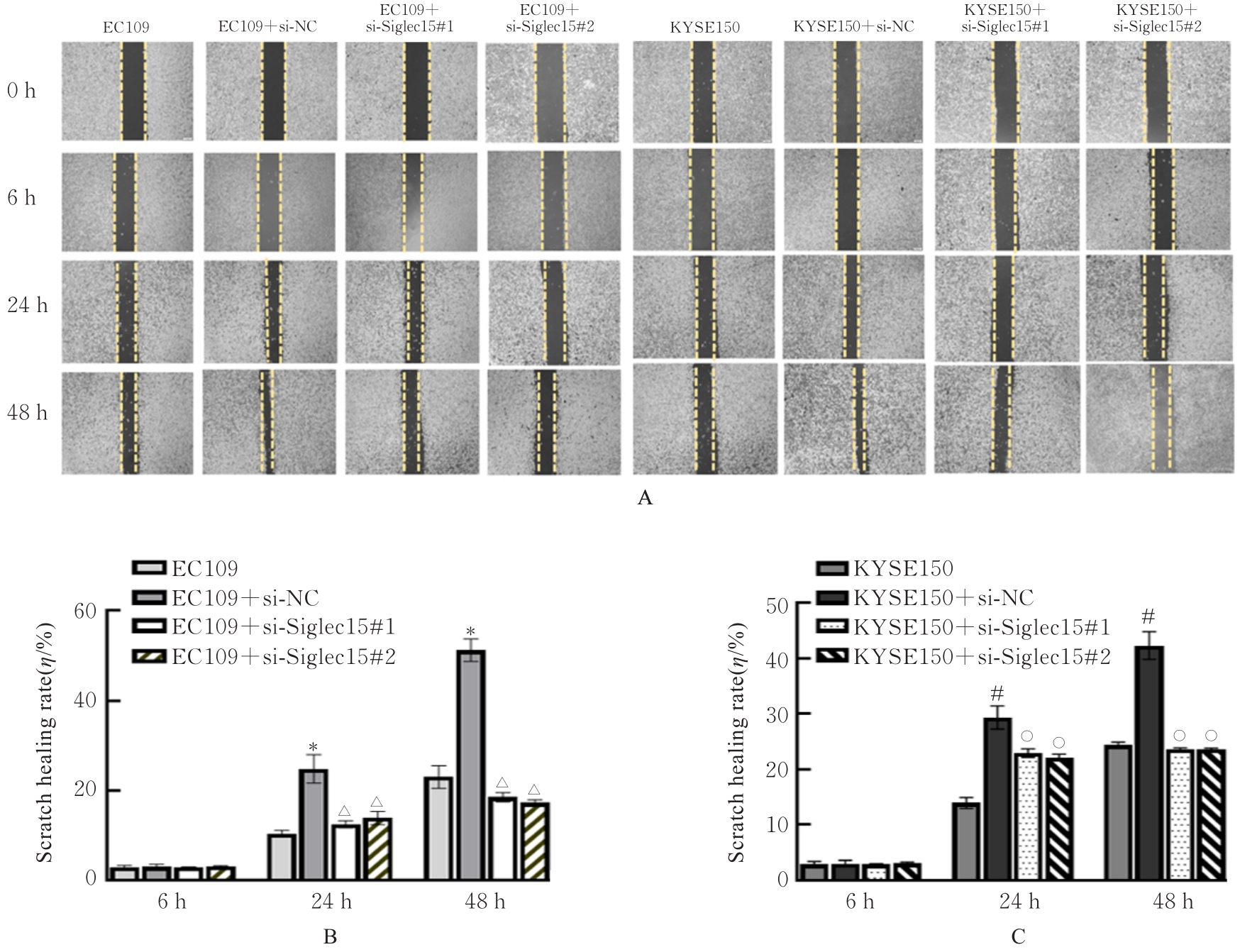
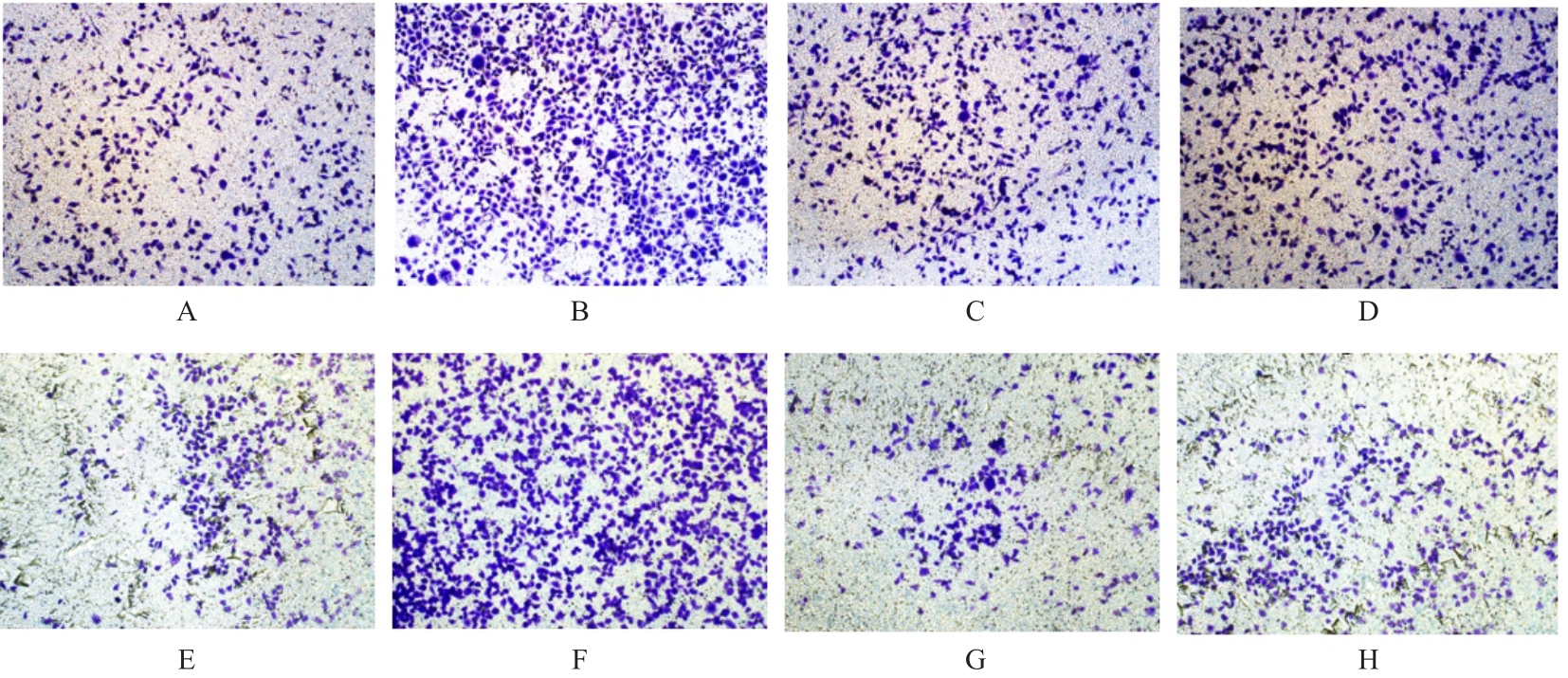
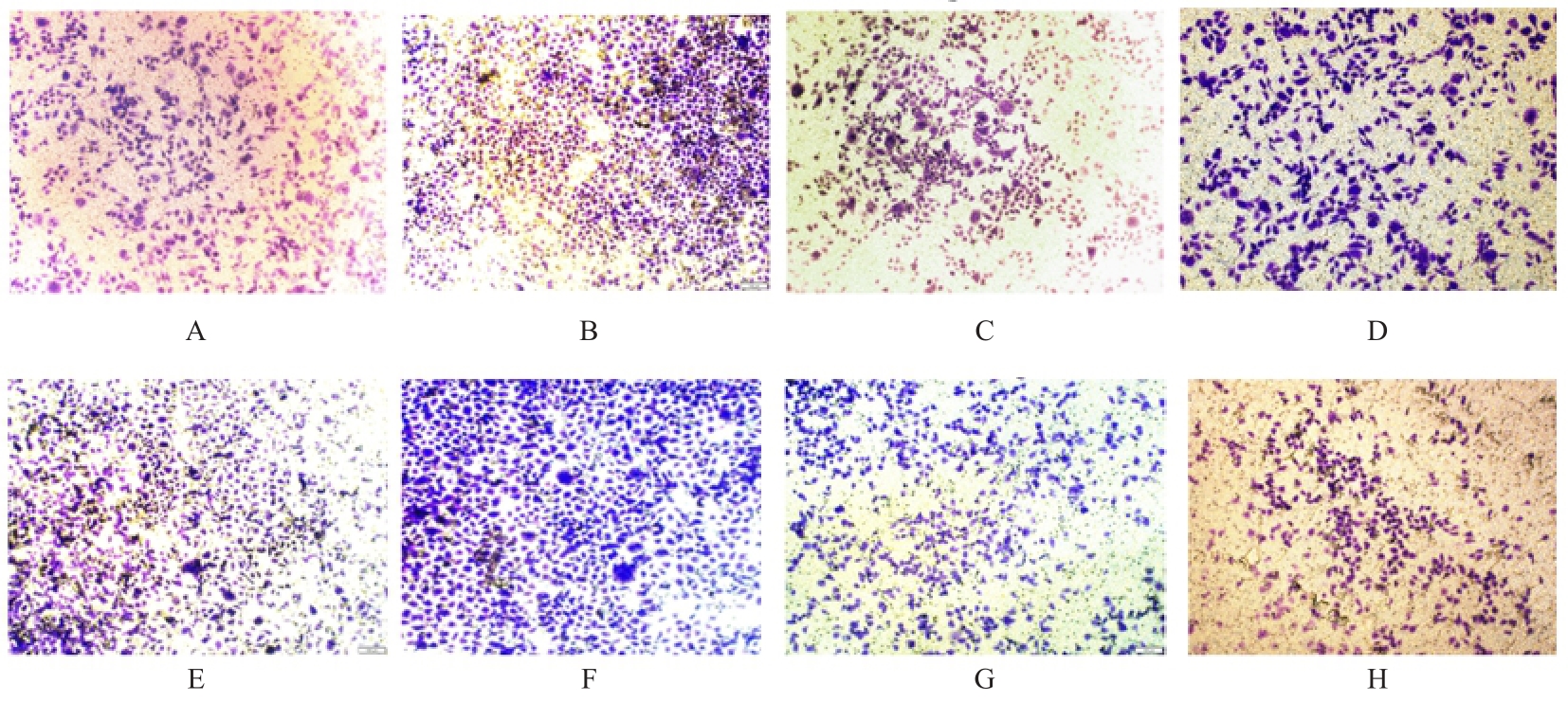
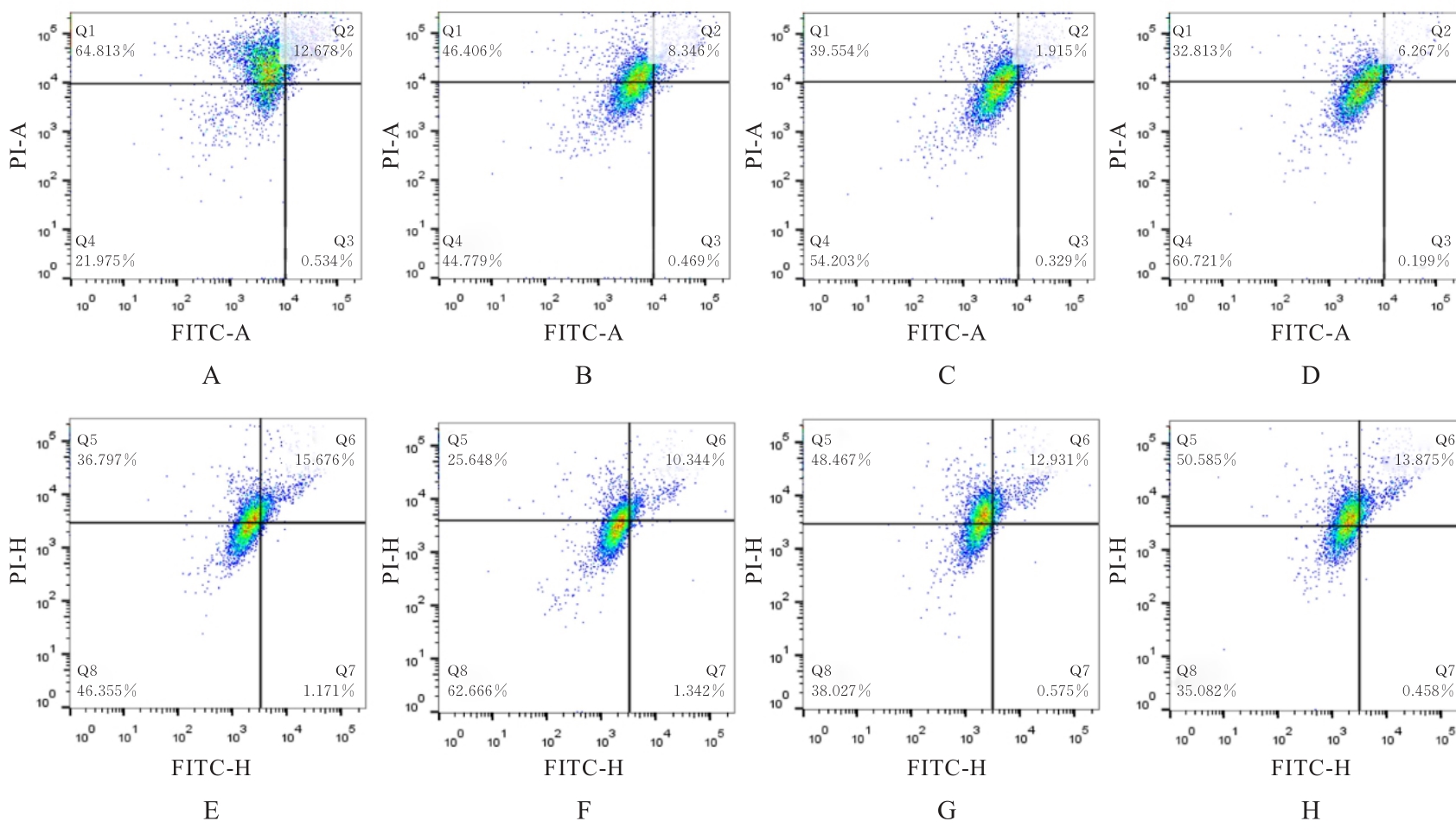
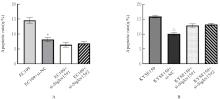
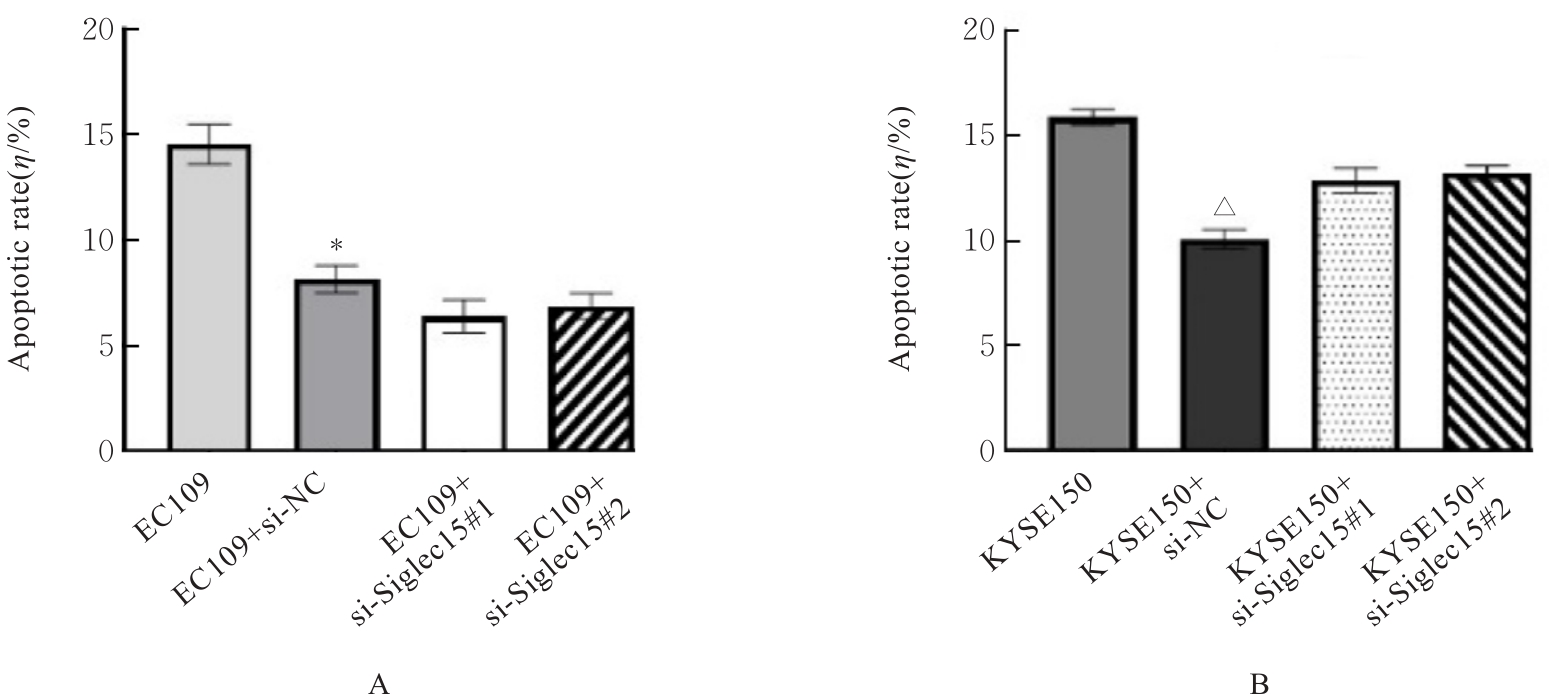
