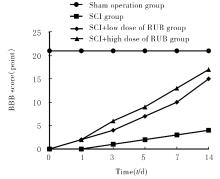
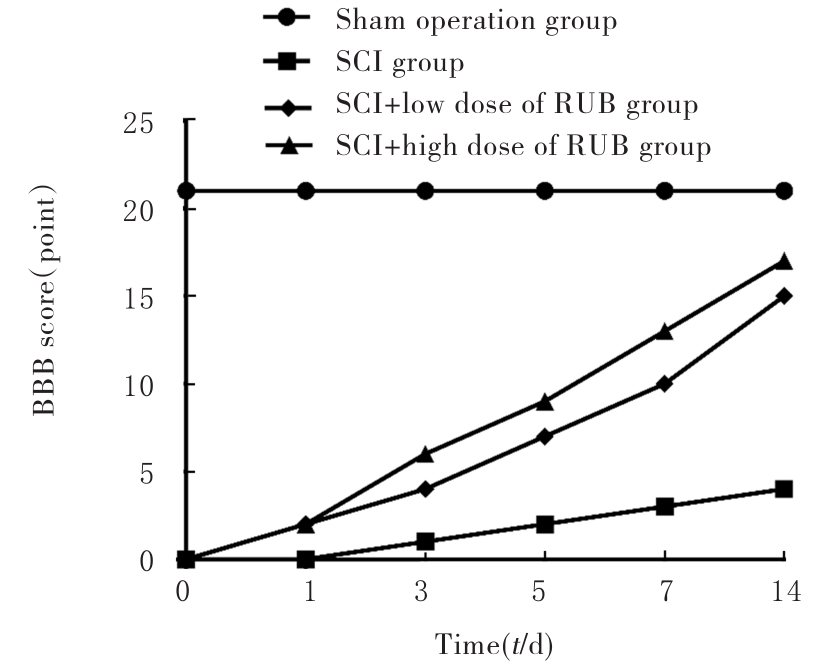
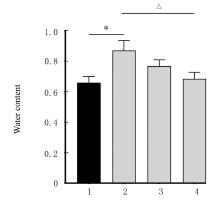
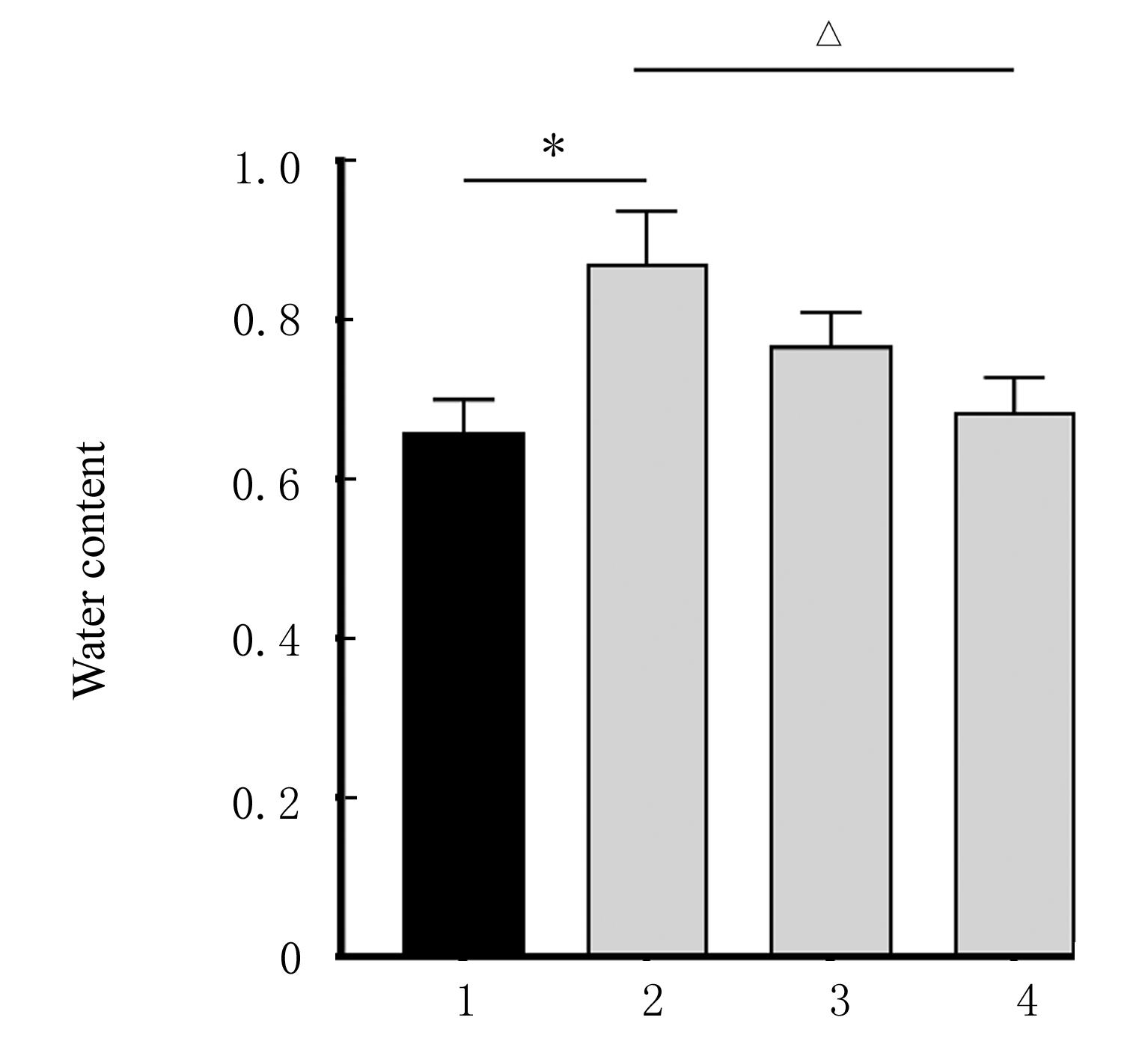
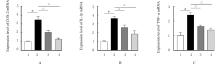
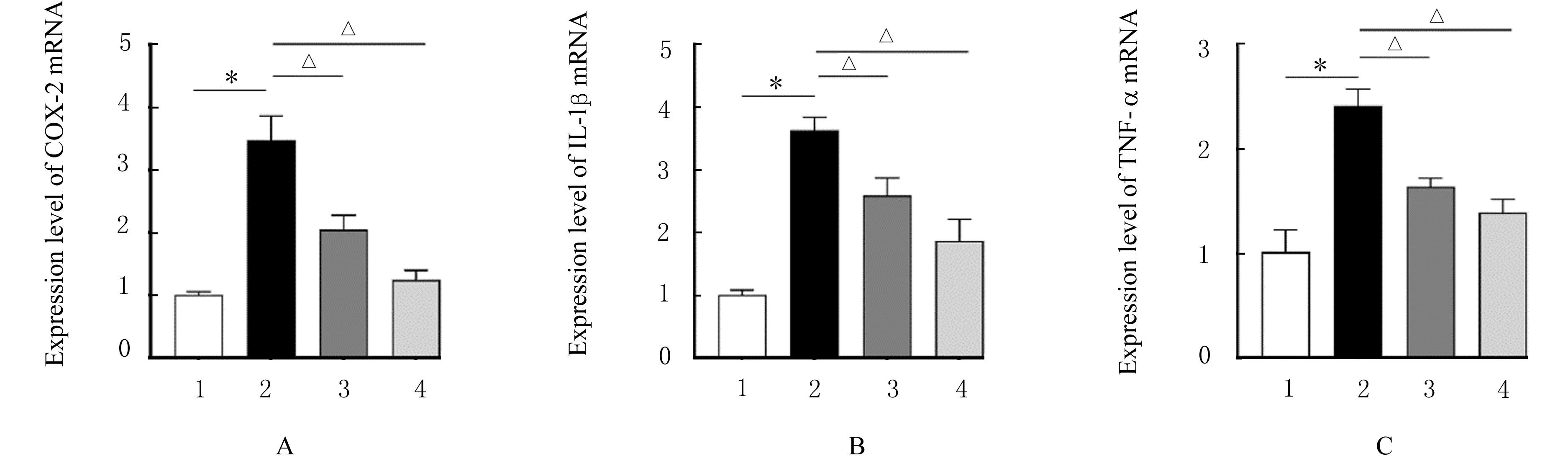
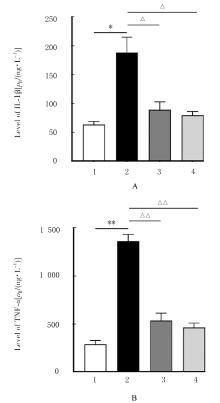
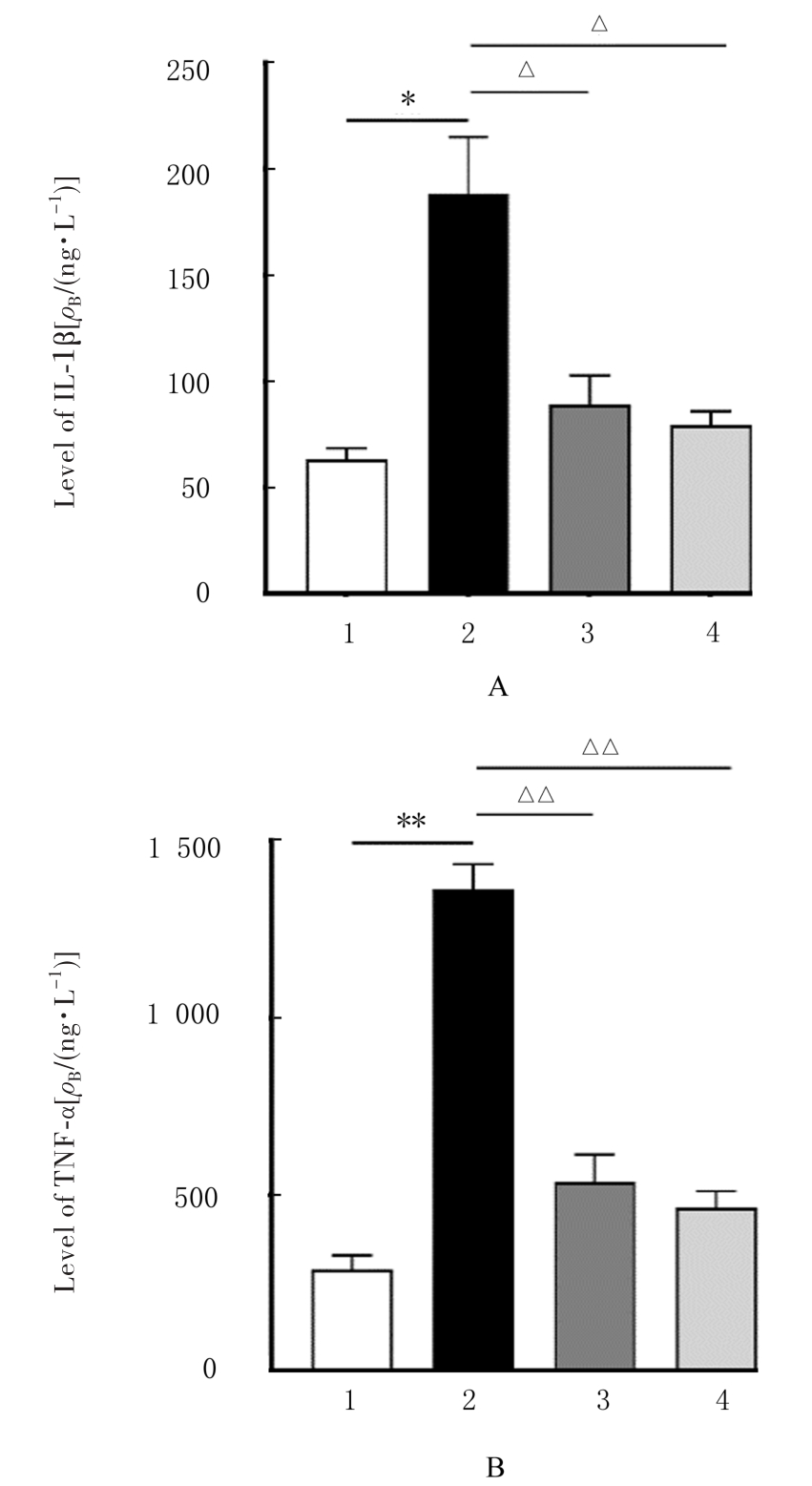
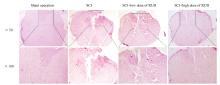
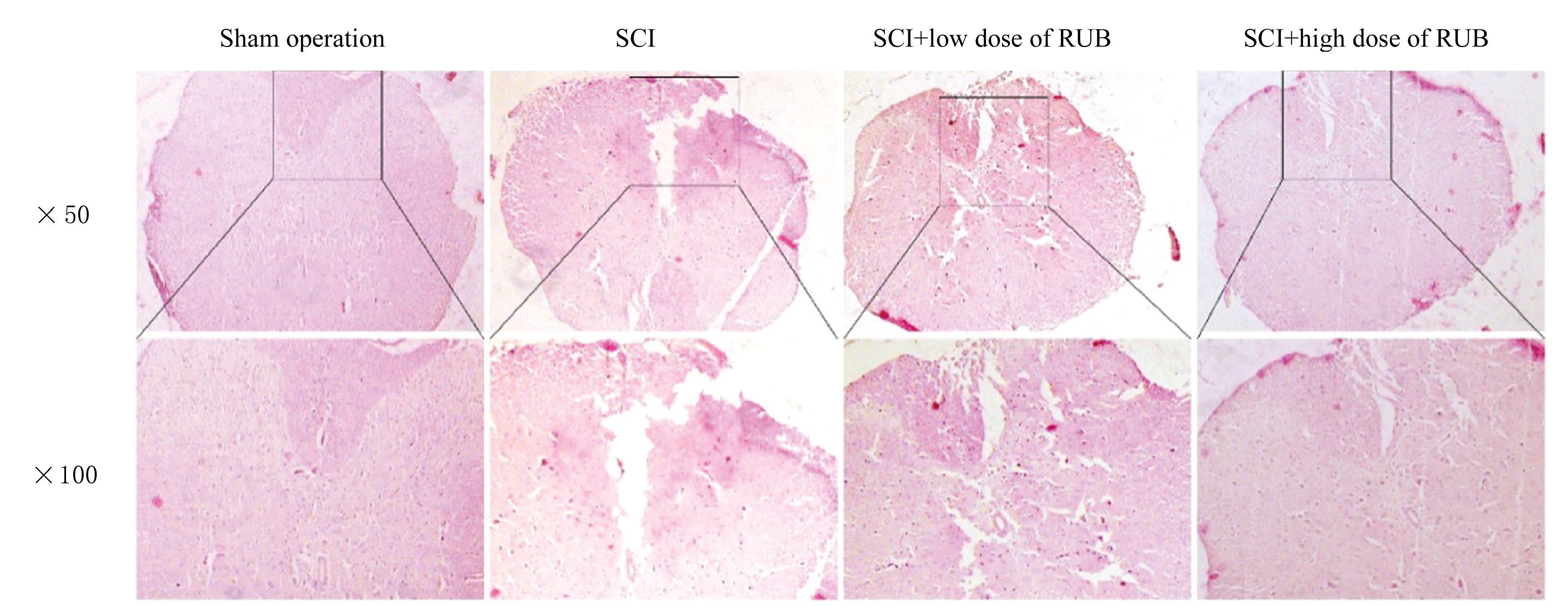
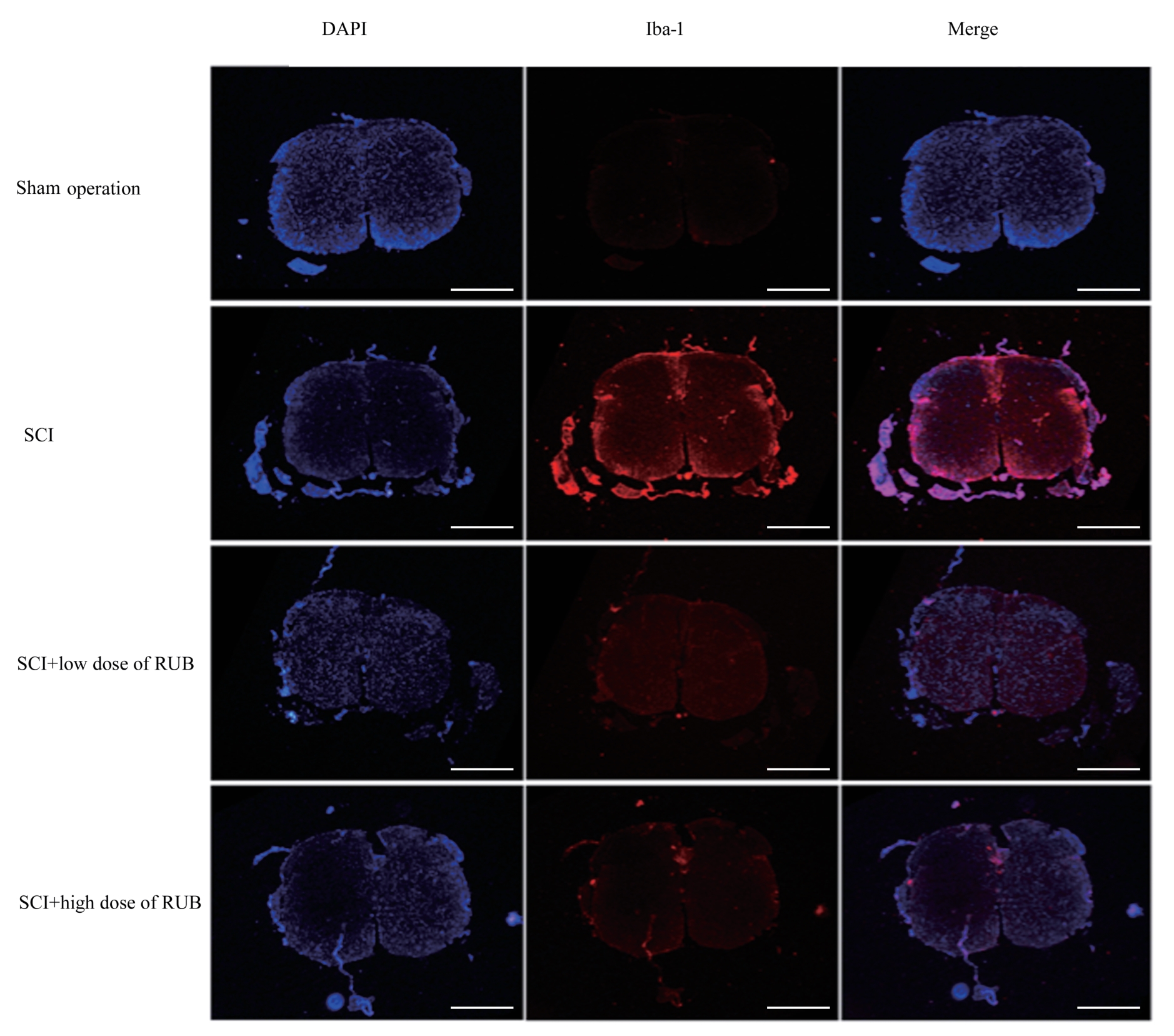
| 1 |
