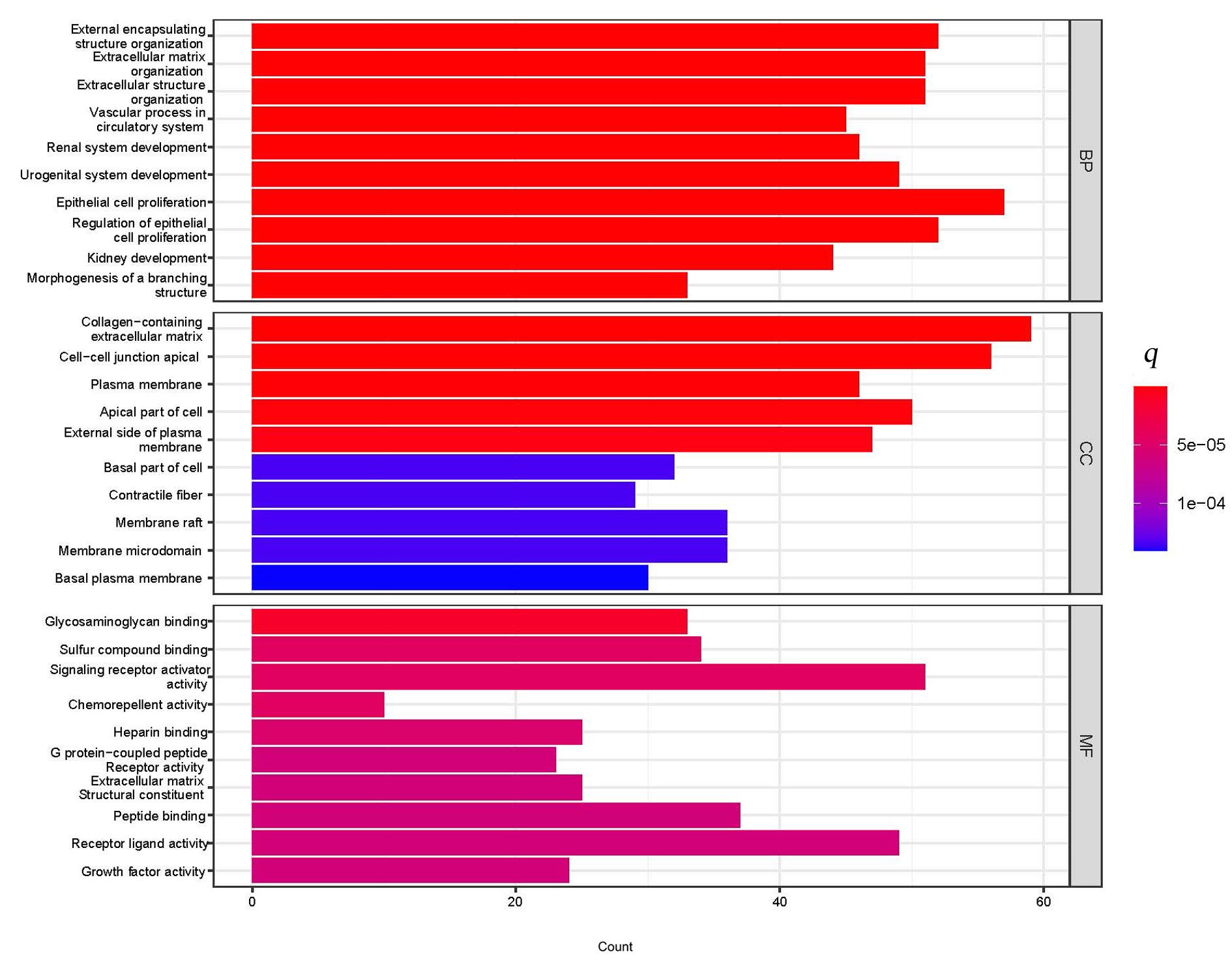
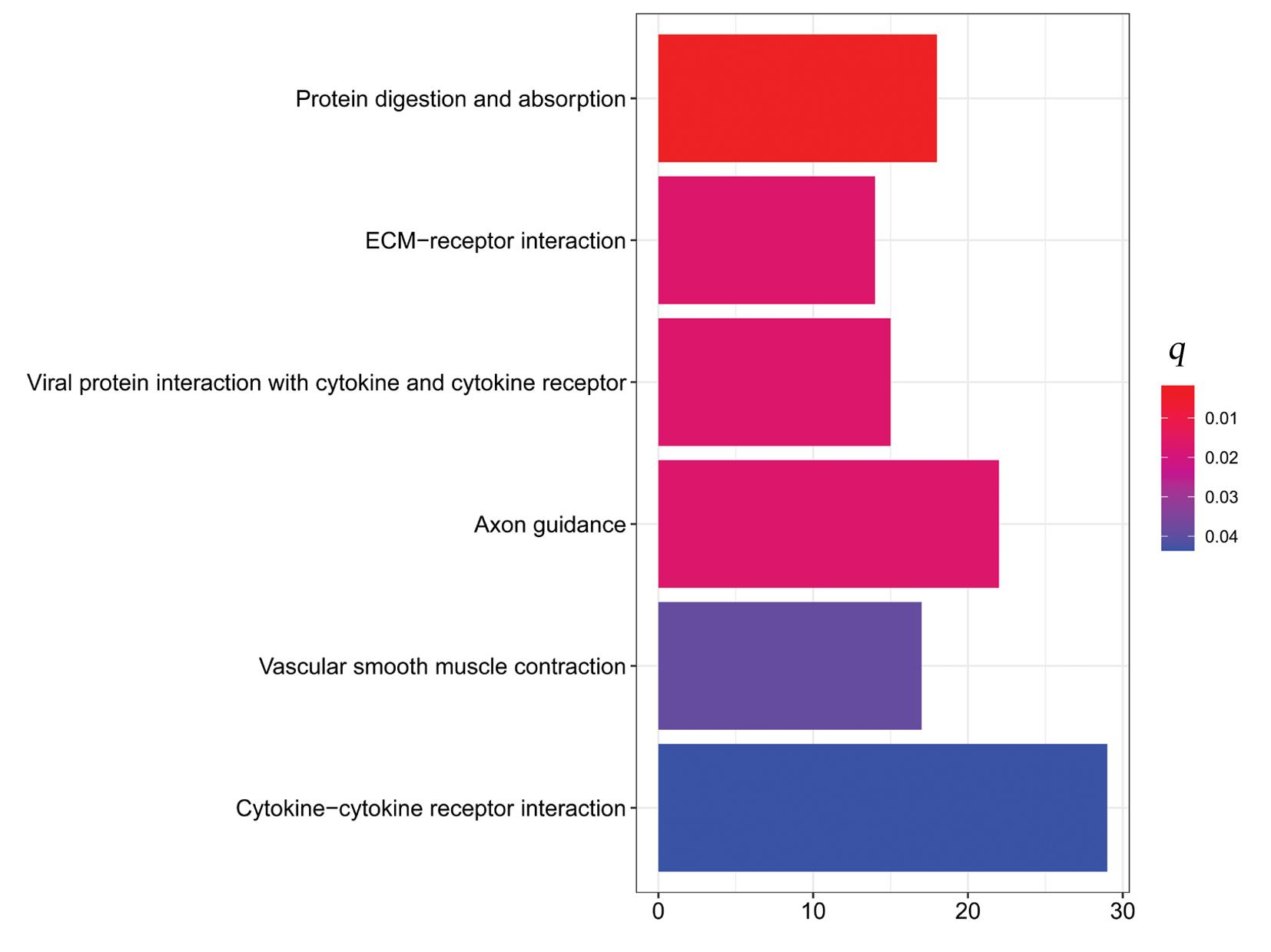
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (6): 1491-1503.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230612
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioinformatics analysis on differentially expressed genes in lung adenocarcinoma based on GEO and TCGA Databases
Hui YE,Zhe SUN,Liting ZHOU,Wen QI( ),Lin YE(
),Lin YE( )
)
- Department of Labor Health and Environmental Sanitation,School of Public Health,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
-
Received:2022-12-14Online:2023-11-28Published:2023-12-22 -
Contact:Wen QI,Lin YE E-mail:qiwen@jlu.edu.cn;yel@jlu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R737.9
Cite this article
Hui YE,Zhe SUN,Liting ZHOU,Wen QI,Lin YE. Bioinformatics analysis on differentially expressed genes in lung adenocarcinoma based on GEO and TCGA Databases[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1491-1503.
