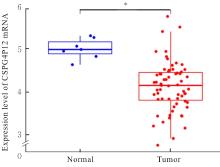
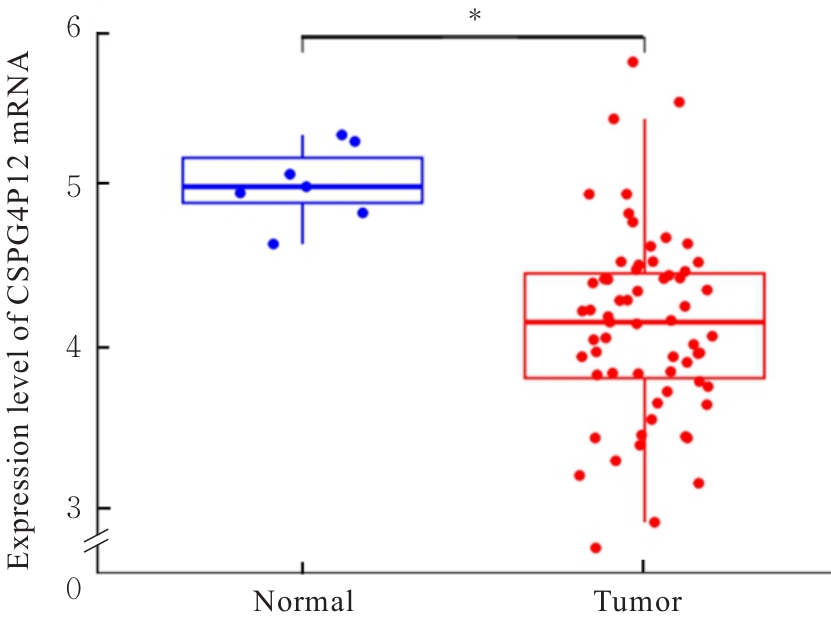
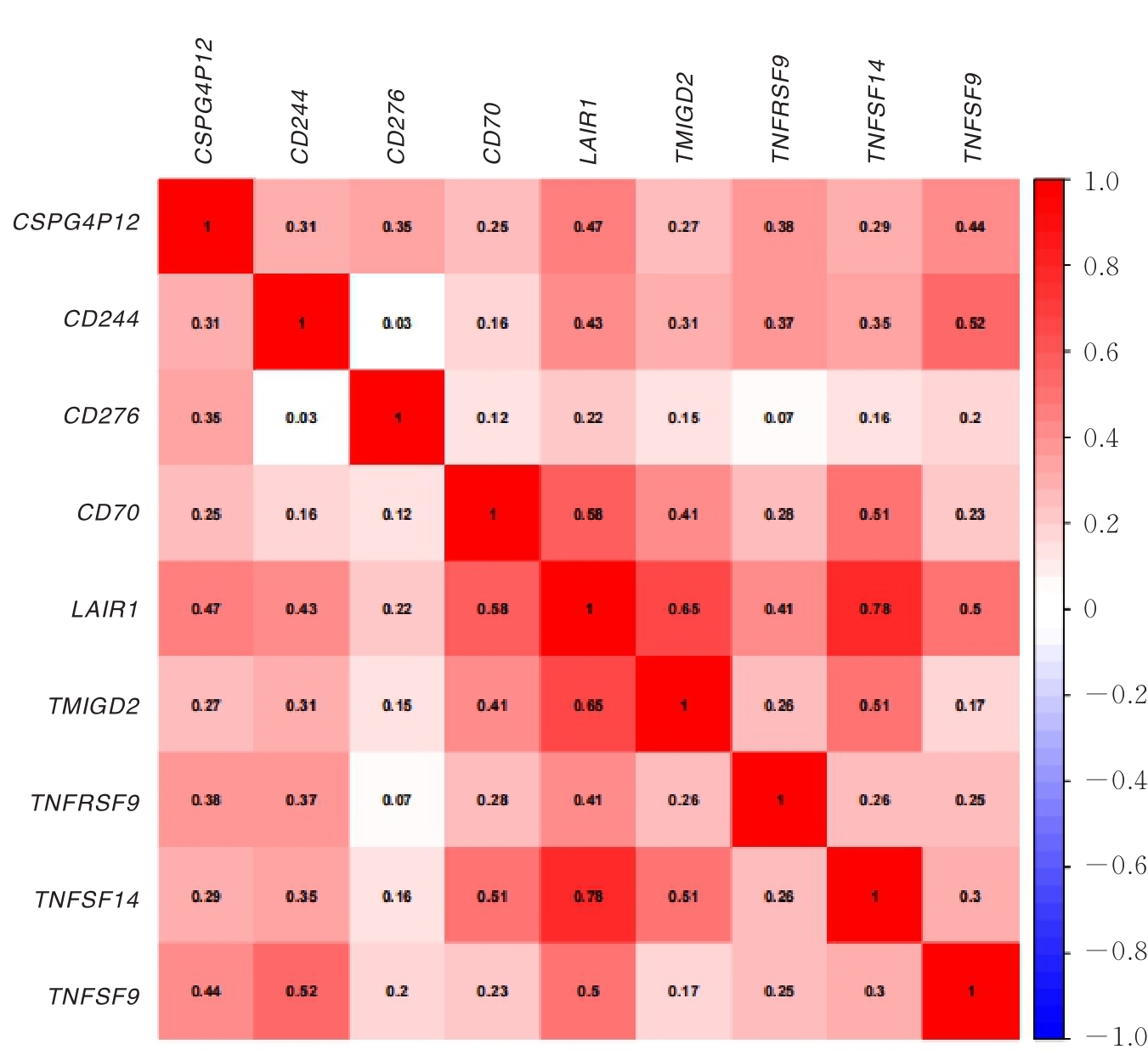
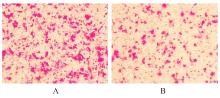
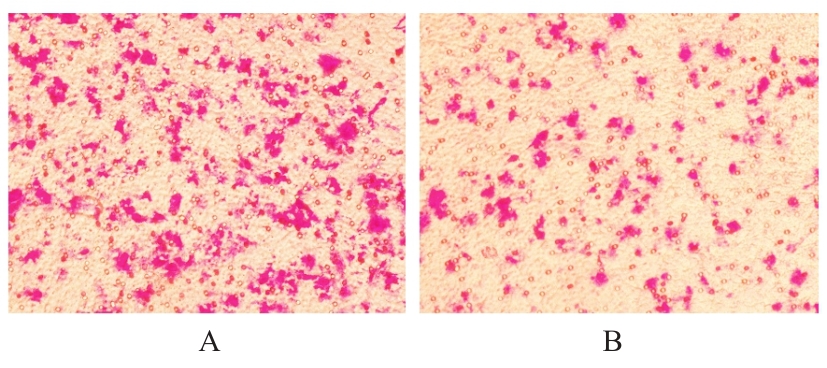
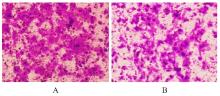
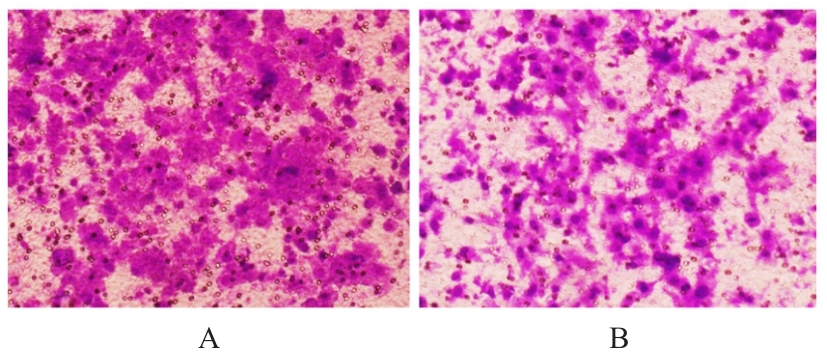
| 1 |
郑荣寿, 陈茹, 韩冰峰, 等. 2022年中国恶性肿瘤流行情况分析[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2024, 46(3): 221-231.
|
| 2 |
王永峰, 曾浈浈, 娄若林, 等. 基于肺癌相关肿瘤标志物的肺癌列线图诊断模型的构建[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2024, 59(4): 513-518.
|
| 3 |
ZHENG R S, ZHANG S W, SUN K X, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2016[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2023, 45(3): 212-220.
|
| 4 |
TRAVIS W D, BRAMBILLA E, RIELY G J. New pathologic classification of lung cancer: relevance for clinical practice and clinical trials[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2013, 31(8): 992-1001.
|
| 5 |
THAI A A, SOLOMON B J, SEQUIST L V, et al. Lung cancer[J]. Lancet, 2021, 398(10299): 535-554.
|
| 6 |
KALEMKERIAN G P, SCHNEIDER B J. Advances in small cell lung cancer[J]. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am, 2017, 31(1): 143-156.
|
| 7 |
YAN Y L, LIU W L, LIU M, et al. Immune cell infiltration influences long-term survivorship of patients with SCLC[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2019, 14(10): e241.
|
| 8 |
ZHOU N N, LUO P, WEN Y, et al. Immune cell infiltration is a strong prognostic indicator in surgical resection of SCLC[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2019, 14(10): e242-e243.
|
| 9 |
RUDIN C M, BRAMBILLA E, FAIVRE-FINN C, et al. Small-cell lung cancer[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2021, 7(1): 3.
|
| 10 |
NICOLOSI P A, DALLATOMASINA A, PERRIS R. Theranostic impact of NG2/CSPG4 proteoglycan in cancer[J]. Theranostics, 2015, 5(5): 530-544.