XIA M J, ZHANG Y N, WU H H, et al. Forsythoside B attenuates neuro-inflammation and neuronal apoptosis by inhibition of NF-κB and p38-MAPK signaling pathways through activating Nrf2 post spinal cord injury[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2022, 111: 109120.
|
| 2 |
XU S, WANG J, ZHONG J J, et al. CD73 alleviates GSDMD-mediated microglia pyroptosis in spinal cord injury through PI3K/AKT/Foxo1 signaling[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2021, 11(1): e269.
|
| 3 |
MI J Y, YANG Y, YAO H, et al. Inhibition of heat shock protein family A member 8 attenuates spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury via astrocyte NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway: HSPA8 inhibition protects spinal ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2021, 18(1): 170.
|
| 4 |
CHEN K Y, LU C S, PANG C Y, et al. Equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 is a target to modulate neuroinflammation and improve functional recovery in mice with spinal cord injury[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2023, 60(1): 369-381.
|
| 5 |
CHEN K Z, LIU S X, LI Y W, et al. Vimentin as a potential target for diverse nervous system diseases[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2023, 18(5): 969-975.
|
| 6 |
邵明昊, 靳明明, 周 萍,等. CD73通过AMPK/mTOR信号通路调控脊髓损伤机制研究[J].中国免疫学杂志, 2020, 36(19): 2357-2360.
|
| 7 |
DUTTA D, KHAN N, WU J F, et al. Extracellular vesicles as an emerging frontier in spinal cord injury pathobiology and therapy[J]. Trends Neurosci, 2021, 44(6): 492-506.
|
| 8 |
MAO Y P, CHEN Z, REN Y H, et al. Whole-cell biocatalyst for rubusoside production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2021, 69(44): 13155-13163.
|
| 9 |
ZHANG F, KOH G Y, HOLLINGSWORTH J, et al. Reformulation of etoposide with solubility-enhancing rubusoside[J]. Int J Pharm, 2012, 434(1/2): 453-459.
|
| 10 |
CHEN J Z, KHISTE S K, FU X M, et al. Rubusoside-assisted solubilization of poorly soluble C(6)-Ceramide for a pilot pharmacokinetic study [J]. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat, 2020, 146: 106402.