share this article
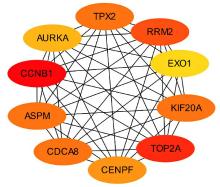
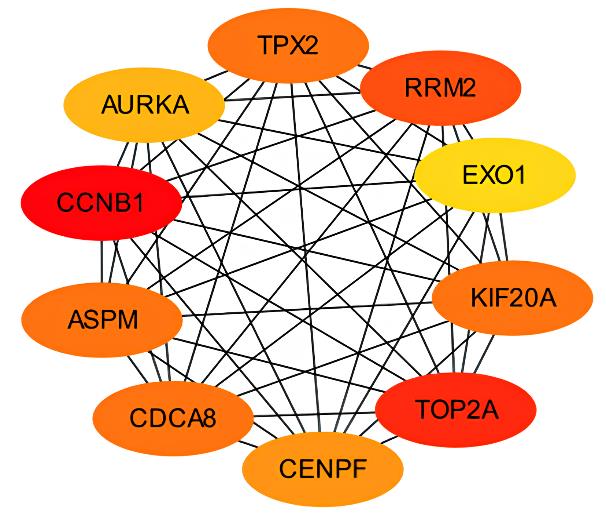
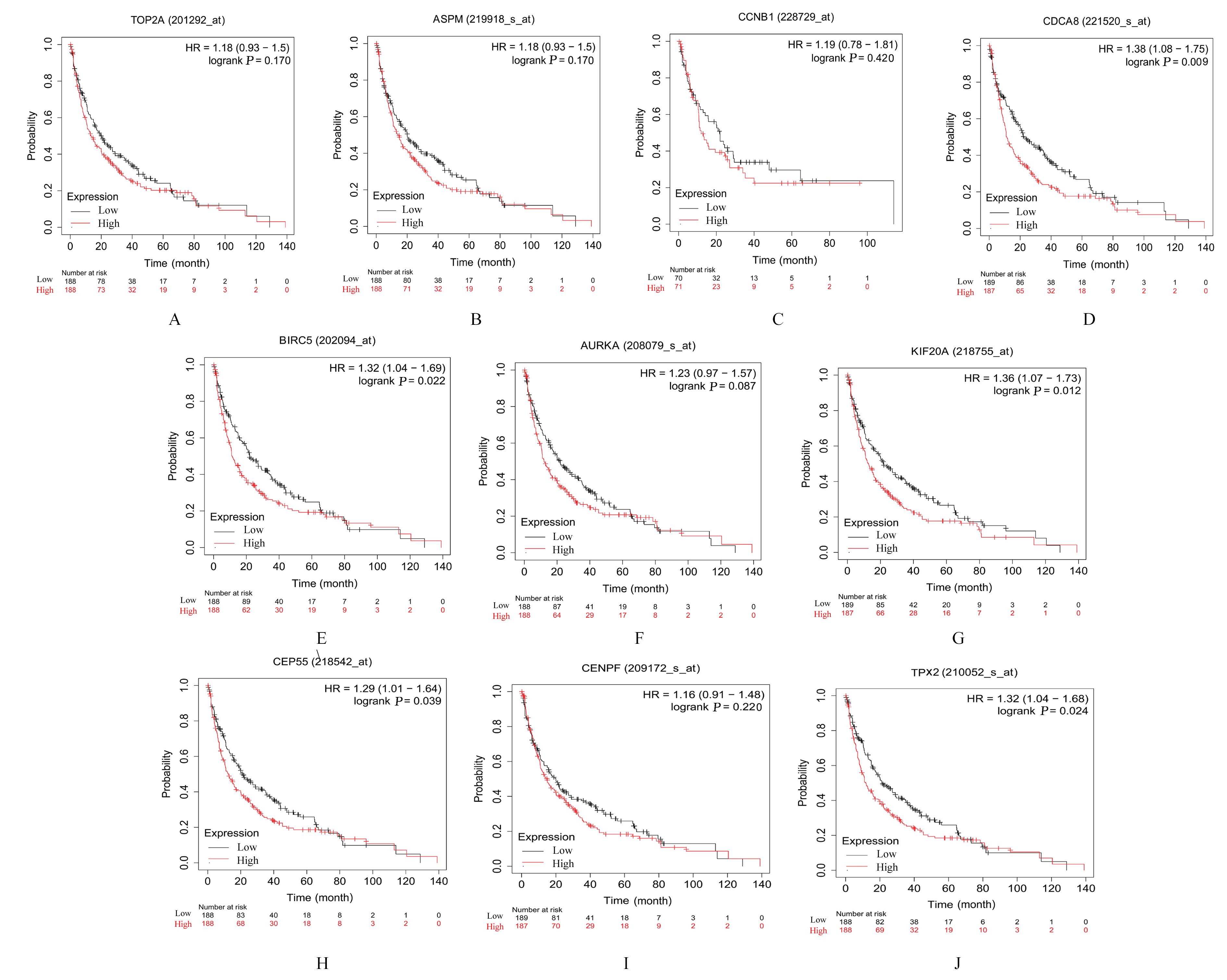
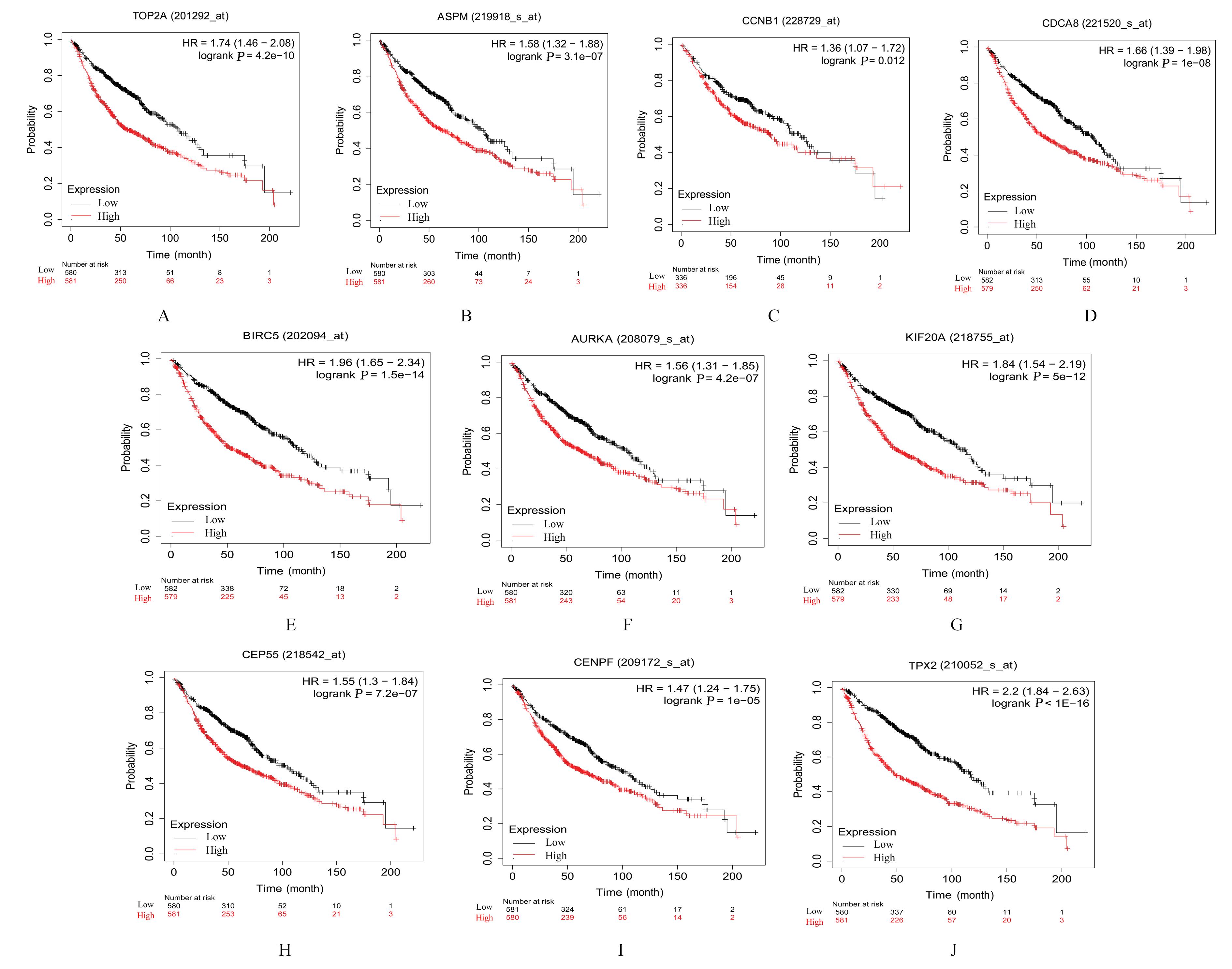
Tab.1
Top 10 key genes in connectivities"
| Gene | Description | Degree |
|---|---|---|
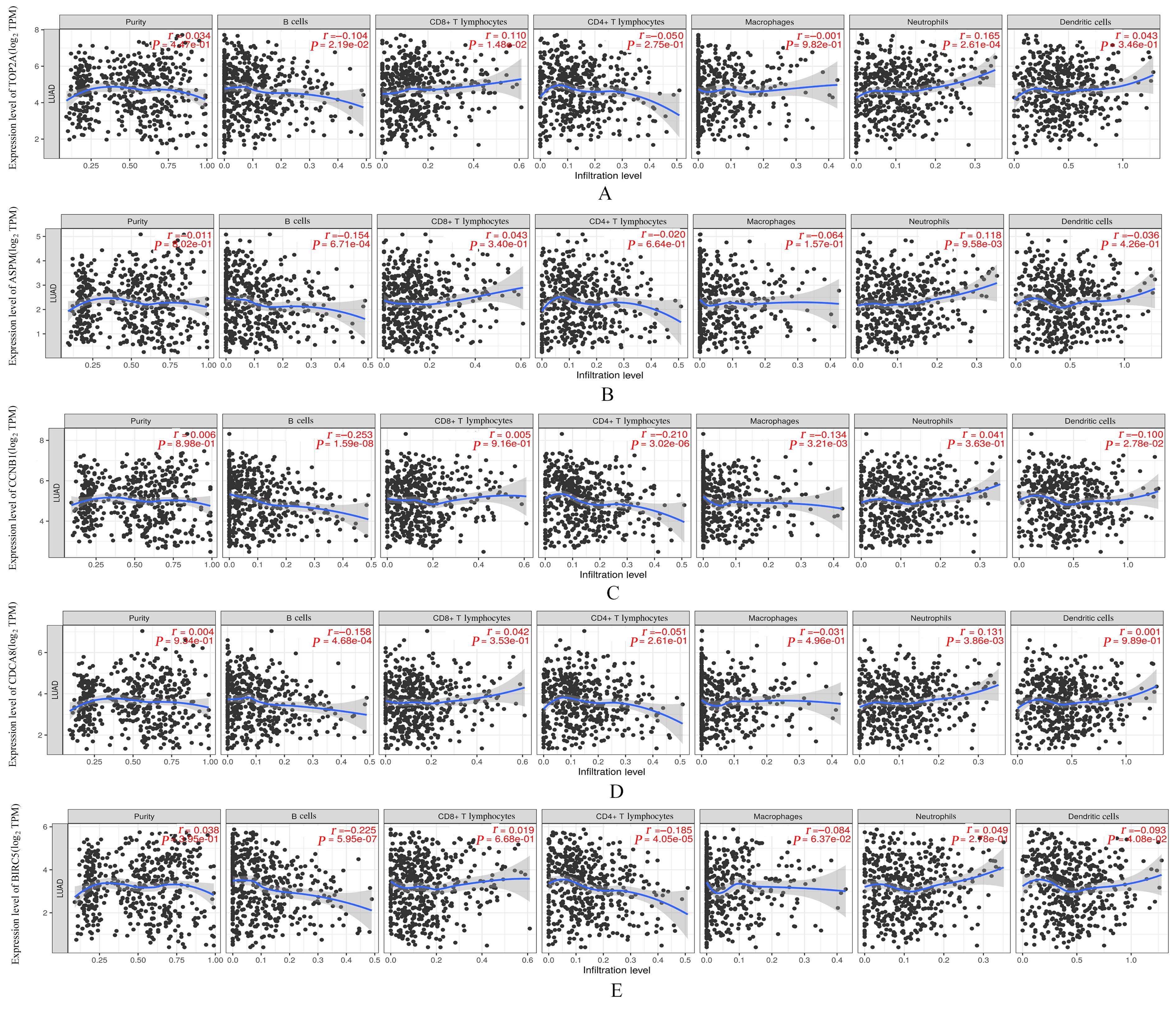
| TOP2A | DNA topoisomerase 2-alpha | 40 |
| ASPM | Abnormal spindle-like microcephaly- associated protein | 34 |
| CCNB1 | Cyclin B1 | 32 |
| CDCA8 | Cell division cycle associated 8 | 30 |
| BIRC5 | Baculoviral IAP repeat containing 5 | 30 |
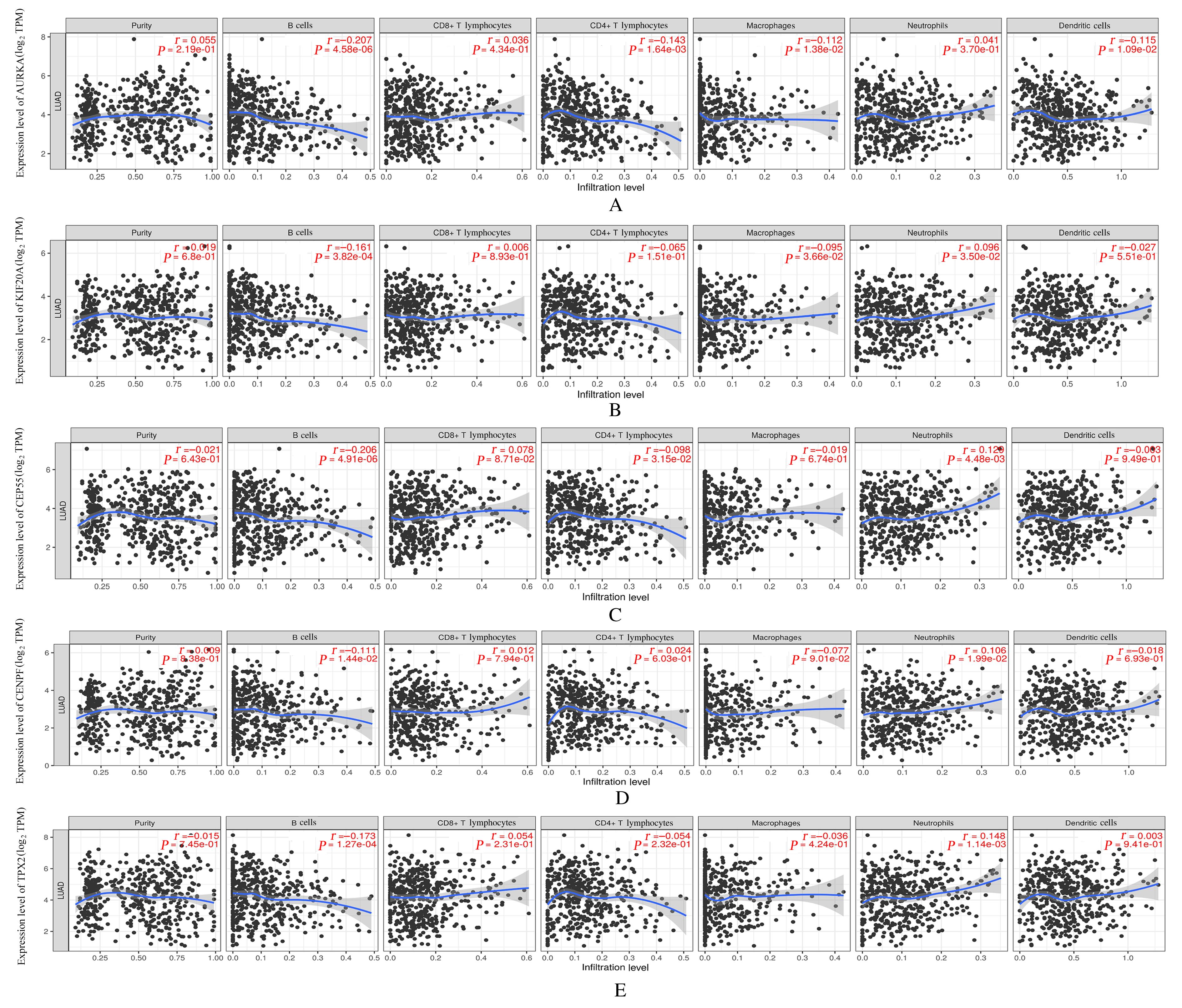
| AURKA | Aurora kinase A | 30 |
| KIF20A | Kinesin family member 20A | 30 |
| CEP55 | Centrosomal protein 55 | 30 |
| CENPF | Centromere protein F | 30 |
| TPX2 | Targeting protein for Xklp2 | 30 |
| 1 | XIA C F, DONG X S, LI H, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants[J]. Chin Med J, 2022, 135(5): 584-590. |
| 2 | 李 林, 杨双宁, 秦国慧, 等. 基于UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS的PD-1抑制剂治疗的晚期肺腺癌患者血清代谢组学研究[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2022, 57(5): 631-634. |
| 3 | CHEN Z, FILLMORE C M, HAMMERMAN P S,et al.Non-small-cell lung cancers: a heterogeneous set of diseases[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2014, 14(8): 535-546. |
| 4 | SIEGEL R L, MILLER K D, JEMAL A. Cancer statistics, 2018[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(1): 7-30. |
| 5 | BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2018,68(6):394-424. |
| 6 | BAO Y L, WANG L, SHI L, et al. Transcriptome profiling revealed multiple genes and ECM-receptor interaction pathways that may be associated with breast cancer[J]. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 2019, 24: 38. |
| 7 | ANDERSEN M K, RISE K, GISKEØDEGÅRD G F, et al. Integrative metabolic and transcriptomic profiling of prostate cancer tissue containing reactive stroma[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 14269. |
