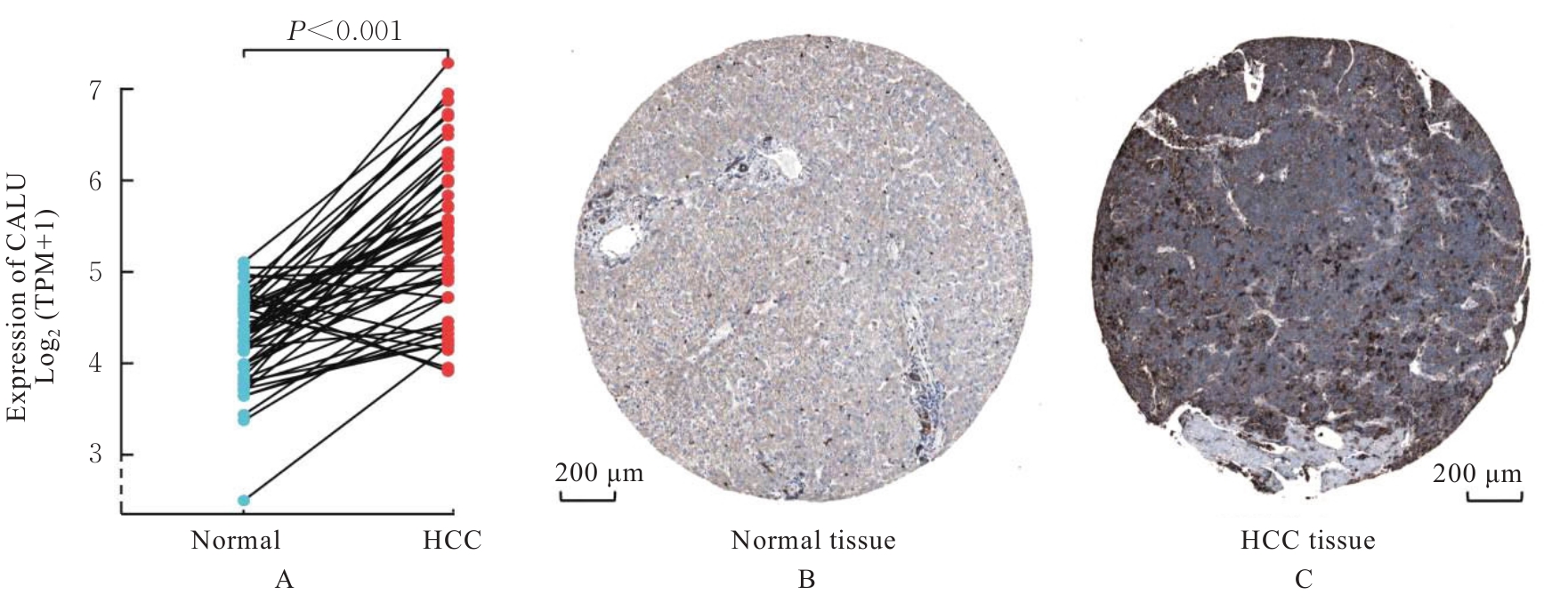
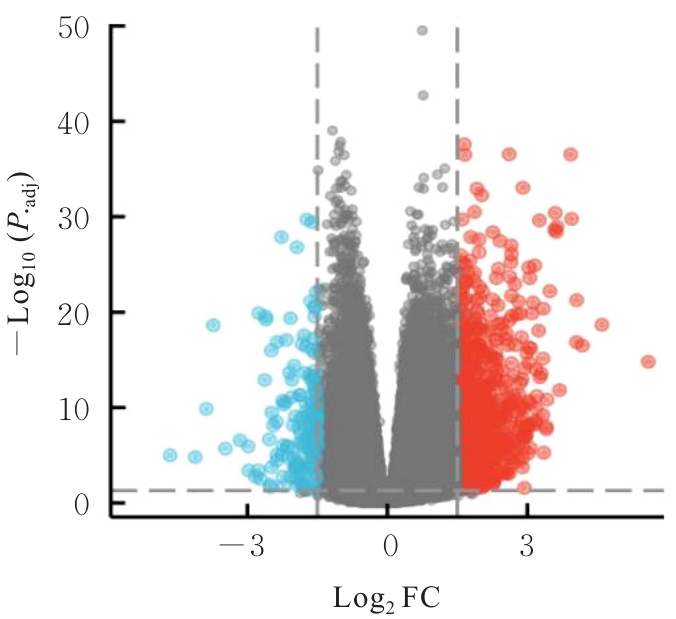
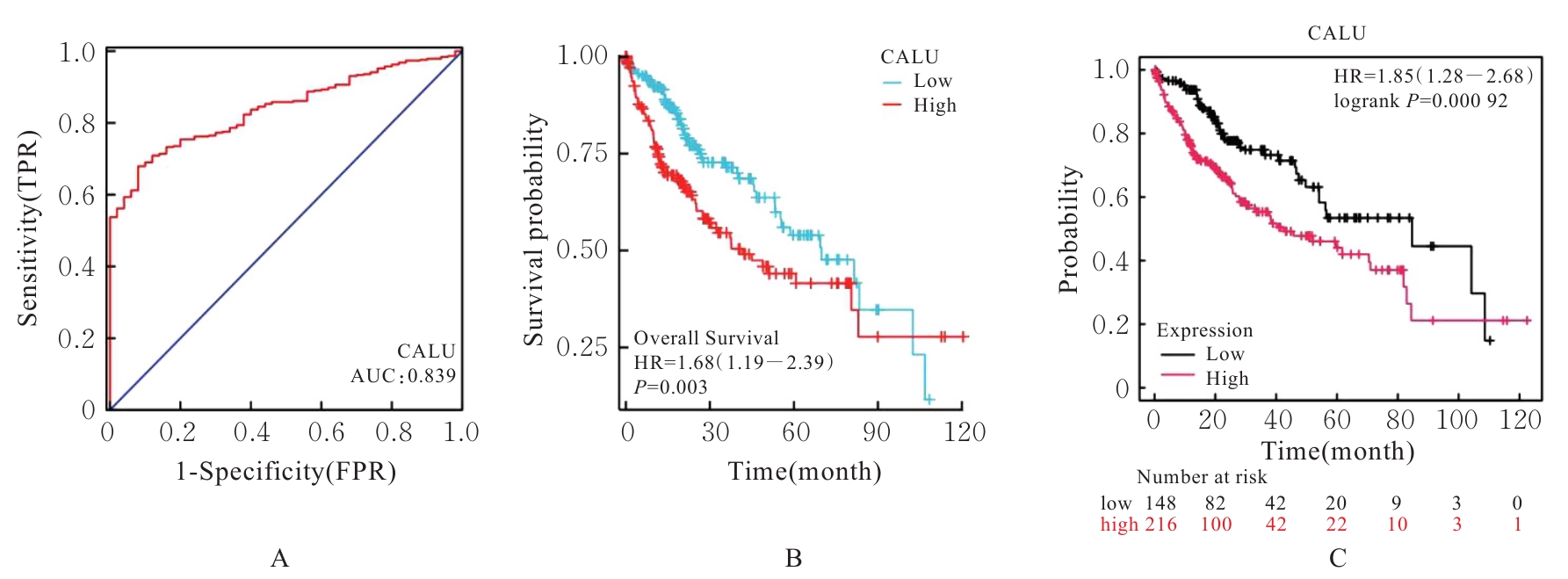
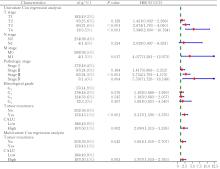
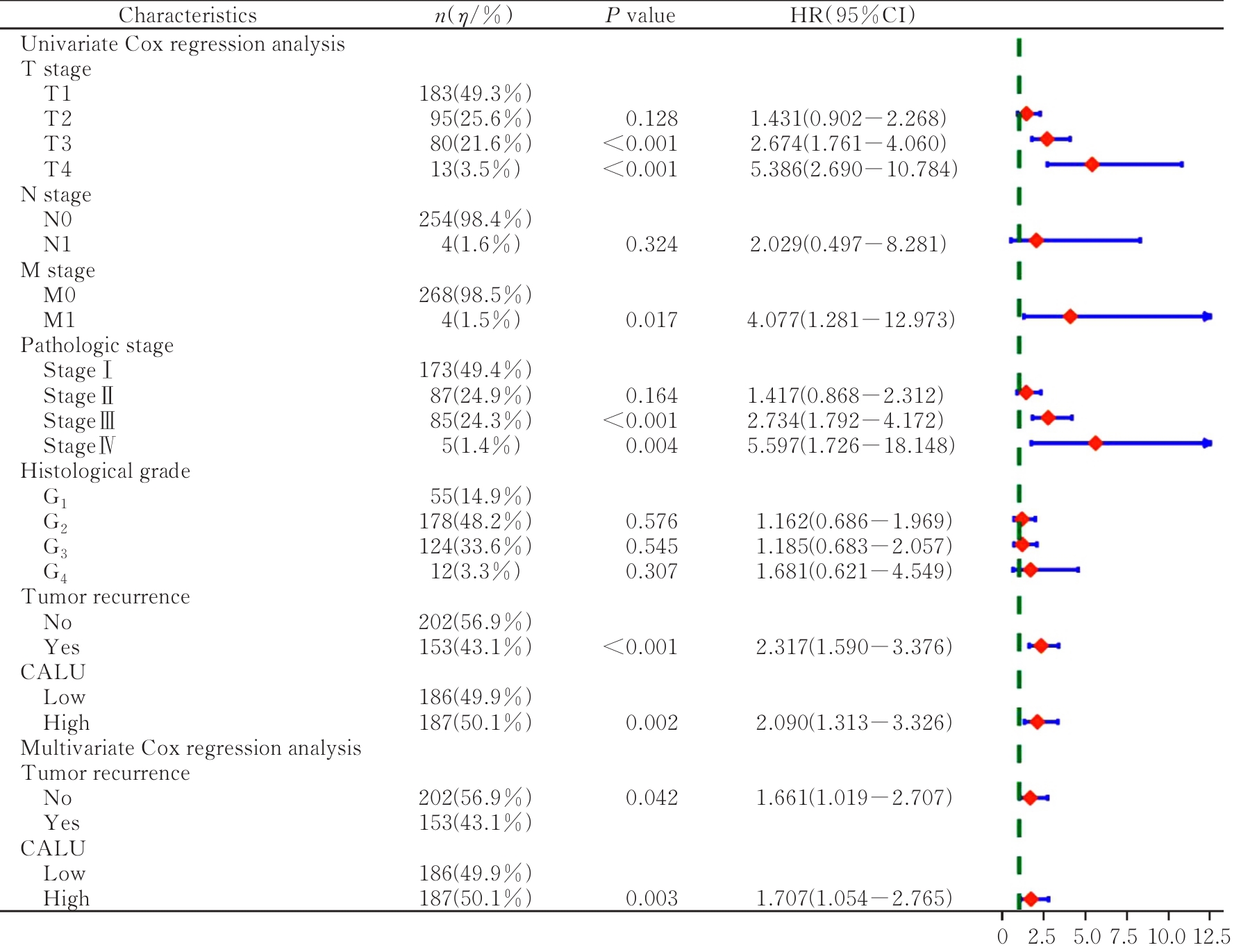
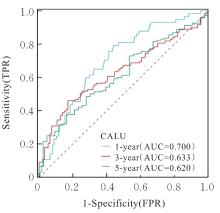
| 1 |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249.
|
| 2 |
LLOVET J M, DE BAERE T, KULIK L, et al. Locoregional therapies in the era of molecular and immune treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 18(5): 293-313.
|
| 3 |
HONORÉ B. The rapidly expanding CREC protein family: members, localization, function, and role in disease[J]. Bioessays, 2009, 31(3): 262-277.
|
| 4 |
LEE J H, KWON E J, KIM D H. Calumenin has a role in the alleviation of ER stress in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2013, 439(3): 327-332.