目的 采用生物信息学方法分析M2型肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(M2-TAMs)来源唾液酸结合免疫球蛋白样凝集素15(Siglec15)促进食管鳞状细胞癌(ESCC)恶性生物学行为的作用,并通过细胞实验对其进行验证。 方法 应用肿瘤免疫评价资源(TIMER)数据库分析Siglec15在泛癌和癌旁正常组织中的表达差异及免疫浸润情况,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测M2-TAMs和ESCC EC109及KYSE150细胞中Siglec15 mRNA表达水平。在M2-TAMs与ESCC细胞非接触性共培养基础上,分别设置EC109/KYSE150组、EC109/KYSE150+si-NC组(转染si-NC序列)和EC109/KYSE150+si-Siglec15组(分别转染si-Siglec15#1和si-Siglec15#2序列),采用CCK-8法检测各组细胞增殖活性,细胞划痕实验检测各组细胞划痕愈合率,Transwell小室实验检测各组细胞中迁移和侵袭细胞数,流式细胞术检测各组细胞凋亡率。 结果 生物信息学分析,与癌旁正常组织比较,食管癌、结肠癌和头颈部鳞状细胞癌等泛癌组织中Siglec15 mRNA表达水平升高(P<0.05或P<0.01),且食管癌组织中Siglec15 mRNA表达水平与巨噬细胞浸润呈明显正相关关系(P<0.05);与EC109细胞和KYSE150细胞比较,M2-TAMs中Siglec15 mRNA表达水平明显升高(P<0.01)。EC109/KYSE150组、EC109/KYSE150+si-NC组和EC109/KYSE150+si-Siglec15组细胞增殖率比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。与EC109/KYSE150组比较,24和48 h时EC109/KYSE150+si-NC组细胞划痕愈合率升高(P<0.01),迁移和侵袭细胞数增加(P<0.05),细胞凋亡率降低(P<0.01);与EC109/KYSE150+si-NC组比较,EC109/KYSE150+si-Siglec15#1组和EC109/KYSE150+si-Siglec15#2组细胞划痕愈合率降低(P<0.05),迁移和侵袭细胞数减少(P<0.05),细胞凋亡率差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 结论 M2-TAMs来源Siglec15可能是促进ESCC细胞迁移和侵袭的关键因子。
中图分类号:
- R735.1