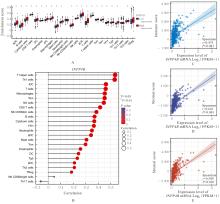
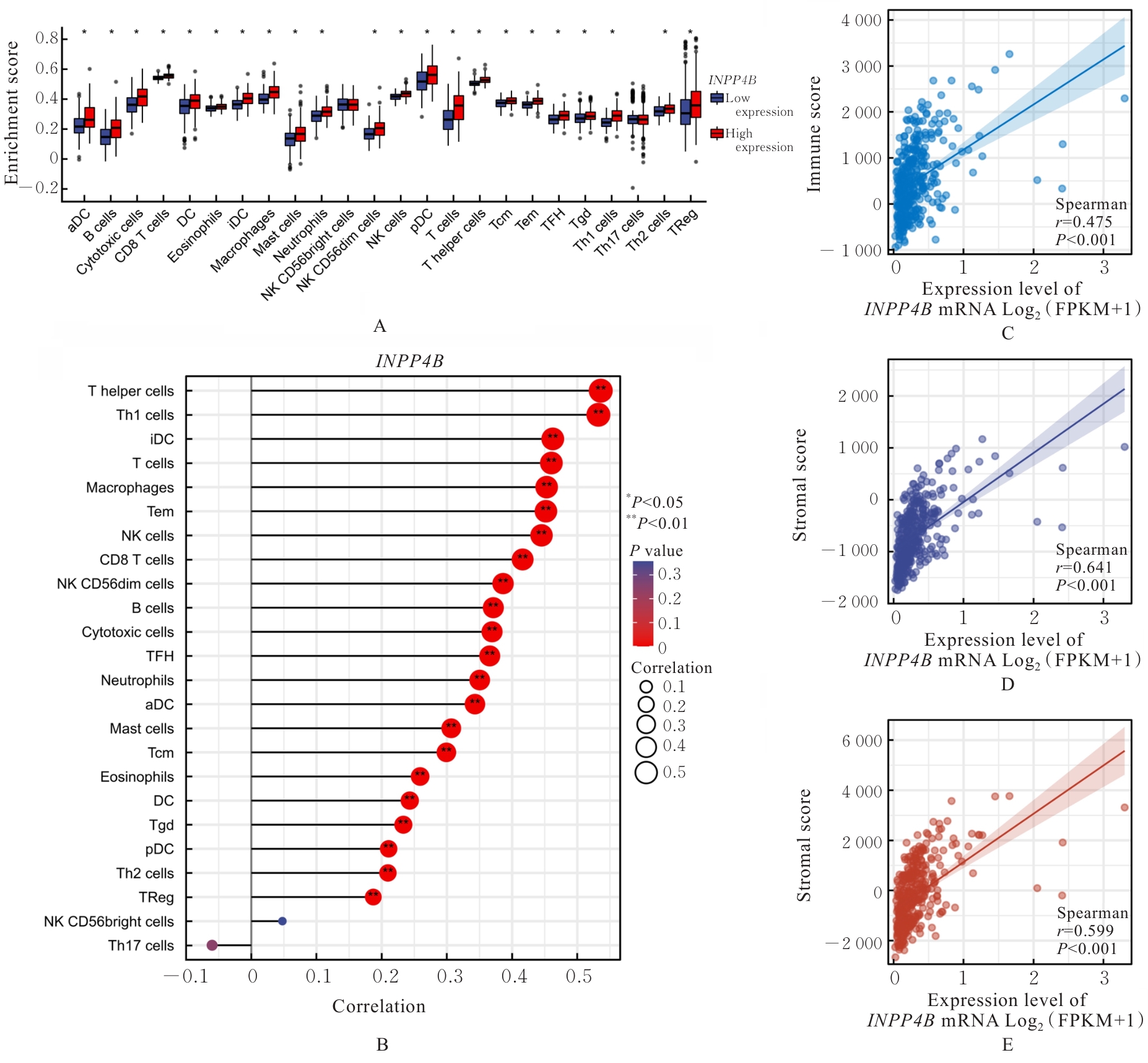
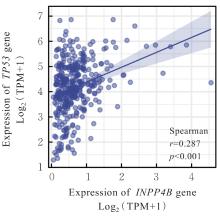
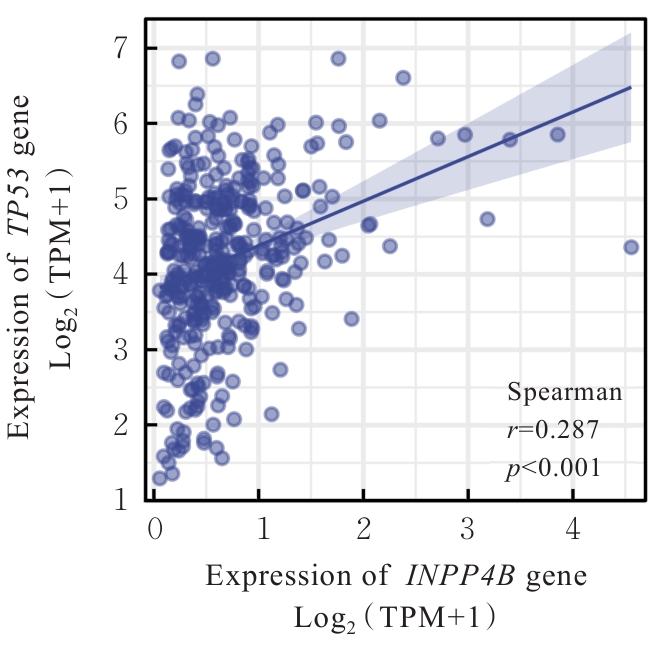