| 8 | YAN P, HE Y C, XIE K X, et al. In silico analyses for potential key genes associated with gastric cancer[J]. Peer J, 2018, 6: e6092. |
| 9 | RAHBARI N N, KEDRIN D, INCIO J,et al.Anti-VEGF therapy induces ECM remodeling and mechanical barriers to therapy in colorectal cancer liver metastases[J].Sci Transl Med,2016,8(360): 360ra135. |
| 10 | LIANG J H, LI H X, HAN J Y, et al. Mex3a interacts with LAMA2 to promote lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(8): 614. |
| 11 | GU S J, QIAN L, ZHANG Y L, et al. Significance of intratumoral infiltration of B cells in cancer immunotherapy: from a single cell perspective[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2021, 1876(2): 188632. |
| 12 | XIONG S M, DONG L L, CHENG L. Neutrophils in cancer carcinogenesis and metastasis[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2021, 14(1): 173. |
| 13 | YU B W, CHEN L, ZHANG W N, et al. TOP2A and CENPF are synergistic master regulators activated in cervical cancer[J].BMC Med Genomics,2020,13(1):145. |
| 14 | GAO S Y, GANG J, YU M, et al. Computational analysis for identification of early diagnostic biomarkers and prognostic biomarkers of liver cancer based on GEO and TCGA databases and studies on pathways and biological functions affecting the survival time of liver cancer[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 791. |
| 15 | CUI Y J, PU R, YE J J, et al. LncRNA FAM230B promotes gastric cancer growth and metastasis by regulating the miR-27a-5p/TOP2A axis[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2021, 66(8): 2637-2650. |
| 16 | PEI Y F, YIN X M, LIU X Q. TOP2A induces malignant character of pancreatic cancer through activating β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2018, 1864(1): 197-207. |
| 17 | WANG K, CHEN R, FENG Z, et al. Identification of differentially expressed genes in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Aging, 2019, 11(23): 11170-11185. |
