吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 599-607.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230307
β-谷甾醇对阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠认知功能的改善作用及其机制
- 1.长春中医药大学中西医结合学院中西医结合实验室, 吉林 长春 130117
2.长春中医药大学第三附属医院脑病科, 吉林 长春 130118
3.长春中医药大学中医学院内分泌科, 吉林 长春 130117
4.长春中医药大学临床医学院生理教研室, 吉林 长春 130117
Improvement effect of β-sitosterol on cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease model mice and its mechanism
Xingye WANG1,2,Xiangri KONG3,Mengli JIN4,Bingmei WANG4,Mingquan LI2( )
)
- 1.Laboratory of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine,School of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
2.Department of Neurology,Third Affiliated Hospital,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130118,China
3.Department of Endocrinology,School of Chinese Medicine,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
4.Department of Physiology,School of Clinical Medicine,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
摘要:
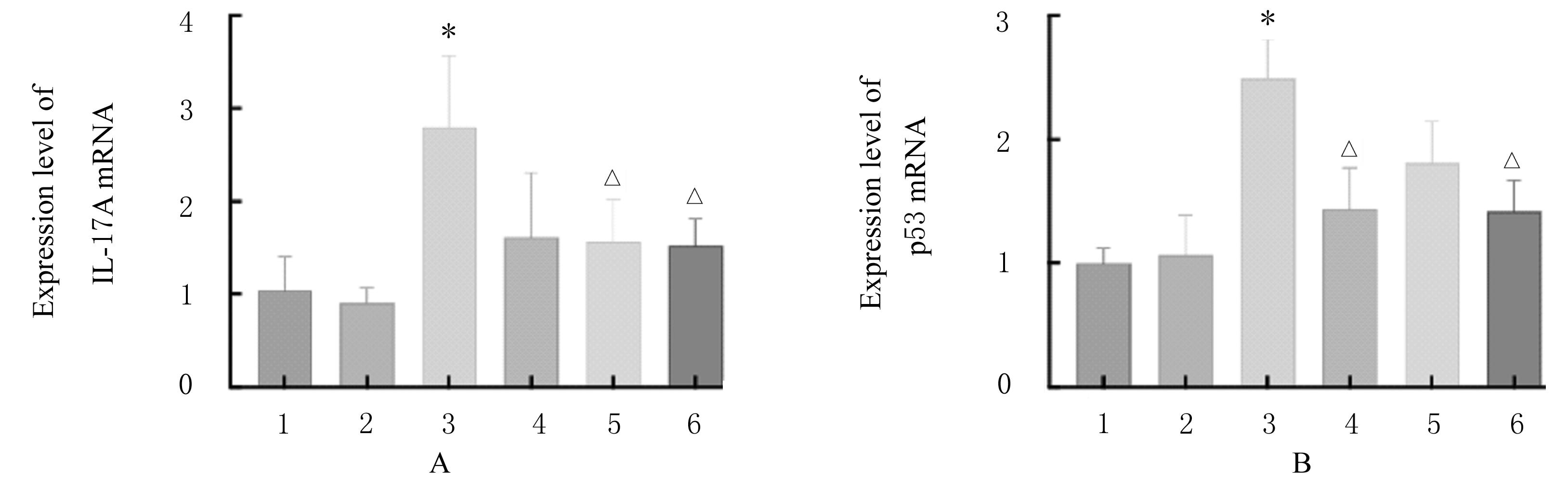
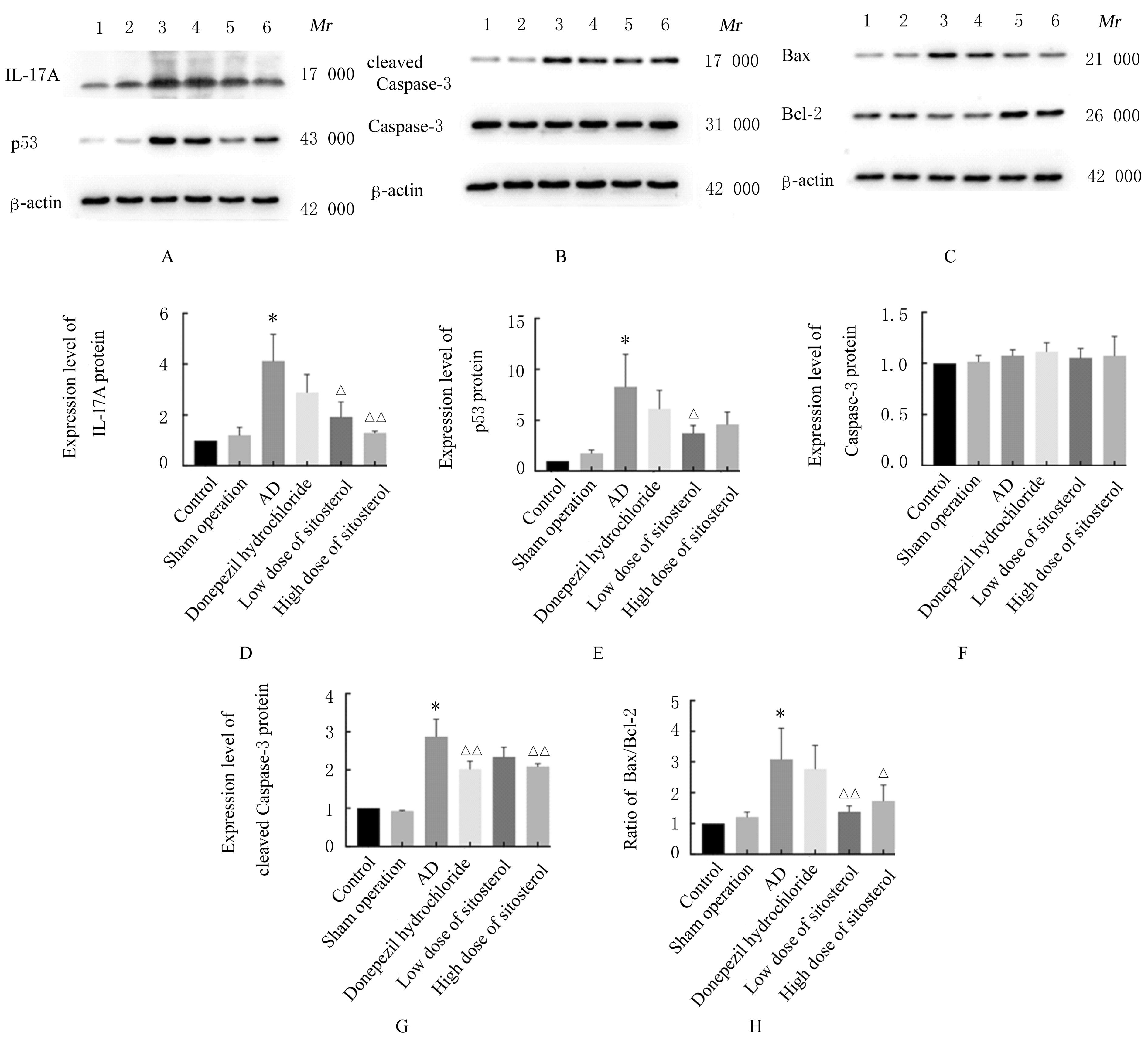
目的 探讨β-谷甾醇对阿尔茨海默病(AD)模型小鼠认知功能的改善作用,并阐明其可能的分子机制。 方法 72只小鼠随机分为对照组、假手术组、AD组、盐酸多奈哌齐(0.6 mg·kg-1)及低(1.0 mg·kg-1)和高(4.0 mg·kg-1)剂量β-谷甾醇组,每组12只。小鼠侧脑室注射β淀粉样蛋白1-42(Aβ1-42)建立AD模型,采用β-谷甾醇进行干预治疗,自主活动实验观察各组小鼠自由活动次数,筑巢行为实验观察各组小鼠筑巢行为评分,新物体辨别实验观察各组小鼠对新物体辨别时间和新旧物体辨别时间的比值(DR),Morris水迷宫实验观察各组小鼠逃避潜伏期和跨越平台次数,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测各组小鼠海马组织中白细胞介素17A(IL-17A)和p53 mRNA表达水平,Western