|
| 5 |
ZHENG P L, WANG Q, TENG J L, et al. Calumenin and fibulin-1 on tumor metastasis: implications for pharmacology[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2015, 99: 11-15.
|
| 6 |
WANG Y, XUAN L Y, CUI X X, et al. Ibutilide treatment protects against ER stress induced apoptosis by regulating calumenin expression in tunicamycin treated cardiomyocytes[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(4): e0173469.
|
| 7 |
NAGANO K, IMAI S, ZHAO X, et al. Identification and evaluation of metastasis-related proteins, oxysterol binding protein-like 5 and calumenin, in lung tumors[J]. Int J Oncol, 2015, 47(1): 195-203.
|
| 8 |
NASRI NASRABADI P, NAYERI Z, GHARIB E, et al. Establishment of a CALU, AURKA and MCM2 gene panel for discrimination of metastasis from primary colon and lung cancers[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(5): e0233717.
|
| 9 |
TANG H, MA M, DAI J, et al. miR-let-7b and miR-let-7c suppress tumourigenesis of human mucosal melanoma and enhance the sensitivity to chemotherapy[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 212.
|
| 10 |
DU Y H, MIAO W H, JIANG X, et al. The epithelial to mesenchymal transition related gene calumenin is an adverse prognostic factor of bladder cancer correlated with tumor microenvironment remodeling, gene mutation, and ferroptosis[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 683951.
|
| 11 |
KURPIŃSKA A, SURAJ J, BONAR E, et al. Proteomic characterization of early lung response to breast cancer metastasis in mice[J]. Exp Mol Pathol, 2019, 107: 129-140.