| 18 | BAO B, YU X J, ZHENG W J. miR-139-5p targeting CCNB1 modulates proliferation, migration, invasion and cell cycle in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Mol Biotechnol, 2022, 64(8): 852-860. |
| 19 | ZHU H Y, ZHENG C N, LIU H T, et al. Significance of macrophage infiltration in the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma patients evaluated by scRNA and bulkRNA analysis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 1028440. |
| 20 | WANG B J, LI X, ZHAO G N, et al. miR-203 inhibits ovarian tumor metastasis by targeting BIRC5 and attenuating the TGFβ pathway[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 37(1): 235. |
| 21 | WANG D C, LIU J, LIU S S, et al. Identification of crucial genes associated with immune cell infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma by weighted gene co-expression network analysis[J]. Front Genet, 2020, 11: 342. |
| 22 | WADSWORTH P. tpx2[J]. Curr Biol, 2015, 25(24): R1156-R1158. |
| 23 | ZHOU F, WANG M, AIBAIDULA M, et al. TPX2 promotes metastasis and serves as a marker of poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2020, 26: e925147. |
| 24 | WANG J, LIANG J H, LI H X, et al. Oncogenic role of abnormal spindle‑like microcephaly‑associated protein in lung adenocarcinoma[J].Int J Oncol,2021,58(5): 23. |
| 25 | DENG T T, LIU Y, ZHUANG J L, et al. ASPM is a prognostic biomarker and correlates with immune infiltration in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma and liver hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 632042. |
| 26 | DAI C, MIAO C X, XU X M, et al. Transcriptional activation of human CDCA8 gene regulated by transcription factor NF-Y in embryonic stem cells and cancer cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2015, 290(37): 22423-22434. |