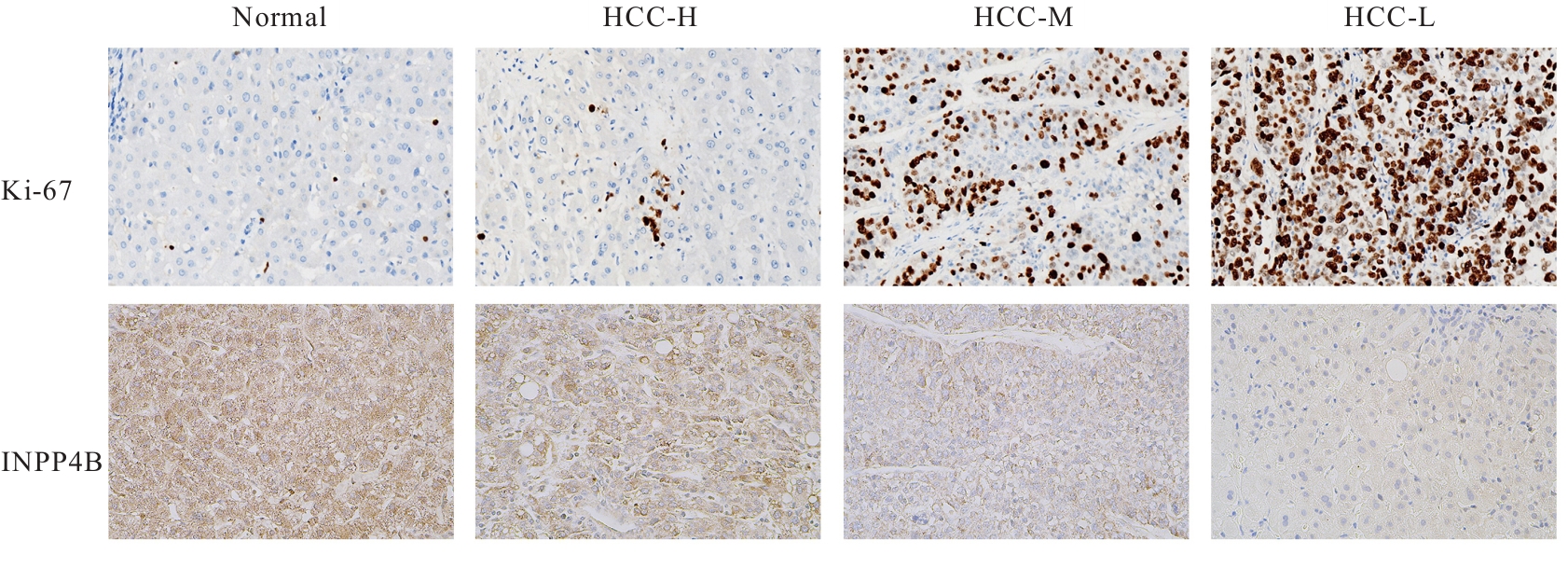
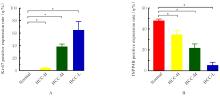
| [1] |
Han LIN,Qiuyan YANG,Jieyue ZHONG,Bolun CHEN,Wangxia TONG.