|
| 12 |
YANG Y, WANG J, XU S H, et al. Calumenin contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition and predicts poor survival in glioma[J]. Transl Neurosci, 2021, 12(1): 67-75.
|
| 13 |
YE J Z, TIAN W, ZHENG B G, et al. Identification of cancer-associated fibroblasts signature for predicting the prognosis and immunotherapy response in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2023, 102(45): e35938.
|
| 14 |
LU S C, LU H M, JIN R Z, et al. Promoter methylation and H3K27 deacetylation regulate the transcription of VIPR1 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2019, 509(1): 301-305.
|
| 15 |
王小燕, 张 豪, 郭泽皓, 等. 肝癌细胞中VIPR1互作蛋白质谱分析及肝癌预后模型的构建[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2023, 31(17): 3176-3182.
|
| 16 |
LOVE M I, HUBER W, ANDERS S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2[J]. Genome Biol, 2014, 15(12): 550.
|
| 17 |
YU G C, WANG L G, HAN Y Y, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters[J]. OMICS, 2012, 16(5): 284-287.
|
| 18 |
HUANG Y, ZHU Y Q, YANG J Y, et al. CMTM6 inhibits tumor growth and reverses chemoresistance by preventing ubiquitination of p21 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(3): 251.
|
| 19 |
XU Y C, ZHANG D X, JI J J, et al. Ubiquitin ligase MARCH8 promotes the malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through PTEN ubiquitination and degradation[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2023, 62(7): 1062-1072.
|
| 20 |
CHEN Q P, ZHENG W, GUAN J, et al. SOCS2-enhanced ubiquitination of SLC7A11 promotes ferroptosis and radiosensitization in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2023, 30(1): 137-151.
|
| 21 |
MATSCHKE V, THEISS C, MATSCHKE J. Oxidative stress: the lowest common denominator of multiple diseases[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2019, 14(2): 238-241.
|
| 22 |
DIXON S J, LEMBERG K M, LAMPRECHT M R, et al. Ferroptosis:an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death[J]. Cell, 2012, 149(5): 1060-1072.
|
| 23 |
陶 倩, 刘 念, 陈 静, 等. 铁死亡与肿瘤免疫[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2024, 49(8): 1309-1315.
|
| 24 |
朱明强, 谢 星, 廖启成, 等. 铜死亡的发生机制及在肝脏疾病中的作用[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40(11): 2332-2337.
|
| 25 |
DE ROSA V, IOMMELLI F, MONTI M, et al. Reversal of Warburg effect and reactivation of oxidative phosphorylation by differential inhibition of EGFR signaling pathways in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2015, 21(22): 5110-5120.
|
| 26 |
GUO J P, CHENG J, ZHENG N N, et al. Copper promotes tumorigenesis by activating the PDK1-AKT oncogenic pathway in a copper transporter 1 dependent manner[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2021, 8(18): e2004303.
|
| 27 |
OSTRAKHOVITCH E A, LORDNEJAD M R, SCHLIESS F, et al. Copper ions strongly activate the phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Akt pathway independent of the generation of reactive oxygen species[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2002, 397(2): 232-239.
|
| 28 |
TURSKI M L, BRADY D C, KIM H J, et al. A novel role for copper in Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2012, 32(7): 1284-1295.
|
| 29 |
TSANG T, POSIMO J M, GUDIEL A A, et al. Copper is an essential regulator of the autophagic kinases ULK1/2 to drive lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2020, 22(4): 412-424.
|
| 30 |
POLISHCHUK E V, MEROLLA A, LICHTMANNEGGER J, et al. Activation of autophagy, observed in liver tissues from patients with Wilson disease and from ATP7B-deficient animals, protects hepatocytes from copper-induced apoptosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 156(4): 1173-1189.e5.
|
| 31 |
WANG L, CHAI X K, WAN R, et al. Disulfiram chelated with copper inhibits the growth of gastric cancer cells by modulating stress response and Wnt/β-catenin signaling[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 595718.
|
| 32 |
CHEN G S, CHEN S Y, LIU S T, et al. Stabilization of the c-myc protein via the modulation of threonine 58 and serine 62 phosphorylation by the disulfiram/copper complex in oral cancer cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(16): 9137.
|
| 33 |
ONUMA T, MIZUTANI T, FUJITA Y, et al. Copper content in ascitic fluid is associated with angiogenesis and progression in ovarian cancer[J]. J Trace Elem Med Biol, 2021, 68: 126865.
|
 )
)