| 27 | HU C X, WU J X, WANG L, et al. miR-133b inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting CDCA8[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2021, 223: 153459. |
| 28 | 万志杰, 王 航, 杜志鹏, 等. 基于TCGA数据库的肺癌和结直肠癌放疗后差异基因筛选、功能及通路研究[J].同济大学学报(医学版),2022,43(4):467-473. |
| 29 | DU R J, HUANG C T, LIU K D, et al. Targeting AURKA in Cancer: molecular mechanisms and opportunities for Cancer therapy[J]. Mol Cancer, 2021, 20(1): 15. |
| 30 | JIN Z, TAO S, ZHANG C, et al. KIF20A promotes the development of fibrosarcoma via PI3K-Akt signaling pathway[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2022, 420(1): 113322. |
| 31 | ZHAO X, ZHOU L L, LI X Y, et al. Overexpression of KIF20A confers malignant phenotype of lung adenocarcinoma by promoting cell proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis[J]. Cancer Med, 2018, 7(9): 4678-4689. |
| 32 | YANG C L, YANG Y, WANG W,et al.CEP55 3'-UTR promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and enhances tumorigenicity of bladder cancer cells by acting as a ceRNA regulating miR-497-5p[J]. Cell Oncol, 2022, 45(6): 1217-1236. |
| 33 | FU L H, LI Z P, WU Y L, et al. Hsa-miR-195-5p inhibits autophagy and gemcitabine resistance of lung adenocarcinoma cells via E2F7/CEP55[J]. Biochem Genet, 2023, 61(4): 1528-1547. |
| 34 | CHEN H J, WU F B, XU H J, et al. Centromere protein F promotes progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through ERK and cell cycle-associated pathways[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2022, 29(7): 1033-1042. |
| 35 | SUN J B, HUANG J Z, LAN J, et al. Overexpression of CENPF correlates with poor prognosis and tumor bone metastasis in breast cancer[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2019, 19: 264. |
| 36 | TANG H X, BAI Y Q, XIONG L C, et al. Knockdown of CENPF inhibits the progression of lung adenocarcinoma mediated by ERβ2/5 pathway[J]. Aging, 2021, 13(2): 2604-2625. |