|
| 11 |
ZIPSER C M, CRAGG J J, GUEST J D, et al. Cell-based and stem-cell-based treatments for spinal cord injury: evidence from clinical trials [J]. Lancet Neurol, 2022, 21(7): 659-670.
|
| 12 |
ZHANG H, QI R L, ZENG Y H, et al. Chinese sweet leaf tea (Rubus suavissimus) mitigates LPS-induced low-grade chronic inflammation and reduces the risk of metabolic disorders in a C57BL/6J mouse model[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2020, 68(1): 138-146.
|
| 13 |
HU X, ZHANG Y F, WANG L, et al. Microglial activation in the motor cortex mediated NLRP3-related neuroinflammation and neuronal damage following spinal cord injury [J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2022, 16: 956079.
|
| 14 |
JIANG F, XIA M J, ZHANG Y N, et al. Cannabinoid receptor-2 attenuates neuroinflammation by promoting autophagy-mediated degradation of the NLRP3 inflammasome post spinal cord injury [J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 993168.
|
| 15 |
CHANG J, QIAN Z Y, WANG B Y, et al. Transplantation of A2 type astrocytes promotes neural repair and remyelination after spinal cord injury [J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2023, 21(1): 37.
|
| 16 |
ZHAO X N, LI X X, GUO H L, et al. Resolvin D1 attenuates mechanical allodynia after burn injury: involvement of spinal glia, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor/tropomyosin-related kinase B signaling[J]. Mol Pain, 2023, 19: 17448069231159970.
|
| 17 |
刘 冬, 朱志杰, 张 昭, 等. 脊髓损伤中坏死性凋亡关键基因的筛选与验证[J]. 解放军医学杂志: 1-14[2023-11-01]. .
|
| 18 |
SUN Q Y, HU T T, ZHANG Y R, et al. IRG1/itaconate increases IL-10 release to alleviate mechanical and thermal hypersensitivity in mice after nerve injury [J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 1012442.
|
| 19 |
LIAO C L, ZHOU H, CHEN H J, et al. DUSP8/TAK1 signaling mediates neuropathic pain through regulating neuroinflammation and neuron death in a spinal nerve ligation (SNL) rat model [J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2022, 113(Pt A): 109284.
|
| 20 |
HONG X, XIA M J, ZHANG Q Y, et al. Deficiency of CD93 exacerbates inflammation-induced activation and migration of BV2 microglia by regulating the TAK1/NF-κB pathway[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2022, 791: 136914.
|
| 21 |
YIN X Y, WANG C C, DU P, et al. Muse cells decrease the neuroinflammatory response by modulating the proportion of M1 and M2 microglia in vitro [J]. Neural Regen Res, 2023, 18(1): 213-218.
|
| 22 |
ZHANG X Q, ZHANG Q, HUANG L L, et al. Pien-Tze-Huang attenuates neuroinflammation in cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rats through the TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK pathway[J]. Pharm Biol, 2021, 59(1): 828-839.
|
| 23 |
WANG J, RAN Q, ZENG H R, et al. Cellular stress response mechanisms of Rhizoma coptidis: a systematic review [J]. Chin Med, 2018, 13: 27.
|
| 24 |
YUAN B C, YANG R, MA Y S, et al. A systematic review of the active saikosaponins and extracts isolated from Radix Bupleuri and their applications [J]. Pharm Biol, 2017, 55(1): 620-635.
|
| 25 |
KIM J K, YANG H J, GO Y. Quercus acuta thunb suppresses LPS-induced neuroinflammation in BV2 microglial cells via regulating MAPK/NF-κB and Nrf2/HO-1 pathway[J]. Antioxidants, 2022, 11(10): 1851.
|
| 26 |
KIM O H, JEON K O, JANG E Y. Alpha-pyrrolidinopentiothiophenone(α-PVT) activates the TLR- NF-κB-MAPK signaling pathway and proinflammatory cytokine production and induces behavioral sensitization in mice[J]. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 2022, 221: 173484.
|
| 27 |
GUO L, LI Y Y, LI W N, et al. Shikonin ameliorates oxidative stress and neuroinflammation via the Akt/ERK/JNK/NF-κB signalling pathways in a model of Parkinson’s disease[J]. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol, 2022, 49(11): 1221-1231.
|
 ),刘文森1,2(
),刘文森1,2( )
)
 ),Wensen LIU1,2(
),Wensen LIU1,2( )
)