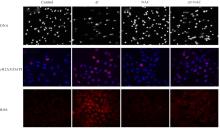
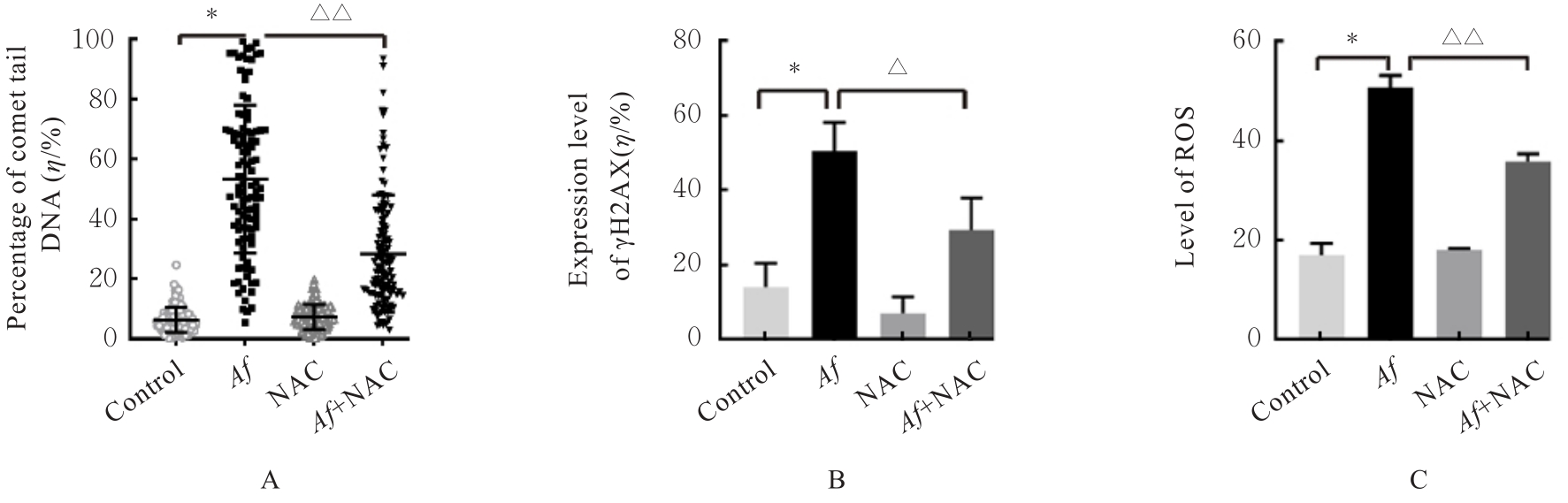
| 1 |
LATGÉ J P. Aspergillus fumigatus and aspergillosis[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 1999, 12(2): 310-350.
|
| 2 |
BIGOT J, GUILLOT L, GUITARD J, et al. Bronchial epithelial cells on the front line to fight lung infection-causing Aspergillus fumigatus [J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 1041.
|
| 3 |
RICHARD N, MARTI L, VARROT A, et al. Human bronchial epithelial cells inhibit Aspergillus fumigatus germination of extracellular conidia via FleA recognition[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 15699.
|
| 4 |
CUI X, CHEN F Y, ZHAO J Y, et al. Involvement of JNK signaling in Aspergillus fumigatus-induced inflammatory factors release in bronchial epithelial cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 1293.
|
| 5 |
DRAKE L Y, KITA H. IL-33: biological properties, functions, and roles in airway disease[J]. Immunol Rev, 2017, 278(1): 173-184.
|
| 6 |
DIETZ C J, SUN H, YAO W C, et al. Aspergillus fumigatus induction of IL-33 expression in chronic rhinosinusitis is PAR2-dependent[J]. Laryngoscope, 2019, 129(10): 2230-2235.
|
| 7 |
YOU J, LIN J, ZHOU Y F, et al. Role of the IL-33/ST2/p38 signaling pathway in the immune response of corneal epithelial cells to Aspergillus fumigatus infection[J]. Int J Ophthalmol, 2019, 12(4): 549-556.
|
| 8 |
KHOSRAVI A R, SHOKRI H, HASSAN AL-HEIDARY S, et al. Evaluation of murine lung epithelial cells (TC-1 JHU-1) line to develop Th2-promoting cytokines IL-25/IL-33/TSLP and genes Tlr2/Tlr4 in response to Aspergillus fumigatus [J]. J Mycol Med, 2018, 28(2): 349-354.