Improvement effect of cordycepin on ferroptosis in HepG2 cells induced by RSL3 and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 576-589.
|
| [2] |
Xiaoyan WANG,Xuelian LI,Bin LIANG,Wenfei TIAN,Hailin MA,Zhijing MO.
Analysis on relationship between CALU and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients and its mechanism based on transcriptome and single cell sequencing data
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 447-459.
|
| [3] |
Jinlian LI,Lanzhen HUANG,Xishi HUANG,Kangzhi LI,Jiali JIANG,Miaomiao ZHANG,Qunying WU.
Bioinformatics analysis on key genes related to prognosis, diagnosis, and immune cell infiltration of hepatocellular carcinoma and their potential therapeutic drugs
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1062-1075.
|
| [4] |
Yongjing YANG,Tianyang KE,Shixin LIU,Xue WANG,Dequan XU,Tingting LIU,Ling ZHAO.
Synergistic sensitization of apatinib mesylate and radiotherapy on hepatocarcinoma cells invitro
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1009-1015.
|
| [5] |
Xiaopeng YU,Renyi YANG,Zuomei HE,Puhua ZENG.
Establishment and validation of nomogram of cancer specific survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma with negative alpha fetoprotein based on SEER Database
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 188-197.
|
| [6] |
Xiaoyan WANG,Hao ZHANG,Zehao GUO,Jun CAO,Zhijing MO.
Screening of UBE2S interacting protein and construction of prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 168-177.
|
| [7] |
Yong DONG,Lingyao XU,Jing HUA,Han LIANG,Dongya LIU,Junbo ZHAO,Zhenglu SUN,Cheng CHENG,Shutang WEI.
Effect of macrophage exosomal lncRNA HULC on migration, invasion,and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1217-1226.
|
| [8] |
Yiming ZHAO,Haiyang XU.
Bioinformatics analysis on related genes and candidate pathways of glioblastoma multiforme
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1280-1289.
|
| [9] |
Yaqi XU,Yanyu WANG,Wenjing ZHANG,Mei HAN,Huaxia MU,Xi YANG,Weixiao BU,Zikun TAO,Yujia KONG,Fuyan SHI,Suzhen WANG.
Bioinformatics analysis on screening of key genes of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma and its relationship with prognosis
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1243-1252.
|
| [10] |
Wenjun DENG,Liantao HU,Binnan ZHAO,Xinyu DONG,Xuebin LI,Jie LI,Xinyan YANG,Xiaoli GUO,Yue LI,Yikun QU,Weiqun WANG.
Effect of CXC chemokine ligand 10 on proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1227-1233.
|
| [11] |
Yuanyuan LIANG,Song ZHAO,Jing HU,Ni AN,Yanlu WEI,Rongjian SU.
Effect of motesanib combined with EZH2 inhibitor GSK126 on proliferation and apoptosis of liver cancer Huh7 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 896-904.
|
| [12] |
Wuyue TANG,Shuojie LI,Lijuan PANG.
Bioinformatics analysis of splicing factor-alternative splicing regulatory network based on alternative splicing data in lung adenocarcinoma tissue
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 139-149.
|
| [13] |
Junyi JIN,Mu LI,Yaoyuan HU,Yihui WANG.
Targeting relationship between miR-150-5p and NCAPG and its inhibitory effect on hepatocellular carcinoma Huh7 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 122-130.
|
| [14] |
Liantao HU,Wenjun DENG,Shizhen LU,Luo SUN,Xuebing LI,Chuhao LI,Xinran WANG,chunbing ZHANG,Yue LI,Weiqun WANG.
Bioinformatics analysis on CC chemokine ligand 20 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue and its effect on prognostic assessment of liver hepatocellular carcinoma
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 1010-1017.
|
| [15] |
YUE Yuan, XU Yinglian, WANG Jingjing, SUN Minying, ZHANG Zenan, ZHAO Xinyue, LI Zongpu, TAI Guixiang.
Inhibitory effects of down-regulation of JNK enzymatic activity on growth of human prostate cancer cells, hepatocellular carcinoma cells and breast cancer cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(05): 1046-1051.
|
 )
)