| [1] | Manying OU,Chunxia HU,Yueping LI. Effect of expression of microtubule inhibitory assembly protein 1 in placenta tissue of pre-eclampsia patients on trophoblast cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1519-1527. |
| [2] | Tao HE,Zhenjiang LI,Bingqian DING. Influence of ligustrazine on growth of glioma stem cells subcutaneous xenografts in nude mice, TGF-β signaling pathway, and epithelial-mesenchymal transiton [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1437-1444. |
| [3] | Yaqi XU,Yanyu WANG,Wenjing ZHANG,Mei HAN,Huaxia MU,Xi YANG,Weixiao BU,Zikun TAO,Yujia KONG,Fuyan SHI,Suzhen WANG. Bioinformatics analysis on screening of key genes of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma and its relationship with prognosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1243-1252. |
| [4] | Dandan WANG,Ning ZHOU,Dongqin LIU,Jie ZHAO,Chao LIANG,Juanjuan DAI,Yan WU. Effect of miR-491-5p over-expression on proliferation and migration of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma HONE-1 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1134-1139. |
| [5] | Haikang CUI,Xudong ZHANG,Xiaoning LI,Xi YANG,Lan YANG,Wenjie ZHANG. Bioinformatics analysis on predition effect of subtypes of cell pyroptosis and APOD on prognosis of gastric cancer patients [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1268-1279. |
| [6] | Chang GAO,Yan LIU,Haoxiang YANG,Cuicui ZHANG. Effect of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 on angiogenesis of human brain microvascular endothelial cells induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation hypoxic [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 832-839. |
| [7] | Lingyao XU,Shutang WEI,Yong DONG,Zhenglu SUN,Junbo ZHAO,Dazheng HAN. Regulatory effect of lncRNA MALAT1 on activation of hepatic stellate cell and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 697-705. |