|
| 9 |
CHAN T K, LOH X Y, PEH H Y, et al. House dust mite-induced asthma causes oxidative damage and DNA double-strand breaks in the lungs[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2016, 138(1): 84-96.e1.
|
| 10 |
NIU B Y, LI W K, LI J S, et al. Effects of DNA damage and oxidative stress in human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to PM2.5 from Beijing, China, in winter[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2020, 17(13): 4874.
|
| 11 |
LI A M, ZHANG Y C, MA Y F, et al. The effects of coal dust exposure on DNA damage and repair of human bronchial epithelial cells[J]. Toxicol Ind Health, 2022, 38(7): 389-398.
|
| 12 |
IMANISHI T, ISHIHARA C, BADR M E L S, et al. Nucleic acid sensing by T cells initiates Th2 cell differentiation[J]. Nat Commun, 2014, 5: 3566.
|
| 13 |
STAV-NORAAS T E, EDELMANN R J, POULSEN L C, et al. Endothelial IL-33 expression is augmented by adenoviral activation of the DNA damage machinery[J]. J Immunol, 2017, 198(8): 3318-3325.
|
| 14 |
HUANG C Q, LIU J Y, HE L, et al. The long noncoding RNA noncoding RNA activated by DNA damage (NORAD)-microRNA-496-Interleukin-33 axis affects carcinoma-associated fibroblasts-mediated gastric cancer development[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12(2): 11738-11755.
|
| 15 |
VAN DE VEERDONK F L, GRESNIGT M S, ROMANI L, et al. Aspergillus fumigatus morphology and dynamic host interactions[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2017, 15(11): 661-674.
|
| 16 |
LATGÉ J P, CHAMILOS G. Aspergillus fumigatus and aspergillosis in 2019[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2019, 33(1): e00140-18.
|
| 17 |
THANNICKAL V J, FANBURG B L. Reactive oxygen species in cell signaling[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2000, 279(6): L1005-L1028.
|
| 18 |
ALBANO G D, GAGLIARDO R P, MONTALBANO A M, et al. Overview of the mechanisms of oxidative stress: impact in inflammation of the airway diseases[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2022, 11(11): 2237.
|
| 19 |
SAÏD-SADIER N, PADILLA E, LANGSLEY G, et al. Aspergillus fumigatus stimulates the NLRP3 inflammasome through a pathway requiring ROS production and the Syk tyrosine kinase[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(4): e10008.
|
| 20 |
SRINIVAS U S, TAN B W Q, VELLAYAPPAN B A, et al. ROS and the DNA damage response in cancer[J]. Redox Biol, 2019, 25: 101084.
|
| 21 |
NEOFYTOU E, TZORTZAKI E G, CHATZIANTONIOU A, et al. DNA damage due to oxidative stress in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2012, 13(12): 16853-16864.
|
| 22 |
SHARMA S, ALDRED M A. DNA damage and repair in pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Genes (Basel), 2020, 11(10): 1224.
|
| 23 |
CAO C, LAI T W, LI M, et al. Smoking-promoted oxidative DNA damage response is highly correlated to lung carcinogenesis[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(14): 18919-18926.
|
| 24 |
SCHMITZ J, OWYANG A, OLDHAM E, et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines[J]. Immunity, 2005, 23(5): 479-490.
|
| 25 |
MARÉCHAL A, ZOU L E. DNA damage sensing by the ATM and ATR kinases[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2013, 5(9): a012716.
|
| 26 |
SALMINEN A, KAUPPINEN A, KAARNIRANTA K. Emerging role of NF-κB signaling in the induction of senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP)[J]. Cell Signal, 2012, 24(4): 835-845.
|
| 27 |
MITCHELL J P, CARMODY R J. NF-κB and the transcriptional control of inflammation[J]. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol, 2018, 335: 41-84.
|
| 28 |
ZHANG L W, WAN Y, MA L, et al. Inhibition of NF-κB/IL-33/ST2 axis ameliorates acute bronchiolitis induced by respiratory syncytial virus[J]. J Immunol Res, 2021, 2021: 6625551.
|
| 29 |
SUN H, XU X Y, TIAN X L, et al. Activation of NF-κB and respiratory burst following Aspergillus fumigatus stimulation of macrophages[J]. Immunobiology, 2014, 219(1): 25-36.
|
| 30 |
CISZEWSKI W M, TAVECCHIO M, DASTYCH J, et al. DNA-PK inhibition by NU7441 sensitizes breast cancer cells to ionizing radiation and doxorubicin[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2014, 143(1): 47-55.
|
 ),张沄(
),张沄( )
)
 ),Yun ZHANG(
),Yun ZHANG( )
)