blottig法检测各组小鼠海马组织中IL-17A、p53、Caspase-3、cleaved Caspase-3、B细胞淋巴瘤2(Bcl-2)和Bcl-2相关X蛋白(Bax)蛋白表达水平,酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA)法检测各组小鼠海马组织中超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性和谷胱甘肽(GSH)、肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)及IL-17A水平。 结果 筑巢行为实验,与对照组比较,AD组小鼠筑巢行为评分明显降低(P<0.01);与AD组比较,盐酸多奈哌齐组和低剂量β-谷甾醇组小鼠筑巢行为评分升高(P<0.05)。新物体辨别实验,与对照组比较,AD组小鼠对新物体辨别时间明显减少(P<0.01),DR明显降低(P<0.01);与AD组比较,盐酸多奈哌齐组和高剂量β-谷甾醇组小鼠对新物体辨别时间明显增加(P<0.01),低剂量β-谷甾醇组小鼠DR升高(P<0.05)。Morris水迷宫实验,训练第3和5天,与对照组比较,AD组小鼠逃避潜伏期明显延长(P<0.01);与AD组比较,盐酸多奈哌齐组、低和高剂量β-谷甾醇组小鼠逃避潜伏期明显延长(P<0.05或P<0.01)。与对照组比较,AD组小鼠跨越平台次数明显增加(P<0.01);与AD组比较,盐酸多奈哌齐组、低和高剂量β-谷甾醇组跨越平台次数明显减少(P<0.01)。RT-qPCR法检测,与对照组比较,AD组小鼠海马组织中IL-17A和p53 mRNA表达水平均明显升高(P<0.01);与AD组比较,低和高剂量β-谷甾醇组小鼠海马组织中IL-17A mRNA表达水平降低(P<0.05),盐酸多奈哌齐组和高剂量β-谷甾醇组小鼠海马组织中p53 mRNA表达水平降低(P<0.05)。Western blottig法检测,与对照组比较,AD组小鼠海马组织中IL-17A、p53和cleaved Caspase-3蛋白表达水平及Bax/Bcl-2比值明显升高(P<0.01);与AD组比较,低剂量β-谷甾醇组小鼠海马组织中IL-17A和p53蛋白表达水平及Bax/Bcl-2比值明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),盐酸多奈哌齐组小鼠海马组织中cleaved Caspase-3蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.01),高剂量β-谷甾醇组小鼠海马组织中IL-17A、cleaved Caspase-3蛋白表达水平和Bax/Bcl-2比值明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。ELISA法检测,与对照组比较,AD组小鼠海马组织中SOD活性和GSH水平明显降低(P<0.01),TNF-α和IL-17A水平明显升高(P<0.01);与AD组比较,高剂量β-谷甾醇组小鼠海马组织中SOD活性和GSH水平明显升高(P<0.01),IL-17A水平降低(P<0.05),低剂量β-谷甾醇组小鼠海马组织中TNF-α水平降低(P<0.05)。 结论 β-谷甾醇可减轻神经炎症并抑制细胞凋亡,进而改善AD模型小鼠的认知功能,其作用机制可能与抑制IL-17-p53信号通路有关。
中图分类号:
- R742