| [8] | Zhiyuan XIAO,Bing SONG,Xinyu MA,Lianhui JIN,Tong ZHENG,Fang CHAI. Bioinformatics analysis on expression of apoptosis related gene CD44 in thyroid carcinoma tissue and its relationship with tumor invasion and immune cell infiltration [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 473-481. |
| [9] | Rui LI,Xiaodong TAN,Yaoyuan HU. Inhibitory effect of pachylic acid on migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 315-323. |
| [10] | Xiaoyan WANG,Yihong HU,Yucheng HAN,Xianqiong ZOU. Bioinformatics analysis on mechanism of COMMD7 in occurrence and development of brain low-grade glioma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 414-424. |
| [11] | Wuyue TANG,Shuojie LI,Lijuan PANG. Bioinformatics analysis of splicing factor-alternative splicing regulatory network based on alternative splicing data in lung adenocarcinoma tissue [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 139-149. |
| [12] | Junjie HOU,Xuguang MI,Xiaonan LI,Xiaonan LI,Ying YANG,Xiaodan LU,Yanqiu FANG,Ningyi JIN. Establishment and evaluation of prognostic model of lung adenocarcinoma based on lactate metabolism gene [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1546-1554. |
| [13] | Jilin FAN,Tingting ZHU,Xiaoling TIAN,Sijia LIU,Jing SU,Shiliang ZHANG. Bioinformatics analysis based on circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network construction and immune cell infiltration in atrial fibrillation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1535-1545. |
| [14] | Meng QYU,Hong ZHENG,Yan LI,Boxue CHEN,Yuzhu JIANG,Shenggao WANG,Chunyan YU,Zhiheng DONG. Inhibitory effect of fermented red ginseng total saponins high glucose-induced renal tubular cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1182-1189. |
| [15] | Yingjie NIU,Yong ZHA,Sijia LI,Qing WANG,Shicong TANG,Hongyang LI. Analysis on prognosis related factors of patients with cholangiocarcinoma after radical resection and establishment of survival prediction model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 979-987. |
|
||