|
| 11 |
PRICE M A, COLVIN WANSHURA L E, YANG J B, et al. CSPG4, a potential therapeutic target, facilitates malignant progression of melanoma[J]. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res, 2011, 24(6): 1148-1157.
|
| 12 |
EGAN C E, STEFANOVA D, AHMED A, et al. CSPG4 is a potential therapeutic target in anaplastic thyroid cancer[J]. Thyroid, 2021, 31(10): 1481-1493.
|
| 13 |
HU Z Y, ZHENG C J, YANG J B, et al. Co-expression and combined prognostic value of CSPG4 and PDL1 in TP53-aberrant triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 804466.
|
| 14 |
SCHOENFELD A J, WANG X H, WANG Y Y, et al. CSPG4 as a prognostic biomarker in chordoma[J]. Spine J, 2016, 16(6): 722-727.
|
| 15 |
WIEST T, HYRENBACH S, BAMBUL P, et al. Genetic analysis of familial connective tissue alterations associated with cervical artery dissections suggests locus heterogeneity[J]. Stroke, 2006, 37(7): 1697-1702.
|
| 16 |
SONG Q Q, XU H X, WU H J, et al. Pseudogene CSPG4P12 inhibits colorectal cancer progression by attenuating epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. Braz J Med Biol Res, 2024, 57: e13645.
|
| 17 |
HU W Q, WU H J, LI A, et al. Pseudogene CSPG4P12affects the biological behavior of non‑small cell lung cancer by Bcl‑2/Bax mitochondrial apoptosis pathway[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2022, 24(6): 734.
|
| 18 |
LI S W, DONG C L, CHEN J Y, et al. Identification of an immune checkpoint gene signature that accurately predicts prognosis and immunotherapy response in endometrial carcinoma[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2021, 13(12): 16696-16712.
|
| 19 |
SEMENOVA E A, NAGEL R, BERNS A. Origins, genetic landscape, and emerging therapies of small cell lung cancer[J]. Genes Dev, 2015, 29(14): 1447-1462.
|
| 20 |
HERZOG B H, DEVARAKONDA S, GOVINDAN R. Overcoming chemotherapy resistance in SCLC[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2021, 16(12): 2002-2015.
|
| 21 |
PENG X, BADER J S, AVRAMOPOULOS D. Schizophrenia risk alleles often affect the expression of many genes and each gene may have a different effect on the risk: a mediation analysis[J]. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet, 2021, 186(4): 251-258.
|
| 22 |
YANG L I, DENG K, MOU Z Q, et al. Pathological images for personal medicine in hepatocellular carcinoma: cross-talk of gene sequencing and pathological images[J]. Oncol Res, 2023, 30(5): 243-258.
|
| 23 |
ZHOU T, LIU L Q, LAN H B, et al. Effects of LAIR-1 on hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion via PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway regulation[J]. Immun Inflamm Dis, 2023, 11(8): e982.
|
| 24 |
JIANG P L, GAO W J, MA T S, et al. CD137 promotes bone metastasis of breast cancer by enhancing the migration and osteoclast differentiation of monocytes/macrophages[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9(10): 2950-2966.
|
| 25 |
LE T, SU S, SHAHRIYARI L. Immune classification of osteosarcoma[J]. Math Biosci Eng, 2021, 18(2): 1879-1897.
|
| 26 |
WANG X S, HAN Y Y, LI J, et al. Multi-omics analysis of copy number variations of RNA regulatory genes in soft tissue sarcoma[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 265: 118734.
|
| 27 |
TOMIOKA K, SAEKI K, OBAYASHI K, et al. Risk of lung cancer in workers exposed to benzidine and/or beta-naphthylamine: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Epidemiol, 2016, 26(9): 447-458.
|
| 28 |
RAMKISSOON A, NAVARANJAN G, BERRIAULT C, et al. Histopathologic analysis of lung cancer incidence associated with radon exposure among Ontario uranium miners[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2018, 15(11): 2413.
|
| 29 |
ZHENG S B, WANG X D, FU Y, et al. Targeted next-generation sequencing for cancer-associated gene mutation and copy number detection in 206 patients with non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12(1): 791-802.
|
| 30 |
WANG Q, GÜMÜS Z H, COLAROSSI C, et al. SCLC: epidemiology, risk factors, genetic susceptibility, molecular pathology, screening, and early detection[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2023, 18(1): 31-46.
|
| 31 |
GAO H, NIU Z R, ZHANG Z, et al. TNFSF15 promoter polymorphisms increase the susceptibility to small cell lung cancer: a case-control study[J]. BMC Med Genet, 2019, 20(1): 29.
|
| 32 |
LI D J, XU X L, LIU J H, et al. Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) incidence and trends vary by gender, geography, age, and subcategory based on population and hospital cancer registries in Hebei, China (2008-2017)[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2020, 11(8): 2087-2093.
|
 )
)